Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
1 0UF Presentations
Transféré par
Moustafa Helmy0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
211 vues55 pagesPresentations
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentPresentations
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
211 vues55 pages1 0UF Presentations
Transféré par
Moustafa HelmyPresentations
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 55
DOW Ultrafiltration
Fundamentals, Product Range & Operation
Summary of the Presentation
What is UF/MF?
UF/MF Membranes & System Configurations
Basic UF/MF Terminology
Advantages of UF/MF vs conventional filtration
UF Desirable Membrane Properties
Specific Features and Benefits of DOW
TM
UF
DOW
TM
UF UF System Operation & Design
Technical Support
Applications & References
What is UF/MF?
UF and MF: membrane processes based on size exclusion
(physical sieving). Reject particles, colloids, SS, oxidized
Fe/Mn, microorganisms...
What UF and MF cannot reject: DOM, Non-Oxidized Fe/Mn,
Hardness, Salts.
Ionic Range Molecular Range Macro Molecular Range Micro Particle Range Macro Particle Range
Dissolved Organics
Viruses
Metal
Ions
Latex / Emulsions
Bacteria
Colloids
Algae
Giardia
Human Hair
Insecticides
Soluble Salts
Antibiotics
Endotoxins/Pyrogens
Crypto
0.0001
Reverse Osmosis
Microfiltration
Nanofiltration
Ultrafiltration
IX
Electrodeionization
0.001 0.01 0.1 1.0 100 10
10
4
10
6
Micrometers (Log Scale)
Angstrom Units (Log Scale)
Particle Filtration
Technology within Dow Water Solutions
Filtration Spectrum
1 10 100 1000
10
5
Membrane Configurations
Tubular Plate & Frame
Hollow Fibers
Spiral Wound
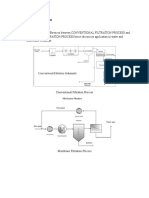
UF/MF System Configurations
Pressurized
Hollow fiber modules where
water is forced either into or out
of the lumen under pressure.
Submerged (or Immersed)
Hollow fiber configurations
where water is pulled into the
fiber lumen by suction.
There are two basic UF/MF configurations:
Pump
Feed
Permeate
Membrane
Feed
Tank
Pump
Permeate
Membrane
UF/MF System Configurations
Pressurized
Hollow fiber modules where
water is forced either into or out
of the lumen under pressure.
Submerged (or Immersed)
Hollow fiber configurations
where water is pulled into the
fiber lumen by suction.
There are two basic UF/MF configurations:
Lower footprint and weight
Higher and more consistent filtrate quality
(Log-Removal credit regardless water source)
Rejects pathogens resistant to chlorination
Lower chemical use (polymer, coagulant, pH
adjustment, chlorination,)
Easier operation and maintenance (highly
automated operation)
Easier expandability
Integrated systems (DOW advantage)
Advantages of UF/MF vs Conventional Filtration
.
Some advantages of UF/MF as pretreatment of RO:
Lower fouling in
RO membranes.
Reduce chemical
cleaning
frequencies
longer life of RO
Posibility to operate
the RO at higher
flux Less
Membranes &
Vessels
Advantages of UF/MF vs Conventional Filtration
.
Some Common UF/MF Terms
Recovery: Ratio of filtrate flow to feed flow [%].
TMP: Transmembrane Pressure (similar to head loss with
conventional granular media filters) [bar or psi]
Flux: Permeate Flow Divided by Membrane Area, [lmh or gfd]
Permeability: Normalized flux divided by TMP (sometimes
called specific flux) [lmh/bar or gfd/psi]
Fouling: Gradual reduction in filtrate flowat constant pressure
due to adsorption or deposition of contaminants within or on
the membrane.
BW: BackWash (also called Reverse Flush, Backflush,
Backpulse)
CIP: Clean In Place (Intensive Cleaning)
CEB: Chemically Enhanced Backwash (other terms: Mini-Clean,
Automatic cleaning, Enhanced flux maintenance, Maintenance
Clean, Chemical Wash)
AS: Air Scour (or Air Scrub)
Some Common UF/MF Terms
Membrane Properties Are all UF the same?
Pore Size: UF vs MF
Fiber Material: Strength, Chemical
Stability, Hydrophilicity
Flow configuration: Out-In vs In-Out
.
Membrane Properties UF vs MF
UF is a filter of smaller water
pollutants
removing pathogens, silt, colloids
and medium to higher molecular
weight organics. UF obtains
higher virus removal than MF.
Flux decline profile more
stable for UF (asymmetric
membrane)
0.1 m
0.03 m
.
Membrane Properties Strength
Strength of raw polymer - use high
molecular weight PVDF
Strength of porous membrane
structure without the use of
reinforcing materials
.
Membrane Properties Chemical Stability
Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Fibers maintain their strength under
continuous harsh chemical cleaning conditions, better than any other
membrane material.
Soaking test
with 5000 ppm
NaOCl for 250
hours
Residual strength of hollow fibers after
soak in 5000 ppm NaOCl solution
Membrane Properties Hydrophilicity
DOW
TM
UF PVDF Membranes are made hydrophilic higher
resistance to fouling by organics.
PES
CA
PAN
PS
PVDF
HDPE
PP
PTFE
PAN
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120
Contact Angle
[Degree, ]
S
u
r
f
a
c
e
T
e
n
s
i
o
n
[
D
y
n
e
/
c
m
]
DOW UF PVDF DOW UF PVDF
38
+ Hydrophilic + Hydrophobic
Flow Configuration: Out-In vs In-Out
Inside / Out
Outside / In
Fiber Material
Module
Layout
Pore
Size
Flow Pattern
H-PVDF
Vertical
Encased
0.03 m Out In
UF - A R-PVDF Submerged 0.04 m Out In
UF - B PVDF
Vertical
Encased
0.04 m Out In
UF - C PVDF
Vertical
Encased
0.1 m
(MF)
Out In
UF - D PES
Vertical
Encased
0.025 m In Out
UF - E PES
Horizontal
Encased
0.025 m In Out
Hollow Fiber UF Manufacturers Comparative
Specific Features and Benefits of
DOW
TM
UF
.
DOW
TM
UF Features and Advantages
Pressurized Outside/In Modular Membrane Product
Tolerance to wide range of Feed Water quality
Simple Vertical Shell Design (no PV needed)
Dead-End Operation
1.3 mm x 0.7 mm H-PVDF Hollow Fibers
Mechanically strong fibers
High Chemical tolerance
Treated for Increased Hydrophilicity (high
fouling resistance)
0.03 m Nominal Pore Size
Sponge-like structure for high filtration efficiency
.
DOW
TM
UF Specifications & Operating Conditions
DOW
TM
UF Model
SFP/SFD -
2660
SFP/SFD -
2860
SFP/SFD -
2880
Module
Specifications
Height 1,860 mm 1,820 mm 2,320 mm
Fibers Length 1,500 mm 1,500 mm 2,000 mm
Module Diameter 165 mm(6.5") 225 mm(8.9") 225 mm(8.9")
Module Surface Area 33 m
2
51 m
2
77 m
2
Volume 16 L 35 L 39 L
Weight (water filled) 41 kg 83 kg 100 kg
Shipping Weight 25 kg 48 kg 61 kg
Flow Range 1.3 - 4.0 m
3
/h 2.0 - 6.1 m
3
/h 3.1 9.3 m
3
/h
Fibers
Features
Flow Configuration Out to In
Fibers Material Hydrophilic-PVDF
Nominal Pore Size 0.03 m
Operating
Conditions
Temperature 1 - 40C
Max. Inlet Pressure Up to 6.3 bar @ 20C; 4.8 bar @ 40C
Max. Operating TMP 2.1 bar
pH, Operating 2-11 (continuous); 1-12 (cleaning)
NaOCl Max. 2,000 ppm
Backwash Flux 100-150 L/m
2
.h
Feed
Requirements
Max. TSS 100 mg/L
Max. Turbidity 300 NTU
Max. Particle Size 300 m
SFP-2660 SFP-2860 SFP-2880
.
Filtration
(20-60 min)
Air Scrub (20s)
Backwash (40-60s)
Forward Flush (30-60s)
(Physical Cleaning)
CEB (On-Line); Every 1-7 days
CIP (Off-Line); Every 1-12 months
(Chemical
Cleaning)
UF System Operation
Filtration
Ultrafiltrate
Raw Water
Filter
150-200 m
Backwash
Tank
Air
Chemicals
Backwash
Pump
Feed Pump
Effluent
Air Scour
Ultrafiltrate
Raw Water
Filter
150-200 m
Backwash
Tank
Air
Chemicals
Backwash
Pump
Feed Pump
Effluent
Air Scour (Drain Step)
Ultrafiltrate
Raw Water
Filter
150-200 m
Backwash
Tank
Air
Chemicals
Backwash
Pump
Feed Pump
Effluent
Backwash Top
Ultrafiltrate
Raw Water
Filter
150-200 m
Backwash
Tank
Air
NaOCl
(optional)
Backwash
Pump
Feed Pump
Effluent
Backwash Bottom
Ultrafiltrate
Raw Water
Filter
150-200 m
Backwash
Tank
Air
Backwash
Pump
Feed Pump
Effluent
NaOCl
(optional)
Forward Flush
Ultrafiltrate
Raw Water
Filter
150-200 m
Backwash
Tank
Air
Chemicals
Backwash
Pump
Feed Pump
Effluent
CEB Top
Ultrafiltrate
Raw Water
Filter
150-200 m
Backwash
Tank
Air
Chemicals
Backwash
Pump
Feed Pump
Effluent
.
CEB Bottom
Ultrafiltrate
Raw Water
Filter
150-200 m
Backwash
Tank
Air
Chemicals
Backwash
Pump
Feed Pump
Effluent
.
CEB
Acid
HCl or H
2
SO
4
@ approx. 500 mg/L (target pH 2)
Frequency is typically every 72 hours or when necessary.
Removes colloids and inorganic salt plugging both inside and
outside of membrane.
Alkali
NaOH @ approx. 500 mg/L (target pH 12)
Generally combined with NaOCl @ approx. 350 mg/L
Frequency is typically every 24 hours or when necessary.
Removes organics and biofoulants from membrane.
CIP
Acid
HCl @ 2,000 ppm
pH 2
Alkali
NaOH @ 1,000 ppm
NaOCl @ 2,000 ppm
pH 12
Frequency is typically every 1-3 months.
Flow rate of 1.5 to 2.0 m
3
/h/module.
Duration is typically 120-150 minutes.
Triggered by transmembrane pressure rise.
CIP Solution
(up to 40 C)
.
Chemical
0.4% HCl
2% Citric
Acid
2% Oxalic
Acid
0.2% NaOCl 0.1% NaOH
Contaminants
Inorganic Recommended
Organic Recommended Possible
Metal Oxides
(Fe,Mn)
Possible Recommended
Colloids /
Particles
Recommended
Silica Recommended
Biological Recommended Possible
Coexistence
polivalent cations
& organic matter
Recommended
/ 1st CIP
Recommended
/ 1st CIP
Recommended /
2nd CIP
CIP General Guidelines
.
CEB CIP
Maintenance cleaning. Intensive cleaning.
Shorter in duration (but higher frequency). Longer in duration (but lower frequency).
Require less operator involvement.
Automatic.
Manually initiated.
It is done with ultrafiltrate. Chemical solution is prepared with demin/RO
water, usually at higher concentrations.
Chemical solution is flushed out fromthe
system.
Chemical solution is recirculated through the
system.
Cleaning occurs at ambient temperature. Heating of the cleaning solution is
recommended.
CEB vs CIP
DOW UF Skid
Typical DOW
TM
UF System
Double Floor DOW
TM
UF System
Double Floor DOW
TM
UF System
Design Software - UFlow
10-Page detailed report, including:
System Flow Diagram.
Plant design details (#UF racks, #UF
modules per rack, recovery, UF module main
features, etc.)
Instantaneous and Average system flows.
Sizing of tanks, valves, piping.
Chemical consumption and cost.
Energy consumption and cost.
Operating Tables.
Design Software - UFlow
Design Guidelines
46
Proposal - Engineering Package
Deliverables:
P&ID Drawings
General Arrangement Drawings
Equipment List
UFlow Projection
Desired Outcomes:
Value-Add Engineering Assistance to OEM
Increase OEM knowledge and comfort with Dow UF product
Engage in dialogue for technical questions & further support
DOW
TM
UF Certificates
NSF/ANSI Standard 61
Drinking Water System Components
PDWE Certification
USEPA ETV
Removal of Microbial Contaminants in Drinking Water
California Surface Water Treatment Rule (SWTR)
California Department Public Health
Title 22 Recycle Criteria
Drinking Water LRV
o 4-log Removal of Cryptosporidium
o 4-log Removal of Giardia
DOW
TM
UF References
Globally more than 800 plants running with DOW
Ultrafiltration
Over 3,000,000 m
3
/day UF capacity Global
Over 85 installations more than 7,500 m
3
/day
capacity
Wide range of Applications:
Prefiltration before Desalination
Surface Water Treatment
Waste Water Treatment
Process Water Treatment
DOW UF References
Examples of DOW
TM
UF Systems
Al Ain, UAE (Waste Water Reuse UF/RO)
Magong, Taiwan (Seawater UF/RO)
Tamar Valley, Tasmania (Surface Water UF/RO/IEX)
Borsodchem, Hungary (River Water UF/RO)
Ataky, Turkey (Secondary Effluent)
Moni, Cyprus (Seawater UF/RO)
Yanshan Refinery, China (Waste Water UF/RO)
Nikolayev, Ukraine (Bore Well Water UF/RO)
Gaojing, China (CTBD Reuse UF/RO/EDI)
WangTan, China (Seawater UF/RO)
Shuozhou Geruite Power Plant Project (Groundwater)
Valencia, Spain (Well Water, UF/RO).
Soft Drink, Spain (Well Water UF/RO)
Mining, Spain (River Water UF/RO)
Madagascar (Surface Water UF)
Damietta, Egypt (Surface Water, UF+RO)
El Shabab, Egypt (Surface Water, UF+2-pass RO)
54
Useful Links about DOW UF
DOW
TM
Ultrafiltration product Overview, Literature & Manuals:
http://www.dowwaterandprocess.com/products/uf/index.htm
Ultrafiltration Product Video and Fiber Repair Video:
http://www.dowwaterandprocess.com/support_training/videos/index.htm
Thank You !
People and Technology Putting Quality Water
Within Your Reach
www.dowwatersolutions.com
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Membrane Technology TestDocument10 pagesMembrane Technology TestfasihaPas encore d'évaluation
- Membrane Technology Overview for Water TreatmentDocument39 pagesMembrane Technology Overview for Water Treatmentarun kumar100% (1)
- Operator - Book-StpDocument113 pagesOperator - Book-StpAce Dynamics IndiaPas encore d'évaluation
- KMS Membrane CleaningDocument2 pagesKMS Membrane CleaningmagzigioPas encore d'évaluation
- 4-MCran Membrane CleaningDocument41 pages4-MCran Membrane CleaningKhalid AbdelRahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Membrane Treatment Processes Offer Versatility and Physical Barrier for Contaminant RemovalDocument8 pagesMembrane Treatment Processes Offer Versatility and Physical Barrier for Contaminant RemovalbazediPas encore d'évaluation
- Sms EngDocument40 pagesSms EngseruizviPas encore d'évaluation
- Training Program ForDocument94 pagesTraining Program Fortata_77Pas encore d'évaluation
- Uf Tech ManualDocument18 pagesUf Tech ManualVemulapalli SaibabuPas encore d'évaluation
- Standard MBR Units PDFDocument9 pagesStandard MBR Units PDFWilmer Martelo Sarabia100% (1)
- SWTP Operation ManualDocument131 pagesSWTP Operation ManualKASHIFPas encore d'évaluation
- MF Uf NFDocument69 pagesMF Uf NFNguyen Huu HieuPas encore d'évaluation
- UNA-620A - Operating InstructionREV02 by B.bennettDocument27 pagesUNA-620A - Operating InstructionREV02 by B.bennettcysauts100% (2)
- PermutitDocument70 pagesPermutitAlfredo HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- MBBR Design StudyDocument18 pagesMBBR Design StudyVedaraman IyerPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultra Pure WaterDocument6 pagesUltra Pure Watergauravgarg115Pas encore d'évaluation
- Metito - TSE RO Presentation KM DC WorkshopDocument24 pagesMetito - TSE RO Presentation KM DC WorkshopMohamed TahounPas encore d'évaluation
- 250 KLD MBR Membrane System DesignDocument2 pages250 KLD MBR Membrane System DesignNithin BharathiPas encore d'évaluation
- UF TORAY PresentationDocument27 pagesUF TORAY PresentationAlfonso José García Laguna100% (1)
- Basic Principles of Pre-Treatment Scheme in Water Treatment SystemDocument16 pagesBasic Principles of Pre-Treatment Scheme in Water Treatment Systemisquare77100% (1)
- Exp 3Document15 pagesExp 3mjunaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Tube SettlersDocument3 pagesTube Settlersmsajidfcc100% (1)
- MBR Design ConsiderationsDocument16 pagesMBR Design ConsiderationsDhanraj BnPas encore d'évaluation
- Role of Microorganisms in Waste Water Treatment FinalDocument12 pagesRole of Microorganisms in Waste Water Treatment FinalAhmad AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Operation and Control of STPDocument11 pagesOperation and Control of STPHari Krishna.MPas encore d'évaluation
- Wasseraufbereitung enDocument16 pagesWasseraufbereitung enVera VeroniquePas encore d'évaluation
- Application of Electro-Membrane Technologies in Zero Liquid Discharge TechnologyDocument27 pagesApplication of Electro-Membrane Technologies in Zero Liquid Discharge TechnologyYesid Tapiero MartínezPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual ENG - Kristal 600ER0820 V1.3b (221110)Document49 pagesManual ENG - Kristal 600ER0820 V1.3b (221110)merifie renegado67% (3)
- Bill of Quantities Sewage Treatment PlanDocument11 pagesBill of Quantities Sewage Treatment PlanMiguel ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- 100 PF01Document87 pages100 PF01Việt Hoàng Bùi100% (2)
- Reverse Osmosis State of The Art in IndonesiaDocument16 pagesReverse Osmosis State of The Art in IndonesiachrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Memcor UF CS CP Changi Singapore 45 D03679 enDocument2 pagesMemcor UF CS CP Changi Singapore 45 D03679 enRiannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reverse OsmosisDocument18 pagesReverse Osmosisvidya_arti100% (1)
- HYDRAcap MAX Presentation - Abril 2012Document32 pagesHYDRAcap MAX Presentation - Abril 2012PC VSPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Treatment: Micro- and Ultrafiltration ExplainedDocument16 pagesWater Treatment: Micro- and Ultrafiltration ExplainedGregor Grbec100% (1)
- Containerisedmbrsystem EngDocument12 pagesContainerisedmbrsystem EngNermeen ElmelegaePas encore d'évaluation
- REVERSE OSMOSIS TECHNOLOGY FOR WATER TREATMENTDocument73 pagesREVERSE OSMOSIS TECHNOLOGY FOR WATER TREATMENTAkhil ShrivastavPas encore d'évaluation
- Reverse Osmosis Data AnalysisDocument74 pagesReverse Osmosis Data AnalysisShark1971Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pre TreatmentDocument65 pagesPre TreatmentSagar SewlaniPas encore d'évaluation
- DM Plant Design CalculationDocument10 pagesDM Plant Design CalculationLutfur RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- EDI TRAINING Processtech October 5 2016Document118 pagesEDI TRAINING Processtech October 5 2016Quang Hiếu Ngô100% (1)
- Seapak Series: Integrated Ultrafiltration and Seawater Reverse Osmosis Platform For 1,000 - 10,000 M /dayDocument2 pagesSeapak Series: Integrated Ultrafiltration and Seawater Reverse Osmosis Platform For 1,000 - 10,000 M /dayadalcayde2514100% (1)
- TMF Lime SofteningDocument2 pagesTMF Lime SofteningRachel HechanovaPas encore d'évaluation
- ProServe - RO Training Course - Part II PDFDocument49 pagesProServe - RO Training Course - Part II PDFmohamed karemPas encore d'évaluation
- EDR Technical Training for GE Sales and MarketingDocument80 pagesEDR Technical Training for GE Sales and MarketingHassan Feki100% (1)
- Reverse Osmosis Model R4X40 Installation InstructionsDocument16 pagesReverse Osmosis Model R4X40 Installation InstructionsWattsPas encore d'évaluation
- Budgetary Offer: Sms Envocare Limited For Muzafarpur CetpDocument41 pagesBudgetary Offer: Sms Envocare Limited For Muzafarpur Cetpsreekanth reddyPas encore d'évaluation
- MAN6110 - EN Pressure Sand FilterDocument2 pagesMAN6110 - EN Pressure Sand FilterDang Hieu NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Coagulation and Ultrafiltration in Seawa PDFDocument227 pagesCoagulation and Ultrafiltration in Seawa PDFGigih PramonoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Water Treatment Process StepsDocument46 pagesChemical Water Treatment Process StepsNazar Abdul KareemPas encore d'évaluation
- Operation and Maintenance Manual: Effluent Treatment PlantDocument49 pagesOperation and Maintenance Manual: Effluent Treatment PlantOmkar BharankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec4 Water and Wastewater TreatmentDocument54 pagesLec4 Water and Wastewater TreatmentKent Harry CumpioPas encore d'évaluation
- DAF Oil RemovalDocument2 pagesDAF Oil RemovalAVIJIT MITRAPas encore d'évaluation
- Adv 885 Ro Pac M QuickrefguideDocument8 pagesAdv 885 Ro Pac M QuickrefguideAlejandroOdioCastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- MBR C0 IntroductionDocument4 pagesMBR C0 IntroductionAlfonso José García LagunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Membrane Bio Reactors ExplainedDocument16 pagesMembrane Bio Reactors Explainedvvrckumar100% (1)
- Hyflux Standard Membrane Systems Brochure - Ver5.1 - ENDocument40 pagesHyflux Standard Membrane Systems Brochure - Ver5.1 - ENIGNyomanAnomWijayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Saadiyat Sewage Treatment Plant, UAE-Abu Dhabi: A Case StudyDocument4 pagesSaadiyat Sewage Treatment Plant, UAE-Abu Dhabi: A Case StudyLexPas encore d'évaluation
- General Marine Loading Arm MaintenanceDocument1 pageGeneral Marine Loading Arm MaintenanceMoustafa HelmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Kao Corporation, S.A.: SK Fert FA80TSDocument1 pageKao Corporation, S.A.: SK Fert FA80TSMoustafa HelmyPas encore d'évaluation
- March 2017 - August 2018: API SIRE Exam Publications Effectivity Sheet - ForDocument2 pagesMarch 2017 - August 2018: API SIRE Exam Publications Effectivity Sheet - ForSlbcar LoogingPas encore d'évaluation
- System AnalysisDocument2 pagesSystem AnalysismustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Potassium Silicate SDSDocument9 pagesPotassium Silicate SDSMoustafa HelmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Machinery Lubricantion Fundamentls Course OutlineDocument1 pageMachinery Lubricantion Fundamentls Course OutlineMoustafa HelmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Auditing Effect On Firm Performance-Final GheatyDocument50 pagesAuditing Effect On Firm Performance-Final GheatyMoustafa HelmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Valve SpecificationsDocument2 pagesValve SpecificationsMoustafa HelmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Report Lecico FinalDocument52 pagesProject Report Lecico FinalMoustafa HelmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Offer letter for Position of Job Title at Company NameDocument1 pageOffer letter for Position of Job Title at Company NameMoustafa HelmyPas encore d'évaluation
- T24117 127Document12 pagesT24117 127Moustafa HelmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Potassium SilicateDocument1 pagePotassium SilicateMoustafa HelmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Pipe Sch 40 SMAW Assumptions and Correction FactorsDocument1 pagePipe Sch 40 SMAW Assumptions and Correction FactorsMoustafa HelmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Corporate GovernanceDocument12 pagesCorporate GovernanceMoustafa HelmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Gift LetterDocument1 pageGift LetterMoustafa HelmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Nitric Acid 60 PR - Product Data SheetDocument1 pageNitric Acid 60 PR - Product Data SheetMoustafa HelmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Storage of Hot Ammonium Nitrate Solutions (BPE)Document48 pagesStorage of Hot Ammonium Nitrate Solutions (BPE)Vanjared OcampoPas encore d'évaluation
- Starbucks Company TimelineDocument5 pagesStarbucks Company TimelineMoustafa HelmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistics Traning ExamDocument6 pagesStatistics Traning ExamMoustafa Helmy100% (2)
- Corporate Governance and AuditDocument12 pagesCorporate Governance and AuditMoustafa HelmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Jungtec - Prospekt - EnglischDocument44 pagesJungtec - Prospekt - EnglischMoustafa HelmyPas encore d'évaluation
- KaolinDocument1 pageKaolinMoustafa HelmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Asset Maintenance ManagementDocument37 pagesAsset Maintenance ManagementMoustafa Helmy100% (1)
- Mcdonald Final 2 140409005910 Phpapp02Document21 pagesMcdonald Final 2 140409005910 Phpapp02Moustafa HelmyPas encore d'évaluation
- VIB Booklet ENDocument36 pagesVIB Booklet ENPetra HeutsPas encore d'évaluation
- Vibxpert-II Brochure Lit.53.400.EnDocument4 pagesVibxpert-II Brochure Lit.53.400.EnMoustafa HelmyPas encore d'évaluation
- M0743-109000 Barrierta L55 2Document4 pagesM0743-109000 Barrierta L55 2Moustafa HelmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance Curve For Firefighting PumpDocument1 pagePerformance Curve For Firefighting PumpMoustafa HelmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Delayed Intermittent ControlDocument2 pagesDelayed Intermittent ControlMoustafa HelmyPas encore d'évaluation
- AQUA26504 Design Guide PDFDocument84 pagesAQUA26504 Design Guide PDFDiego GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Akshay - A20104016011 - Assignment 2 - CEA - BAR 906 PDFDocument6 pagesAkshay - A20104016011 - Assignment 2 - CEA - BAR 906 PDFAkshayPas encore d'évaluation
- Gri g4 Ngo Sector DisclosuresDocument48 pagesGri g4 Ngo Sector DisclosuresbeearacerPas encore d'évaluation
- Social Science Class 10 Important Questions Geography Chapter 6 Manufacturing IndustriesDocument20 pagesSocial Science Class 10 Important Questions Geography Chapter 6 Manufacturing IndustriesMedhunPas encore d'évaluation
- SCELI Course (Answer Sheet)Document4 pagesSCELI Course (Answer Sheet)Jay MasagcaPas encore d'évaluation
- Akram CV Final 2Document5 pagesAkram CV Final 2akram husseinPas encore d'évaluation
- OdishaDocument36 pagesOdishanirvana.7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Crop Water Requirement in Irrigation Scheduling For Orange Keprok 55 in Selorejo Village Using Cropwat 8.0Document10 pagesCrop Water Requirement in Irrigation Scheduling For Orange Keprok 55 in Selorejo Village Using Cropwat 8.0nunung lutfiyahPas encore d'évaluation
- BUSM2580 - Vinamilk's Green Initiative Awards ACES-1Document19 pagesBUSM2580 - Vinamilk's Green Initiative Awards ACES-1nhitrandkmtPas encore d'évaluation
- Step 3 - Exposure DatabaseDocument78 pagesStep 3 - Exposure DatabaseRodel UrianPas encore d'évaluation
- Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument102 pagesRefrigeration and Air ConditioningYuvaperiyasamy MayilsamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Biosperse 250 Pail 25L UsDocument16 pagesBiosperse 250 Pail 25L UsOmokaro GordonPas encore d'évaluation
- GMCC Manual Provides Overview of Rotary Compressor ProductsDocument24 pagesGMCC Manual Provides Overview of Rotary Compressor ProductsIgor BaleraPas encore d'évaluation
- Internship ProjectDocument13 pagesInternship Projectapi-542655871Pas encore d'évaluation
- Annex B 2 - 05 - Kfar Hanasi - FS3V-12°-16 - DUODocument1 pageAnnex B 2 - 05 - Kfar Hanasi - FS3V-12°-16 - DUOmatan dvirPas encore d'évaluation
- Green Building Strategies and BenefitsDocument6 pagesGreen Building Strategies and BenefitsAlinda Gupta AbhroPas encore d'évaluation
- SWMP - ZamboangitaDocument127 pagesSWMP - ZamboangitakeeshabutedPas encore d'évaluation
- MALAYSIA'S ENERGY POLICIES AND EFFICIENCY STANDARDSDocument99 pagesMALAYSIA'S ENERGY POLICIES AND EFFICIENCY STANDARDSZaidi RasipPas encore d'évaluation
- Wetlands of Uttarakhand ReportDocument194 pagesWetlands of Uttarakhand ReportSuman SaurabhPas encore d'évaluation
- CAMILE ULOcDocument8 pagesCAMILE ULOcKaguraPas encore d'évaluation
- Climate Factors that Affect RegionsDocument7 pagesClimate Factors that Affect Regionsmylene neviarPas encore d'évaluation
- Land and Sea Breezes ExplainedDocument2 pagesLand and Sea Breezes ExplainedFatima Abacan ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- 1globe Telecom Inc Chap 3Document6 pages1globe Telecom Inc Chap 3John Cedrick TaguibaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nature of Communication ModelsDocument10 pagesNature of Communication ModelsPatrick Rómulo CabilingPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Storage and Power Management: Sustainable SolutionsDocument36 pagesEnergy Storage and Power Management: Sustainable SolutionsTunji AlabiPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument16 pagesUntitledHenry NketiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Humeceptor: Technical ManualDocument44 pagesHumeceptor: Technical ManualAsifPas encore d'évaluation
- EPA Water Filtration ManualDocument160 pagesEPA Water Filtration ManualBelmokre AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Ilda Safira - 200721639694 - B - Analisis Pengelolaan Wisata Taman Rolak Dan Pure Luhur Dwijawarsa Kecamatan Kedungkandang, Kota MalangDocument11 pagesIlda Safira - 200721639694 - B - Analisis Pengelolaan Wisata Taman Rolak Dan Pure Luhur Dwijawarsa Kecamatan Kedungkandang, Kota MalangIlda SafiraPas encore d'évaluation
- K to 12 curriculum explores living things reproductionDocument12 pagesK to 12 curriculum explores living things reproductionBik BokPas encore d'évaluation