Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Ac Ups Sizing
Transféré par
gbaludb0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
22 vues8 pagesups
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentups
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
22 vues8 pagesAc Ups Sizing
Transféré par
gbaludbups
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 8
AC UPS Sizing
From Open Electrical
Jump to: navigation, search
Contents
[hide]
1 Introduction
o 1.1 Why do the calculation?
o 1.2 When to do the calculation?
2 Calculation ethodology
o 2.1 !tep 1: Collect the "C #$! %oads
o 2.2 !tep 2: %oad $ro&ile, 'esign %oad and 'esign (nergy
o 2.) !tep ): *attery !i+ing
2.).1 ,ominal *attery -or 'C %in./ 0oltage
2.).2 ,um1er o& Cells in !eries
o 2.2 !tep 2: #$! !i+ing
2.2.1 3verall #$! !i+ing
2.2.2 4ecti&ier 5 Charger !i+ing
2.2.) Inverter !i+ing
2.2.2 !tatic !6itch !i+ing
) Wor.ed (7ample
o ).1 !tep 1 and 2: Collect the "C #$! %oads and Construct %oad $ro&ile
o ).2 !tep ): *attery !i+ing
o ).) !tep 2: #$! !i+ing
).).1 3verall !i+ing
).).2 4ecti&ier !i+ing
).).) Inverter and !tatic !6itch !i+ing
2 8emplate
9 Computer !o&t6are
: What ne7t?
Introduction
8his calculation deals 6ith the si+ing o& an "C uninterrupti1le po6er supply -#$!/
system -i.e. recti&ier, 1attery 1an. and inverter/. In this calculation, it is assumed that the
"C #$! is a dou1le conversion type 6ith a 1asic system topology as sho6n in ;igure 1.
;igure 1 < "C #$! 1asic system topology
"n e7ternal maintenance 1ypass s6itch and galvanic isolation trans&ormers are other
common additions to the 1asic topology, 1ut these have 1een omitted &rom the system as
they are irrelevant &or the si+ing calculation.
Why do the calculation?
"n "C #$! system is used to support critical 5 sensitive "C loads. It is typically a
1attery<1ac.ed system 6hich 6ill continue to operate &or a speci&ied amount o& time
-called the autonomy/ a&ter a main po6er supply interruption. "C #$! systems are also
used as sta1le po6er supplies that provide a reasona1ly constant voltage and &re=uency
output, independent o& voltage input. 8his is particularly use&ul &or sensitive electrical
e=uipment on main po6er supplies that are prone to voltage 5 &re=uency &luctuations or
insta1ility.
8he "C #$! si+ing calculation determines the ratings &or the main "C #$! system
components: 1/ recti&ier, 2/ 1attery 1an.s and )/ inverter.
In some cases, the manu&acturer 6ill independently si+e the system and it is only
necessary to construct the "C #$! load schedule and load pro&ile. >o6ever the
calculation results 6ill also help determine the indicative dimensions o& the e=uipment
-e.g. si+e o& 1attery 1an.s/ &or preliminary layout purposes.
When to do the calculation?
8he "C #$! si+ing calculation can 1e done 6hen the &ollo6ing prere=uisite in&ormation
is .no6n:
#$! loads that need to 1e supported
Input 5 3utput "C voltage
"utonomy time-s/
*attery type
Calculation Methodology
8he calculation procedure has &our main steps:
1/ 'etermine and collect the prospective "C #$! loads
2/ Construct a load pro&ile and determine the #$! design load -0"/ and design
energy -0"h/
)/ Calculate the si+e o& the stationary 1attery -num1er o& cells in series and "h
capacity/
2/ 'etermine the si+e o& the inverter, recti&ier5 charger and static s6itch
Step ! Collect the AC UPS "oads
8he &irst step is to determine the type and =uantity o& loads that the "C #$! system 6ill
1e e7pected to support. ;or industrial &acilities, this 6ill typically 1e critical
instrumentation and control loads such as the 'C! and (!' processor and marshalling
hard6are, critical 6or.stations and >I?s, telecommunications e=uipment and sensitive
electronics. 8he necessary load data should 1e availa1le &rom the instrumentation and
control engineers.
;or commercial &acilities, #$! loads 6ill mainly 1e server, data 5 net6or. and
telecommunications hard6are.
Step #! "oad Pro$ile% &esign "oad and &esign Energy
4e&er to the %oad $ro&ile Calculation &or details on ho6 to construct a load pro&ile,
calculate the design load - / and design energy - /. 8he @"utonomy method@ &or
constructing load pro&iles is typically used &or "C #$! systems.
8he autonomy time is o&ten speci&ied 1y the Client -i.e. in their standards/. "lternatively,
I((( 22:, @I((( 4ecommended $ractice &or (mergency and !tand1y $o6er !ystems &or
Industrial and Commercial "pplications@ has some guidance -particularly 8a1le )<2/ &or
autonomy times. !ometimes a single autonomy time is used &or the entire "C #$! load,
6hich o1viously ma.es the construction o& the load pro&ile easier to compute.
Step '! (attery Sizing
4e&er to the *attery !i+ing Calculation &or details on ho6 to si+e the 1attery &or the "C
#$! system. 8he &ollo6ing sections provide additional in&ormation speci&ic to 1attery
si+ing &or "C #$! applications.
)ominal (attery *or &C "in+, -oltage
8he nominal 1attery 5 'C lin. voltage is o&ten selected 1y the "C #$! manu&acturer.
>o6ever, i& re=uired to 1e selected, the &ollo6ing &actors need to 1e considered:
'C output voltage range o& the recti&ier A the recti&ier must 1e a1le to
output the speci&ied 'C lin. voltage
'C input voltage range o& the inverter A the 'C lin. voltage must 1e
6ithin the input voltage tolerances o& the inverter. ,ote that the 1attery
end o& discharge voltage should 1e 6ithin these tolerances.
,um1er o& 1attery cells re=uired in series A this 6ill a&&ect the overall
dimensions and si+e o& the 1attery rac.. I& physical space is a constraint,
then less 1atteries in series 6ould 1e pre&era1le.
8otal 'C lin. current -at &ull load/ A this 6ill a&&ect the si+ing o& the 'C
ca1les and inter<cell 1attery lin.s. 31viously the smaller the 1etter.
In general, the 'C lin. voltage is usually selected to 1e close to the nominal output
voltage.
)um.er o$ Cells in Series
8he num1er o& 1attery cells re=uired to 1e connected in series must 1e 1et6een the t6o
&ollo6ing limits:
-1/
-2/
6here Nmax is the ma7imum num1er o& 1attery cells
Nmin is the minimum num1er o& 1attery cells
Vdc is the nominal 1attery 5 'C lin. voltage -0dc/
Vi,max is the inverter ma7imum input voltage tolerance -B/
Vi,min is the inverter minimum input voltage tolerance -B/
Vf is the nominal cell &loat -or 1oost/ voltage -0dc/
Veod is the cell end o& discharge voltage -0dc/
8he limits are 1ased on the input voltage tolerance o& the inverter. "s a ma7imum, the
1attery at &loat voltage -or 1oost i& applica1le/ needs to 1e 6ithin the ma7imum input
voltage range o& the inverter. %i.e6ise as a minimum, the 1attery at its end o& discharge
voltage must 1e 6ithin the minimum input voltage range o& the inverter.
!elect the num1er o& cells in 1et6een these t6o limits -more or less ar1itrary, though
some6here in the middle o& the min5ma7 values 6ould 1e appropriate/.
Step /! UPS Sizing
O0erall UPS Sizing
ost o& the time, all you need to provide is the overall #$! .0" rating and the #$!
vendor 6ill do the rest. Civen the design load - in 0" or .0"/ calculated in !tep 2,
select an overall #$! rating that e7ceeds the design load. 0endors typically have standard
#$! ratings, so it is possi1le to simply select the &irst standard rating that e7ceeds the
design load. ;or e7ample, i& the design load 12.0", then the ne7t si+e unit -e.g. 19.0"
#$!/ 6ould 1e selected.
1ecti$ier 2 Charger Sizing
8he recti&ier 5 charger should 1e si+ed to supply the inverter at &ull load and also charge
the 1atteries -at the ma7imum charge current/. 8he design 'C load current can 1e
calculated 1y:
6here IL,dc is the design 'C load current -&ull load/ -"/
S is the selected #$! rating -.0"/
Vdc is the nominal 1attery 5 'C lin. voltage -0dc/
8he ma7imum 1attery charging current can 1e computed as &ollo6s:
6here Ic is the ma7imum 'C charge current -"/
C is the selected 1attery capacity -"h/
kl is the 1attery recharge e&&iciency 5 loss &actor -typically 1.1/ -pu/
tc is the minimum 1attery recharge time -hours/
8he total minimum 'C recti&ier 5 charger current is there&ore:
!elect the ne7t standard recti&ier 5 charger rating that e7ceeds the total minimum 'C
current a1ove.
In0erter Sizing
8he inverter must 1e rated to continuously supply the #$! loads. 8here&ore, the inverter
can 1e si+ed using the design "C load current -1ased on the selected #$! .0" rating/.
;or a three<phase #$!:
;or a single<phase #$!:
6here IL is the design "C load current -&ull load/ -"/
S is the selected #$! rating -.0"/
Vo is the nominal output voltage -line<to<line voltage &or a three phase #$!/ -0ac/
!elect the ne7t standard inverter rating that e7ceeds the design "C load current.
Static S3itch Sizing
%i.e the inverter, the static s6itch must 1e rated to continuously supply the #$! loads.
8here&ore, the static s6itch can 1e si+ed using the design "C load current -as a1ove &or
the inverter si+ing/.
Wor+ed E4ample
Step and #! Collect the AC UPS "oads and Construct "oad Pro$ile
%oad pro&ile &or this e7ample
;or this e7ample, 6e shall use the same loads and load pro&ile detailed in the (nergy
%oad $ro&ile Calculation e7ample. 8he load pro&ile is sho6n in the &igure right and the
&ollo6ing =uantities 6ere calculated:
'esign load Sd D E:F 0"
'esign energy demand Ed D ),21: 0"h
Step '! (attery Sizing
;or this e7ample, 6e shall use the same 1attery si+es calculated in the *attery !i+ing
Calculation 6or.ed e7ample. 8he selected num1er o& cells in series is :2 cells and the
minimum 1attery capacity is 22.2 "h. " 1attery capacity o& 9G "h is selected.
Step /! UPS Sizing
O0erall Sizing
Civen the design load o& E:F 0", then a 1 .0" #$! 6ould 1e appropriate.
1ecti$ier Sizing
Civen a nominal dc lin. voltage o& 12G0dc, the design 'C load current is:
"
!uppose the minimum 1attery recharge time is 2 hours and a recharge e&&iciency &actor o&
1.1 is used. 8he ma7imum 1attery charging current is:
"
8here&ore the total minimum 'C recti&ier 5 charger current is:
"
" 'C recti&ier rating o& 2G" is selected.
In0erter and Static S3itch Sizing
!uppose the nominal output voltage is 22G0ac. 8he design "C load current is:
"
"n inverter and static s6itch rating o& 9" is selected.
5emplate
" pro&essional, &ully customisa1le (7cel spreadsheet template o& the "C #$! calculation
can 1e purchased &rom %ulu.
8he template is 1ased on the calculation procedure descri1ed in this page and includes the
&ollo6ing &eatures:
%oad schedule and automatic load pro&ile generation
*attery si+ing
#$! component si+ing -e.g. recti&ier, inverter, etc/
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Fire Tender 2014Document37 pagesFire Tender 2014gbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- Supply, Installation & Testing and Commissioning of P.A. System, Tower AC & Water Cooler Cum Purifier For IHM & Different Panthanivas of OTDC LTDDocument9 pagesSupply, Installation & Testing and Commissioning of P.A. System, Tower AC & Water Cooler Cum Purifier For IHM & Different Panthanivas of OTDC LTDgbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- M Tender 514Document5 pagesM Tender 514gbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- National Institute of Fashion Technology, KolkataDocument9 pagesNational Institute of Fashion Technology, KolkatagbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- Tender 767Document2 pagesTender 767gbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- Pa System Analogue SpecificationDocument2 pagesPa System Analogue SpecificationgbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- Tender For CCTV New - Copy 1Document12 pagesTender For CCTV New - Copy 1gbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- Tender For Sitc of Pa Systems - Nabard MproDocument30 pagesTender For Sitc of Pa Systems - Nabard MprogbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- Govt. of National Capital Territory Delhi Delhi Subordinate Services Selection Board Fc-18, Institutional Area, Karkardooma, Delhi-110092Document7 pagesGovt. of National Capital Territory Delhi Delhi Subordinate Services Selection Board Fc-18, Institutional Area, Karkardooma, Delhi-110092gbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- Tender Form Pa SystemsDocument3 pagesTender Form Pa SystemsgbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- 05 WiproDocument26 pages05 WiprogbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- WP155002EN Optimizing Rack LRDocument4 pagesWP155002EN Optimizing Rack LRgbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- For The Works of Near: Unit QTY Rate AmountDocument3 pagesFor The Works of Near: Unit QTY Rate AmountgbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- AMCPASDocument3 pagesAMCPASgbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- PAS TenderDocument8 pagesPAS TendergbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- Chennai Port Trust: TENDER No. MEE/15/2013/ DCME (EC/OS)Document56 pagesChennai Port Trust: TENDER No. MEE/15/2013/ DCME (EC/OS)gbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- Tender For Sound System For Class RoomsDocument5 pagesTender For Sound System For Class RoomsgbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- Cissca v2 Catalog en W o MarkDocument2 pagesCissca v2 Catalog en W o MarkgbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless Address Able Smoke DetectorDocument1 pageWireless Address Able Smoke DetectorgbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- WVP 25118 - 218 - 126 - 226 NSDocument1 pageWVP 25118 - 218 - 126 - 226 NSgbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- Datashe T E: Input Interface UnitDocument1 pageDatashe T E: Input Interface UnitgbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- Intellivox DS180 Data 011614Document12 pagesIntellivox DS180 Data 011614gbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide To Commercial InstallationsDocument42 pagesGuide To Commercial InstallationsgbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- 7Hfkqlfdo8Qlyhuvlw/ $VDFKL, Dvl%Oyg'0Dqjhurqqrwhoyyduydud#UgvolqnurDocument4 pages7Hfkqlfdo8Qlyhuvlw/ $VDFKL, Dvl%Oyg'0Dqjhurqqrwhoyyduydud#UgvolqnurgbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
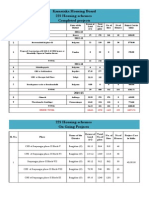
- 225 Ongoing Projects CompletedDocument4 pages225 Ongoing Projects CompletedgbaludbPas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Ice305 Lab5Document13 pagesIce305 Lab5Arnab SarkerPas encore d'évaluation
- ISD1820 Voice Recorder Module User Guide: Rev 1.0, Oct 2012Document5 pagesISD1820 Voice Recorder Module User Guide: Rev 1.0, Oct 2012HARFA industriesPas encore d'évaluation
- ROLAN BART Zadovoljstvo U TekstuDocument56 pagesROLAN BART Zadovoljstvo U Tekstujokokokl100% (18)
- None C9efb7c9Document6 pagesNone C9efb7c9liana iwiwPas encore d'évaluation
- Is B or H The Fundamental Magnetic FieldDocument8 pagesIs B or H The Fundamental Magnetic FieldcfsenelPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of Heat ExchangersDocument12 pagesClassification of Heat Exchangersvishal samundrePas encore d'évaluation
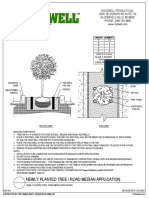
- Newly Planted Tree / Road Median ApplicationDocument1 pageNewly Planted Tree / Road Median ApplicationmooolkaPas encore d'évaluation
- X-Ray Diffraction: Geoenvironmental Research Group Laboratory Manual 2008Document4 pagesX-Ray Diffraction: Geoenvironmental Research Group Laboratory Manual 2008Nhan Nguyen VanPas encore d'évaluation
- A словаDocument297 pagesA словаailisha libraPas encore d'évaluation
- Nora Alexander: ProfileDocument1 pageNora Alexander: ProfilenorajuliaalexanderPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5.0.2018 - Retaining WallDocument36 pagesChapter 5.0.2018 - Retaining WallHawaiiChongPas encore d'évaluation
- Who Am I MemoDocument2 pagesWho Am I Memoapi-652685391Pas encore d'évaluation
- PDFDocument764 pagesPDFDe JavuPas encore d'évaluation
- Ladd CC 1964 - Stress-Strain Behavior of Saturated Clay and Basic Strength Principles PDFDocument125 pagesLadd CC 1964 - Stress-Strain Behavior of Saturated Clay and Basic Strength Principles PDFSaraswati NoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Candy System Functionalities ListDocument4 pagesCandy System Functionalities ListPauloKupesaPas encore d'évaluation
- IPCA Precast Concrete Frames GuideDocument58 pagesIPCA Precast Concrete Frames GuideMaurício Ferreira100% (1)
- Code ArduinoDocument3 pagesCode ArduinoSuaib DanishPas encore d'évaluation
- Tracing The Location of A Typhon Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesTracing The Location of A Typhon Lesson PlanJoh A Nna100% (2)
- Bahria University (Karachi Campus) : Department of Electrical Engineering Assignment # 03Document11 pagesBahria University (Karachi Campus) : Department of Electrical Engineering Assignment # 03rizwan ahmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Program in Less Than 24 MonthsDocument2 pagesProgram in Less Than 24 MonthsHermi BurquesPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 A Study of Encryption AlgorithmsDocument9 pages4 A Study of Encryption AlgorithmsVivekPas encore d'évaluation
- Using Fonts Installed in Local Texlive - TeX - LaTeX Stack ExchangeDocument8 pagesUsing Fonts Installed in Local Texlive - TeX - LaTeX Stack ExchangeFuncionario CepaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fmparente Erftc Porto 20090605Document78 pagesFmparente Erftc Porto 20090605ChiefpereraPas encore d'évaluation
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Part - 2, Lecture - 12: Unification in First-Order LogicDocument18 pagesArtificial Intelligence (AI) Part - 2, Lecture - 12: Unification in First-Order LogicMazharul RahiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan Letter MDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Letter Mapi-307404579Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ashtakavarga PredictionDocument5 pagesAshtakavarga Predictionmagicalseas40% (5)
- 7.proceeding Snib-Eng Dept, Pnp-IndonesiaDocument11 pages7.proceeding Snib-Eng Dept, Pnp-IndonesiamissfifitPas encore d'évaluation
- Sr. No. Reference - Id Name NQT - Reference - Id Email - Id Highest Institute Name Qualification SpecializationDocument6 pagesSr. No. Reference - Id Name NQT - Reference - Id Email - Id Highest Institute Name Qualification SpecializationKinzang NamgayPas encore d'évaluation
- MBA MCA Fee 2012Document53 pagesMBA MCA Fee 2012Sudhir KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- MCE Cambridge Primary Maths 2E Stage6 PPT C05Document25 pagesMCE Cambridge Primary Maths 2E Stage6 PPT C05Novi YufitriPas encore d'évaluation