Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Ovalent Bond
Transféré par
darkmantrastore0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
30 vues2 pagesOvalent Bond Data
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentOvalent Bond Data
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
30 vues2 pagesOvalent Bond
Transféré par
darkmantrastoreOvalent Bond Data
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
ovalent bond
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
"Covalent" redirects here. For other uses, see Covalent (disambiguation).
A covalent bond forming H
2
(right) where two hydrogen atoms share the two electrons
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms.
The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms when they share electrons is
known as covalent bonding.
[1]
For many molecules, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to
attain the equivalent of a full outer shell, corresponding to a stable electronic configuration.
Covalent bonding includes many kinds of interactions, including -bonding, -bonding, metal-
to-metal bonding, agostic interactions, and three-center two-electron bonds.
[2][3]
The term
covalent bond dates from 1939.
[4]
The prefix co- means jointly, associated in action, partnered to
a lesser degree, etc.; thus a "co-valent bond", in essence, means that the atoms share "valence",
such as is discussed in valence bond theory. In the molecule H
2, the hydrogen atoms share the two electrons via covalent bonding.
[5]
Covalency is greatest
between atoms of similar electronegativities. Thus, covalent bonding does not necessarily require
that the two atoms be of the same elements, only that they be of comparable electronegativity.
Covalent bonding that entails sharing of electrons over more than two atoms is said to be
delocalized.
There are three types of covalent bond depending upon the number of shared electron
pairs.
SINGLE COVALENT BOND
DOUBLE COVALENT BOND
TRIPLE COVALENT BOND
SINGLE COVALENT
BOND
A covalent bond formed by the mutual sharing of one electron pair between two atoms is
called a "Single Covalent bond."
It is denoted by single short line( )
Examples:
In single bond formation each atom provide one electron.
DOUBLE COVALENT
BOND
A covalent bond formed between two atoms by the mutual sharing of two electron pairs is
called a "double covalent bond". It is denoted by double short line ( )
For latest information , free computer courses and high impact notes visit :
www.citycollegiate.com
Examples:
TRIPLE COVALENT
BOND
A covalent bond formed by the mutual sharing of three electron pairs is called a "Triple
covalent bond". It is denoted by triple short line ( ).
Examples:
POLAR COVALENT
BOND
A covalent bond formed between two different atoms is known as Polar covalent bond.
For example when a Covalent bond is formed between H and Cl , it is polar in nature
because Cl is more electronegative than H atom . Therefore, electron cloud is shifted
towards Cl atom. Due to this reason a partial -ve charge appeared on Cl atom and an
equal +ve charge on H atom
Examples:
NON-POLAR BOND
A covalent bond formed between two like atoms is known as Non-polar bond. Since
difference of
electro negativity is zero therefore, both atoms attract electron pair equally and no charge
appears on
any atom and the whole molecule becomes neutral.
Examples:
H - H
Cl - Cl
F - F
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Chem 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesChem 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical BondingKuo SarongPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Bonding Short Notes Raftaar NItesh Devnani PDF CrdownloadDocument5 pagesChemical Bonding Short Notes Raftaar NItesh Devnani PDF Crdownloadaadil0% (1)
- ChembondDocument51 pagesChembondNovelynLozano-EdrosoPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 NCERT Book Chapter 4Document36 pages11 NCERT Book Chapter 4Pankaj MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Energetics of Jahn Teller EffectDocument8 pagesEnergetics of Jahn Teller EffectFalak NazPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 3 Q2 Gen Chem I v.2Document10 pagesModule 3 Q2 Gen Chem I v.2ariinnggg onichaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Study GuideDocument6 pagesChemistry Study GuidePaye BagnonPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 5 - Chemical Bond (5.1 - 5.3) 8 JulyDocument25 pagesCHAPTER 5 - Chemical Bond (5.1 - 5.3) 8 JulyNur100% (1)
- Ionic CompoundDocument3 pagesIonic CompoundAngel RingorPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 20 - Naming Chemical CompoundsDocument60 pagesChapter 20 - Naming Chemical CompoundsAlwielland BelloPas encore d'évaluation
- Polar and Nonpolar MoleculesDocument32 pagesPolar and Nonpolar MoleculeshensoncarlosjrPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties: Some Important Points and Terms of The ChapterDocument7 pages3.classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties: Some Important Points and Terms of The ChapterShivaPas encore d'évaluation
- G 11 BondingDocument11 pagesG 11 BondingTarek FaramawyPas encore d'évaluation
- Print 1 PDFDocument2 pagesPrint 1 PDFBernadette NaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Valence Bond Theory: 4 Meet On Chemical Bond CourseDocument52 pagesValence Bond Theory: 4 Meet On Chemical Bond Courselina lathifaPas encore d'évaluation
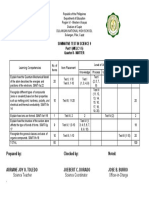
- Summative Test Tos 2ndquarter Part 1Document1 pageSummative Test Tos 2ndquarter Part 1ARRIANE JOY TOLEDO100% (1)
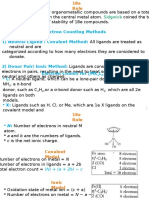
- Electron Counting Methods 1) Neutral Ligand / Covalent MethodDocument8 pagesElectron Counting Methods 1) Neutral Ligand / Covalent MethodRakshitTiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Bonding Graphic Organizer RubricDocument1 pageChemical Bonding Graphic Organizer Rubricapi-439932199100% (1)
- (BOOK CHAPTER) - 2015 - The Covalent Bond Classification Method and Its Application To Compounds That Feature 3-Center 2-Electron Bonds - GreenDocument61 pages(BOOK CHAPTER) - 2015 - The Covalent Bond Classification Method and Its Application To Compounds That Feature 3-Center 2-Electron Bonds - Greenperico palotesPas encore d'évaluation
- CY 1001 - Organic Chemistry: Anbarasan CY1001 Anbarasan CY1001Document21 pagesCY 1001 - Organic Chemistry: Anbarasan CY1001 Anbarasan CY1001Rashmi AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- 2..chemical Bonding Theory-12-12Document1 page2..chemical Bonding Theory-12-12Ashish SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ap Chemistry 2010 Scoring GuidelinesDocument10 pagesAp Chemistry 2010 Scoring GuidelinessdjilfPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 3. INTERMOLECULAR FORCESDocument2 pagesLesson 3. INTERMOLECULAR FORCESmariaisabelmatala22Pas encore d'évaluation
- SHS Physical Science Q1 SLM - 3Document25 pagesSHS Physical Science Q1 SLM - 3Adalee ColleenPas encore d'évaluation
- Intermolecular Forces: INTRAMOLECULAR Forces Are Basically The Forces That Hold Atoms Together Within A MoleculeDocument3 pagesIntermolecular Forces: INTRAMOLECULAR Forces Are Basically The Forces That Hold Atoms Together Within A MoleculeAra GonzagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Bonding, Tutorial Sheet 4Document2 pagesChemical Bonding, Tutorial Sheet 4Kelvin SichingaPas encore d'évaluation
- ReviewerDocument8 pagesReviewerRainer VicencioPas encore d'évaluation
- F321 Bonding and StructureDocument10 pagesF321 Bonding and StructureDoc_Croc100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Thesis IdeasDocument4 pagesOrganic Chemistry Thesis Ideasafkntwbla100% (2)
- Periodic Properties - Part 3Document38 pagesPeriodic Properties - Part 3Bhavesh GargPas encore d'évaluation