Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Efficiency
Transféré par
mariaceciliareonalDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Efficiency
Transféré par
mariaceciliareonalDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Efficiency generally describes the extent to which time, effort or cost is well
us: http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/performance.html#ixzz3Awmev7tqhttp://www.ehow.com/about_5374144
_death-certificate.htmlhttp://www.ehow.com/about_5374144_death-certificate.htmled for the intended task or
purpose. It is often used with the specific purpose of relaying the capability of a specific application of effort to
produce a specific outcome effectively with a
: http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/performance.html#ixzz3Awmev7tqhttp://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/pe
rformance.html#ixzz3Awmev7tqA marriage certificate is an official statement that two people are married. In most
jurisdictions, a marriage certificate is issued by a government official only after the civil registration of the
marriage.
In some jurisdictions, especially in the United States, a marriage certificate is the official record that two people
have undertaken a marriage ceremony. This includes jurisdictions where marriage licenses do not exist. In
some other jurisdictions, a marriage license serves a dual purpose of granting permission for a marriage to take
place and then endorsing the same document to record the fact that the marriage has been performed.
A marriage certificate may be required for a number of reasons. It may be required as evidence of change of a
party's name, on issues oflegitimacy of a child, during divorce proceedings, or as part of a genealogical history,
besides other purposes.
minimum amount or quantity of waste, expense, or unnecessary effort. "Efficiency" has widely varying
meanings in different disciplines.
The term "efficient" is very much confused and misused with the term "effective". In general, efficiency is a
measurable concept, quantitatively determined by the ratio of output to input. "Effectiveness", is a relatively
vague, non-quantitative concept, mainly concerned with achieving objectives. In several of these cases,
efficiency can be expressed as a result as percentage of what ideally could be expected, hence with 100% as
ideal case. This does not always apply, not even in all cases where efficiency can be assigned a numerical
value, e.g. not for specific impulse.
A simple way of distinguishing between efficiency and effectiveness is the saying, "Efficiency is doing things
right, while Effectiveness is doing the right things." This is based on the premise that selection of objectives of a
process are just as important as the quality of that process.
noun
1. Efficiency is defined as the ability to produce something with a minimum amount of effort.
An example of efficiency is a reduction in the number of workers needed to make a car.
Performance measurement is the process of collecting, analyzing and/or reporting information regarding the
performance of an individual, group, organization, system or component.
the execution of an action
b : something accomplished : DEED, FEAT
2
: the fulfillment of a claim, promise, or request :
The accomplishment of a given task measured against preset known standards of accuracy, completeness, cost, and speed. In
a contract, performance is deemed to be the fulfillment of an obligation, in a manner that releases the performer from
all liabilities under the contract.
Read more: http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/performance.html#ixzz3Awmev7tq
A marriage certificate is an official statement that two people are married. In most jurisdictions, a marriage
certificate is issued by a government official only after the civil registration of the marriage.
In some jurisdictions, especially in the United States, a marriage certificate is the official record that two people
have undertaken a marriage ceremony. This includes jurisdictions where marriage licenses do not exist. In
some other jurisdictions, a marriage license serves a dual purpose of granting permission for a marriage to take
place and then endorsing the same document to record the fact that the marriage has been performed.
A marriage certificate may be required for a number of reasons. It may be required as evidence of change of a
party's name, on issues oflegitimacy of a child, during divorce proceedings, or as part of a genealogical history,
besides other purposes.
In political science, implementation refers to the carrying out of public policy. Legislatures pass laws that are
then carried out by public servants working in bureaucratic agencies. This process consists of rule-making,
rule-administration and rule-adjudication. Factors impacting implementation include the legislative intent, the
administrative capacity of the implementing bureaucracy, interest group activity and opposition, and
presidential or executive support.
Social and Health Sciences[edit]
"Implementation is defined as a specified set of activities designed to put into practice an activity or program of
known dimensions. According to this definition, implementation processes are purposeful and are described in
sufficient detail such that independent observers can detect the presence and strength of the "specific set of
activities" related to implementation. In addition, the activity or program being implemented is described in
sufficient detail so that independent observers can detect its presence and strength."
[1]
the act of implementing, or putting into effect; fulfillment:
The implementation of policies to conserve energy will involvepersonal sacrifice.
Implementation is the carrying out, execution, or
practice of a plan, a method, or any design for
doing something. Implementation is the action that
must follow any preliminary thinking in order for
something to actually happen.
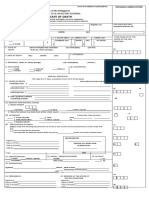
A birth certificate is a vital record that documents the birth of a child. The term "birth certificate" can refer to
either the original document certifying the circumstances of the birth or to a certified copy of or representation
of the ensuing registration of that birth. Depending on the jurisdiction, a record of birth might or might not
contain verification of the event by such as a midwife or doctor.
The Division of Vital Records maintains records of births that occurred from 1906 to the
present. Certified copies of birth certificates (with a raised seal) are issued and acceptable
for various uses, such as:
Personal identification
Employment
Passport application
Social Security
The phrase death certificate can describe either a document issued by a medical practitioner certifying the
deceased state of a person or popularly to a document issued by a person such as a registrar of vital
statistics that declares the date, location and cause of a person'sdeath as later entered in an official register of
deaths.
Death certificates are legal forms that declare someone's death. Doctors and medical examiners are typically
the people held responsible for filling out these forms and filing them with the local Department of Vital
Statistics. Death certificates are necessary for the family to take care of certain things on the decedent's behalf.
Read more : http://www.ehow.com/about_5374144_death-certificate.html A marriage license is
a document issued, either by a church or state authority, authorizing a couple to marry. The procedure for
obtaining a license varies between countries and has changed over time. Marriage licenses began to be issued
in the Middle Ages, to permit a marriage which would otherwise be illegal (for instance, if the necessary period
of notice for the marriage had not been given).
Marriage licenses are required in every state. A marriage license is provided as proof that a couple is
legally allowed to be married in the state that they wish to be married. In general, couples must provide
documentation as proof of facts listed on their marriage.
A death certificate is a legal document which lists the location, time, and manner of death for someone who has
passed away. Such documents are considered vital certificates, along with birth certificates and marriage
certificates, which means that they must be filed with regional keepers of such certificates, such as county
clerks. In many regions of the world, death certificates are also public records, which means that anyone can
obtain a copy of one by making a formal request, although concerns about identity theft have made some
nations question this practice.
Typically, a death certificate is filled out by a doctor or medical examiner. When the cause of death is readily
evident, sometimes police officers are also allowed to fill out a certificate of death. As a general rule, the
certificate must be issued as soon as possible, and doctors may be subject to penalties for failing to complete a
death certificate. If someone has been autopsied to determine the cause of death, this may be indicated on the
certificate of death.
Death certificates are also sometimes issued without the presence of a body in certain circumstances. For
example, when people are presumed to be lost at sea or in catastrophic accidents, a certificate of death will be
filled out so that surviving family members can file for benefits. These documents are also issued when
someone has vanished for seven years or more, as the long absence strongly suggests death.
Civil registration is the system by which a government records the vital events of its citizens and residents.
The resulting repository or database is called civil register orregistry, or population registry. The primary
purpose of civil registration is to create legal documents that are used to establish and protect the civil rights of
individuals. A secondary purpose is to create a data source for the compilation of vital statistics. In most
countries, there is a legal requirement to notify the relevant authority of any life event which affects the registry.
The first nation to establish a nationwide register over its population was Sweden in 1631. This register was
organized by the Church of Sweden but on the demand of The Crown.
civil registration as "the continuous, permanent, compulsory and universal recording of the occurrence and
characteristics of vital events pertaining to the population as provided through decree or regulation in
accordance with the legal requirements of a country. Civil registration is carried out primarily for the purpose of
establishing the legal documents provided by the law. These records are also a main source of vital statistics.
Complete coverage, accuracy and timeliness of civil registration are essential for quality vital statistics.
[1]
Commonwealth Act No. 3753
Law on Registry of Civil Status
Section 1. Civil Register. A civil register is established for recording the civil status of persons, in
which shall be entered: (a) births; (b) deaths; (c) marriages; (d) annulments of marriages; (e)
divorces; (f) legitimations; (g) adoptions; (h) acknowledgment of natural children; (i) naturalization;
and (j) changes of name.
Section 2. Civil Registrar-General his duties and powers. The director of the National Library
shall be Civil Registrar-General and shall enforce the provisions of this Act. The Director of the
National Library, in his capacity as Civil Registrar-General, is hereby authorized to prepare and issue,
with the approval of the Secretary of Justice, regulations for carrying out the purposes of this Act, and
to prepare and order printed the necessary forms for its proper compliance. In the exercise of his
functions as Civil Registrar-General, the Director of the National Library shall have the power to give
orders and instructions to the local Civil registrars with reference to the performance of their duties as
such. It shall be the duty of the Director of the National Library to report any violation of the
provisions of this Act and all irregularities, negligence or incompetency on the part of the officers
designated as local civil registrars to the (Chief of the Executive Bureau or the Director of the Non-
Christian Tribes) Secretary of the Interior, as the case may be, who shall take the proper disciplinary
action against the offenders.
Section 3. Local Civil Registrars. Except in the City of Manila, where the duties of local civil
registrar shall be performed by the officer of the Philippine Health Service designated by the Director
of said service, the Treasurers of the regular municipalities, municipal districts and cities shall be local
civil registrars of the respective municipalities, municipal districts or cities and shall perform the duties
imposed upon them by this Act without extra compensation, in addition to their ordinary duties. In his
capacity as local civil registrar, the officer designated by the Director of the Health Service as local
civil registrar of Manila and the treasurers above mentioned shall be under the direction and
supervision of the Civil Registrar-General.
Section 4. Civil Register Books. The local registrars shall keep and preserve in their offices the
following books, in which they shall, respectively make the proper entries concerning the civil status of
persons:
1. Birth and death register;
2. Marriage register, in which shall be entered not only the marriages solemnized but also divorces
and dissolved marriages.
3. Legitimation, acknowledgment, adoption, change of name and naturalization register.
Section 5. Registration and Certification of Birth. The declaration of the physician or midwife in
attendance at the birth or, in default thereof, the declaration of either parent of the newborn child,
shall be sufficient for the registration of a birth in the civil register. Such declaration shall be exempt
from the documentary stamp tax and shall be sent to the local civil registrar not later than thirty days
after the birth, by the physician, or midwife in attendance at the birth or by either parent of the newly
born child.
In such declaration, the persons above mentioned shall certify to the following facts: (a) date and
hour of birth; (b) sex and nationality of infant; (c) names, citizenship, and religion of parents or, in
case the father is not known, of the mother alone; (d) civil status of parents; (e) place where the
infant was born; (f) and such other data may be required in the regulation to be issued.
In the case of an exposed child, the person who found the same shall report to the local civil registrar
the place, date and hour of finding and other attendant circumstances.
In case of an illegitimate child, the birth certificate shall be signed and sworn to jointly by the parents
of the infant or only the mother if the father refuses. In the latter case, it shall not be permissible to
state or reveal in the document the name of the father who refuses to acknowledge the child, or to
give therein any information by which such father could be identified.
Any fetus having human features which dies after twenty four hours of existence completely
disengaged from the maternal womb shall be entered in the proper registers as having been born and
having died.
Section 6. Death certificate and register. No human body shall be buried unless the proper
death certificate has been presented and recorded in the office of the local civil registrar. The
physician who attended the deceased or, in his default the health officer concerned, or in default of
the latter, any member of the family of the deceased or any person having knowledge of the death,
shall report the same to the local health authorities, who shall issue a death certificate and shall order
the same to be recorded in the office of the local civil registrar. The death certificate, which shall be
issued by the attending physician of the deceased or, in his default, by the proper health officer, shall
contain the following data be furnished by the person reporting the death; (a) date and place of
death; (b) full name, (c) age, (d) sex, (e) occupation or profession, (f) residence; (g) status as
regards marriage, (h) nationality of the deceased, and (i) probable cause of death.
During epidemics, bodies may be buried provided the proper death certificates have been secured,
which shall be registered not later than five days after the burial of the body.
Section 7. Registration of marriages. All civil officers and priests or ministers authorized to
solemnize marriages shall send a copy of each marriage contract solemnized by them to the local civil
registrar within the time limit specified in the existing Marriage Law.
In cases of divorce and annulment of marriage, it shall be the duty of the successful petitioner for
divorce or annulment of marriage to send a copy of the final decree of the court to that local civil
registrar of the municipality where the dissolved or annulled marriage was solemnized.
In the marriage register there shall be entered the full name and address of each of the contracting
parties, their ages, the place and date of the solemnization of the marriage, the names and addresses
of the witnesses, the full name, address, and relationship of the minor contracting party or parties or
the person or persons who gave their consent to the marriage, and the full name, title, and address of
the person who solemnized the marriage.
In cases of divorce or annulment of marriages, there shall be recorded the names of the parties
divorced or whose marriage was annulled, the date of the decree of the court, and such other details
as the regulations to be issued may require.
Section 8. Registration of legitimations by subsequent marriage. The acknowledgment of the
children legitimated by subsequent marriage, referred to in article one hundred and twenty-one of the
Civil Code, may be recorded in the legitimation register, entering: (a) The names of the parents; (b)
that at the time when the children were conceived, the aforesaid parents could have contracted
marriage, and that they actually contracted marriage, stating the date and place when such marriage
was solemnized, the minister who officiated, and the civil register where such marriage was recorded;
(c) the names of the children legitimated with reference to their birth certificates.
Section 9. Registration of acknowledgment by public instrument. Any voluntary
acknowledgment by the natural parents or by only one of them by public instrument, shall be recorded
in the acknowledgment register of the civil registrar of the municipality where the decree was issued.
The names of the interested parties and such other data as may be required by the regulations to be
issued shall be entered in register.
It shall be the duty of the natural parents whose voluntary acknowledgment was may be means of a
public instrument to send a certified copy thereof to the local civil registrar of the municipality in the
civil register whereof the birth of the acknowledged child was recorded, not later than twenty days
after the execution of such instrument, for the registration thereof.
Section 10. Registrations of adoptions, changes of name, and naturalization. In cases of
adoptions, changes of name, and naturalization, it shall be the duty of the interested parties or
petitioners to register the same in the local civil registrar of the municipality where the birth of the
acknowledged child was registered setting forth the following data: (a) full name of the natural child
acknowledged; (b) age; (c) date and place of birth; (d) status as to marriage, and residence of the
child acknowledged; (e) full name of the natural father or mother who makes the acknowledgment; (f)
full name of the notary public before whom the document was acknowledged; (g) full names of
witnesses to document; (h) date and place of acknowledgment of said document and entry and page
number of the notarial register in which the name was recorded.
Section 11. Duties of clerks of Court to register certain decisions. In cases of legitimation,
acknowledgment, adoption, naturalization and change of given or family name, or both, upon the
decree which issued the decree to ascertain whether the same has been registered, and if this has not
been done, to have said decree recorded in the office of the civil registrar of the municipality where
the court is functioning.
Section 12. Duties of local civil registrar. Local civil registrars shall (a) file registrable
certificates and documents presented to them for entry; (b) complete the same monthly and prepare
and send any information required of them by the Civil Registrar-General; (c) issue certified
transcripts or copies of any certificate or document registered upon payment of proper fees; (d) order
the binding, properly classified, of all certificates or documents registered during the year; (e) send to
the Civil Registrar-General, during the first ten days of each month, a copy of the entries made during
the preceding month for filing; (f) index the same to facilitate search and identification in case any
information is required, and (g) administer oaths, free of charge, for civil register purposes.
Section 13. Documents registered are public documents. The books making up the civil
register and all documents relating thereto shall be considered public documents and be prima facie
evidence of the truth of the facts therein contained. They shall be open to the public during office
hours and shall be kept in a suitable safe which shall be furnished to the local civil registrar at the
expense of the general fund of the municipality concerned. The local registrar shall not under any
circumstances permit any document entrusted to his care to be removed from his office, except by
order of a court, in which case the proper receipt shall be taken. The local civil registrar may issue
certified copies of any document filed, upon payment of the proper fees required in this Act.
Section 14. Expenses and fees of the office of the civil registrar. All expenses in connection
with the establishment of local civil registers shall be paid out of municipal funds, and for this purpose,
municipal councils and boards shall make the necessary appropriation out of their available general
funds:
For the registration of documents and for certified copies of documents on file in the local civil
registrars office, fees shall be charged in accordance with the following schedule:
For registration of legitimations P2.00
For registration of an adoption 2.00
For registration of an annulment of marriage 10.00
For registration of a divorce 10.00
For registration of naturalization 20.00
For registration of a change of name 2.00
For certified copies of any documents in the register, for each one hundred words 20.00
The Civil Registrar General or any local civil registrar may issue certified copies of documents free of
charge for official use or at the request of a competent court. All fees collected for such purposes shall
accrue to the general fund of the municipality concerned.
Section 15. Preservation of present register books. All birth, death and marriage registers and
other papers relating thereto at present in the keeping of the municipal secretaries or the clerk of the
Municipal Court of Manila shall be transferred by the same to the officers acting as local civil registrars
in each city or municipality and shall form part of the archives of the latter.
Section 16. False statement. Any person who shall knowingly make false statement in the forms
furnished and shall present the same for entry in the civil register, shall be punished by imprisonment
for not less than one month nor more than six months, or by a fine of not less than two hundred
pesos nor more than five hundred or both, in the discretion of the court.
Section 17. Failure to report. Other violations. Any person whose duty is to report any fact
concerning the civil status of persons and who knowingly fails to perform such duty, and any person
convicted of having violated any of the provisions of this Act shall be punished by a fine of not less
than ten pesos nor more than two hundred.
Section 18. Neglect of duty with reference to the provisions of this Act. Any local registrar
who fails properly to perform his duties in accordance with the provisions of this Act and of the
regulations issued hereunder, shall be punished for the first offense, by an administrative fine in a
sum equal to his salary for not less than fifteen days nor more than three months, and for a second or
repeated offense, by removal from the service.
Section 19. Application of this Act to the special provinces. The Director of the National
Library, in his capacity as Civil Registrar-General, is hereby authorized upon recommendation of the
(Director of Bureau of Non-Christian Tribes) Secretary of the Interior, to designate the municipalities
in the specially organized provinces where the provisions of this Act shall be applied.
Section 20. Transitory provisions. All rights, duties and powers established by Act Numbered
thirty-six hundred and thirteen, entitled the Marriage Law, with the reference to the procedure for the
issuance of the marriage license prior to the solemnization of marriage, the registration, of marriages,
and the filing of the documents in connection therewith, conferred and imposed by said Act upon the
clerk of the Municipal Court of Manila and the municipal secretaries, are hereby transferred to the
officer of the Health Service in accordance with section three of this Act, and to the municipal
treasurers, respectively, in their capacity as local registrars.
All duties and powers established by subsections (d) and (e) of section twenty-one hundred and
twelve of the Administrative Code, imposed and conferred by said section upon the municipal
secretaries, are hereby likewise transferred to the municipal treasurers in their capacity as local civil
registrars.
Section 21. All acts or parts of acts inconsistent herewith are hereby repealed.
Section 22. This Act shall take effect three months after its approval.
Approved, November 26, 1930.
clientele are the customers of a business or professional.
1. The body or class of people who frequent an establishment or purchase a service, especially when
considered as forming a more-or-less homogeneous group of clients in terms of values or habits.
[quotations ]
As a sex worker, Helen's clientele encompasses a broad range of different ages, races and social
statuses.
staffs for 68, 10, 11.
1.
a group of persons, as employees, charged with carrying out the workof an establishment or
executing some undertaking.
a : the officers chiefly responsible for the internal operations of an institution or business
b : a group of officers appointed to assist a civil executive or commanding officer
satisfactory giving or affording satisfaction; fulfilling all demands or requirements:
a satisfactory solution.
good or good enough for a particular need or purpose:The teachers seem to think his work is
satisfactory.We hope very much to find a satisfactory solution to the problem.The result of
the match was highly satisfactory (= very pleasing).
Definition of 'Efficiency'
A level of performance that describes a process that uses the lowest amount of inputs to
create the greatest amount of outputs. Efficiency relates to the use of all inputs in producing
any given output, including personal time and energy.
Efficiency is an important attribute because all inputs are scarce. Time, money
and raw materials are limited, so it makes sense to try to conserve them while
maintaining an acceptable level of output or a general production level.
the ability to do something or produce something without wasting materials, time, or energy : the
quality or degree of being efficient ( technical )
A marriage license is a document issued, either by a church or state authority, authorizing a couple to marry.
The procedure for obtaining a license varies between countries and has changed over time. Marriage licenses
began to be issued in the Middle Ages, to permit a marriage which would otherwise be illegal (for instance, if
the necessary period of notice for the marriage had not been given).
Marriage licenses are required in every state. A marriage license is provided as proof that a couple is
legally allowed to be married in the state that they wish to be married. In general, couples must provide
documentation as proof of facts listed on their marriage.
free from bias, dishonesty, or injustice:
a fair decision; a fair judge.
2.
legitimately sought, pursued, done, given, etc.; proper under the rules:
a fair fight.
fair
adjective \fer\
: agreeing with what is thought to be right or acceptable
: treating people in a way that does not favor some over others
: not too harsh or c marked by impartiality and honesty : free from self-interest, prejudice, or
favoritism <a very fair person to do business with>ritical
a. Having or exhibiting a disposition that is free of favoritism or bias; impartial: a fair mediator.
b. Just to all parties; equitable: a compromise that is fair to both factions.
7. Being in accordance with relative merit or significance: She wanted to receive her fair share of the proceeds.
8. Consistent with rules, logic, or ethics: a fair tactic. staffs for 68, 10, 11.
1.
a group of persons, as employees, charged with carrying out the workof an establishment or
executing some undertaking.
a : the officers chiefly responsible for the internal operations of an institution or business
b : a group of officers appointed to assist a civil executive or commanding officer
satisfactory giving or affording satisfaction; fulfilling all demands or requirements:
a satisfactory solution.
9. Moderately good; acceptable or satisfactory: gave only a fair performance of the play; in fair health.
10. Superficially true or appealing; specious: Don't trust his fair promises.
11. Lawful to hunt or attack: fair game.
12. Archaic Free of all obstacles.
adv.
1. In a proper or legal manner: playing fair.
2. Directly; straight: a blow caught fair in the sto
not able to function properly <weak eyes>
b (1) : lacking skill or proficiency <tutoring for weakerstudents> (2) : indicative of a lack of skill or
aptitude<history was my weakest subject>
c : wanting in vigor of expression or effect <a weaktranslation of the poem>
5
a : deficient in the usual or required ingredients : DILUTE<weak coffee>
deficient in magnitude; barely perceptible; lacking clarity or brightness or loudness etc
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- Certificate of DeathDocument2 pagesCertificate of DeathAngel Urbano67% (3)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Medical Certification of Death 0Document146 pagesMedical Certification of Death 0NascelAguilarGabito100% (1)
- In Defense of Smokers. The Benefits of Natural Tobacco - Colby, Lauren A PDFDocument51 pagesIn Defense of Smokers. The Benefits of Natural Tobacco - Colby, Lauren A PDFClara M. HidalgoPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Succession CertificateDocument14 pagesWhat Is Succession CertificateAnonymous KRQaT2PnYqPas encore d'évaluation
- Ielts Refund Test Date Transfer Form 002-26 OctDocument4 pagesIelts Refund Test Date Transfer Form 002-26 OctAbu BakerPas encore d'évaluation
- Personal Affidavit of Attendant at Death For Delayed RegistrationDocument20 pagesPersonal Affidavit of Attendant at Death For Delayed Registrationrussell apura galvezPas encore d'évaluation
- Application For Closure of BusinessDocument2 pagesApplication For Closure of BusinessallanPas encore d'évaluation
- Obtain Valid Marriage LicenseDocument5 pagesObtain Valid Marriage LicenseRS McpasPas encore d'évaluation
- DeathCertificate PDFDocument3 pagesDeathCertificate PDFUrischarPas encore d'évaluation
- Digging Deep - A VT Guide To BurialsDocument32 pagesDigging Deep - A VT Guide To BurialsJoel Banner BairdPas encore d'évaluation
- Sss 10Document2 pagesSss 10Aila ReoptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Transfer Cancellation Application Form PDFDocument7 pagesTransfer Cancellation Application Form PDFSrini SidralaPas encore d'évaluation
- 732-F - Pen - DT - 12 - 11 - 08-PensionDocument3 pages732-F - Pen - DT - 12 - 11 - 08-PensionArpan SenPas encore d'évaluation
- 16.apathbandu Application FormDocument2 pages16.apathbandu Application FormHashimMohdPas encore d'évaluation
- Court Rules on Cause of Death in Insurance ClaimDocument9 pagesCourt Rules on Cause of Death in Insurance ClaimmonagbayaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Register Births & Deaths DelhiDocument6 pagesRegister Births & Deaths DelhiblhrPas encore d'évaluation
- CDIB Application RequirementsDocument3 pagesCDIB Application RequirementsKen Myers0% (1)
- FinAidApp AcknowledgeSlipDocument4 pagesFinAidApp AcknowledgeSlipYash GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Transfer and Transmission of SecuritiesDocument6 pagesTransfer and Transmission of Securitiesbarkha chandnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Checklist GGPDocument2 pagesChecklist GGPbiffbuff99Pas encore d'évaluation
- GSIS benefits overviewDocument3 pagesGSIS benefits overviewAC100% (1)
- Tolentino v. Paras DigestDocument2 pagesTolentino v. Paras DigestKayeCie RL100% (1)
- Checklist For Registration of Birth CertificatesDocument5 pagesChecklist For Registration of Birth CertificatesAnnMaureenNavarroPas encore d'évaluation
- C o N T e N T S: Map Guide To The U.S. Federal Censuses, 1790-1920Document11 pagesC o N T e N T S: Map Guide To The U.S. Federal Censuses, 1790-1920shawneemacPas encore d'évaluation
- Sav 0022Document21 pagesSav 0022MichaelPas encore d'évaluation
- Citizens Charter Registration DepartmentDocument26 pagesCitizens Charter Registration DepartmentOpsiddharth PerumalPas encore d'évaluation
- Mutation FormDocument10 pagesMutation FormmohdakeelPas encore d'évaluation
- Colorado Birth Certificate ApplicationDocument2 pagesColorado Birth Certificate ApplicationmrhedgePas encore d'évaluation
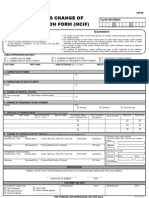
- MEMBER’S CHANGE OF INFORMATION FORM (MCIF) INSTRUCTIONSDocument2 pagesMEMBER’S CHANGE OF INFORMATION FORM (MCIF) INSTRUCTIONSWacky LarimPas encore d'évaluation
- MeeSeva PDFDocument3 pagesMeeSeva PDFmunna777Pas encore d'évaluation