Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
C1 Respiratory System Worksheet
Transféré par
lccjane8504Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
C1 Respiratory System Worksheet
Transféré par
lccjane8504Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Respiratory System Worksheet
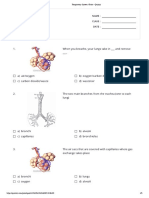
1. Add the following labels to the diagram of the respiratory system of a dog below:
trachea; bronchioles; diaphragm; bronchi; ribs; larynx; intercostal muscle;
rings of cartilage around trachea; alveoli.
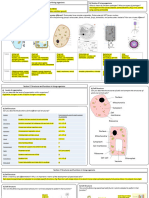
Diagram 2 shows the gaseous exchange in an alveolus.
Diagram 3 shows a model of the respiratory system.
DIagram 2
Rubber
sheet
Stoppe
r
Glass
tube
alloo
n
Diagram 3
Respiratory System Worksheet
1. Add the following labels to the diagram of the respiratory system of a dog below:
trachea; bronchioles; diaphragm; bronchi; ribs; larynx; intercostal muscle;
rings of cartilage around trachea; alveoli.
Diagram 2 shows the gaseous exchange in an alveolus.
Diagram 3 shows a model of the respiratory system.
DIagram 2
Rubber
sheet
Stoppe
r
Glass
tube
alloo
n
Diagram 3
!a"Identify the gases labelled # and $.
Gas #% &&&&&&&&&&&&&&.. Gas $%
&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&..
2. List the structures below in the order in which air passes them as it travels from the nose to the lungs
alveoli; trachea; bronchi; bronchioles; larynx; pharynx.
3. Which is the odd one out?
trachea; oesophagus; nasal cavity; larynx; bronchi; bronchioles
. !ow are dust particles that enter the respiratory system in the air e"pelled?
#. Add the correct terms from the list below to the following descriptions.
A. Alveoli; B. Trachea; . Bronchioles; !. "alate; #. "leura; $. !iaphragm;
%. "harynx; &. #xpiration; '. #piglottis; (. Tidal volume.
a$ %mallest respiratory passageways.
b$ %eparates the mouth from the nose.
d$ Windpipe.
e$ Where gas e"change ta&es place.
f$ %tops food 'going the wrong way( ie cho&ing during swallowing.
g$ )oth air and food pass through this.
h$ *he movement of air out of the lungs.
i$ *he main muscle involved in inspiration.
+$ ,embranes that cover the lungs and line the pleural cavity.
&$ *he volume of air inhaled or e"haled at each normal breath.
-. Arrange these statements in the right order to describe inspiration.
A. *he air pressure in the air tight pleural cavities decreases
). *he muscles between the ribs contract to move the ribs cranially and laterally
.. Air is drawn down the trachea into the lungs
/. *he diaphragm contracts and flattens
0. *he lungs e"pand to fill the space created
1. *rue or false?
a$ *he pericardium is the membrane surrounding the lungs. * 2 3
b$ *he tidal volume describes the ma"imum amount of air that can be inhaled into the lungs. * 2 3
c$ *idal volume can be measured with a pea& flow meter * 2 3
d$ 4nspiration ta&es up energy but e"piration 5during normal at rest breathing$ is a passive
process not normally re6uiring energy. * 2 3
e$ *he diaphragm is made of smooth muscle. * 2 3
f$ *he epiglottis closes off the laryn" during swallowing. * 2 3
g$ *he rate of breathing is controlled by the pituitary gland. * 2 3
h$ When an animal e"ercises the rate of breathing increases because the carbon dio"ide in the
blood increases. * 2 3
i$ .arbon dio"ide dissolved in the blood ma&es the blood al&aline. * 2 3
+$ .arbon dio"ide in the blood is mainly carried in the blood plasma.* 2 3
&$ 7"ygen moves from the alveoli into the capillaries by the process of osmosis. * 2 3
l$ 0"pired air contains about 1-8 o"ygen. * 2 3
9. Add the following labels to the diagram of a section cut across lung alveoli shown below.
alveoli; thin layer of )ater; area of high oxygen concentration; area of high carbon dioxide
concentration;
movement of oxygen; movement of carbon dioxide; air flo)ing in and out of alveoli; blood
flo)ing along capillary.
:. Which of the statements below gives the best definition of gas e"change?
a$ swapping o"ygen for digested food in the gut capillaries.
b$ using energy to breathe.
c$ e"changing inhaled air for e"haled air in the lungs.
d$ e"changing o"ygen for carbon dio"ide in the lung alveoli.
1;. Which of the following help the lungs to be such good gas e"change organs? 5.hoose at least $.
*hey are close to the heart.
*hey are surrounded by pleural membranes.
*hey have a large surface area.
*he air in the alveoli and blood in the capillaries are separated by a 2 very thin layers of cells.
*he blood flows more slowly in the lung capillaries as they are so narrow.
*he haemoglobin carries lots of o"ygen.
)reathing constantly changes the air in the alveoli.
Active transport increases the rate at which the two gases move.
11. Add the terms from the list below to the blan&s in the following statements.
Active transport ; B. Air of the alveoli to the capillary blood; . arbon dioxide *poor and
oxygen +rich; !. apillary blood to alveolar air; #. apillary blood to tissue cells; $.
!iffusion; %. &igher concentration; &. ,o)er concentration; '. -xygen*poor and carbon
dioxide + rich; (. Tissue cells to capillary blood.
<as e"change ta&es place bt the process of 51$ .............=
When substances move in this way> they pass from areas of 52$ ................. to areas of their 53$.................
*hus in the alveoli of the lungs o"ygen continually passes from the 5$................ and then in the tissues
from the 5#$................. .onversely in the tissues carbon dio"ide moves from the5-$................. and in the
lungs from 51$................... 3rom the lungs it passes out of the body during e"piration. As a result of gas
e"change> the blood in 5most$ arteries tends to be 59$.................. while the blood in 5most$ veins is
5:$ ...................
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Respiratory System WorksheetDocument4 pagesRespiratory System WorksheetcutienatsPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Factsheet: The Kidney: Excretion and OsmoregulationDocument4 pagesBio Factsheet: The Kidney: Excretion and OsmoregulationjesvinjesvinPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple-Choice Test Chapter 8: Transport in Plants: 1 A B C D 2 A B C D 3 A B C D 4 A B C D 5 A B C DDocument2 pagesMultiple-Choice Test Chapter 8: Transport in Plants: 1 A B C D 2 A B C D 3 A B C D 4 A B C D 5 A B C DsybejoboPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzymes (AS Level Bio)Document23 pagesEnzymes (AS Level Bio)DrMufaddal RampurwalaPas encore d'évaluation
- IBO 2010 Korea Theory Paper 2Document73 pagesIBO 2010 Korea Theory Paper 2Bikash Ranjan RayPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Choice Questions For 9th IgcseDocument14 pagesMultiple Choice Questions For 9th IgcseFatma Zorlu100% (1)
- Respiratory System WorksheetDocument2 pagesRespiratory System WorksheetelizabethPas encore d'évaluation
- SAPS Photosynthesis Survival Guide Teachers NotesDocument9 pagesSAPS Photosynthesis Survival Guide Teachers NotesTechie HarryPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andDocument62 pagesCirculatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andBlister Count100% (1)
- Respiratory System - Print - QuizizzDocument5 pagesRespiratory System - Print - QuizizzosamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Active Transport Worksheet AnswersDocument1 pageActive Transport Worksheet AnswersLola Bee0% (1)
- 1st Mid Exam Science 9.1Document4 pages1st Mid Exam Science 9.1Jass AllasPas encore d'évaluation
- MYP Science 10: Lab Report Writing GuideDocument2 pagesMYP Science 10: Lab Report Writing GuideTiberiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Transport in Plants CIE IGCSE Biology 610 Classified Paster Paper 2Document21 pagesTransport in Plants CIE IGCSE Biology 610 Classified Paster Paper 2IGCSE Physics & ChemistryPas encore d'évaluation
- 7th Class Respiratory SystemDocument14 pages7th Class Respiratory SystemCas Tan100% (1)
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocument8 pagesCell Organelles WorksheetJohn OsbornePas encore d'évaluation
- Human Body System Regents QuestionsDocument11 pagesHuman Body System Regents Questionsabisantiago613125% (4)
- Cell-Structure-And-Organization-Mark-Schemes-For-Practical-Skills-And Discussion-QuestionsDocument4 pagesCell-Structure-And-Organization-Mark-Schemes-For-Practical-Skills-And Discussion-Questionsapi-26867053067% (3)
- Cells Regents ReviewDocument16 pagesCells Regents ReviewJ15Pas encore d'évaluation
- Transport in PlantsDocument6 pagesTransport in PlantsFred H HalderPas encore d'évaluation
- Population Ecology Graph Worksheet - KEY PDFDocument4 pagesPopulation Ecology Graph Worksheet - KEY PDFBinal DaliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Prokaryotic Cells: Cell Membrane Cell Wall Capsule Pili Plasmid Flagella Nucleoid Region Ribosomes CytoplasmDocument3 pagesProkaryotic Cells: Cell Membrane Cell Wall Capsule Pili Plasmid Flagella Nucleoid Region Ribosomes CytoplasmErvin WilliamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Cie Alevel BiologyDocument24 pagesCie Alevel BiologyArun Ghatan100% (1)
- IGCSE Answers Chapters 01 05Document7 pagesIGCSE Answers Chapters 01 05María Eugenia MolteniPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell SurfaceDocument3 pagesCell SurfaceNabindra RuwaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 TestDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Testapi-485795043Pas encore d'évaluation
- Transport in Plants AnswersDocument3 pagesTransport in Plants AnswersEncik Amir Kamal20% (5)
- Respiration and Excretion Chapter 16 TestDocument4 pagesRespiration and Excretion Chapter 16 TestAnonymous KgU0Oh3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exam CirculatoryDocument1 pageExam CirculatoryLuisa RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Nihal Gabr: 2A Membrane, and TransportDocument55 pagesNihal Gabr: 2A Membrane, and Transportbody fayezPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary Notes - Topic 6 Microbiology, Immunity and Forensics - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-LevelDocument11 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 6 Microbiology, Immunity and Forensics - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-LevelsalmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biotechnology & Genetic Engineering 2 QPDocument8 pagesBiotechnology & Genetic Engineering 2 QPAzween SabtuPas encore d'évaluation
- Transport in Animals Revision NotesDocument11 pagesTransport in Animals Revision Notesamr ahmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Organelles Cheat SheetDocument8 pagesOrganelles Cheat Sheetapi-55809756Pas encore d'évaluation
- Circulation POGILDocument4 pagesCirculation POGILDave KPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 9 Plant Biology IB Biology 9.2 Transport in The Phloem of Plants Nature of Science: Developments in Scientific Research Follow Improvements in Apparatus: ExperimentalDocument4 pagesTopic 9 Plant Biology IB Biology 9.2 Transport in The Phloem of Plants Nature of Science: Developments in Scientific Research Follow Improvements in Apparatus: ExperimentalMoahmed Mahmoud IB15A 363KAGYPas encore d'évaluation
- Excretion in Humans 2 QPDocument11 pagesExcretion in Humans 2 QPMikiko Fujiwara SamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocument3 pagesDiffusion and OsmosisNURUL AZZAHPas encore d'évaluation
- Binomial ClassificationDocument14 pagesBinomial ClassificationadiPas encore d'évaluation
- OCR Biology F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport Revision NotesDocument4 pagesOCR Biology F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport Revision Notes24wrightphilip100% (1)
- Chapter 9 Transport in Plants - Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesChapter 9 Transport in Plants - Lecture Notesapi-3728508100% (5)
- iGCSE-revision-mindmaps-new-specification-double-award ANSWERS Year 10 ModDocument25 pagesiGCSE-revision-mindmaps-new-specification-double-award ANSWERS Year 10 Modlily wongPas encore d'évaluation
- Cellular Respiration and Fermentation NotesDocument5 pagesCellular Respiration and Fermentation NotesStealthstr1kePas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 1 Test - Cells & Organisms 2019.pdf AnsDocument9 pagesTopic 1 Test - Cells & Organisms 2019.pdf AnsHal OglePas encore d'évaluation
- Biotic Indices WorksheetDocument4 pagesBiotic Indices WorksheetPichakorn100% (2)
- Osmosis Lab ReportDocument3 pagesOsmosis Lab Reportapi-350496922Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ap Biology Mid Term PretestDocument30 pagesAp Biology Mid Term PretestKrisnavimala Krishnan0% (1)
- Cell Division LabDocument3 pagesCell Division LabDoctorzo67% (6)
- Checked - Unit 5 Respiration, Internal Environment, Coordination and Gene Technology - Exam BookletDocument63 pagesChecked - Unit 5 Respiration, Internal Environment, Coordination and Gene Technology - Exam BookletEllane leePas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Molecule Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesBio Molecule Review WorksheetBianca BiancaPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiration QuestionsDocument2 pagesRespiration QuestionsAnonymous Azxx3Kp9100% (1)
- IGCSE Biology Section 5 Lesson 1Document92 pagesIGCSE Biology Section 5 Lesson 1salmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis QuestionsDocument22 pagesPhotosynthesis QuestionstrekPas encore d'évaluation
- Meiosis Lab 211Document8 pagesMeiosis Lab 211Tracy LykaPas encore d'évaluation
- 10th Biology New Book 2021-22 Latest2Document86 pages10th Biology New Book 2021-22 Latest2kaziamna62Pas encore d'évaluation
- 50 The Gas Exchange SystemDocument5 pages50 The Gas Exchange SystemSarahPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Exchange NewDocument30 pagesGas Exchange Newmariaamkhaann22Pas encore d'évaluation
- Breathing - and - Gas Exchange Igcse BiologyDocument88 pagesBreathing - and - Gas Exchange Igcse BiologyEllie HousenPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory ReviewerDocument8 pagesRespiratory ReviewerBLAIRY ZYPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 Biology Notes ch17-pdf1Document9 pages11 Biology Notes ch17-pdf1LishaPas encore d'évaluation
- RPH SC Form 2Document50 pagesRPH SC Form 2lccjane8504Pas encore d'évaluation
- RPH Sains f2 f3 2017Document28 pagesRPH Sains f2 f3 2017lccjane8504Pas encore d'évaluation
- Module Science Pt3Document11 pagesModule Science Pt3lccjane8504Pas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Plan Science f2Document26 pagesYearly Plan Science f2lccjane8504Pas encore d'évaluation
- RPH SC Form 2Document50 pagesRPH SC Form 2lccjane8504Pas encore d'évaluation
- PBS Band 5 Form 2 Chapter 9Document4 pagesPBS Band 5 Form 2 Chapter 9lccjane8504Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sekolah Tinggi Kota Kinabalu Sekolah Kluster Kecemerlangan Ujian Pertengahan Penggal DUA 2015 Bahasa Ingeeris Tingkatan 5 1 Jam 15 Minit Section Marks A 15 B 10 C 10 D 20 Total 55Document3 pagesSekolah Tinggi Kota Kinabalu Sekolah Kluster Kecemerlangan Ujian Pertengahan Penggal DUA 2015 Bahasa Ingeeris Tingkatan 5 1 Jam 15 Minit Section Marks A 15 B 10 C 10 D 20 Total 55lccjane8504Pas encore d'évaluation
- Food Web WorksheetDocument8 pagesFood Web Worksheetlccjane8504100% (1)
- SIX Simple MachinesDocument3 pagesSIX Simple Machineslccjane8504Pas encore d'évaluation
- Earth & Solar SyatemDocument5 pagesEarth & Solar Syatemlccjane8504Pas encore d'évaluation
- BS en 1096-3-2012 - (2022-08-18 - 04-11-32 Am)Document22 pagesBS en 1096-3-2012 - (2022-08-18 - 04-11-32 Am)Free MousePas encore d'évaluation
- Instruction Manual Directional Overcurrent Protection Relay Grd140 - XXXDDocument438 pagesInstruction Manual Directional Overcurrent Protection Relay Grd140 - XXXDEpsp MedPas encore d'évaluation
- Greenhouse EffectDocument15 pagesGreenhouse EffectNoor AdlinPas encore d'évaluation
- Perkins 1104DDocument158 pagesPerkins 1104Dsj1202100% (17)
- Analysis of Mechanical SystemDocument16 pagesAnalysis of Mechanical SystembigbangPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Procedure and Settings of RCCDocument5 pagesTest Procedure and Settings of RCCkundan kunalPas encore d'évaluation
- Yang-Mills Theory On The Light ConeDocument14 pagesYang-Mills Theory On The Light Cones4suchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Study of Power System Security in Indian Utility 62 Bus SystemDocument10 pagesStudy of Power System Security in Indian Utility 62 Bus SystempjPas encore d'évaluation
- Francis Pegler 1.2.17Document148 pagesFrancis Pegler 1.2.17Kaushaveer GhooraPas encore d'évaluation
- E-10 Storage Batteries - 1465729800 - E-10Document10 pagesE-10 Storage Batteries - 1465729800 - E-10nicolas.travailPas encore d'évaluation
- Basics of Petroleum GeologyDocument23 pagesBasics of Petroleum GeologyShahnawaz MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: MD Maruf Hossain, Mohd. Hasan AliDocument9 pagesRenewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: MD Maruf Hossain, Mohd. Hasan AliJuan MPas encore d'évaluation
- Natural Gas Dehydration: October 2012Document21 pagesNatural Gas Dehydration: October 2012ShakerMahmoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan For Fuze FFV 651 HeatDocument9 pagesLesson Plan For Fuze FFV 651 HeatVikas ChandraPas encore d'évaluation
- Indian Automobile Sector Analysis January 2023 1693838553Document1 pageIndian Automobile Sector Analysis January 2023 1693838553Rohit PareekPas encore d'évaluation
- SNJB's Late Sau. Kantabai Bhavarlalji Jain College of Engineering, ChandwadDocument10 pagesSNJB's Late Sau. Kantabai Bhavarlalji Jain College of Engineering, ChandwadAkash JadhavPas encore d'évaluation
- Company ProfileDocument189 pagesCompany ProfileplanningPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalogo DynapacDocument36 pagesCatalogo DynapacblaktionPas encore d'évaluation
- Free Space OpticsDocument27 pagesFree Space Opticsapi-19937584Pas encore d'évaluation
- En D6T CatalogDocument20 pagesEn D6T CatalogHeddy ErizalPas encore d'évaluation
- Shell Pakistan Stock in Trade: Horizontal AnalysisDocument12 pagesShell Pakistan Stock in Trade: Horizontal Analysisfahad pansotaPas encore d'évaluation
- Africa's Youth Can Save The WorldDocument21 pagesAfrica's Youth Can Save The WorldThe Wilson CenterPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics PapermakingDocument25 pagesFluid Mechanics PapermakingM. Sultan MirajPas encore d'évaluation
- LM 358 IC: Component DiscriptionDocument15 pagesLM 358 IC: Component DiscriptionLokesh RawatPas encore d'évaluation
- June 2017 (v1) QP - Paper 4 CIE Chemistry A-LevelDocument16 pagesJune 2017 (v1) QP - Paper 4 CIE Chemistry A-LevelMustafa ShaukatPas encore d'évaluation
- Your Guide To Hydraulic FracturingDocument1 pageYour Guide To Hydraulic FracturingMartin GriffinPas encore d'évaluation
- Atex Zone 2 Definition MIRETTI Category 3G Conversion Equipment For Atex Zone 2Document3 pagesAtex Zone 2 Definition MIRETTI Category 3G Conversion Equipment For Atex Zone 2Ir RaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Notice Installation Maintenance GE215000aDocument40 pagesNotice Installation Maintenance GE215000amuhammad nazirPas encore d'évaluation
- University of Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal SubjectDocument40 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal SubjectbobPas encore d'évaluation
- MSRA-T&C Electrical SystemDocument18 pagesMSRA-T&C Electrical SystemSharvin NageebPas encore d'évaluation