Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Hormome Deficiency by Increasing The Size
Transféré par
pjoanneloisaTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Hormome Deficiency by Increasing The Size
Transféré par
pjoanneloisaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
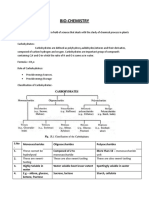
CHAPTER 4
IRON
Present in some forms whenever
respiration occurs
In the respiration chain, transports
molecular O2 in the higher organism
Essential to the metabolic processes in
cell
All depend on the ability of iron to exist in
coordination compound in different
states of oxidation and bonding.
Body Components of Fe
Blood System/Hemoglobin & Plasma/ Heme &
transferrin/ O2 and Fe transport
Tissue/ Functional or the Storage Iron/Heme &
ferretin and hemosiderin/Cell Respiration and
Iron pool detoxification
Proteins associated with Iron
1. Hemoproteins- iron containing proteins
responsible for
Respiration
For carrying O2
Cytochrome C- respiratory enzymes in
which Fe is a complex in a porphyrin
(heme)ring bonded covalently with
protein portion of molecules.
Oxygen carrier
Can be present as Fe2+ and Fe3+ as it
picks electron in the process of
electron transfer.
Myoglobin and Hemoglobin are
homeproteins responsible for
storing/transporting O2.
Hemoglobin have 4 protein chains
2. Iron-storage and /or Transport Protein
Ferrittin water soluble,
crystallizable iron protein build from
apoferritin and micelles of Ferric OH
phosphate complex.
o Stored in Ferric form but
released as a Fe2+
Hemosiderin water insoluble and
considered as dehydrated ferritin
Both are found in the Liver, Spleen and Bone
marrow
The major iron transport protein is
glycoprotein = transferrin
Anemia- less number of bloods in the body
Lower oxygen capacity of the blood
Causes:
Blood destruction (in drug therapy,
infections and toxins)
Excessive blood loss (hemorrhage)
Decrease blood formation
When Iron prescribed = orally = astringent,
Better after meals or between meals for greater
absorption.
Most absorption occurs in duodenum and
unabsorbed iron will excrete out.
FERROUS SULFATE (FeSO5 . 2H2O)
Iron Sulfate, Copperas, Green/Iron Vitriol
Properties:
Pale, bluish green crystals
Odorless
Saline, styptic taste
Efflorescent in dry air
Oxidizes readily in moist air brownish
yellow basic Ferric Sulfate (Fe4 (OH)2
(SO4)4)
Do not use ferrous sulfate coated with
brownish yellow basic salt
Soluble in water, alcohol ang B water
Preparation:
Commercial ferrous sulfate(Feso5 2h2o)
copperas
By product in picking up steel steel
+HCL vat liquor crystallization
Mineral pyrite (iron pyrite or fool gold)
subjective to atmospheric oxidation
After sometimes the mass is extracted
with water treated with scarp iron-
convert ferric to ferrous evap to crys
Uses:
Hematinic orally iron deficieny anemia
IODIDE
- Synthesis oF the 2 hormones produced by
the thyroid glands : triiodothyronine and
thyroxine.
- Internally iodine iodide converted
in the intestinal act
- Daily dose of iodine 140 mcg (male) 100
mcg (female)
- Lack of iodine- enlargement of thyroid
gland, known as a simple or colloid goiter
- Swelling at the neck
- It is a compensatory mechanism whereby
the body attempts to make up
the hormome deficiency by increasing the size
- Used Therapeutically
Ameliorating- improve HyperTy
Fibrolytic agent in syphilis, leprosy
Expectorant
Alternative(reestablish the health of an
individual)
Administration of iodide that exceed a certain level
Irritative phenomena to the skin and mucuos
membrane
Termed as IODISM
Exhibited by coryza (head cold), rashes,
headache, laryngitis and stuff
Should NOT be given in case of ACNE.
Admn. of NaCl may aid in more rapid elimination
od I-.
COPPER
Necessary for normal metabolism
Found in adequate amounts in food, water
and cooking utensils
Roles Cu in body metabolism, specifically hemoglobin
formation:
1. Facilitate iron absorption
2. Stimulating the enzymes in the heme and
or/globin biosynthetic pathways
3. Involved in mobilization of stored iron,
preparatory to utilization of iron into
hemoglobin molecules
Wilsons disease excessive Copper storage in the
liver.
Symptoms- hepatic cirrhosis, brain damage
and demyelination and kidney defects
Drug Choice penicillamine
ZINC
Widely distributed in the body assoc with
o metalloenzymes
o lie alcohol dehydrogenase
o lactic dehydrogenase
o carbonic anhydrase
o carboxypeptidase
deficiency in zinc impared growth,
parakeratosis thickened, scaly inflamed
skin and retarded sexual maturation
meat, mil, fish, nuts and legumes
investigated as wound healing
CHROMIUM
improve/ normalize impaired glucose
tolerance
SELENIUM
antioxidant in the conjuction of Vit E.
seborrhea dermatitis
NON ESSENTIAL IONS
- Li, Sr, Al, Pb, As, F, Br, Ag, Au, Hg, Cd
1. LITHIUM
Depressant in the CNS and to circulation of
the manic-depressive disorder
Has a diuretic action
3.ALUMINUM
Soluble Al comp. = astringent and antiseptic
Deodorants
4. LEAD TOXIC POISONS
Ingestion paint chips of old houses
Phenomenon called = PICA referring to
MAGPIE and its indiscriminate eating habits.
Serious symptoms encephalopathy- brain
damage or mental retardation
5.ARSENIC
Potassium arsenite solution Fowlers
solution
Arsenic trioxide
Potassium bicarbonate
LEUKEMIA lowers leukolyte counts
Arsenicals treatment trypasonomiasis and
amoebiasis
6. FLUORIDE
Anticariogenic action (inhibition of dental
cavity development)
7. BROMIDE
Depression to CNS in small doses (0.2-2g)
Depress all reflex in large doses (4-8g)
medication to epileptic seizures
8. SILVER
Protein precipitant
Siliver ion to tissue ranges from antiseptic,
astringent , irritant to corrosive as free silver
increases
9. GOLD
Rheumatism arthritis and lupus
erythematous
10. MERCURY
Used as diuretics rid of excess fluid caused
by cardiac edema
Antiseptic, parasiticide and fungicide
Mercury poisoning can be avoided by strict
dosage schedule
11. CADMIUM - TOXIC POISONING
Itai-itai (ouch ouch)
Water contaminated by cadmium
Symptoms bone pain, waddling gait,
aminoaciduria, severe osteomalacia (bone
softening)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Essential Ions - Specialized Biochemical FunctionsDocument10 pagesEssential Ions - Specialized Biochemical FunctionsmegmayorPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 Essential Trace and Nonessential IonDocument8 pagesChapter 3 Essential Trace and Nonessential IonAnthony V. DaquilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 1 InorganicDocument33 pagesLec 1 Inorganiciam2117Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry of Minerals-IIDocument29 pagesChemistry of Minerals-IIȘudîpțo ȘhăhîdPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry of Minerals-IIDocument29 pagesChemistry of Minerals-IIȘudîpțo ȘhăhîdPas encore d'évaluation
- Essential & Trace Elements: Iron, Copper, Zinc CompoundsDocument38 pagesEssential & Trace Elements: Iron, Copper, Zinc CompoundsVinod MulePas encore d'évaluation
- Jaselle A. Pante 1F-Pharmacy Exercises On Chapter IvDocument1 pageJaselle A. Pante 1F-Pharmacy Exercises On Chapter IvJasellePantePas encore d'évaluation
- Hematinic PreparationsDocument19 pagesHematinic PreparationsAbdur RaquibPas encore d'évaluation
- Iron Deficiency & IdaDocument40 pagesIron Deficiency & IdajarvantaraPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOCHEMISTRYDocument11 pagesBIOCHEMISTRYPmmi SehnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic K. 8Document3 pagesBasic K. 8Demisachew TenaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Pharmacology of Iron: Absorption, Transport, and SupplementationDocument38 pagesThe Pharmacology of Iron: Absorption, Transport, and SupplementationSalmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Iron Deficiency AnemiaDocument88 pagesIron Deficiency AnemiaAbubakar JallohPas encore d'évaluation
- Major & Trace MineralsDocument5 pagesMajor & Trace MineralsRhenier S. IladoPas encore d'évaluation
- RNS Haematinics Poison AstringentsDocument33 pagesRNS Haematinics Poison AstringentsVaibhav PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- An Def Fe Tk4Document17 pagesAn Def Fe Tk4putridwierlindaPas encore d'évaluation
- Metabolisme FeDocument109 pagesMetabolisme FeVivin Syamsul ArifinPas encore d'évaluation
- Minerals in FoodsDocument27 pagesMinerals in FoodsUmang GajeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Iron Metabolism and its Role in Health and DiseaseDocument24 pagesUnderstanding Iron Metabolism and its Role in Health and DiseaseShweta IyerPas encore d'évaluation
- Oleh: Sri Sumarmi: Pelangi GiziDocument55 pagesOleh: Sri Sumarmi: Pelangi GiziRika AmeiliawatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of VitaminsDocument12 pagesTypes of VitaminsDesign worldPas encore d'évaluation
- k1. Anemia Def FeDocument25 pagesk1. Anemia Def FeReza Muhamad NugrahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Trace Elements Essential for Human BodyDocument21 pagesTrace Elements Essential for Human BodyPitambar PoudelPas encore d'évaluation
- Naturopathic Nutrition: Sodium, Chlorine, Iron & SiliconDocument25 pagesNaturopathic Nutrition: Sodium, Chlorine, Iron & Siliconglenn johnstonPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell SaltsDocument8 pagesCell SaltsminunatPas encore d'évaluation
- CalciumDocument5 pagesCalciumjnssmylpz16Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8Document8 pagesChapter 8Jackson VonkPas encore d'évaluation
- Лекция №2АнемииDocument16 pagesЛекция №2Анемии772footballPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs For Hematologic DisordersDocument35 pagesDrugs For Hematologic DisordersAngeli Marie PadillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mineral Nutrition RuminantDocument35 pagesMineral Nutrition RuminantSoraya Rizki SaniditaPas encore d'évaluation
- Globular Proteins: Dr. Sujin Bao, SJSMDocument27 pagesGlobular Proteins: Dr. Sujin Bao, SJSMethanPas encore d'évaluation
- Haematinics MasterDocument72 pagesHaematinics MastervimalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hematinics (Iron and Vitamin B12)Document53 pagesHematinics (Iron and Vitamin B12)shareksultan5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hansen 2010 April 13 Mineral Nutrition RuminantDocument37 pagesHansen 2010 April 13 Mineral Nutrition RuminantyosysilalahiPas encore d'évaluation
- Therapeutic NutritionDocument13 pagesTherapeutic NutritionAlyssa EdelingPas encore d'évaluation
- Study of Irritant Poisons: Aresenic Album Poisoning (Sankhya, Somalkhar)Document17 pagesStudy of Irritant Poisons: Aresenic Album Poisoning (Sankhya, Somalkhar)Tej PrajapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Anemia of Abnormal Iron MetabolismDocument17 pagesAnemia of Abnormal Iron MetabolismJoezer Gumangan VeranoPas encore d'évaluation
- IRONDocument48 pagesIRONSarthak RunkhPas encore d'évaluation
- HIS1-K22 Drugs Used For AnemiaDocument43 pagesHIS1-K22 Drugs Used For AnemiaEga FlorencePas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition and DietDocument11 pagesNutrition and DietAlyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lead (Shisha)Document7 pagesLead (Shisha)ssuhass243Pas encore d'évaluation
- Trace Elements: Sharlyn B. AustriaDocument7 pagesTrace Elements: Sharlyn B. Austriaaida bPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledMing GamonganPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecq HemaDocument42 pagesEcq HemaJoezer Gumangan VeranoPas encore d'évaluation
- Minerals in FoodsDocument27 pagesMinerals in FoodsLaine AcainPas encore d'évaluation
- InorganicDocument34 pagesInorganicManWol JangPas encore d'évaluation
- Ferrous sulfate for anemiaDocument3 pagesFerrous sulfate for anemiafahadPas encore d'évaluation
- Mineral PoisoningDocument35 pagesMineral PoisoningFira'ol BogalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Oxygenation 2Document11 pagesOxygenation 2Mary June BulawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Vitamins and Minerals: Essential Organic Compounds for Body FunctionsDocument57 pagesVitamins and Minerals: Essential Organic Compounds for Body FunctionsWorku KiflePas encore d'évaluation
- mineral metabolism - P, Fe.Document30 pagesmineral metabolism - P, Fe.Shivanand MaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Minerals Iron by Dr. Faisal Hassan Shah (06.04.2020)Document141 pagesMinerals Iron by Dr. Faisal Hassan Shah (06.04.2020)Laraib SohailPas encore d'évaluation
- Group3 BSPH 2F1Document126 pagesGroup3 BSPH 2F1Ames Morales TorresPas encore d'évaluation
- Sis and AnemiaDocument4 pagesSis and AnemiaElit IbrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Cog 13 - MineralsDocument26 pagesCog 13 - MineralsTahpehs PhiriPas encore d'évaluation
- IronDocument3 pagesIronΜάριος ΣπύρουPas encore d'évaluation
- Vitamin A: (Retinol, Vision, Maintenance of Cornea, Epithelial Cells, Beta-Carotene: SpinachDocument5 pagesVitamin A: (Retinol, Vision, Maintenance of Cornea, Epithelial Cells, Beta-Carotene: SpinachVictoria EisenbergPas encore d'évaluation
- Haematopoietic Agents & Erythropoeitin: Dr. Rishi Pal Assistant Professor Department of PharmacologyDocument43 pagesHaematopoietic Agents & Erythropoeitin: Dr. Rishi Pal Assistant Professor Department of PharmacologyDERRICK AAGYEREYIR SAANUMEPas encore d'évaluation
- Haematinics and Erythropoietin: An OverviewDocument51 pagesHaematinics and Erythropoietin: An OverviewanushkaPas encore d'évaluation
- OrgChem VITKDocument3 pagesOrgChem VITKpjoanneloisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Iinternship 13Document35 pagesIinternship 13Darwin MangabatPas encore d'évaluation
- Finals Drug ListDocument1 pageFinals Drug ListpjoanneloisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hormome Deficiency by Increasing The SizeDocument3 pagesHormome Deficiency by Increasing The SizepjoanneloisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Terpin HydrateDocument5 pagesTerpin HydratepjoanneloisaPas encore d'évaluation
- MS EXCEL LectureDocument4 pagesMS EXCEL LecturepjoanneloisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Implants: Pornillos, Ma. Eloisa Joanne EDocument28 pagesImplants: Pornillos, Ma. Eloisa Joanne EpjoanneloisaPas encore d'évaluation
- (Yaranaika) MS EXCEL 2010Document3 pages(Yaranaika) MS EXCEL 2010Kenrick EvanderPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Critique A Scholarly Journal ArticleDocument1 pageHow To Critique A Scholarly Journal ArticlepocketfoxPas encore d'évaluation
- Creams and OintmentsDocument3 pagesCreams and OintmentspjoanneloisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Page 1Document1 pagePage 1pjoanneloisaPas encore d'évaluation
- XylocaineDocument1 pageXylocainepjoanneloisaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1Document1 page1pjoanneloisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Internship - RX Drugs (Part 1)Document4 pagesInternship - RX Drugs (Part 1)pjoanneloisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Status Report: Presenter Name Presentation DateDocument11 pagesProject Status Report: Presenter Name Presentation DateG Chandra SekharPas encore d'évaluation
- 1Document1 page1pjoanneloisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Francium Exists As An Unstable Radioactive Species: Group 1 A - Alkali MetalsDocument3 pagesFrancium Exists As An Unstable Radioactive Species: Group 1 A - Alkali MetalspjoanneloisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Eczema and PsoriasisDocument16 pagesEczema and PsoriasisLamy SPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Brain BarrierDocument7 pagesBlood Brain BarrierStela GretchenPas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous System DisordersDocument6 pagesNervous System DisordersAde YantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study For OligohydramniosDocument7 pagesCase Study For Oligohydramniosbjhilario86% (14)
- Exam-4 Ecpe 1 2014 TeDocument22 pagesExam-4 Ecpe 1 2014 TePoc100% (2)
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument23 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsKM_ArunPas encore d'évaluation
- Msds Glycerine Oil PDFDocument6 pagesMsds Glycerine Oil PDFknabpshoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing responsibilities for cardiac drugsDocument19 pagesNursing responsibilities for cardiac drugsMarie Kelsey Acena MacaraigPas encore d'évaluation
- Vocal TrainingDocument8 pagesVocal Trainingleballet22Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy-Esophagus & StomachDocument5 pagesAnatomy-Esophagus & StomachAlbert CorderoPas encore d'évaluation
- ZoologyDocument46 pagesZoologyRahul Kumar SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lie DetectionDocument6 pagesLie DetectionElla RafaelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthesis and Properties of Indole and its DerivativesDocument28 pagesSynthesis and Properties of Indole and its DerivativesRobert Exner100% (1)
- Principles of Animal Classification - 2020 PDFDocument33 pagesPrinciples of Animal Classification - 2020 PDFCallista Aulia ClairenePas encore d'évaluation
- Kuretase Case Report 2Document3 pagesKuretase Case Report 2Lydia AmaliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology of Consciousness: Gerald M. Edelman, Joseph A. Gally and Bernard J. BaarsDocument7 pagesBiology of Consciousness: Gerald M. Edelman, Joseph A. Gally and Bernard J. Baarskfun90Pas encore d'évaluation
- Vascular PlantsDocument2 pagesVascular PlantsAurea Jasmine DacuycuyPas encore d'évaluation
- Four Major Divisions of Auditory System - AnatomyDocument9 pagesFour Major Divisions of Auditory System - AnatomyJoshuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Arju 5Document3 pagesArju 5arjumardi azrahPas encore d'évaluation
- Paleo Cures: Tota L Hea LTH Acceler AtorDocument9 pagesPaleo Cures: Tota L Hea LTH Acceler AtorLavanya Priya SathyanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Ergonomic Design of Classroom Furniture:computer Work Station For First Graders in The Elementary School PDFDocument11 pagesThe Ergonomic Design of Classroom Furniture:computer Work Station For First Graders in The Elementary School PDFDebrina Puspitarini100% (2)
- Diagnostic Test Natual Science 2º Primary BymeDocument3 pagesDiagnostic Test Natual Science 2º Primary BymeIsmael CV hvbvbvuvcgcg CC v FCC Chaves80% (5)
- Baryat Carb DescriptionDocument2 pagesBaryat Carb DescriptionpgurPas encore d'évaluation
- Neuroanatomy Topic OutlineDocument2 pagesNeuroanatomy Topic OutlineEdmar SumagaysayPas encore d'évaluation
- Acid-Base Equilibria in Aqueous SolutionsDocument48 pagesAcid-Base Equilibria in Aqueous SolutionsAdrian ChombaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 015Document9 pagesChapter 015Christopher EndicottPas encore d'évaluation
- Annotated Bibliography 1Document8 pagesAnnotated Bibliography 1api-432883682Pas encore d'évaluation
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 3Document3 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 3Prityutpann DeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Birth PPDocument5 pagesWater Birth PPAzi SamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell types and adaptations for specialized functionsDocument24 pagesCell types and adaptations for specialized functionsJae Ann CaliñadaPas encore d'évaluation