Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
DTC P0011
Transféré par
Ronald MoonDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
DTC P0011
Transféré par
Ronald MoonDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
DTC P0011 "A" CAMSHAFT POSITION-TIMING OVER-ADVANCED OR SYSTEM PERFORMANCE
(BANK 1)
Component Location
Zoom
Sized for Print
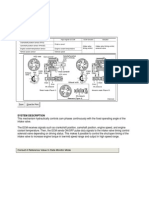
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The CVVT (Continuously Variable Valve Timing) system is installed to the chain sprocket of the exhaust
camshaft. There is no variation in valve timing of the exhaust cam because the exhaust camshaft is
driven by the timing belt. The timing of the intake cam is varied by the relative operation the CVVT vane
to the housing. The CVVT controller regulates the intake camshaft angle using oil pressure through the
OCV (Oil Control Valve). As result, the relative position between the camshaft and the crankshaft
becomes optimal, and the engine torque improves, fuel economy improves, exhaust emissions decrease
by changing the valve open/close timing of the intake camshaft.
DTC DESCRIPTION
The deviation of the camshaft position from the target point is evaluated during stable driving condition.
The ECM accumulates this deviation for a certain period and sets DTC P0011 when the accumulated
deviation is too high. The target camshaft position is predetermined value depending on engine speed
and throttle angle in the ECM.
DTC Detecting Condition
Zoom
Sized for Print
Specification
Zoom
Sized for Print
Schematic Diagram
Zoom
Sized for Print
Signal Waveform And Data
Zoom
Sized for Print
MONITOR DTC STATUS
1. Connect scan tool and select "Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)" mode.
2. Press F4 (DTAL) to select DTC information from the DTCs menu.
3. Confirm that "DTC Readiness Flag" indicates "Complete". If not, drive the vehicle within
conditions noted in the freeze frame data or enable conditions.
Zoom
Sized for Print
4. Read "DTC Status" parameter.
5. Is parameter displayed "History (Not Present) fault"?
NOTE:
History (Not Present) fault : DTC occurred but has been cleared.
Present fault : DTC is occurring at present time.
YES - Fault is intermittent caused by poor contact in the sensor's and/or ECM's connector or was repaired
and ECM memory was not cleared. Thoroughly check connectors for looseness, poor connection,
bending, corrosion, contamination, deterioration, or damage. Repair or replace as necessary and then go
to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.
NO - Go to next step as below.
COMPONENT INSPECTION
CHECK OCV AND FILTER
1. Check resistance of OCV.
1. Ignition "OFF".
2. Disconnect intake OCV connector.
3. Measure resistance between terminals 1 and 2 of the intake OCV connector. (Component side)
Specification : Approx. 6.9 - 7.9 Ohms at 20 C (68 F)
4. Is resistance within the specification?
YES - Go to next step as below.
NO - Replace OCV and then go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.
2. Check operation of OCV
1. Start the engine and let it idle.
Specification
Zoom
Sized for Print
2. With OCV connector still disconnected, connect 12 V and a ground to 2 and 1 of the OCV
(Component side).
3. Has a problem been found?
YES - Go to next step as below.
NO - Go to "Check CVVT (Continuously Variable Valve Timing) Assembly" procedure.
3. Check OCV and Filter.
1. Ignition "OFF".
2. Check OCV filter for sticking or contamination.
3. Remove the OCV and visually check the spool column of OCV for contamination.
4. Has a problem been found?
YES - Clean or replace as necessary and then go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.
NO - Go to next step as below.
5. Apply 12 V and a ground to 2 and 1 terminals of the OCV (Component side).
6. Verify that a "clicking" sound is heard when applying the battery voltage.
Zoom
Sized for Print
7. Repeat this procedure 4 or 5 times to ensure intake OCV reliability.
8. Is OCV working properly?
YES - Go to next step as below.
NO - Check OCV for contamination, deterioration, or damage. Substitute with a known-good OCV and
check for proper operation. If the problem is corrected, replace OCV and then go to "Verification of
Vehicle Repair" procedure.
CHECK CVVT (CONTINU0USLY VARIABLE VALVE TIMING) ASSEMBLY
1. Remove the CVVT assembly. Refer to "Removal Procedure" in Workshop Manual.
2. Check that the CVVT assembly is locked.
Zoom
Sized for Print
3. The one of the 2 holes on the cam journal is for advances (upper) and the rest is for retards
(lower). Apply masking tape to all oil path holes except the one advance hole ("B") indicated by
the arrow as shown in the figure.
4. To release the CVVT lock pin, wrap some tape around the tip of an air pressure adapter and
apply low air pressure of approx. 150 kPa (1.5 kg/sq.cm, 21 psi) to the exposed camshaft port.
Wrap a shop towel or rag around the CVVT because residual oil may leak out of the unit when
applying air pressure.
Zoom
Sized for Print
5. With low air pressure applied, turn the CVVT to the ADVANCE direction as indicated in the figure.
NOTE: If too much air leaks when applying the low air pressure, the CVVT lock pin may not release and
the CVVT may not turn.
6. Allow the CVVT assembly to move in the ADVANCE and DELAY directions to ensure there is no
binding and that it moves freely. (Movable smoothly in the range about 20 )
7. Turn the CVVT by hand and make sure it locks in the maximum delay angle position.
8. Is CVVT assembly working properly?
YES - Go to next step as below.
NO - Replace the CVVT assembly and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.
TERMINAL AND CONNECTOR INSPECTION
1. Many malfunctions in the electrical system are caused by poor harness(es) and terminals. Faults
can also be caused by interference from other electrical systems, and mechanical or chemical
damage.
2. Thoroughly check connectors for looseness, poor connection, bending, corrosion, contamination,
deterioration, or damage.
3. Has a problem been found?
YES - Repair as necessary and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.
NO - Check valve timing. Refer to "P0016: Crankshaft Position-Camshaft Position Correlation (Bank1)"
procedure. Repair as necessary and go to "Verification of Vehicle Repair" procedure.
VERIFICATION OF VEHICLE REPAIR
After a repair, it is essential to verify that the fault has been corrected.
1. Connect scan tool and select "Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)" mode.
2. Press F4 (DTAL) and confirm that "DTC Readiness Flag" indicates "Complete". If not, drive the
vehicle within conditions noted in the freeze frame data or enable conditions.
3. Read "DTC Status" parameter.
4. Is parameter displayed "History (Not Present) fault"?
YES - System performing to specification at this time. Clear the DTC
NO - Go to the applicable troubleshooting procedure.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- GM Automatic Overdrive Transmission Builder's and Swapper's GuideD'EverandGM Automatic Overdrive Transmission Builder's and Swapper's GuideÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (8)
- Bendix Air Brake System Schematic PDFDocument1 pageBendix Air Brake System Schematic PDFraidhemed67% (3)
- TRANSFER CASE BW44-46 - Service Information - Ram Pickup PDFDocument42 pagesTRANSFER CASE BW44-46 - Service Information - Ram Pickup PDFcharles100% (1)
- Volvo - S60 - Workshop Manual - 2000 - 2003Document3 231 pagesVolvo - S60 - Workshop Manual - 2000 - 2003James StaffPas encore d'évaluation
- Automotive Actuators and EVAP System TestingD'EverandAutomotive Actuators and EVAP System TestingÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (4)
- Diesel Engine Care and Repair: A Captain's Quick GuideD'EverandDiesel Engine Care and Repair: A Captain's Quick GuideÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Renault Semiauto GearboxDocument88 pagesRenault Semiauto GearboxSteve Gaddis95% (21)
- Engine Pressure Sensor Open or Short PDFDocument14 pagesEngine Pressure Sensor Open or Short PDFNydRomG100% (2)
- Injector Solenoid Circuit - Test (RENR5096)Document7 pagesInjector Solenoid Circuit - Test (RENR5096)Josip MiškovićPas encore d'évaluation
- C9 Injection Actuation Pressure TestDocument18 pagesC9 Injection Actuation Pressure Testharikrishnanpd3327100% (1)
- Continuously Variable Valve TimingDocument12 pagesContinuously Variable Valve TiminggamerpipePas encore d'évaluation
- Injection Actuation PressureDocument20 pagesInjection Actuation Pressureabdelrhmangbr8682% (11)
- Automatic TransmissionDocument382 pagesAutomatic TransmissionYee Leong Yap100% (3)
- A 240Document89 pagesA 240Mario Diaz Lopez100% (1)
- Engine Cranks But Will Not StartDocument52 pagesEngine Cranks But Will Not Startphuong lamhoang100% (8)
- Injection Actuation Pressure - TestDocument18 pagesInjection Actuation Pressure - TestDanielly GersonPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.2l Engine PDFDocument451 pages3.2l Engine PDFLoredana Dorobantu100% (1)
- 4 Tne 106 GeDocument50 pages4 Tne 106 Gezakki ahmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Injector Solenoid Circuit - Test: TroubleshootingDocument13 pagesInjector Solenoid Circuit - Test: TroubleshootingGolbert GolbiPas encore d'évaluation
- "Transmission Drive Pump Pressure Override Calibration": Illustration 1 g02500239 Cat ET Calibrations MenuDocument6 pages"Transmission Drive Pump Pressure Override Calibration": Illustration 1 g02500239 Cat ET Calibrations MenuNurdin0% (1)
- A32 at PDFDocument293 pagesA32 at PDFOmar RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- P000b-Bank 1 Camshaft 2 Position Slow ResponseDocument7 pagesP000b-Bank 1 Camshaft 2 Position Slow Responseflash_24014910Pas encore d'évaluation
- P1656 PDFDocument3 pagesP1656 PDFTalleban TalPas encore d'évaluation
- DAF CF Gearbox Service Manual PDFDocument504 pagesDAF CF Gearbox Service Manual PDFMike QPas encore d'évaluation
- PCV SystemDocument4 pagesPCV Systemmkisa70Pas encore d'évaluation
- Trans. de 140hDocument4 pagesTrans. de 140hvictor franco gallegos100% (1)
- (FMC) B350 Sept 1997Document687 pages(FMC) B350 Sept 1997Jeeva RathinamPas encore d'évaluation
- Actual Crankshaft Manufacturer: Inhouse: Raw Material Production + CNC MachiningDocument16 pagesActual Crankshaft Manufacturer: Inhouse: Raw Material Production + CNC Machiningglobalindospareparts100% (1)
- 8FG (D) U15-32, 8FGCU20-32 Repair Manual Supplement CU066Document227 pages8FG (D) U15-32, 8FGCU20-32 Repair Manual Supplement CU066Nguyễn Huỳnh ĐứcPas encore d'évaluation
- The Book of the Singer Junior - Written by an Owner-Driver for Owners and Prospective Owners of the Car - Including the 1931 SupplementD'EverandThe Book of the Singer Junior - Written by an Owner-Driver for Owners and Prospective Owners of the Car - Including the 1931 SupplementPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Diagrams Series6 Nov2006Document78 pagesElectric Diagrams Series6 Nov2006MACHINERY101GEAR100% (3)
- Diagnostico Con E.T. (Corte de Cilindros)Document14 pagesDiagnostico Con E.T. (Corte de Cilindros)Jose Luis Calla Huanca100% (1)
- Parts Manual: D6T Track-Type TractorDocument54 pagesParts Manual: D6T Track-Type TractorFabio MacielPas encore d'évaluation
- GR00004300C 13aDocument260 pagesGR00004300C 13aEduardo Enrique Rojas ValenzuelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fuel System: SectionDocument13 pagesFuel System: Sectiontomallor101Pas encore d'évaluation
- 745 Cat EtDocument6 pages745 Cat EtLucky advanturePas encore d'évaluation
- Get PDFDocument5 pagesGet PDFRonald Moon100% (1)
- M - Series Alo Loader WSM en PDFDocument84 pagesM - Series Alo Loader WSM en PDFFrançois CharrièrePas encore d'évaluation
- 301.6C 301.8C PDFDocument2 pages301.6C 301.8C PDFŁukasz Adamczak67% (3)
- ED4A51E0: Spare Parts CatalogueDocument62 pagesED4A51E0: Spare Parts CatalogueingridPas encore d'évaluation
- P0011 - DTC 2006 Kia SpectraDocument5 pagesP0011 - DTC 2006 Kia Spectraangelvalladares100% (1)
- NTB02 033Document3 pagesNTB02 033PMPas encore d'évaluation
- 164-11 Falla D6 DragaSurDocument11 pages164-11 Falla D6 DragaSurManuel ContrerasPas encore d'évaluation
- Troubel Shoting Piston PumpDocument7 pagesTroubel Shoting Piston PumpAmir Bambang YudhoyonoPas encore d'évaluation
- P0011 Hyundai I20 A Camshaft Position-Timing Over-Advanced or System PerformanceDocument4 pagesP0011 Hyundai I20 A Camshaft Position-Timing Over-Advanced or System PerformancevivekpateljPas encore d'évaluation
- Injection Actuation Pressure - Test: TroubleshootingDocument19 pagesInjection Actuation Pressure - Test: TroubleshootingMbahdiro KolenxPas encore d'évaluation
- PEEC Electronic System Functional TestsDocument66 pagesPEEC Electronic System Functional TestsRichard Chua0% (1)
- HKS EVC V Boost Controller Setup InstructionsDocument7 pagesHKS EVC V Boost Controller Setup InstructionsDave_B100% (2)
- Hks EvcDocument16 pagesHks EvcKok Leong WongPas encore d'évaluation
- Fuel Control ValveDocument12 pagesFuel Control ValveALVARO OLACHICAPas encore d'évaluation
- Pajero 1991 Cruise Control SystemDocument28 pagesPajero 1991 Cruise Control SystemnadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Motor 3126b Prueba de ActuacionDocument9 pagesMotor 3126b Prueba de ActuacionEckard GuendelPas encore d'évaluation
- Prueba Sensores PM1360Document7 pagesPrueba Sensores PM1360miguel oswaldo gonzalez benitezPas encore d'évaluation
- NUMBER: 4-10-13 S.M. REF.: Listed in Table ENGINE: EPA07 Series 60 DATE: April 2013Document12 pagesNUMBER: 4-10-13 S.M. REF.: Listed in Table ENGINE: EPA07 Series 60 DATE: April 2013Walter A Gómez de la CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Tech at Blog - Hyundai Trouble Shooting & General Description - How To Inspect The Electrical Circuit of Code P0743Document6 pagesTech at Blog - Hyundai Trouble Shooting & General Description - How To Inspect The Electrical Circuit of Code P0743Zool Car زول كارPas encore d'évaluation
- Auto TransmissionDocument61 pagesAuto Transmissionlamping_apPas encore d'évaluation
- 0022-11 Primary To Secondary Engine Speed Signal CalibrationDocument2 pages0022-11 Primary To Secondary Engine Speed Signal CalibrationMarioAlbertoBustamanteSierraPas encore d'évaluation
- General Engine Information: Section: 1ADocument11 pagesGeneral Engine Information: Section: 1AXavier OrtizPas encore d'évaluation
- d5n Bma Calib Clucth d5nDocument10 pagesd5n Bma Calib Clucth d5nChristian Vinueza VillavicencioPas encore d'évaluation
- EN FANOXTD GUIDE SIA OCEFSecondaryDist SIAB000B0010AA R03Document32 pagesEN FANOXTD GUIDE SIA OCEFSecondaryDist SIAB000B0010AA R03cosme pereiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti-Lock Brake System: Model IdentificationDocument34 pagesAnti-Lock Brake System: Model IdentificationMitchPas encore d'évaluation
- Service Manual ExtractDocument6 pagesService Manual ExtractNovica ŽivanovićPas encore d'évaluation
- 2008 Nissan Teana J32 Service Manual-FLDocument11 pages2008 Nissan Teana J32 Service Manual-FLMrihexPas encore d'évaluation
- Fuel Shutoff - TestDocument7 pagesFuel Shutoff - TestAdolfo Dario SaavedraPas encore d'évaluation
- 2010 TRANSMISSION Automatic Transmission (RE0F08B) - CubeDocument233 pages2010 TRANSMISSION Automatic Transmission (RE0F08B) - CubeGuillermo BenitezPas encore d'évaluation
- Motor Daewoo Lanos Mecanica ElectricidadDocument615 pagesMotor Daewoo Lanos Mecanica ElectricidadSergio Isaac Lagos LagosPas encore d'évaluation
- Fuel Filter Differential Pressure Switch Circuit - Test (RENR5096)Document3 pagesFuel Filter Differential Pressure Switch Circuit - Test (RENR5096)Josip MiškovićPas encore d'évaluation
- Product - Support-Precor-Service Manuals-Commercial Treadmill-C956i (240 VAC) (Serial Code Z5)Document69 pagesProduct - Support-Precor-Service Manuals-Commercial Treadmill-C956i (240 VAC) (Serial Code Z5)Gabino Ubilio MurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- NissanDocument24 pagesNissanUbaldo SanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitD'EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitPas encore d'évaluation
- 2003 Volkswagen Jetta Sedan ATFDocument2 pages2003 Volkswagen Jetta Sedan ATFRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Oxygen Sensor LocationDocument1 pageOxygen Sensor LocationRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Heated Oxygen Sensors PDFDocument2 pagesHeated Oxygen Sensors PDFRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Disconnecting Connectors PDFDocument4 pagesDisconnecting Connectors PDFRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.5 Labor TimeDocument1 page2.5 Labor TimeRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Disconnect The Battery Negative Cable PDFDocument36 pagesDisconnect The Battery Negative Cable PDFRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Intake Air Temperature SensorDocument1 pageIntake Air Temperature SensorRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Removal Cam SensorDocument3 pagesRemoval Cam SensorRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Crank SensorDocument3 pagesCrank SensorRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Get PDFDocument3 pagesGet PDFRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Replacing Intake Air Temperature SensorDocument2 pagesReplacing Intake Air Temperature SensorRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Rear Seat PDFDocument2 pagesRear Seat PDFRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Intake Air Temperature SensorDocument2 pagesIntake Air Temperature SensorRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Lock Carrier With AttachmentsDocument6 pagesLock Carrier With AttachmentsRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Input Speed Sensor PDFDocument3 pagesInput Speed Sensor PDFRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Warning PDFDocument9 pagesWarning PDFRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- DTC P0011 Ivt ControlDocument4 pagesDTC P0011 Ivt ControlRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Bumper Bumper: Front Front, Removing, Installing and Assembly OverviewDocument4 pagesBumper Bumper: Front Front, Removing, Installing and Assembly OverviewRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Removal PDFDocument5 pagesRemoval PDFRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyundai SonataDocument3 pagesHyundai SonataRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- 2002 Altima - Engine RemovalDocument4 pages2002 Altima - Engine RemovalRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- 2001 Volkswagen Jetta GL SedanDocument4 pages2001 Volkswagen Jetta GL SedanRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission Output Speed Senso1Document3 pagesTransmission Output Speed Senso1Ronald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission Input Speed Sensor PDFDocument5 pagesTransmission Input Speed Sensor PDFRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Drain The Engine Oil PDFDocument2 pagesDrain The Engine Oil PDFRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- 1995 Mazda Protege L4Document2 pages1995 Mazda Protege L4Ronald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- DTC p0441 EvapDocument1 pageDTC p0441 EvapRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Possible Causes:: TCM Terminal No. Measured Voltage Gear Selector PositionDocument2 pagesPossible Causes:: TCM Terminal No. Measured Voltage Gear Selector PositionRonald MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Compresor Thomas PDFDocument4 pagesCompresor Thomas PDFpsycopaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Sheet No.1Document1 pageProblem Sheet No.1Imran TahirPas encore d'évaluation
- Dimensions - (Pneumatic) In. G/GC-SeriesDocument33 pagesDimensions - (Pneumatic) In. G/GC-SeriesZts MksPas encore d'évaluation
- B+V Manual - Safety Clamp Type T REV 003-JUL-2009Document5 pagesB+V Manual - Safety Clamp Type T REV 003-JUL-2009ZEESHAN ASHRAFPas encore d'évaluation
- Main Principles of Pumps SelectionDocument14 pagesMain Principles of Pumps SelectionMMM000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Safety Precautions . . .. ..2 About U600 . .. . ..4Document32 pagesSafety Precautions . . .. ..2 About U600 . .. . ..4NablabsPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm D-908Document133 pagesAstm D-908Andrés Jonathan Cepeda GuerronPas encore d'évaluation
- TsubakiDocument45 pagesTsubakiBastanta NainggolanPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Title Course Level: UG Credit Units: Course Code: MAE301Document3 pagesCourse Title Course Level: UG Credit Units: Course Code: MAE301Himanshu JangidPas encore d'évaluation
- All Line QpumpsDocument18 pagesAll Line QpumpsEdgar ApontePas encore d'évaluation
- Mid Diesel Engine Range: All The Power You NeedDocument12 pagesMid Diesel Engine Range: All The Power You Needegbert axelPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Turbine Power PlantDocument11 pagesGas Turbine Power PlantCK Godinez100% (1)
- 2011 Parts Cat Ride RMDocument50 pages2011 Parts Cat Ride RMMotokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Unique Small Single Seat ValveDocument14 pagesUnique Small Single Seat ValvePhrynocephalus ItaliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Como Instalar Una Bomba SumergibleDocument23 pagesComo Instalar Una Bomba Sumergibleoscar_m_avilaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4756 Civic 96-2000 D16y8 Performer XDocument3 pages4756 Civic 96-2000 D16y8 Performer XRafael Isaac Lòpez Vargas100% (1)
- Internship ReportDocument6 pagesInternship Reportdarshan randivePas encore d'évaluation
- Mitsubishi Canter SpecificationsDocument5 pagesMitsubishi Canter SpecificationsAnonymous wpUyixsjPas encore d'évaluation
- Picklist VCMM Xc60 b85604Document3 183 pagesPicklist VCMM Xc60 b85604shukur86Pas encore d'évaluation