Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Ici Reduction Techniques in Ofdm System Paper
Transféré par
Rakesh MandalCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Ici Reduction Techniques in Ofdm System Paper
Transféré par
Rakesh MandalDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Journal of Engineering Research and Technology (IJERT)
ISSN : 2278-08!"olu#e $! Issue 0! %ug 20$! && 0-0'
((()i*er+)org
COMPARISON ON ICI REDUCTION TECHNIQUES IN
OFDM SYSTEM
Madhavi Goswami
1
(Elec+ronics , Tele) Research Scholar! - ."R/! IN0I%)
ABSTRACT : 1r+hogonal fre2uency di3ision #ul+i4le5ing (1607) is a 4ro#ising +echni2ue for +he
8road8and (ireless co##unica+ion sys+e#) 9o(e3er! +he in+er-carrier-in+erference (I.I) 4roduced 8y +he 4hase
noise of +ranscei3er local oscilla+or is a serious 4ro8le#) The 3aria+ions in Ti#e 1ffse+ (T1) can lead +o in+er-
sy#8ol-in+erference (ISI) in case of fre2uency selec+i3e channel) :i+era+ure sur3ey of any research filed or
su8*ec+ is #us+ re2uired! 8efore con+ri8u+ing in +he research of +ha+ field) The li+era+ure re3ie( gi3es a de+ailed
s+udy of e5is+ing 4u8lished #a+erial for clear unders+anding of +ha+ area) Therefore! +his &a4er 4resen+s a
de+ailed li+era+ure sur3ey of +he area +a;en (i)e)! 1607)) The s+udy in +his 4a4er highligh+s differen+ 4ro8le#s
or issues of 1607 sys+e# li;e high &%&R! synchroni<a+ion! and In+er-.arrier-In+erference (I.I)) This re3ie(
also su##ari<es +he #e+hods a3aila8le in +he li+era+ure +o o3erco#e +hese 4ro8le#s)
Keywords - 1607! I.I! S.!7:E!&S
I. INTRODUCTION
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) has grown to a popular communication technique for
high speed communication in the last decade !eing an important mem"er of the multicarrier modulation (M#)
techniques$ Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)$ is also called Discrete Multitone
Modulation %t is "ased upon the principle of frequency division multiplexing (FDM) where each frequency
channel is modulated with simpler modulation scheme %t splits a high rate data stream into a num"er of lower
rate streams that are transmitted simultaneously over a num"er of orthogonal su"carriers Orthogonal Frequency
Division Multiplexing is a form of multi carrier modulation technique with high spectral efficiency$ ro"ustness
to channel fading$ immunity to impulse interference$ uniform average spectral density capacity of handling very
strong echoes and non&linear distortion Despite of its many advantages$ OFDM suffers from two main
draw"ac's$ ie$ high pea' to average power ratio (()(*) and inter&carrier interference (%#%)$ which may "e
caused "y Doppler shift in the channel or "y the difference "etween the transmitter and receiver local oscillator
frequencies %n such situations$ the orthogonally of the carriers is no longer maintained$ which result in %nter&
carrier %nterference (%#%)
+he pro"lem of %#% can "e solved "y various techniques proposed "y various researchers which include +ime
domain windowing$ Frequency domain equali,ation$ Maximum -i'elihood estimation (M-.)$ (ulse /haping
and %#% self cancellation technique +his paper discusses all the prominent %#% reduction technique descri"ed
a"ove
II. OFDM SYSTEM MODEL
+he discrete time "ase"and OFDM system model with 0 su"carriers is shown in Figure 11 %t consists of
transmitter$ channel and receiver "loc's which are descri"ed "elow
Fig 1.1 OFDM System Blo! Di"g#"m
.o#4arison on I.I Reduc+ion Techni2ues in 1607 Sys+e#
)t the transmitter$ the user information "it sequence is first su"1ected to channel encoding to reduce the
pro"a"ility of error at the receiver due to the channel effects 2sually$ convolution encoding is preferred +hen
the "its are mapped to sym"ols of either 13&4)M or 4(/5 +he sym"ol sequence is converted to parallel
format and %FF+ (OFDM modulation) is applied and the sequence is once again converted to the serial format
Guard time provided "etween the OFDM sym"ols and the guard time filled with the cyclic extension of the
OFDM sym"ol 6indowing is applied to the OFDM sym"ols to ma'e the fall&off rate of the spectrum steeper
+he resulting sequence is converted to an analog signal using a D)# and passed on to the *F modulation stage
+he resulting *F modulated signal is$ then$ transmitted to the receiver using the transmit antennas 7ere$
directional "eam&forming can "e achieved using antenna array$ which allows for spectrum reuse "y providing
spatial diversity +herefore OFDM sym"ol can "e expressed as$
( ) ( )
1
8
9
1
n
* n#
N
#
5 n 5 # e
N
(1)
6here x (n) denotes the sample of the OFDM signal$ :(m) denotes the modulated sym"ol within su"carrier and
0 is the num"er of su"carriers
)t the receiver$ first *F demodulation is performed +hen$ the signal is digiti,ed using an )D# and timing and
frequency synchroni,ation are performed +he guard time is removed from each OFDM sym"ol and the
sequence is converted to parallel format and FF+ (OFDM demodulation) is applied +he output is then seriali,ed
and sym"ol demapping is done to get "ac' the coded "it sequence #hannel decoding is$ then$ done to get the
user "it sequence +he demodulated sym"ol stream is given "y$
( ) ( ) ( )
1
8
9
N
* n#
N
n
y # y n e ( #
(8)
where w (m) corresponds to the FF+ of the samples of the w (n)
III. ICI REDUCTION TECHNIQUES
F#e$%e&y Dom"i& E$%"li'"tio&( +he fading distortion in the channel causes %#% in the OFDM demodulator
+he pattern of %#% varies from frame to frame for the demodulated data "ut remains invariant for all sym"ols
within a demodulated data frame #ompensation for fading distortion in the time domain introduces the pro"lem
of noise enhancement /o frequency domain equali,ation process is approached for reduction of %#% "y using
suita"le equali,ation techniques 6e can estimate the %#% for each frame "y inserting frequency domain pilot
sym"ols in each frame as shown in figure 18
Fig 1.) Pilot S%*"##ie# A##"&geme&t
+his technique can only reduce the %#% caused "y fading distortion which is not the ma1or source of %#% +he
ma1or source of %#% is due to the frequency mismatch "etween the transmitter and receiver +he a"ove method
cannot address to it )gain it is only suita"le for flat fading channels$ "ut in mo"ile communication the channels
are frequency selective fading in nature "ecause of multipath components 7ere also the channel needs to "e
estimated for every frame .stimation of channel is complex$ expensive ; time consuming 7ence this method
is not an effective one
wwwi1ertorg 8 < (age
.o#4arison on I.I Reduc+ion Techni2ues in 1607 Sys+e#
Time Dom"i& +i&,o-i&g( OFDM signal has widely spread power spectrum /o if this signal is transmitted in
a "and limited channel$ certain portion of the signal spectrum will "e cut off$ which will lead to inter carrier
interference +o diminish the interference the spectrum of the signal wave form need to "e more concentrated
+his is achieved "y windowing the signal !asically windowing is the process of multiplying a suita"le function
to the transmitted signal wave form +he same window is used in the receiver side to get "ac' the original
signal +he %#% will "e eliminated if the product of the window functions satisfies the 0yquist vestigial
symmetry criterion
+his method only reduces the %#% caused "y "and limited channel which is not the ma1or source of %#% +he
ma1or source of %#% is due to the frequency mismatch "etween the transmitter and receiver$ and the Doppler
shift Further windowing is done frame "y frame ; hence it reduces the spectral efficiency to a large extent
7ence this method is not an effective one
M".im%m Li!eli/oo, Estim"tio&( )nother method for frequency offset correction ie M- estimation in
OFDM systems was suggested "y Moose %n this approach$ the frequency offset is first statistically estimated
using a maximum li'elihood algorithm and then cancelled at the receiver +his technique involves the
replication of an OFDM sym"ol "efore transmission and comparison of the phases of each of the su"carriers
"etween the successive sym"ols +he maximum li'elihood estimate is a conditionally un"iased estimate of the
frequency offset and can "e computed "y using received data +he maximum li'elihood estimate of the
normali,ed frequency offset is given "y$
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
=
8
8
=
1
8
1
>
8
*e
=
; =
=
; =
l#> ; > ;
> ; > ;
1
1
1
1
1
]
(?)
Once the frequency offset is 'nown$ the %#% distortion in the data sym"ols is reduced "y multiplying the
received sym"ols with a complex con1ugate of the frequency shift and applying the FF+
( ) ( )
8 * ne
N
? n 66T > n e
' ;
(@)
ICI Sel0 C"&ell"tio& S/eme( +he self&cancellation schemes wor's in two very simple steps )t the
transmitter side$ one data sym"ol is modulated onto a group of ad1acent su"carriers with a group of weighting
coefficients +he weighting coefficients are designed so that the %#% caused "y the channel frequency errors can
"e minimi,ed )t the receiver side$ "y linearly com"ining the received signals on these su"carriers with
proposed coefficients$ the residual %#% contained in the received signals can then "e further reduced +his
method is suita"le for multipath fading channels as here no channel estimation is required "ecause in multipath
case channel estimation fails as the channel changes randomly
%n an OFDM communication system$ assuming the channel frequency offset normali,ed "y the su"carrier
separation is
$ the received signal on su"carrier ; can "e written as$
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
1
9$
9
N
;
i l ;
r ; ? ; S ? l S l ; n
+ +
(A)
where 0 is the total num"er of the su"carriers ? (;) denotes the transmitted sym"ol for the
+h
;
su"carrier and
;
n is additive noise +he first term in the right&hand side of (A) represents the desired signal +he second term
is the %#% components +he sequence S (l-;) is defined as the %#% coefficient "etween
+h
l
and
+h
;
su"carriers$
which can "e expressed as$
( )
( ) ( )
( )
( ) ( ) ( )
1
sin
exp 1
sin
N
l ;
S l ; * l ;
N l ;
N
+
+
_
+
,
(3)
wwwi1ertorg ? < (age
.o#4arison on I.I Reduc+ion Techni2ues in 1607 Sys+e#
P%lse S/"1i&g( +he figure 1? illustrates the transmitter "loc' diagram of a N su"&carrier OFDM system using
pulse shaping 7ere the incoming data is first modulated in "ase"and using a "andwidth efficient modulation
(4(/5 modulation) +he "ase"and modulated stream$ with data rate -Ts is then split into N parallel streams
.ach stream is shaped "y a time waveform (pulse shaping waveform) and transmitted over a given su"carrier
+hus the OFDM transmitted signal can "e expressed as$
( ) ( ) ( )
1
8
9
;
+
N
* ;
T
n
;
5 + ? ; & + e
(B)
Fig.1.2 OFDM T#"&smitte# Mo,el Usi&g P%lse S/"1i&g
where ( )
n
? ; the modulated data sym"ol of su"&carrier is ; $ T is the duration of the OFDM "loc' %f we can
reduce the side lo"e significantly then the %#% power will also "e reduced significantly 7ence a num"er of pulse
shaping functions are proposed having an aim to reduce the side lo"e as much as possi"le
I3. CONCLUSION
)fter learning all those a"ove techniques$ % conclude that conventional technique for %#% *eduction li'e time
domain equali,ation$ windowing technique$ self cancelation$ maximum li'elihood does not properly reduce %#%
at the receiver side "ecause in these techniques$ %#% reduces only "and limited channel which is not a ma1or
source of %#% +he ma1or source of %#% is due to frequency mismatch "etween transmitter and receiver$ this
pro"lem is reduced "y pulse shaping method
REFERENCES
4o%#&"l P"1e#s(
@A M )grawal$ / /harma$ &erfor#ance of 7I71-1607 sys+e# using :inear 7a5i#u# :i;elihood %la#ou+i 0ecoder$
In+erna+ional Journal of 0is+ri8u+ed and &arallel Sys+e#s! $($)! 202! 2-$)
@2A ) %dris$ 5 Dimyati$ .valuating a new su"carrier mapping %#%&/# /cheme 2sing -inear Maximum -i'elihood )lamouti
#om"iner (-M-)#) Decoding +echnique ! Journal of Engineering Science and Technology!B(B)!20! BBC-B7$
wwwi1ertorg @ < (age
.o#4arison on I.I Reduc+ion Techni2ues in 1607 Sys+e#
$ In+erna+ional Journal of 0is+ri8u+ed and &arallel Sys+e#s! $($)! 202! 2-$)
@$A / Gupta$ 2 Dalal$ I#4le#en+a+ion of &ulse Sha4ing Techni2ue in 1607 Sys+e#$ In+erna+ional Journal of .o#4u+er
%44lica+ions! B8(0)! 20$! D-2$)
@CA ) Gupta$ G Gandhi$ I#4le#en+a+ion of &ulse Sha4ing Ne(r0-6u<<y Techni2ue in 1607 Sys+e#$ In+erna+ional Journal of
.o#4u+er %44lica+ions! B7(0)! 202! 2'-$0)
@'A 7 Chou$ D Fang 7aung$ 7a5i#u#-:i;elihood .arrier 6re2uency 1ffse+ Es+i#a+ion for 1607 Sys+e#s in 6ading .hannels$
IEEE! C(22)! 20! B8-78)
@BA M Matthaiou$ G 5 5aragiannidis$ 14+i#i<ed EFe++er ThanG Raised-.osine &ulse for Reduced I.I in 1607 Sys+e#s$ IEEE!
7(D)! 200D! 2CD-2'2) )
T/eses(
@7A *avite1 )mish $ Theory In+ercarrier in+erference cancela+ionin 1607 Sys+e# $ doctoral diss$ 0ational %nstitute of +echnology$
*our'ela$ M+ech$ 899E
No+e +ha+ +hesis +i+le is se+ in i+alics and +he uni3ersi+y +ha+ gran+ed +he degree is lis+ed along (i+h loca+ion infor#a+ion
wwwi1ertorg A < (age
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- VV Nc91175d Az1ir2t1 Motorized LensDocument3 pagesVV Nc91175d Az1ir2t1 Motorized Lensfady shahatPas encore d'évaluation
- H3C S5120-SI Series Switches DatasheetDocument4 pagesH3C S5120-SI Series Switches DatasheetjcrlimaPas encore d'évaluation
- 20221438A AI70 Instruction ManualDocument148 pages20221438A AI70 Instruction ManualCristina Franco100% (1)
- Technical Specialist - Job DescriptionDocument2 pagesTechnical Specialist - Job DescriptionPrasad KshirsagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Sd-Wan Deployment Guide: Steelconnect 2.10Document160 pagesSd-Wan Deployment Guide: Steelconnect 2.10Alexia Robles CejaPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A Trojan?: Overt ChannelDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Trojan?: Overt Channelnitin_manjPas encore d'évaluation
- Account Usage and Recharge Statement From 09-Jan-2024 To 11-Jan-2024Document8 pagesAccount Usage and Recharge Statement From 09-Jan-2024 To 11-Jan-2024Jahnavi BathinaPas encore d'évaluation
- 9500 Series Lines Card and Fabric ModulesDocument10 pages9500 Series Lines Card and Fabric Modulesvalliappan alPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 0 R&S®VCS 4G Voice Communication System System DescriptionDocument244 pages10 0 R&S®VCS 4G Voice Communication System System Descriptionanhdq.rndPas encore d'évaluation
- Gomaco GT3400 Smart Cylinder CableDocument2 pagesGomaco GT3400 Smart Cylinder CableJuan AcostaPas encore d'évaluation
- Setting Up A Virtual Switch For A HyperDocument5 pagesSetting Up A Virtual Switch For A Hyperaleksandar71Pas encore d'évaluation
- A#1Document7 pagesA#1ammad ahmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Procedure Examples MTC RRCDocument6 pagesProcedure Examples MTC RRCShefrin MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- 01-09 Basic IPv6 Configuration PDFDocument49 pages01-09 Basic IPv6 Configuration PDFHamoud BourjPas encore d'évaluation
- Database Management System From SanfoundryDocument98 pagesDatabase Management System From SanfoundryPradip Kumar PanditPas encore d'évaluation
- User Manual FMT ServiceDocument28 pagesUser Manual FMT ServicesunitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Golden Parameters - LTEDocument156 pagesGolden Parameters - LTEaamirmosharrafPas encore d'évaluation
- PRO-95 Owner's ManualDocument124 pagesPRO-95 Owner's Manualu7orionPas encore d'évaluation
- Mirici E1t1 2.0 MNDocument108 pagesMirici E1t1 2.0 MNalexf rodPas encore d'évaluation
- RC3000 Antenna Controller With An Idirect 7000 Satellite RouterDocument7 pagesRC3000 Antenna Controller With An Idirect 7000 Satellite Routermaksi1Pas encore d'évaluation
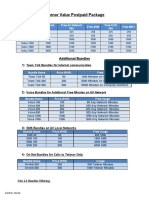
- Telenor Value Postpaid PackageDocument3 pagesTelenor Value Postpaid PackageImeNPas encore d'évaluation
- WaveLogic Encryption - Technical Deck (November 2017)Document14 pagesWaveLogic Encryption - Technical Deck (November 2017)Irfan AshrafPas encore d'évaluation
- EBoK ENIP Troubleshooting Jan2016Document109 pagesEBoK ENIP Troubleshooting Jan2016universoemdesencantoPas encore d'évaluation
- B1/B1z/HB1 Model List: Module Name SpecificationDocument2 pagesB1/B1z/HB1 Model List: Module Name SpecificationAmmar Al-KindyPas encore d'évaluation
- 537 3083 4 PBDocument7 pages537 3083 4 PBSupriyanto SupriyantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Opportunistic Scheduling in Wireless NetworksDocument31 pagesOpportunistic Scheduling in Wireless NetworksjaisudanPas encore d'évaluation
- LTE Mobility StrategyDocument97 pagesLTE Mobility StrategyNoor Alam100% (8)
- Broadband Power LevelsDocument2 pagesBroadband Power LevelsvargasPas encore d'évaluation
- BT2035 TechSpecs 8430Document1 pageBT2035 TechSpecs 8430Mohamed AdelPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment6 PDFDocument14 pagesAssignment6 PDFBilalPas encore d'évaluation