Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology of RHD
Transféré par
shmily_08100 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
231 vues4 pagesRheumatic heart disease is caused by an untreated streptococcal infection which allows antibodies to cross-react with proteins in heart valves, causing inflammation and damage over time. This can lead to valvular stenosis or regurgitation as the valves thicken and do not open/close properly, forcing blood to backflow. Left untreated, the condition can progress to heart failure and death as the heart's ability to pump blood effectively is compromised.
Description originale:
Pathophy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentRheumatic heart disease is caused by an untreated streptococcal infection which allows antibodies to cross-react with proteins in heart valves, causing inflammation and damage over time. This can lead to valvular stenosis or regurgitation as the valves thicken and do not open/close properly, forcing blood to backflow. Left untreated, the condition can progress to heart failure and death as the heart's ability to pump blood effectively is compromised.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
231 vues4 pagesPathophysiology of RHD
Transféré par
shmily_0810Rheumatic heart disease is caused by an untreated streptococcal infection which allows antibodies to cross-react with proteins in heart valves, causing inflammation and damage over time. This can lead to valvular stenosis or regurgitation as the valves thicken and do not open/close properly, forcing blood to backflow. Left untreated, the condition can progress to heart failure and death as the heart's ability to pump blood effectively is compromised.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
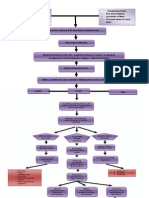
Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart Disease
Precipitating Factors Etiology Predisposing Factors
> Cold and damp weather/climate (Group eta!hemolytic "treptococci# > Genetic "usceptiility
> $mproper use of antiiotics/ > Gender (more women% &'(% are
improper antiiotic therapy "treptococci gains entry through rea)s in affected than men% *'(#
the s)in and mucous memranes > Pre+ious infections caused y
G,-H"
$n+ades the pharyn. $n+ades the tonsils $n+ades the s)in Pathogens gain entry in the loodstream
Edema in the syno+ial /oints
Pharyngitis/"trepthroat 0onsillitis $mpetigo Goes to the heart
Pancarditis
1onocytes phagocyti2e the streptococci
1onocytes present pieces of the Endocardium 1yocardium Pericardium
pathogens to Helper 0 cells
Helper 0 cells acti+ate - cells and induce production of antiodies against the cell wall of streptococci
,ntiodies not only react against 31 proteins4% polymers found on the cell wall of G,-H"% ut also react (cross react# with cardiac cardiac myofier%
syno+ial /oints and other connecti+e tissues
Rheumatic Fe+er
- lymphocytes produces immunogloulins and ,cti+ation of serum complement cascade Chemota.is of phagocytes of the immune response
Rheumatic factors of the $gG and $g1 classes
$nfiltration of acti+ated 0 cells
Deposited in the tissues
Pro+ides a arrier against diffusion of
"yno+ial /oints Heart nutrients to the cartilage
5asodilation of lood +essels Formation of granulation tissues at the Production of e.cess syno+ial fluid
in the syno+ial /oints syno+ial lining (,schoff -odies# "yno+ium cartilages is irritated and thic)ens
Production of en2ymes that cause tissue damage
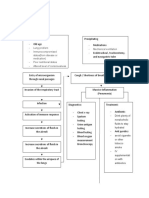
c d
a
a
e
e
a
f g
"yno+ial /oint cells use up all the nutrients 6nderlying one egins to disintegrate 7-C cannot enter as the +al+es of the heart do not actually
recei+e any lood supply of their own
Glucose le+el in the tissues drop E+ident /oint destruction
"treptococci estalishes a hold on the +al+e
"tar+ation and death of cartilage cells
"treptococci attach and enmeshed in the protein% firin% and platelets
5egetate on the margins of the +al+e leaflets
0he leaflets gradually thic)en and shorten $nflamed margins of the +al+e leaflet ecome adherent and fuse along the commissures
and the chordae tendinae fuse and erode
Failure of the mitral +al+e to close completely 5al+ular "tenosis Reduced leaflet motion
Difficulty of lood to lea+e from the left atrium to go tot the left +entricle 8structing the forward flow of lood
Forcing lood to flow ac)ward through the mitral +al+e as the left +entricle contracts -ac) flow of lood into the pulmonary circulation
Pulmonary -P/ Pulmonary congestion
Distention of lood +essels in the pulmonary circulation
7hen pressure in the pulmonary +ein reaches 9:mmHg% the fluids egin to push from the Cardiac output
pulmonary capillary memrane into the interstitial spaces surrounding the al+eoli themsel+es
"ystemic -P
Pulmonary edema Fluids accumulate in the pleural ca+ity Peripheral +asoconstriction occurs to systemic -P
Pleural Effusion
Pressure in the pulmonary capillaries
f
Rheumatoid ,rthritis
g
5al+ular Regurgitation
Heart
1urmurs
Rapid and wea) thready
pulse
8rthopne
a
Paro.ysmal ;octurnal Dyspnea
h i
)
)
Rupture of pulmonary capillaries Fluid coats the al+eolar e.change space
"mall amounts of lood lea) into the al+eoli $nterfering C89<89 e.change
89 saturation of the lood
$schemia HR Di22iness and confusion 7ea)ness Easy fatigaility
myocardial contractility
Cardiac ,rrest
Cardiac output
-lood circulation ceases
Pericardium roughen Fluids accumulate in the pericardial space
pressure in the pericardial space
less lood enters the +entricles
Forces the septum to end to the left +entricle
"tro)e +olume
"hoc)
h
Producti+e cough of lood spec)ed
sputum
i
,ngina
pectoris
5entricular
firillation
Deat
h
d
Friction
ru
/
/
c
Rapid and wea) thready
pulse
)
Pulmonary +al+e stenosis/tricuspid +al+e stenosis
8utput of the right +entricle is less than the lood +olume recei+ed y the right atrium form the +ena ca+a
Congestion of the systermic +enous circulation and cardiac output to the lungs
-ac) pressure to the +ena ca+a
=ess lood goes to the aorta/ systemic circulation
Pressure in the +ena ca+a
Distention of /ugular +eins
)
Peripheral
edema
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsD'EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Management of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)D'EverandManagement of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Pathophysiology and Pharmacotherapy of Myocardial InfarctionD'EverandThe Pathophysiology and Pharmacotherapy of Myocardial InfarctionNabil El-SherifPas encore d'évaluation
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument33 pagesTetralogy of FallotjeenaejyPas encore d'évaluation
- Laryngeal CA MangaserDocument26 pagesLaryngeal CA MangaserBob McRoniePas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome: Contemporary Insights On The Clinicopathological SpectrumDocument16 pagesMultiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome: Contemporary Insights On The Clinicopathological SpectrumNurul Kamilah SadliPas encore d'évaluation
- PneumoniaDocument8 pagesPneumoniaNader Smadi100% (2)
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyD'EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Metabolic Alkalosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandMetabolic Alkalosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Nursing Knowledge and SkillsDocument10 pagesBasic Nursing Knowledge and SkillsFatima CorpuzPas encore d'évaluation
- Hemorrhagic Cerebro Vascular DiseaseDocument37 pagesHemorrhagic Cerebro Vascular Diseasejbvaldez100% (1)
- A Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsD'EverandA Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Rheumatic FeverDocument50 pagesAcute Rheumatic Feversunaryo lPas encore d'évaluation
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideD'EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- DR Anuj Raj BijukchheDocument95 pagesDR Anuj Raj BijukchheMUHAMMAD JAWAD HASSANPas encore d'évaluation
- PTBDocument71 pagesPTBAnonymous 9fLDcZrPas encore d'évaluation
- Ebstein Anomaly, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandEbstein Anomaly, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- How Low Can You Endure The Pain, Mr. Bond?Document70 pagesHow Low Can You Endure The Pain, Mr. Bond?Venny VeronicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Overdose and ManagementDocument9 pagesDrug Overdose and ManagementKoRnflakes100% (1)
- NCM103 12th Endoc IIDocument9 pagesNCM103 12th Endoc IIKamx MohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study (Bronchiectasis Chest)Document1 pageCase Study (Bronchiectasis Chest)Sarra Mood Iman100% (1)
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument45 pagesCongenital Heart DiseaseBrandedlovers OnlineshopPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Assessment (Ippa)Document14 pagesPhysical Assessment (Ippa)Barbara HsuPas encore d'évaluation
- EENT Disorders StudentsDocument26 pagesEENT Disorders StudentsPye Antwan DelvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cavite State University: I. ObjectivesDocument7 pagesCavite State University: I. ObjectivesChamy CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- ASTHMADocument51 pagesASTHMAMOSES M CHILALAPas encore d'évaluation
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocument43 pagesValvular Heart Diseaseurmila prajapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology RHDDocument1 pagePathophysiology RHDRellette Shane DangdangPas encore d'évaluation
- Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)Document7 pagesIdiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)Rizqka PertiwiPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Ventricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandVentricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory Alkalosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandRespiratory Alkalosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Hepatic Encephalopathy: Causes, Tests, and Treatment OptionsD'EverandHepatic Encephalopathy: Causes, Tests, and Treatment OptionsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- Congestive Heart Failure OverviewDocument12 pagesCongestive Heart Failure OverviewkazellePas encore d'évaluation
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideD'EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- Case Presentation RamosDocument35 pagesCase Presentation RamosJose Bryan NacillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case StudyNursing AssessmentDocument7 pagesCase StudyNursing AssessmentArindomPas encore d'évaluation
- Cellular AberrationDocument71 pagesCellular AberrationMichael CoronadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Swollen Kidney, (Hydronephrosis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandSwollen Kidney, (Hydronephrosis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Health Education PlanDocument1 pageHealth Education PlanDahnel MagumparaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Battle Against Covid-19 Filipino American Healthcare Workers on the Frontlines of the Pandemic ResponseD'EverandThe Battle Against Covid-19 Filipino American Healthcare Workers on the Frontlines of the Pandemic ResponsePas encore d'évaluation
- Fetal Circulation QuizDocument2 pagesFetal Circulation QuizJubaida JemiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sirs, Shock, Sepsis, ModsDocument8 pagesSirs, Shock, Sepsis, ModsthubtendrolmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandDisseminated Intravascular Coagulation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal in Medical WardDocument4 pagesJournal in Medical WardApol PenPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebrovascular Accident: TypesDocument10 pagesCerebrovascular Accident: TypesJulia SalvioPas encore d'évaluation
- Myocarditis, (Inflamed Heart Muscles) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandMyocarditis, (Inflamed Heart Muscles) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Atelectasis, (Lung Collapse) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related DiseasesD'EverandAtelectasis, (Lung Collapse) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related DiseasesPas encore d'évaluation
- TracheostomyDocument4 pagesTracheostomyJyothiPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Scenario InfectiousDocument2 pagesCase Scenario InfectiousKasandra Dawn Moquia BerisoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology PneumoniaChiro Rouy Malaluan100% (2)
- Thyroid Case StudyDocument68 pagesThyroid Case Studyshadydogv5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hiv Case StudyDocument2 pagesHiv Case Studyapi-485814878Pas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical MethodsDocument13 pagesClinical MethodsHashimIdreesPas encore d'évaluation
- A Simple Guide to Circulatory Shock, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsD'EverandA Simple Guide to Circulatory Shock, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Manila Doctors Hospital Top Level Organizational Chart (Board of Directors To Division)Document1 pageManila Doctors Hospital Top Level Organizational Chart (Board of Directors To Division)shmily_08100% (1)
- Rosiglitazone 4mg OD: Furosemide 20mg/IV NowDocument1 pageRosiglitazone 4mg OD: Furosemide 20mg/IV Nowshmily_0810Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plans (NCPS)Document10 pagesNursing Care Plans (NCPS)Melissa SalayogPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Assessment: Area Assessed Technique Used Normal Findings Actual Findings AnalysisDocument5 pagesPhysical Assessment: Area Assessed Technique Used Normal Findings Actual Findings Analysisshmily_0810Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Next Sequel: Scarring My HeartDocument56 pagesThe Next Sequel: Scarring My Heartshmily_0810Pas encore d'évaluation
- Patho - Acute Myocardial Infarction&Bronchial AsthmaDocument7 pagesPatho - Acute Myocardial Infarction&Bronchial Asthmashmily_0810Pas encore d'évaluation
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument20 pagesMyocardial Infarctionshmily_0810100% (2)
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPshmily_0810Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument8 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationshmily_0810Pas encore d'évaluation
- CVA PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesCVA Pathophysiologyshmily_0810Pas encore d'évaluation
- Soujanya Reddy (New)Document6 pagesSoujanya Reddy (New)durgaPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Gearbox ZF 4HP 20Document40 pagesAutomatic Gearbox ZF 4HP 20Damien Jorgensen100% (3)
- 1Document3 pages1Stook01701Pas encore d'évaluation
- List of Some Common Surgical TermsDocument5 pagesList of Some Common Surgical TermsShakil MahmodPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructions For Preparing Manuscript For Ulunnuha (2019 Template Version) Title (English and Arabic Version)Document4 pagesInstructions For Preparing Manuscript For Ulunnuha (2019 Template Version) Title (English and Arabic Version)Lailatur RahmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Item Analysis and Test BankingDocument23 pagesItem Analysis and Test BankingElenita-lani Aguinaldo PastorPas encore d'évaluation
- HSCC SRH 0705 PDFDocument1 pageHSCC SRH 0705 PDFBhawna KapoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Babe Ruth Saves BaseballDocument49 pagesBabe Ruth Saves BaseballYijun PengPas encore d'évaluation
- Implications of A Distributed Environment Part 2Document38 pagesImplications of A Distributed Environment Part 2Joel wakhunguPas encore d'évaluation
- Ajmera - Treon - FF - R4 - 13-11-17 FinalDocument45 pagesAjmera - Treon - FF - R4 - 13-11-17 FinalNikita KadamPas encore d'évaluation
- Convection Transfer EquationsDocument9 pagesConvection Transfer EquationsA.N.M. Mominul Islam MukutPas encore d'évaluation
- NABARD R&D Seminar FormatDocument7 pagesNABARD R&D Seminar FormatAnupam G. RatheePas encore d'évaluation
- Stentofon Pulse: IP Based Intercom SystemDocument22 pagesStentofon Pulse: IP Based Intercom SystemCraigPas encore d'évaluation
- Frellwits Swedish Hosts FileDocument10 pagesFrellwits Swedish Hosts FileAnonymous DsGzm0hQf5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Draft PDFDocument166 pagesDraft PDFashwaq000111Pas encore d'évaluation
- Formula:: High Low Method (High - Low) Break-Even PointDocument24 pagesFormula:: High Low Method (High - Low) Break-Even PointRedgie Mark UrsalPas encore d'évaluation
- Draft JV Agreement (La Mesa Gardens Condominiums - Amparo Property)Document13 pagesDraft JV Agreement (La Mesa Gardens Condominiums - Amparo Property)Patrick PenachosPas encore d'évaluation
- Dec JanDocument6 pagesDec Janmadhujayan100% (1)
- Odisha State Museum-1Document26 pagesOdisha State Museum-1ajitkpatnaikPas encore d'évaluation
- Civ Beyond Earth HotkeysDocument1 pageCiv Beyond Earth HotkeysExirtisPas encore d'évaluation
- EAC Inquiry SDCDocument9 pagesEAC Inquiry SDCThe Sustainable Development Commission (UK, 2000-2011)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 - Basic ProbabilityDocument37 pagesChapter 4 - Basic Probabilitynadya shafirahPas encore d'évaluation
- RMC 102-2017 HighlightsDocument3 pagesRMC 102-2017 HighlightsmmeeeowwPas encore d'évaluation
- ResumeDocument3 pagesResumeapi-280300136Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Kicker TranscriptionDocument4 pagesThe Kicker TranscriptionmilesPas encore d'évaluation
- Feasibility Study For Cowboy Cricket Farms Final Report: Prepared For Prospera Business Network Bozeman, MTDocument42 pagesFeasibility Study For Cowboy Cricket Farms Final Report: Prepared For Prospera Business Network Bozeman, MTMyself IrenePas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulic Mining ExcavatorDocument8 pagesHydraulic Mining Excavatorasditia_07100% (1)
- ENT 300 Individual Assessment-Personal Entrepreneurial CompetenciesDocument8 pagesENT 300 Individual Assessment-Personal Entrepreneurial CompetenciesAbu Ammar Al-hakimPas encore d'évaluation
- FinalDocument18 pagesFinalAkash LadPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines For Prescription Drug Marketing in India-OPPIDocument23 pagesGuidelines For Prescription Drug Marketing in India-OPPINeelesh Bhandari100% (2)