Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
FM 1
Transféré par
Selva KumarDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
FM 1
Transféré par
Selva KumarDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Foundations of Fluid Mechanics Tutorial 1- on Viscosity, Surface Tension
Q (1*) The velocity distribution for laminar flow between parallel plates is given by: 2
max
2 1 = h y
U U where h is the distance separating the plates and the origin is placed midway between the
plates. Consider flow of water at 15C with maximum speed of 0.05 m/s and h=5 mm. Calculate the
force on a 0.3 m2 section of the lower plate and give its direction. From Tables, = 1.14x10 -3 Ns/
m2
Q (2) A female freestyle ice skater, weighing 112 lbf, glides on one skate at speed V = 20.5 ft/s. Her
weight is supported by a thin film of liquid water melted from the ice by the pressure of the skate
blade. Assume the blade is L = 11.5in. long and w = 0.125in. wide, and that the water film is h =
0.0000575 in. thick. Estimate the deceleration of the skater that results from viscous shear in the
water film, if end effects are neglected. From Tables, = 3.66x10 -5 lbf s/ ft2
Q (3) A concentric cylinder viscometer may be formed by rotating the inner member of a pair of
closely fitting cylinders. For small clearances, a linear velocity profile may be assumed in the liquid
filling the annular clearance gap. A viscometer has an inner cylinder of 75 mm diameter and 150 mm
height, with a clearance gap width of 0.02 mm. A torque of 0.021 N.m is required to turn the inner
cylinder at 100 rpm. Determine the viscosity of the liquid in the clearance gap of the viscometer.
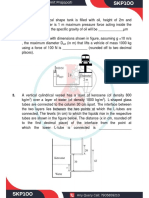
Q (4*) A conical pointed shaft turns in a conical bearing (as shown in FIG 1). The gap between shaft
and bearing is filled with heavy oil having the viscosity of SAE 30 at 30C. Obtain an algebraic
expression for the shear stress that acts on the surface of the conical shaft. Calculate the viscous
torque (T) that acts on the shaft. From Tables, = 0.2Ns/ m2 (Hint : To start with, S.T.
2 cos tan3 4 a H T = ).
FIG 1
Q (5*) A child produces soap bubbles using a tube of diameter 1 mm. What is the maximum over
pressure that he should exert to get good bubbles ? From Table, Surface tension = 2x10-2 N/m
Q(6*) Blood sample is drawn into a fine glass capillary of diameter 1mm, by touching one end of it to
a freshly pictured fingertip. If the surface tension of blood is approximately = 5x10-2 N/m and its
contact angle with glass is 0 and its density 1056 kg/m3, estimate the volume of blood sample
drawn.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Ayush ShrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Vandit GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- IIT Dhanbad Fluid Mechanics TutorialDocument3 pagesIIT Dhanbad Fluid Mechanics TutorialBishal DasPas encore d'évaluation
- AssignDocument2 pagesAssignlaudaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 1 Chapter 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1 Chapter 1Marzs MarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter-1: Fundamental Concepts Set-B: Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesChapter-1: Fundamental Concepts Set-B: Page 1 of 2SWAGATAM BAZPas encore d'évaluation
- Agustin - Mark Joshua - Ce142p-2 - E02 - CW3Document20 pagesAgustin - Mark Joshua - Ce142p-2 - E02 - CW3mark agustinPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 1-AFM-FLUID MECHANICSDocument2 pagesAssignment 1-AFM-FLUID MECHANICSEcneicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet#1 Fluid ProertiesDocument3 pagesSheet#1 Fluid ProertiesmoazsrourdPas encore d'évaluation
- FMDocument4 pagesFMvishalPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Chapter 1 2018Document3 pagesTutorial Chapter 1 2018Ain Syahira0% (1)
- Fluid Properties Viscosity and Surface Tension ProblemsDocument4 pagesFluid Properties Viscosity and Surface Tension ProblemsBrijesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Tutorial Fluid Properties Sept19Document4 pages1 Tutorial Fluid Properties Sept19hairinnisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Çalışma Soruları - 1Document6 pagesÇalışma Soruları - 1emreasker22Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet 1-Fluid DefinitionDocument2 pagesSheet 1-Fluid DefinitionUNKNOWNPas encore d'évaluation
- Crowe - Cap 7Document9 pagesCrowe - Cap 7panzerkirbyPas encore d'évaluation
- Che 4009 Transport Phenomena Assignment # 1Document7 pagesChe 4009 Transport Phenomena Assignment # 1Bao-Ngoc HoangPas encore d'évaluation
- Ce 371 Homework 1Document3 pagesCe 371 Homework 1andreinarodPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pagesFluid MechanicsPraven IndranPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics Assignment Force CalculationsDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics Assignment Force CalculationsSanju HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Sheet For Oct - Students 2017Document7 pagesFluid Sheet For Oct - Students 2017S.A. BeskalesPas encore d'évaluation
- FMDocument46 pagesFMகருப்பசாமிPas encore d'évaluation
- Ce 371 Home Exercises-1 1) The Velocity Distribution For The Flow of ADocument3 pagesCe 371 Home Exercises-1 1) The Velocity Distribution For The Flow of AEnes YavuzPas encore d'évaluation
- 2005 Exam3Document2 pages2005 Exam3nageshPas encore d'évaluation
- FM 16 Mark - 2019Document16 pagesFM 16 Mark - 2019Praveen Sakthivel. C6Pas encore d'évaluation
- FM Practice Questions 1682618846111Document38 pagesFM Practice Questions 1682618846111Hasan javedPas encore d'évaluation
- Aryabhatt Academy Fluid Numericals PhysicsDocument2 pagesAryabhatt Academy Fluid Numericals PhysicsSrajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of Momentum EquationDocument88 pagesApplication of Momentum EquationMahmud Rahman BizoyPas encore d'évaluation
- HW2 SolutionDocument6 pagesHW2 SolutionHamka HidayahPas encore d'évaluation
- FMDocument2 pagesFMepnaseefPas encore d'évaluation
- Problems: P (5 - KX) eDocument61 pagesProblems: P (5 - KX) eMuhammad AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Tarea 1Document13 pagesTarea 1Mario GonzalezPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework of Chapter (1) (Solution)Document7 pagesHomework of Chapter (1) (Solution)Dark AcePas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics Assignment-5 (Momentum Conservation) : Aditya BandopadhyayDocument9 pagesFluid Mechanics Assignment-5 (Momentum Conservation) : Aditya BandopadhyayGunda Venkata SaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1Essam Radwan BerikaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mech ProblemsDocument2 pagesFluid Mech ProblemsMarky SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 1 2014Document7 pagesTutorial 1 2014sotdePas encore d'évaluation
- B48BB Tutorial Questions v3Document16 pagesB48BB Tutorial Questions v3aidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundmental Concepts - ProblemsDocument2 pagesFundmental Concepts - Problemsadharb21Pas encore d'évaluation
- HW 1Document3 pagesHW 1Madison CallowayPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics Properties and EquationsDocument6 pagesFluid Mechanics Properties and EquationscharlesgmartinPas encore d'évaluation
- Sathyabama University: Register NumberDocument4 pagesSathyabama University: Register NumberRAVIPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment ME401 For GATE PreparationDocument26 pagesAssignment ME401 For GATE Preparationhameem mohdPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Sheet1Document1 pageTutorial Sheet1Swati SachanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet No. 2-Vicous FlowDocument2 pagesSheet No. 2-Vicous Flowمحمد خريبطPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Mass LinMomentumDocument5 pagesAssignment Mass LinMomentumSusheel SrinivasPas encore d'évaluation
- Aalim Muhammed Salegh College of Engineering Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument6 pagesAalim Muhammed Salegh College of Engineering Department of Mechanical EngineeringMaran ElangovanPas encore d'évaluation
- Viscous Incompressible Flow Problem SheetDocument2 pagesViscous Incompressible Flow Problem SheetSouparna Banerjee50% (2)
- Module 1 Numericals QuestionsDocument3 pagesModule 1 Numericals QuestionsTOP DHAMAKAPas encore d'évaluation
- HW2 SolutionDocument6 pagesHW2 SolutionHamzaJehadPas encore d'évaluation
- Prop Ri Été Fluid EsDocument1 pageProp Ri Été Fluid EsDebora PandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Bank MechDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank MechSandeep MorePas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics: Tutorial: 1 Date: 24/06/2015Document1 pageFluid Mechanics: Tutorial: 1 Date: 24/06/2015Er M HnPas encore d'évaluation
- Me301 Heat & Flow 3 Tutorial Questions (7) : PistonDocument1 pageMe301 Heat & Flow 3 Tutorial Questions (7) : PistonJeswin MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics Tute Sheet No.1Document2 pagesFluid Mechanics Tute Sheet No.1Tanuj YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment I SKPU1123 1213 2Document4 pagesAssignment I SKPU1123 1213 2Rajab AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Density, Elasticity, Viscosity, Surface Tension, Fluid Pressure MeasurementDocument5 pagesDensity, Elasticity, Viscosity, Surface Tension, Fluid Pressure Measurementanon_182348362Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Sheet 1Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 1oginoweijPas encore d'évaluation
- Enhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsD'EverandEnhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- CamScanner Scans PDFs QuicklyDocument4 pagesCamScanner Scans PDFs QuicklySelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Shot Peening?: Improving Resistance To FatigueDocument1 pageShot Peening?: Improving Resistance To FatigueSelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Spring Pin DesignDocument16 pagesSpring Pin DesignSelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Normalization Is An Annealing Process Applied To Ferrous Alloys To Give The Material ADocument1 pageNormalization Is An Annealing Process Applied To Ferrous Alloys To Give The Material ASelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Shot Peening?: Improving Resistance To FatigueDocument1 pageWhat Is Shot Peening?: Improving Resistance To FatigueSelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics of ShotpeenDocument3 pagesMechanics of ShotpeenSelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Trochoid: Roulette Circle Curve CycloidDocument1 pageTrochoid: Roulette Circle Curve CycloidSelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Shotpeen ShotDocument1 pageShotpeen ShotSelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Cut Wire Shot Media for Shot Peening and FinishingDocument1 pageCut Wire Shot Media for Shot Peening and FinishingSelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Normal I SingDocument1 pageNormal I SingSelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Normalising MathDocument1 pageNormalising MathSelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Peening - 4 Shor CoverDocument1 pagePeening - 4 Shor CoverSelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Database NormalizationDocument1 pageDatabase NormalizationSelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Shotpeen CurveDocument1 pageShotpeen CurveSelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Process and Equipment: Laser Peening Cut WireDocument1 pageProcess and Equipment: Laser Peening Cut WireSelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- How Shot Peening Improves Fatigue Life and Stress Corrosion Resistance in Metal SurfacesDocument1 pageHow Shot Peening Improves Fatigue Life and Stress Corrosion Resistance in Metal SurfacesSelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Surface HardeningDocument1 pageWhat Is Surface HardeningSelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Centre DistanceDocument1 pageCentre DistanceSelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- PJT Manment - 8Document1 pagePJT Manment - 8Selva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- PJT Manment - 6Document2 pagesPJT Manment - 6Selva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Base Cylinder: The Base Cylinder Corresponds To The, and Is The From Which Surfaces Are DevelopedDocument1 pageBase Cylinder: The Base Cylinder Corresponds To The, and Is The From Which Surfaces Are DevelopedSelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- PJT Manment - 4Document2 pagesPJT Manment - 4Selva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- PJT Manment - 3Document10 pagesPJT Manment - 3Selva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Shot PeenDocument1 pageShot PeenSelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- PJT Manment - 5Document2 pagesPJT Manment - 5Selva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- PJT Manment - 1Document2 pagesPJT Manment - 1Selva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Bull GearDocument1 pageBull GearSelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Base Diameter: The Base Diameter of An Is The Diameter of TheDocument1 pageBase Diameter: The Base Diameter of An Is The Diameter of TheSelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- PJT Manment - 2docxDocument5 pagesPJT Manment - 2docxSelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Case Hardening of SteelDocument1 pageWhat Is Case Hardening of SteelSelva KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Cyrstal GrowthDocument7 pagesCyrstal GrowthkarticPas encore d'évaluation
- CHM 1025c Final Exam Practice WCDocument5 pagesCHM 1025c Final Exam Practice WCMiguel SuarezPas encore d'évaluation
- Brocure DuPont ELVALOYDocument3 pagesBrocure DuPont ELVALOYdonni canraPas encore d'évaluation
- Ulman Part 1Document1 000 pagesUlman Part 1Yana RahmadaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Rti Process Manual IntDocument183 pagesRti Process Manual IntdlebreromPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 PackedColumnDesignDocument68 pages10 PackedColumnDesignMy best Of bestPas encore d'évaluation
- DVC 99wierDocument2 pagesDVC 99wierMohamed ElmakkyPas encore d'évaluation
- TRUEDocument50 pagesTRUECLARISSA TAGUBAPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6Document13 pagesChapter 6aregawi weleabezgiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sapal Rtu PDFDocument2 pagesSapal Rtu PDFJay ar TenorioPas encore d'évaluation
- BS en 10149-1 1996Document16 pagesBS en 10149-1 1996ibson045001256100% (1)
- 1-Pump Selection Guide by Goulds - Rev - PSG PDFDocument24 pages1-Pump Selection Guide by Goulds - Rev - PSG PDFMelvin MagbanuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bambu Lab A1 3DDocument6 pagesBambu Lab A1 3DAngel Jacobo Figueroa ArriolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Duplex Stainless Steel 2304 Spec Sheet for Weight Savings & Corrosion ResistanceDocument2 pagesDuplex Stainless Steel 2304 Spec Sheet for Weight Savings & Corrosion ResistanceDeepak TdPas encore d'évaluation
- Nickyta Tanryan - 2106729915 - UtsgamtekDocument2 pagesNickyta Tanryan - 2106729915 - UtsgamtekNickyta TanryanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Use of Silicone Materials in Close Proximity PDFDocument4 pagesThe Use of Silicone Materials in Close Proximity PDFLBPas encore d'évaluation
- Saep 1145Document20 pagesSaep 1145Amit shah100% (1)
- Mandatory Appendix 41: EIH Support Plate DesignDocument5 pagesMandatory Appendix 41: EIH Support Plate DesignHanafi BasriPas encore d'évaluation
- Modes of Shear Failure of SoilDocument3 pagesModes of Shear Failure of SoilAnkush PendhariPas encore d'évaluation
- PN JunctionDocument36 pagesPN JunctionTiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Cópia de Column-Beam Bolted Splice Calculation - ASD AISC 9th - 22-Ago-2017Document19 pagesCópia de Column-Beam Bolted Splice Calculation - ASD AISC 9th - 22-Ago-2017cludioPas encore d'évaluation
- Davies Epoxy Enamel Coating GuideDocument2 pagesDavies Epoxy Enamel Coating GuideStanley Saavedra100% (1)
- AM Breeze Block DesignDocument92 pagesAM Breeze Block DesignMattPas encore d'évaluation
- Marco Material Datasheet Z1216Document1 pageMarco Material Datasheet Z1216radziPas encore d'évaluation
- PJK Project 2011 Form 2 (Word 2010)Document30 pagesPJK Project 2011 Form 2 (Word 2010)Charmaine Yeo Shern LiPas encore d'évaluation
- Concreto Pretensado-NAWY - Cap 11 PDFDocument82 pagesConcreto Pretensado-NAWY - Cap 11 PDFCarlos Alberto Pacheco SierraPas encore d'évaluation
- Packaging MachinesDocument16 pagesPackaging MachinesDhruba JyotiPas encore d'évaluation
- Infrared Plastic Solar CellDocument19 pagesInfrared Plastic Solar CellAjay Mv100% (2)
- Shell Thickness CalculationsDocument2 pagesShell Thickness CalculationsskocogluPas encore d'évaluation
- Wire Reinforcement InstituteDocument6 pagesWire Reinforcement InstituteVu NguyenPas encore d'évaluation