Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
INTUBASI
Transféré par
Aditya Rangga FandiartaCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
INTUBASI
Transféré par
Aditya Rangga FandiartaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
INTUBASI
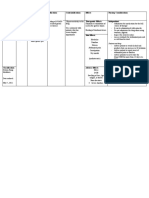
PREMEDIKASI SEDASI
rug Name
Generic
(Trade)
Adult Dose
Onset
of
Action
Duration
of Action
Advantages Cautions
Etomidate
(Amidate)
0.3 mg/kg IV
push (normal
adult dose
about 20 mg)
0.5-1
min
3-5 min Does not alter hemodynamics or
intracranial pressure (ICP); no
histamine release; generally does
not induce apnea; useful for patients
with multiple trauma and
hypotension (does not alter systemic
BP)
Commonly causes myoclonus;
pain upon injection; adrenal suppression (typically
no clinical significance with one bolus)
[21]
;
does not suppress sympathetic response to
laryngoscopy; nausea;
vomiting;
lowers seizure threshold;
does not provide analgesia
Ketamine
(Ketalar)
1-2 mg/kg slow
IV push (not to
exceed 0.5
mg/kg/min)
0.5-1
min
5-10 min Bronchodilatory effects
advantageous if hypotension or lung
disease present (leaves airway and
other protective reflexes intact);
rarely used in adults; may possess
neuroprotective affects and increase
CPP
May increase ICP (though lacking evidence
showing clinical significance), hallucinations;
increases sympathetic tone, potent cerebral
vasodilation, cardiovascular stimulation (do not
use with ischemic heart disease); emergence
delirium common, but more of a concern when
used for conscious sedation with painful
procedures (approximately 12%) in adults < 65 y
Propofol
(Diprivan)
2-3 mg/kg IV
push
Decrease dose
if patient
unstable
< 1 min 3-10 min Provides rapid onset and brief
duration; cerebroprotective
(decreases ICP); amnestic
properties; extremely potent
Causes cardiovascular depression and
hypotension; respiratory depression is dose-
dependent
PRETREATMENT
Drug Name
Generic
(Trade)
Adult Dose
Onset of
Action
Duration
of Action
Advantages Cautions
Fentanyl 1-2 mcg/kg slow IV push
(over 1-2 min)
Immediate 0.5-1 h Primary pretreatment drug to provide sedation
and analgesia; decreases hypertensive
response to intubation though at this time, no
conclusive evidence supports the use of
opioids in routine RSI
[13]
Hypotension; chest
wall rigidity at high
doses (ie, >15
mcg/kg)
Lidocaine 1.5 mg/kg IV push 1-2 min 10-20 min Useful in patients with asthma/COPD to Hypotension
(Xylocaine) decrease hypertensive response
Atropine 0.02 mg/kg (usually about
0.4 mg) IV push
Typically administered for
pediatric patients 1 y
2-4 min Up to 4 h Antisialagogue Tachycardia
Vecuronium
(Norcuron)
Defasciculating dose: 0.01
mg/kg IV push (typically
about 1 mg, or 10% of
intubation dose)
... ... Decreases fasciculation and potassium
release from cells; particularly useful if intend
to use succinylcholine
Avoid higher doses
that may produce
paralytic effect
Rocuronium
(Zemuron)
Defasciculating dose: 0.06
mg/kg IV push (typically
about 10% of intubation
dose)
... ... Decreases fasciculation and potassium
release from cells; particularly useful if intend
to use succinylcholine
Avoid higher doses
that may produce
paralytic effect
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Preview of "MyDietAnalysis - Report"Document2 pagesPreview of "MyDietAnalysis - Report"LeovergeldediosPas encore d'évaluation
- The Aksys Personal Hemodialysis SystemDocument3 pagesThe Aksys Personal Hemodialysis SystemNatik Bi IllahPas encore d'évaluation
- Determining The Cause of Pulmonary Nodules in HIV-Positive PatientsDocument3 pagesDetermining The Cause of Pulmonary Nodules in HIV-Positive PatientsAditya Rangga FandiartaPas encore d'évaluation
- Current Issues in Health: Henni Djuhaeni Public Health DepartmentDocument15 pagesCurrent Issues in Health: Henni Djuhaeni Public Health DepartmentAditya Rangga FandiartaPas encore d'évaluation
- Current Treatment of Dyspepsia: DR Wita Kartika Nurani SP - PDDocument15 pagesCurrent Treatment of Dyspepsia: DR Wita Kartika Nurani SP - PDAditya Rangga FandiartaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sickle Cell Disease: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument13 pagesSickle Cell Disease: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleAditya Rangga Fandiarta100% (1)
- Checklist On Intramuscular InjectionDocument2 pagesChecklist On Intramuscular InjectionClarice Jamille RazonPas encore d'évaluation
- Aic 28 4 2000 363Document12 pagesAic 28 4 2000 363danielguerinPas encore d'évaluation
- ChemotherapyDocument1 pageChemotherapyGerardLum100% (2)
- QB For Mock Test JurisprudenceDocument4 pagesQB For Mock Test JurisprudencePurvak MahajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs of AbuseDocument2 pagesDrugs of AbuseDr. RemedyPas encore d'évaluation
- Licorice Root On Burn HealingDocument19 pagesLicorice Root On Burn HealingAbang OzielPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study:: Bipolar I DisorderDocument4 pagesDrug Study:: Bipolar I DisorderSolsona Natl HS MaanantengPas encore d'évaluation
- GriseofulvinDocument1 pageGriseofulvinRhadezahara PatrisaPas encore d'évaluation
- What Are Drugs!!Document6 pagesWhat Are Drugs!!CS AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Utilization ReviewDocument7 pagesDrug Utilization ReviewFaizaNadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Ipt For Social Anxiety DisorderDocument2 pagesIpt For Social Anxiety DisorderPramita BanikPas encore d'évaluation
- B Pharm - 2019 - 3 - Pharmacology PDFDocument1 pageB Pharm - 2019 - 3 - Pharmacology PDFTripti PadaliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary Barang Masuk Dan Keluar: Nama Item Kategori Item Kode ItemDocument96 pagesSummary Barang Masuk Dan Keluar: Nama Item Kategori Item Kode ItemTitha RahmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Health Teaching of Patients With Tuberculosis TreatmentDocument34 pagesHealth Teaching of Patients With Tuberculosis TreatmentFarhanaRahimPas encore d'évaluation
- AHFS CategoriesDocument12 pagesAHFS CategoriesEidetikosPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 13: Antiparkinsonian DrugsDocument5 pagesChapter 13: Antiparkinsonian DrugsKT100% (1)
- Myofascial Release 2020Document2 pagesMyofascial Release 2020UmaSankar mohanPas encore d'évaluation
- Abediterol (LAS100977), A Novel Long-Acting B - Agonist: Efficacy, Safety and Tolerability in Persistent AsthmaDocument6 pagesAbediterol (LAS100977), A Novel Long-Acting B - Agonist: Efficacy, Safety and Tolerability in Persistent AsthmaFi NoPas encore d'évaluation
- NURSINGDocument4 pagesNURSINGJessicha DAPas encore d'évaluation
- Cology Text Book - CompressedDocument168 pagesCology Text Book - CompressedChillones GamingPas encore d'évaluation
- The Effects of Ice MassageDocument8 pagesThe Effects of Ice MassageCristopher Castro RdPas encore d'évaluation
- EsomeprazoleDocument2 pagesEsomeprazolenikki shein bullongPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Comment Dosage: Table 44-3. Pediatric Drug DosagesDocument7 pagesDrug Comment Dosage: Table 44-3. Pediatric Drug Dosageschocolat_stripesPas encore d'évaluation
- Use of Herbal Bioenhancers To Increase The Bioavailability of DrugsDocument13 pagesUse of Herbal Bioenhancers To Increase The Bioavailability of DrugsRatan Deep ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Midwifery Pharmacology-9Document1 pageMidwifery Pharmacology-9georgeloto12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Brochure Rev04Document2 pagesBrochure Rev04nickj702Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bioavailability and BioequivalenceDocument28 pagesBioavailability and Bioequivalencekulbhushan singhPas encore d'évaluation
- DoxycyclineDocument2 pagesDoxycyclinesleep whatPas encore d'évaluation