Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
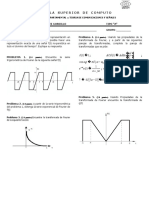
04 Sistema No Homogeneo
Transféré par
Paul RizzoCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
04 Sistema No Homogeneo
Transféré par
Paul RizzoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SISTEMA DE ECUACIONES ORDINARIAS NO HOMOGENEAS
X A.X gt
MTODO DE COEFICIENTES INDETERMINADOS
In[53]:= A
2 1
1 2
;
g
2
t
3 t
;
In[55]:= E2
1 0
0 1
;
P DetA r E2
Out[56]= 3 4 r r
2
In[57]:= SolveP 0, r
Out[57]= r 3, r 1
In[58]:= r 3;
A r E2 MatrixForm
Out[59]//MatrixForm=
1 1
1 1
1
a
b
a
a
a
1
1
In[60]:= r 1;
A r E2 MatrixForm
Out[61]//MatrixForm=
1 1
1 1
1
a
b
a
a
a
1
1
In[72]:= X c1
1
1
3 t
c2
1
1
t
;
Simplify
t
X A.X MatrixForm
Out[73]//MatrixForm=
0
0
LUEGO DE DETERMINAR LA SOLUCION DEL SISTEMA HOMOGENEO
AHORA DETERMINAREMOS LA SOLUCIN PARTICULAR :
g
2
t
3 t
2
0
t
0
3
t
Por el principio de superposicin calculamos la solucin parcial solo para la parte g1
2
0
t
y luego g2
0
3
t
OBSERVAMOS. g1
2
0
t
y es parte de una de las soluciones
por tanto buscaremos la solucin as : a t
t
b
t
In[74]:= X
a
b
t
t
c
d
t
;
Simplify
t
X A.X MatrixForm
Out[75]//MatrixForm=
t
a c d a t b t
t
b c d a t b t
Para que sea solucin particular los coeficientes tienen que ser igual g1
2
0
t
: a c d 2;
a b 0; b c d 0; a b 0; el sistema se expresa en la forma de Gauss en el orden a b c d
In[76]:= m
1 0 1 1 2
1 1 0 0 0
0 1 1 1 0
1 1 0 0 0
;
RowReducem MatrixForm
Out[77]//MatrixForm=
1 0 0 0 1
0 1 0 0 1
0 0 1 1 1
0 0 0 0 0
entonces a 1; b 1; c 1 d; d es una variable libre por tanto la solucin particular
X
1
1
t
t
1 d
d
t
1
1
t
t
1
0
t
d
1
1
t
;
Obviamente la parte d
1
1
t
es la solucion
del sistema homogeneo por tanto la solucin particular es
In[78]:= X
1
1
t
t
1
0
t
;
Simplify
t
X A.X MatrixForm
Out[79]//MatrixForm=
2
t
0
Este resultado verifica que este es una la solucin particular buscada
___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ __
Ahora buscamos la otra solucin particular para g2
0
3
t
La buscamos de la forma X
a
b
t
c
d
;
2 04_Sistema_no_homogeneo.nb
In[80]:= X
a
b
t
c
d
;
Simplify
t
X A.X MatrixForm
Out[81]//MatrixForm=
a 2 c d 2 a t b t
b c 2 d a t 2 b t
Este resultado debe ser igual a :
0
3
t
0
3 t
Por tanto tenemos un sistema :
a 2 c d 0;
2 a b 0;
b c 2 d 0;
a 2 b 3;
Expresamos este sistema en la forma de Gauss, tenemos :
In[82]:= m
1 0 2 1 0
2 1 0 0 0
0 1 1 2 0
1 2 0 0 3
;
RowReducem MatrixForm
Out[83]//MatrixForm=
1 0 0 0 1
0 1 0 0 2
0 0 1 0
4
3
0 0 0 1
5
3
De este sistema tenemos a 1; b 2; c
4
3
; d
5
3
;
por tanto la solucion particular es X
1
2
t
4
3
5
3
1
2
t
1
3
4
5
;
Verificamos que este resultado satisface la ecuacin
In[88]:= X
1
2
t
1
3
4
5
;
Simplify
t
X A.X MatrixForm
Out[89]//MatrixForm=
0
3 t
Ahora la solucion General y su verificacin
In[90]:= X c1
1
1
3 t
c2
1
1
t
1
1
t
t
1
0
t
1
2
t
1
3
4
5
;
Simplify
t
X A.X MatrixForm
Out[91]//MatrixForm=
2
t
3 t
04_Sistema_no_homogeneo.nb 3
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Examenes de RedesDocument7 pagesExamenes de RedesPaul RizzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Guía 5Document8 pagesGuía 5Paul RizzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Guía 6Document8 pagesGuía 6Paul RizzoPas encore d'évaluation
- 352 Guia%2BN1%2Bde%2BRedesDocument11 pages352 Guia%2BN1%2Bde%2BRedesPaul RizzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Marca Unsa PDFDocument20 pagesManual Marca Unsa PDFFiorella Campos RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Estructura de Tesis Agrarias - Dr. Marcial Mendo VelasquezDocument24 pagesEstructura de Tesis Agrarias - Dr. Marcial Mendo VelasquezLuz Ocas QuilichePas encore d'évaluation
- TV Samsung Ue5000Document6 pagesTV Samsung Ue5000hetfiellPas encore d'évaluation
- Unidad III Seguridad FisicaDocument15 pagesUnidad III Seguridad FisicaEdgar Jimenez King100% (1)
- Cromatografo de Gases Ficha TecnicaDocument54 pagesCromatografo de Gases Ficha Tecnicajavierpenagos92Pas encore d'évaluation
- Clases Laterales-Algebra ModernaDocument4 pagesClases Laterales-Algebra ModernaDaniel E. Taveras100% (1)
- Proyecto de GilatDocument10 pagesProyecto de GilatBryan OréPas encore d'évaluation
- Practicaselectronica4 160113183137 PDFDocument25 pagesPracticaselectronica4 160113183137 PDFJoseMelMPPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluke 744Document4 pagesFluke 744Rc PedroPas encore d'évaluation
- Ci 555Document11 pagesCi 555perrogiPas encore d'évaluation
- Inv Publica Hacktivkdad - Lógica y Automatas Celulares - Juan Cortes. (Final)Document10 pagesInv Publica Hacktivkdad - Lógica y Automatas Celulares - Juan Cortes. (Final)fedoerigoPas encore d'évaluation
- ES Guía Rápida VEGAPULS 61 4... 20 Ma HART Dos Hilos (Plics)Document20 pagesES Guía Rápida VEGAPULS 61 4... 20 Ma HART Dos Hilos (Plics)VladimirPas encore d'évaluation
- Orientacion VocacionalDocument165 pagesOrientacion VocacionalYulyx OrdòñezPas encore d'évaluation
- 2022-1 Guia - 02 - Laboratorio - ExpresionesDocument5 pages2022-1 Guia - 02 - Laboratorio - ExpresionesNatalia AcostaPas encore d'évaluation
- El Transistor Como Interruptor PDFDocument3 pagesEl Transistor Como Interruptor PDFaledangiePas encore d'évaluation
- Stored Procedures EjerciciosDocument2 pagesStored Procedures EjerciciosIngenieria SistemasPas encore d'évaluation
- OrtronicsDocument85 pagesOrtronicsEmmanuel Deewoldy Aguilar LagunasPas encore d'évaluation
- Avance ScrumDocument32 pagesAvance ScrumNestor Hernandez SagasteguiPas encore d'évaluation
- Libro PaginadoDocument18 pagesLibro PaginadoIan Francesc Puchol WongPas encore d'évaluation
- Factor de Daño y Su Comportamiento de Afluencia PDFDocument146 pagesFactor de Daño y Su Comportamiento de Afluencia PDFdanielPas encore d'évaluation
- Guia Packet TracerDocument21 pagesGuia Packet TracerHector Alejandro Velasco BeltranPas encore d'évaluation
- 1er DepartamentalDocument1 page1er DepartamentalAdrian Hdz VegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Clase 3 Derivadas ComplejasDocument17 pagesClase 3 Derivadas ComplejasElvisJohel100% (1)
- TG 05 U2-AplicacionsDEcsLinealesDocument6 pagesTG 05 U2-AplicacionsDEcsLinealesIrineo Moody Chow0% (1)
- Circuitos AritmeticosDocument6 pagesCircuitos AritmeticosDaniel MartinezPas encore d'évaluation
- DEFINICIONnDEnUNnSISTEMAnDEnCONTROL1 88618c4f5db899fDocument25 pagesDEFINICIONnDEnUNnSISTEMAnDEnCONTROL1 88618c4f5db899fJonathann M MarttinezPas encore d'évaluation
- Devenir Historico Del Colegio de Bachillerato Técnico IndustrialDocument17 pagesDevenir Historico Del Colegio de Bachillerato Técnico IndustrialMaría Camila PortillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tarea 4 - Cuestionario - Contenido Del CursoDocument6 pagesTarea 4 - Cuestionario - Contenido Del CursoJonathan Valencia NavarroPas encore d'évaluation
- Informe Especial - Oc-24-22Document29 pagesInforme Especial - Oc-24-22La Isla OestePas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Instructivo - de - Configuracion - en - Campo - Tellabs - 7300 - 2013 - 05 - 06 - Rev05Document30 pages01 Instructivo - de - Configuracion - en - Campo - Tellabs - 7300 - 2013 - 05 - 06 - Rev05Armin Hernández100% (1)
- Guía práctica para la refracción ocularD'EverandGuía práctica para la refracción ocularÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Había una vez el átomo: O cómo los científicos imaginan lo invisibleD'EverandHabía una vez el átomo: O cómo los científicos imaginan lo invisibleÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Electricidad: Fundamentos y problemas de electrostática, corriente continua, electromagnetiD'EverandElectricidad: Fundamentos y problemas de electrostática, corriente continua, electromagnetiÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (5)
- Mi proyecto escolar Matemáticas Lúdicas: Adaptaciones curriculares para preescolar, primaria y secundariaD'EverandMi proyecto escolar Matemáticas Lúdicas: Adaptaciones curriculares para preescolar, primaria y secundariaÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (5)
- Armónicas en Sistemas Eléctricos IndustrialesD'EverandArmónicas en Sistemas Eléctricos IndustrialesÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (12)
- El Tao de la física: Una exploración de los paralelismos entre la física moderna y el misticismo orientalD'EverandEl Tao de la física: Una exploración de los paralelismos entre la física moderna y el misticismo orientalÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- La teoría de casi todo: El modelo estándar, triunfo no reconocido de la física modernaD'EverandLa teoría de casi todo: El modelo estándar, triunfo no reconocido de la física modernaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (32)
- Fundamentos de mecánica de fluidos.: Con ejercicios parcialmente resueltosD'EverandFundamentos de mecánica de fluidos.: Con ejercicios parcialmente resueltosPas encore d'évaluation