Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Unit - 5 Human Population and Environment Objective
Transféré par
Balakumar Murugesan0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
18 vues4 pagesPopulation en!it": Number of individuals of the population per unit area or per unit volume. Rapid population growth is due to decrease in death rate and increase in birth rate. Pyramid shaped 4 %ndia, angladesh, 'thiopia,!. Ell shaped 4 5rance, 67+, 68 $. 6rn shaped - 9ermany, %taly, and :apan.
Description originale:
Titre original
Unit 5 Modified 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentPopulation en!it": Number of individuals of the population per unit area or per unit volume. Rapid population growth is due to decrease in death rate and increase in birth rate. Pyramid shaped 4 %ndia, angladesh, 'thiopia,!. Ell shaped 4 5rance, 67+, 68 $. 6rn shaped - 9ermany, %taly, and :apan.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
18 vues4 pagesUnit - 5 Human Population and Environment Objective
Transféré par
Balakumar MurugesanPopulation en!it": Number of individuals of the population per unit area or per unit volume. Rapid population growth is due to decrease in death rate and increase in birth rate. Pyramid shaped 4 %ndia, angladesh, 'thiopia,!. Ell shaped 4 5rance, 67+, 68 $. 6rn shaped - 9ermany, %taly, and :apan.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
UNIT 5
HUMAN POPULATION AND ENVIRONMENT
Objective:
To get a knowledge on human population and human rights
To educate the students on value education
To equip the students towards the modern technology with respect to
environment and human health.
Population en!it":
Number of individuals of the population per unit area or per unit volume.
Parameters affecting population size:
1. irth rate or Natality
!. "eath rate or #ortality
$. %mmigration
&. 'migration
Population #$o%t&
The rapid growth of the global(s population for the past 1)) years from the difference
between the rate of birth and death.
*auses of rapid population growth:
1. The rapid population growth is due to decrease in death rate and increase in
birth rate
!. +vailability of antibiotics, immunization, increased food production, clean
water and air decreases the famine-related deaths
$. %n agricultural based countries, children are required to help parents in the
field that is why population increases in the developing countries.
'&a$acte$i!tic! o( population )$o%t&:
1. '.ponential growth
!. "oubling time
$. %nfant mortality rate
&. total fertility rate
/. 0eplacement level
1. #ale2female ratio
3. "emographic transition
Va$iation o( population ba!e on a)e !t$uctu$e
1. Pyramid shaped 4 %ndia , angladesh, 'thiopia,
!. ell shaped 4 5rance, 67+, 68
$. 6rn shaped - 9ermany, %taly, and :apan.
Population E*plo!ion
The enormous increase in population due to low death rate and high birth rate.
'au!e!:
#odern medical facilities, life e.pectancy, illiteracy,
E((ect!:
Poverty, 'nvironmental degradation, ;ver 4e.ploitation of natural resources
,Treat, *ommunal war
0emedy:- Through birth control programmes.
+a,il" %el(a$e p$o)$a,,e:
Objective!:
7lowing down the population e.plosion
;ver e.ploitation of natural resources
5amily planning programme:
;b<ectives=
0educe infant mortality rate
'ncourage late marriages
%mprove women(s health
*ontrol of communal diseases>
Envi$on,ent an &u,an &ealt&:
1. Physical ?azards 4 0adioactive and 6@ radiations, 9lobal warming,
*hlorofluro carbons, Noise etc.
!. *hemical ?azards 4 *ombustion of 5ossil fuels, industrial effluence,
pesticides, heavy metals,
$. iological ?azards- acteria, @iruses, Parasites
Hu,an $i)&t!:
1. ?uman right to freedom
!. ?uman right to property
$. ?uman right to freedom of religion
&. ?uman right to culture and education
/. ?uman right to constitutional remedies
1. ?uman right to equality
3. ?uman right against e.ploitation
A. ?uman right to food and environment
B. ?uman right to good health.
Value eucation:
Types:
1. 5ormal education
!. @alue education
$. @alue - based environmental education
;b<ectives
1. To improve the integral growth of human beign
!. To create attitudes and improvement towards sustainable lifestyle.
$. To increase awareness about our national history our cultural heritage,
constitutional rights, national integration, community develoBpment and
environment.
&. To create and develop awareness about the values and their significance and
role
/. To know about various living and non- living organisms and their interaction
with environment.
Types of values:
1. 6niversal values
!. *ultural values
$. %ndividual values
&. global values
/. 7piritual values
HIV -AID.
+%"7 is the abbreviated form for +cquired %mmuno "eficiency 7yndrome caused
by a virus called ?%@.
'ffects=
1. "eath
!. Coss of labor
$. %nability to work
&. Cack of energy
/o,an an c&il %el(a$e:
;b<ectives:
1. to provide education
!. To impart vocational training
$. To generate awareness
&. To improve employment opportunities
/. To restore dignity, equality and respect.
0ole of information technology in environment:
Re,ote !en!in):
*omponent- + platform, aircraft, + balloon, rocket, and satellite.
5unctions:
1. ;rigin of electro magnetic energy
!. Transmission of energy
$. %nteraction of energy
&. "etection of energy
/. Preprocessing of data
1. "ata analysis and interpretation
3. %ntegration and other applications.
+pplications:
%n agriculture, forestry, land cover, water resources
"ata ase- *ollection of inter related data on various sub<ects.
+pplications:
1. #inistry of environment and forest
!. National management information system
$. 'nvironmental information system
9eographical information system:
+pplication:
Thematic maps are super imposed using soft wares.
%nterpretation of polluted zones
To check unplanned growth and related environmental problems
7atellite data:
1. ?elps in providing reliable information and data about forest cover
!. Provide information about forecasting weather
$. 0eserves of oil , minerals can be discovered.
D;0C" D%"' D': *urrent data.
+pplications:
1. ;nline learning
!. "igital files or photos, animations on environmental studies.
0ole of information technology in human health:
The health service technology involves three systems
1. 5inance and accounting
!. Pathology
$. Patient +dministration 4 clinical system.
+pplications:
1. "ata regarding birth and death rates
!. To monitor the health of the people effectively
$. The information regarding the outbreak of epidemic diseases.
&. ;nline *onsultation
/. "rugs and its replacement..
*onclusion:
9aining in-depth knowledge regarding human health, human rights and role
Played by modern technology to the environment.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Human Population and EnvironmentDocument5 pagesHuman Population and EnvironmentRahul0% (1)
- Integrated Resource Management: Agroforestry for DevelopmentD'EverandIntegrated Resource Management: Agroforestry for DevelopmentPas encore d'évaluation
- Module VIIDocument24 pagesModule VIINeeti JapraPas encore d'évaluation
- Geography SummaryDocument65 pagesGeography Summaryyoriko angelinePas encore d'évaluation
- Sustainable Agricultural Development: An Economic PerspectiveD'EverandSustainable Agricultural Development: An Economic PerspectivePas encore d'évaluation
- Overpopulation MLS 2E (Revised)Document23 pagesOverpopulation MLS 2E (Revised)Yvonne Mae CapatayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Class 10Document4 pagesPhysics Class 10mohammedumar7864521Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter01 107Document7 pagesChapter01 107homamunfatPas encore d'évaluation
- SOCIETY - Population PerspectiveDocument22 pagesSOCIETY - Population PerspectiveJesse100% (1)
- Project Report On Population ExplosionDocument11 pagesProject Report On Population ExplosionFarnaz Bharwani60% (5)
- Effect of Population On Environment-Case Study-NitcDocument53 pagesEffect of Population On Environment-Case Study-Nitcppv6nitc100% (1)
- DiversityDocument2 pagesDiversitydjalarinPas encore d'évaluation
- EVS Assignment-1: Name: V. Gopinath Class: B11 (AERO) ROLLNO:311019101013Document20 pagesEVS Assignment-1: Name: V. Gopinath Class: B11 (AERO) ROLLNO:311019101013GopinathPas encore d'évaluation
- Population Dynamics (CSEC Geography)Document25 pagesPopulation Dynamics (CSEC Geography)Kym Singh100% (2)
- Unit 8 Towards Sustainable FutureDocument19 pagesUnit 8 Towards Sustainable FutureKrishna RamaPas encore d'évaluation
- A New World Order: The Coming Transition from Fossil Fuels and Capitalism to Nuclear Energy and Eco-SocialismD'EverandA New World Order: The Coming Transition from Fossil Fuels and Capitalism to Nuclear Energy and Eco-SocialismPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics of Integrated Pest Management of Insects, TheD'EverandEconomics of Integrated Pest Management of Insects, ThePas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 8: Human Systems and Resource Use (16 Hours)Document5 pagesTopic 8: Human Systems and Resource Use (16 Hours)Michael SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- International Journal of Asian Social Science, 2013, 3 (3) :741-761Document21 pagesInternational Journal of Asian Social Science, 2013, 3 (3) :741-761Ahmad HaziqPas encore d'évaluation
- Global Demograp HY: By: Mary Joy B. CausinDocument45 pagesGlobal Demograp HY: By: Mary Joy B. CausinChekahay ni 'Cher Ojie ug 'Cher Alven DiazPas encore d'évaluation
- ENV 107 Introduction To Environmental Science: Lecture 8-9: Population and EnvironmentDocument53 pagesENV 107 Introduction To Environmental Science: Lecture 8-9: Population and EnvironmentWorld's GalleryPas encore d'évaluation
- Evs PPT KunalDocument13 pagesEvs PPT Kunalgddydss6tPas encore d'évaluation
- Concepcion, BIO 10.02-CC-S, Second Long ExamDocument13 pagesConcepcion, BIO 10.02-CC-S, Second Long ExamRafael ConcepcionPas encore d'évaluation
- 2013-Driving Sustainable DevelopmentDocument6 pages2013-Driving Sustainable DevelopmentArte ZaragozaPas encore d'évaluation
- EVS UNIT 5 Notes CBCS For ERPDocument12 pagesEVS UNIT 5 Notes CBCS For ERPBrindha SPas encore d'évaluation
- EED 4118 Lesson 3Document9 pagesEED 4118 Lesson 3KevinPas encore d'évaluation
- Master of PsychologyDocument15 pagesMaster of PsychologyIbrahimAdiamonUsmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Amad Uloc Ge15Document4 pagesAmad Uloc Ge15Rolando AmadPas encore d'évaluation
- STS ReportDocument9 pagesSTS ReportKay AbawagPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Population and Environment ObjectiveDocument24 pagesHuman Population and Environment ObjectiveSindhura ValluriPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecology Ch11 Part 3Document34 pagesEcology Ch11 Part 3Sydney BullardPas encore d'évaluation
- Ess - Apuntes Topic 8Document11 pagesEss - Apuntes Topic 8Julia MastralPas encore d'évaluation
- "Global Demography": The "PERILS" of OverpopulationDocument2 pages"Global Demography": The "PERILS" of OverpopulationPamela Dawn B. Mansibugan100% (8)
- PEECO-FINAL Clint E. MosenabreDocument36 pagesPEECO-FINAL Clint E. MosenabreJea MosenabrePas encore d'évaluation
- Sci105 Environmental Science M4 CompleteDocument23 pagesSci105 Environmental Science M4 CompleteRojel Jan Ocampo GalzotePas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 5Document28 pagesLec 5mohamed sherifPas encore d'évaluation
- Euthenics, the science of controllable environment a plea for better living conditions as a first step toward higher human efficiencyD'EverandEuthenics, the science of controllable environment a plea for better living conditions as a first step toward higher human efficiencyPas encore d'évaluation
- STS ReportDocument10 pagesSTS ReportKay AbawagPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 2 Sustainable Dev Issues PDFDocument64 pagesCH 2 Sustainable Dev Issues PDFHaya JahanPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 6 PopulationsDocument2 pagesUnit 6 Populationsapi-332813379Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Economics of Sustainable Food: Smart Policies for Health and the PlanetD'EverandThe Economics of Sustainable Food: Smart Policies for Health and the PlanetPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethics in an Age of Technology: Gifford Lectures, Volume TwoD'EverandEthics in an Age of Technology: Gifford Lectures, Volume TwoÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (1)
- The Population Explosion: Causes and ConsequencesDocument11 pagesThe Population Explosion: Causes and ConsequencesShashi CampherPas encore d'évaluation
- We Cannot Save The Environment Without Fighting Poverty.' Do You AgreeDocument4 pagesWe Cannot Save The Environment Without Fighting Poverty.' Do You Agreeh1generalpaperPas encore d'évaluation
- Composition ParagraphDocument4 pagesComposition ParagraphRafnan RezwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Population Growth and Greenhouse Gas EmissionsDocument2 pagesHuman Population Growth and Greenhouse Gas EmissionsThe Wilson Center100% (1)
- Human Population EVS ProjectDocument14 pagesHuman Population EVS Projectdhiraj67% (42)
- Food and HealthDocument87 pagesFood and HealthlolmemPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Paper Food SecurityDocument7 pagesResearch Paper Food Securitylixdpuvkg100% (1)
- Running Head: Ecology 1Document32 pagesRunning Head: Ecology 1Mimi Puopolo PhilipsPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecosoc, Topic ADocument4 pagesEcosoc, Topic ASheheryar ZaidiPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 3 ENVI SCIDocument24 pagesGroup 3 ENVI SCIJose mar m. RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Right To Healthy Environment in The Era of GlobalizationDocument17 pagesRight To Healthy Environment in The Era of GlobalizationAnuj KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Population Growth: World Population Now Over ?? BillionDocument43 pagesPopulation Growth: World Population Now Over ?? BillionEdz SeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Eco 202Document7 pagesEco 202amr khaledPas encore d'évaluation
- Population Explosion and ControlDocument22 pagesPopulation Explosion and Controlpratiktripathy55Pas encore d'évaluation
- Socio 63 Group 1 Report - OverpopulationDocument23 pagesSocio 63 Group 1 Report - OverpopulationKristian ForestPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 Human Population and EnvironmentDocument16 pagesChapter 7 Human Population and Environmentjieeniola1Pas encore d'évaluation
- GST 211 NoteDocument4 pagesGST 211 Noteakinmadejesuloba5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mobile App ANSWER KEYDocument5 pagesMobile App ANSWER KEYKavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- SAS One CreditDocument23 pagesSAS One CreditKavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Nandha Engineering College, Erode Department of Cse Iii Cse A NamelistDocument5 pagesNandha Engineering College, Erode Department of Cse Iii Cse A NamelistKavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- True B.) False: Sas QuestionsDocument6 pagesTrue B.) False: Sas QuestionsKavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Cse Board of Studies - 9 AttendanceDocument9 pagesCse Board of Studies - 9 AttendanceKavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Welcome Slides For II & III Yr Students About R17 AmendmentsDocument33 pagesWelcome Slides For II & III Yr Students About R17 AmendmentsKavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Statements FOR HACKATHONDocument4 pagesProblem Statements FOR HACKATHONKavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Google Classroom DetailsDocument1 pageGoogle Classroom DetailsKavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- SAS One CreditDocument23 pagesSAS One CreditKavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- True B.) False: Sas QuestionsDocument6 pagesTrue B.) False: Sas QuestionsKavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- One Credit Course: Chef Automation & Saas Ii CseDocument4 pagesOne Credit Course: Chef Automation & Saas Ii CseKavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Welcome Slides For II & III Yr Students About R17 AmendmentsDocument33 pagesWelcome Slides For II & III Yr Students About R17 AmendmentsKavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Cse Board of Studies - 9 AttendanceDocument9 pagesCse Board of Studies - 9 AttendanceKavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- One Credit Course: Chef Automation & Saas Ii CseDocument4 pagesOne Credit Course: Chef Automation & Saas Ii CseKavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Po and Co MappingDocument1 pagePo and Co MappingKavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Nandha Engineering College, Erode Department of Cse Iii Cse A NamelistDocument5 pagesNandha Engineering College, Erode Department of Cse Iii Cse A NamelistKavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Arrear List Upto Vi SemDocument205 pagesLab Arrear List Upto Vi SemKavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Staff & Class Handling (I, II, III, IV Yr UG-PG)Document1 pageStaff & Class Handling (I, II, III, IV Yr UG-PG)Kavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Google Classroom DetailsDocument1 pageGoogle Classroom DetailsKavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Expected Marks To Attainment 0.7 0.7 0.7 0.7 0.7 1.4 1.4 1.4 1.4 1.4 4.9 7 2.8 4.9 4.9 9.8 9.8Document6 pagesExpected Marks To Attainment 0.7 0.7 0.7 0.7 0.7 1.4 1.4 1.4 1.4 1.4 4.9 7 2.8 4.9 4.9 9.8 9.8Kavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Student Databse For Letter GenerationDocument1 pageStudent Databse For Letter GenerationKavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Software Engineering Objective Type QuestionsDocument4 pagesSoftware Engineering Objective Type QuestionsKavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- No.: E Mail ID:: (Can Be Claimed Once But Cannot Be Every Year)Document3 pagesNo.: E Mail ID:: (Can Be Claimed Once But Cannot Be Every Year)Kavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Dma 8257Document22 pagesDma 8257Kavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- 80286Document28 pages80286Kavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Co ProcessorDocument42 pagesCo ProcessorKavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Nandha Engineering College, Erode-52: Continuous Assessment Test - III 15Cs404 Mobile ComputingDocument2 pagesNandha Engineering College, Erode-52: Continuous Assessment Test - III 15Cs404 Mobile ComputingKavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- 8279Document32 pages8279Kavitha SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
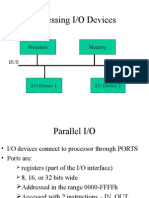
- Accessing I/O Devices: Processor Memory BUSDocument22 pagesAccessing I/O Devices: Processor Memory BUSSrikanth PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- OPTCL-Fin-Bhw-12Document51 pagesOPTCL-Fin-Bhw-12Bimal Kumar DashPas encore d'évaluation
- Coding DecodingDocument21 pagesCoding DecodingAditya VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Entero SequencesDocument12 pagesEntero SequencesKelvin SueyzyPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise On Word Formation 2 (Unit 2 - Advanced) : Tran Dai Nghia High School For The GiftedDocument3 pagesExercise On Word Formation 2 (Unit 2 - Advanced) : Tran Dai Nghia High School For The GiftedEveryonehateshiuzo 2.0Pas encore d'évaluation
- Coffee Quality Manual by Abra Rand Nig Use IDocument25 pagesCoffee Quality Manual by Abra Rand Nig Use IIpungPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Filling MachineDocument15 pagesWater Filling Machinepallab D RozarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 Dopant Diffusion - IDocument32 pagesChapter 7 Dopant Diffusion - I강준호Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mega StructuresDocument2 pagesMega StructuresSanthosh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Tips For A Healthy PregnancyDocument2 pagesTips For A Healthy PregnancyLizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Train OperationDocument6 pagesAutomatic Train OperationAnupam KhandelwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Volvo Penta GensetDocument4 pagesVolvo Penta GensetafandybaharuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- c270 KW NTA855G2 60 HZDocument31 pagesc270 KW NTA855G2 60 HZAhmad El KhatibPas encore d'évaluation
- Bagpipe LV 1-5Document228 pagesBagpipe LV 1-5Sathia Kdms100% (2)
- The History of AstrologyDocument36 pagesThe History of AstrologyDharani Dharendra DasPas encore d'évaluation
- 988611457NK448908 Vehicle Scan ReportDocument5 pages988611457NK448908 Vehicle Scan ReportVictor Daniel Piñeros ZubietaPas encore d'évaluation
- Recruitment and Selection in Canada 7Th by Catano Wiesner Full ChapterDocument22 pagesRecruitment and Selection in Canada 7Th by Catano Wiesner Full Chaptermary.jauregui841100% (51)
- ECE199R-C12 Final Document OJTDocument48 pagesECE199R-C12 Final Document OJTRigel ZabatePas encore d'évaluation
- 1F-Korean-Nami Mun - Miles From NowhereDocument4 pages1F-Korean-Nami Mun - Miles From NowhereNeil PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- 15 Benefits of CyclingDocument8 pages15 Benefits of CyclingJoycs PintoPas encore d'évaluation
- Harmonic Analysis of Separately Excited DC Motor Drives Fed by Single Phase Controlled Rectifier and PWM RectifierDocument112 pagesHarmonic Analysis of Separately Excited DC Motor Drives Fed by Single Phase Controlled Rectifier and PWM RectifierGautam Umapathy0% (1)
- Human Wildlife Conflict Resolution PDFDocument9 pagesHuman Wildlife Conflict Resolution PDFdemiPas encore d'évaluation
- Theoretical CyclesDocument49 pagesTheoretical CyclesMariaEzzaSyUyPas encore d'évaluation
- MSDS DowthermDocument4 pagesMSDS DowthermfebriantabbyPas encore d'évaluation
- Tabla de Avances de AcesoriosDocument3 pagesTabla de Avances de AcesoriosPedro Diaz UzcateguiPas encore d'évaluation
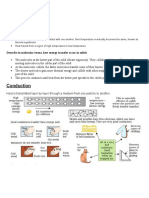
- Notes Transfer of Thermal EnergyDocument12 pagesNotes Transfer of Thermal Energymahrosh mamoon100% (2)
- VavDocument8 pagesVavkprasad_56900Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gujral FCMDocument102 pagesGujral FCMcandiddreamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Prevailing Torque Locknut Technical SpecificationsDocument3 pagesPrevailing Torque Locknut Technical SpecificationsLiu YangtzePas encore d'évaluation
- Tabla9 1Document1 pageTabla9 1everquinPas encore d'évaluation
- Carrefour-SA Shopping Center TurkeyDocument2 pagesCarrefour-SA Shopping Center TurkeyVineet JogalekarPas encore d'évaluation