Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
CS372 Final Exam Solution
Transféré par
Noel Montero Urrutia0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
783 vues10 pagesThis document contains the solutions to a final exam for a computer science course. It is divided into 5 problems testing different topics:
1. Multiple choice questions covering public key cryptography, networking hardware and protocols, wireless networking standards, and networking layers.
2. Short answer questions about network addressing, mobility, and the hidden node problem in wireless networks.
3. Questions about network layer concepts including drawing a network topology, assigning IP addresses and subnets.
4. Questions about the Dijkstra routing algorithm and finding least cost paths.
5. Questions about implementing encryption, signatures and hashes to provide security like confidentiality, integrity and authentication for email. This includes encrypting and decrypting messages and evaluating
Description originale:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThis document contains the solutions to a final exam for a computer science course. It is divided into 5 problems testing different topics:
1. Multiple choice questions covering public key cryptography, networking hardware and protocols, wireless networking standards, and networking layers.
2. Short answer questions about network addressing, mobility, and the hidden node problem in wireless networks.
3. Questions about network layer concepts including drawing a network topology, assigning IP addresses and subnets.
4. Questions about the Dijkstra routing algorithm and finding least cost paths.
5. Questions about implementing encryption, signatures and hashes to provide security like confidentiality, integrity and authentication for email. This includes encrypting and decrypting messages and evaluating
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
783 vues10 pagesCS372 Final Exam Solution
Transféré par
Noel Montero UrrutiaThis document contains the solutions to a final exam for a computer science course. It is divided into 5 problems testing different topics:
1. Multiple choice questions covering public key cryptography, networking hardware and protocols, wireless networking standards, and networking layers.
2. Short answer questions about network addressing, mobility, and the hidden node problem in wireless networks.
3. Questions about network layer concepts including drawing a network topology, assigning IP addresses and subnets.
4. Questions about the Dijkstra routing algorithm and finding least cost paths.
5. Questions about implementing encryption, signatures and hashes to provide security like confidentiality, integrity and authentication for email. This includes encrypting and decrypting messages and evaluating
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 10
Page 1 of 10
CS 372 Final Exam Solution
Summer 2014
August 13, 2014
Instructor: Mohamed Grissa
Duration: 50 minutes
Student Name: ____________________________ OSU ID: ______________
Problem Points Possible
1 29
2 12
3 21
4 17
5 21
Total 100
Instructions
Answer the questions in the spaces provided on the question sheets.
If you run out of room for an answer, continue on the back of the page.
Show your work. State any assumptions made.
One two-sided sheet of notes is allowed.
Good luck!!
Page 2 of 10
Problem I: Multiple Choice Questions (29 points, 4 minutes)
Choose the correct answer.
1. (4 points) Which of the following is a public key cryptography algorithm?
a) Monoalphabetic Cipher
b) Polyalphabetic Cipher
c) Block Cipher Chaining
d) Rivest, Shamir, Adleman algorithm
2. (4 points) What is a NIC?
a) Network Interface Controller
b) Network Interface Card
c) No Internet Connection
d) Network Internet Connection
3. (4 points) In the 802.11 standard, IEEE specifies what type of access method?
a) CSMA/CD
b) CSMA/CA
c) FDMA
d) TDMA
4. (4 points) Which of the following options hides the details of a home network from the rest
of the Internet?
a) ARP
b) DHCP
c) NAT
d) ICMP
Page 3 of 10
5. (4 points) Which layer is responsible for transferring data to adjacent network nodes over a
physical medium?
a) Transport Layer
b) Application Layer
c) Link Layer
d) Network Layer
6. (4 points) The protocol that requires a master node to grant access to each node in a collision
domain, in a round-robin fashion is called a
a) Token-passing protocol
b) Polling protocol
c) Random access protocol
d) None of the responses above is correct.
7. (2 points) The reasons for handling routing differently in Inter-AS and Intra-AS routing are
based On
a) Differences in router capabilities
b) Distance vector versus link state information
c) Policy, scale and performance
d) Imposed standards for packaging messages
8. (3 points) Random access protocols in shared bus networks use ______ to provide listen
before speaking and stop talking if someone else already is talking rules.
a) CSMA
b) SMDP
c) ALOHA
d) Slotted ALOHA
Page 4 of 10
9. (Bonus 2 points) Given the This protocol is used for error reporting in network layer
a) OSPF
b) ICMP
c) TCP
d) ARP
Page 5 of 10
Problem II: General Short Answer (21 points, 5 minutes)
a) (4 points) Given the following forwarding table, complete the table below by specifying
on which of the outgoing interfaces each destination address will be forwarded.
b) (5 points) If a node has a wireless connection to the Internet, does that node have to be
mobile? Suppose that a user with a laptop walks around her house with her laptop, and
always accesses the Internet through the same access point. Is the user mobile from a
network standpoint? Explain!
Answer: No. User usually stays connected to a single access point while roaming around the
house.
c) (2 points)True or False, Datagram networks do not require call setup at the network
layer.
Answer: True
d) (Bonus 2 points) Briefly explain the hidden node problem.
Answer: A cannot detect a transmission from C and vice versa. If A and C start sending
simultaneously to B a collision at B will happen but A and C will not become aware of the
collision
Page 6 of 10
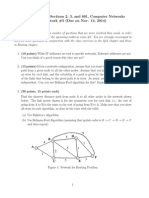
Problem III: Network Layer (21 points, 14 minutes)
For this problem your task is to create a network that consists of 3 routers. Each
router has 3 interfaces. On each router, 2 of these interfaces are connected to another
(distinct) router and one is connect to a host.
(a) (6 points) Draw the resulting topology of that network.
(b) (3 points) How many subnets does this network contain?
6
(c) (6 points) Assign an IP subnet address to each of these subnets such that a
maximum of 30 hosts can be connected to each subnet.
Look figure
(d) (6 points) Assign an IP address to each interface
Look figure
Page 7 of 10
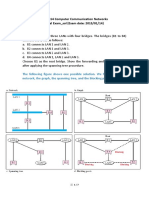
Problem VI: Routing Algorithms (17 points, 11 minutes)
Consider the network shown below.
Figure 1
a) (12 Points) Show the operation of Dijkstras (LinkState) algorithm for computing the
least cost path from u to all destinations.
N
D(v), P(v) D(w), P(w) D(x), P(x) D(y), P(y) D(z), P(z)
u 6,u 5,u 6,u infinity infinity
u w 6,u - 6,u 14,w 6,w
u w v - - 6,u 14,w 6,w
u w v x - - - 12,x 6,w
u w v x z - - - 7,z -
u w v x z y - - - - -
b) (5 points) From these results, show the least cost path from u to all other nodes.
Answer: u-to-v, u-to-w, u-to-x, u-to-w-to-z-to-y, u-to-w-to-z.
Page 8 of 10
Problem V: Security (21 points, 16 minutes)
In order to provide confidentiality, integrity and authentication there are certain security
measures that need to be taken. Given the following diagram explain what Alice needs to do to
satisfy these security requirements for sending a secure email to Bob by filling in the boxes with
the correct notation using KS(.), K
-
A(.), K
+
A(.), K
-
B(.), K
+
B(.), H(.).
a. (5 points) Secure Email
Figure 3
b. (5 points) How does Bob decrypt the message, check for authentication and
integrity (using same notation from above)
Page 9 of 10
c. (6 points) Assume Bobs RSA public key is (n,e) and corresponding private key
is (n,d). Which of the following could be used as RSA key pairs (ignoring the
fact that they are too small)? For those that are valid key pairs, show that they
meet all the requirements for a key pair, for those that are not, explain why they
are not.
1. (31,5) (31,11): could not be used since n = 31 cannot be decomposed into a
product of two prime numbers
Page 10 of 10
2. (77,7) (77,43): n = 77 = 7*11 = p*q, z = (p-1)(q-1) = 6*10 = 60
e = 7, d = 43, e has no common factor with d.
ed-1 = 7*43-1 = 300 which is divisible by z = 60.
So this is a valid key pair
3. (55,7) (55,41): n = 55 = 5*11 = p*q, z = (p-1)(q-1) = 4*10 = 40
e = 7, d = 41, e has a common factor with d which is 3
So this is not a valid key pair
d. (4 points) Consider the pair (91,5), (91,29). Assume the first is the encryption
key and the second is the decryption key. What is the encrypted value of the
number 10?
Answer : m = 10, e = 5, n = 91. The ciphertext c = m
e
mod n = 10
5
mod 91 = 82
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Sol 2Document3 pagesSol 2Subrota Kumar MondalPas encore d'évaluation
- Determination of Transformer Parameters from Open Circuit TestDocument7 pagesDetermination of Transformer Parameters from Open Circuit TestSur ShriPas encore d'évaluation
- Einstein Theory of RelativityDocument29 pagesEinstein Theory of RelativityVelariYogeshkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Tanggang's Tragic FateDocument5 pagesTanggang's Tragic FateSiti Nur Izzati ShuibPas encore d'évaluation
- Absence LetterDocument2 pagesAbsence LetterNur' AisyahPas encore d'évaluation
- TeslaDocument12 pagesTeslaMihai BairacPas encore d'évaluation
- Short Vowel Words Workbook PDFDocument20 pagesShort Vowel Words Workbook PDFYaya Nur HidayahPas encore d'évaluation
- ElectrostaticDocument77 pagesElectrostaticMritunjay KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Sci F2 T1 (E)Document7 pagesSci F2 T1 (E)Nad RamliPas encore d'évaluation
- Analisis Inventori Minat KerjayaDocument1 pageAnalisis Inventori Minat KerjayaMohdRidzwanSaibinePas encore d'évaluation
- Capturing the Opportunity of the Global Green EconomyDocument65 pagesCapturing the Opportunity of the Global Green Economylee jin huiPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Analysis of Leaather Industry BanglaadeshDocument58 pagesFinancial Analysis of Leaather Industry Banglaadeshتنويرمحمداحسان50% (2)
- Nikola Tesla - Genius Inventor Who Lit the WorldDocument15 pagesNikola Tesla - Genius Inventor Who Lit the WorldVukosava Milic Torres100% (2)
- Should University Education Should Be FreeDocument9 pagesShould University Education Should Be FreethiagosibsPas encore d'évaluation
- GPU Programming EE 4702-1 Final Examination: Exam TotalDocument10 pagesGPU Programming EE 4702-1 Final Examination: Exam TotalmoienPas encore d'évaluation
- CryptoGraphy Exam PaperDocument8 pagesCryptoGraphy Exam PaperMesincahaya Masa KagebunshinPas encore d'évaluation
- 2021 - CC - ASSIGN - 8weeks CourseDocument34 pages2021 - CC - ASSIGN - 8weeks CoursesaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Spring2015Document7 pagesFinal Spring2015edePas encore d'évaluation
- Ip Ms Pre Board II XiiDocument7 pagesIp Ms Pre Board II XiiTRAP GAMINGPas encore d'évaluation
- 3213 Final Winter2008 SolutionsDocument17 pages3213 Final Winter2008 SolutionsMohammedMikhaelYahyaPas encore d'évaluation
- CA Obe FolderDocument4 pagesCA Obe Foldermiqbal66126612Pas encore d'évaluation
- T215B - MTA - Spring 2014-2015 AKDocument7 pagesT215B - MTA - Spring 2014-2015 AKChristina FingtonPas encore d'évaluation
- Feb 2Document15 pagesFeb 2Abhi RockzzPas encore d'évaluation
- Gate Question PapersDocument43 pagesGate Question PapersRahul KalePas encore d'évaluation
- COMP3334 Mid-Term 2223 Sample SolutionsDocument8 pagesCOMP3334 Mid-Term 2223 Sample SolutionsFouillandPas encore d'évaluation
- Sri Lanka Institute of Information Technology B.Sc. Honours Degree Ill Information Technology Final ExaminationDocument9 pagesSri Lanka Institute of Information Technology B.Sc. Honours Degree Ill Information Technology Final ExaminationTtfcfgbbPas encore d'évaluation
- Gate-Cs 2005Document31 pagesGate-Cs 2005tomundaPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Exam Questions for Computer Networks CourseDocument3 pagesFinal Exam Questions for Computer Networks CourseBuali SinaPas encore d'évaluation
- TCS Latest Placement Paper-2018Document4 pagesTCS Latest Placement Paper-2018Eswar100% (1)
- Test 1 SampleDocument4 pagesTest 1 SampleErmias MesfinPas encore d'évaluation
- Question 1 - Short Answer Questions: (2 Marks)Document6 pagesQuestion 1 - Short Answer Questions: (2 Marks)Nouman KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Test of Operating Systems and Computer Networks ExamDocument5 pagesTest of Operating Systems and Computer Networks ExamBob BobPas encore d'évaluation
- Examination Paper: May/June 2020 COMP2211-WE01Document6 pagesExamination Paper: May/June 2020 COMP2211-WE01africa threePas encore d'évaluation
- ENSC427 Final 1231Document4 pagesENSC427 Final 1231477889997mPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Material XI Computer ScienceDocument120 pagesStudy Material XI Computer SciencePriyanshu0% (1)
- HW 5Document2 pagesHW 5Siddharth SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- HCL Placement PapersDocument52 pagesHCL Placement PapersShruthi SweetPas encore d'évaluation
- Xii CS PB1Document10 pagesXii CS PB1lalita nagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Blanc Comp Net Exam Fall 08Document18 pagesBlanc Comp Net Exam Fall 08jerome_bovay5831Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mock Exam SolutionDocument5 pagesMock Exam SolutionAnushka KallaPas encore d'évaluation
- Asn HS07Document6 pagesAsn HS07saravanan_nallusamyPas encore d'évaluation
- AnswersFinalExam159334 2009Document10 pagesAnswersFinalExam159334 2009Pramod Kumar ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- MidtermSol KEDDocument12 pagesMidtermSol KEDNs SPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution Sheet - Mid-Semester Test 2009: Question 1 - Short Answer QuestionsDocument13 pagesSolution Sheet - Mid-Semester Test 2009: Question 1 - Short Answer QuestionsArshad KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Computing and Information Technology 2 Final ExaminationDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Computing and Information Technology 2 Final ExaminationKhalidPas encore d'évaluation
- Networking Fundamentals AssignDocument8 pagesNetworking Fundamentals AssignNadia BakerPas encore d'évaluation
- Final SolDocument7 pagesFinal SolTài Lâm100% (4)
- Unit 3 Test (CH 4 5 6) 11-6-2013 KEYDocument31 pagesUnit 3 Test (CH 4 5 6) 11-6-2013 KEYOsama MaherPas encore d'évaluation
- It Test Total Time: 3 HoursDocument8 pagesIt Test Total Time: 3 HoursApu KunduPas encore d'évaluation
- M.Sc. - Comp. SciDocument70 pagesM.Sc. - Comp. SciGanapatibo GanapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- October 2012: Questions Must Be Answered in Accordance With The FollowingDocument31 pagesOctober 2012: Questions Must Be Answered in Accordance With The FollowingAndrew CordonPas encore d'évaluation
- 2008S Fe PM QDocument40 pages2008S Fe PM Qthaiday10Pas encore d'évaluation
- G12cs-Ms-Preboard1 2022-23Document21 pagesG12cs-Ms-Preboard1 2022-23shabazdxb8Pas encore d'évaluation
- TCS Ninja Programming MCQ's SyllabusDocument11 pagesTCS Ninja Programming MCQ's SyllabusAtifa TabassumPas encore d'évaluation
- Networking Sample Exam Questions Marking Scheme - 2003-4 Semester 2Document9 pagesNetworking Sample Exam Questions Marking Scheme - 2003-4 Semester 2abraha gebruPas encore d'évaluation
- MCA104Document2 pagesMCA104Abhi MittalPas encore d'évaluation
- Paul DuraiiDocument8 pagesPaul Duraiipaspatisah9663Pas encore d'évaluation
- Research Paper Coordination BondingDocument11 pagesResearch Paper Coordination BondingSIDHARTH SINHPas encore d'évaluation
- IP-Class 12 - Half Yearly - 2021Document11 pagesIP-Class 12 - Half Yearly - 2021Diya sharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- CS2700 Tutorial 6: Binary Search Trees and AVL TreesDocument4 pagesCS2700 Tutorial 6: Binary Search Trees and AVL TreesKAKUNURI SHASHANK REDDYPas encore d'évaluation
- Thought Works Tech Radar August 2010 UK AUS ColourDocument8 pagesThought Works Tech Radar August 2010 UK AUS Colourfranck.rasoloPas encore d'évaluation
- Migration From Unicenta PDFDocument7 pagesMigration From Unicenta PDFNoel Montero UrrutiaPas encore d'évaluation
- DPDocument53 pagesDPsam.uhcPas encore d'évaluation
- I Le ExamplesDocument131 pagesI Le ExamplesNoel Montero UrrutiaPas encore d'évaluation
- LectureDocument3 pagesLecturelesterPas encore d'évaluation
- Enterprise-Wide Process Integration and Innovation: With Enterprise Content ManagementDocument11 pagesEnterprise-Wide Process Integration and Innovation: With Enterprise Content ManagementsaruhansahinPas encore d'évaluation
- 20140926160951chapter One MES3033Document44 pages20140926160951chapter One MES3033Banu NayarPas encore d'évaluation
- SRS - CamStudio (Version 2.7)Document27 pagesSRS - CamStudio (Version 2.7)Alejandro S. RaimundoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ainsworth PDFDocument5 pagesAinsworth PDFJhonattan Valencia100% (2)
- CDP LLDP SecurityDocument46 pagesCDP LLDP SecurityChandan VedavyasPas encore d'évaluation
- Opti-6100 Provision - 61184500L1-6JDocument340 pagesOpti-6100 Provision - 61184500L1-6JRobert Freeman100% (1)
- XCP ReferenceBook V1.0 ENDocument113 pagesXCP ReferenceBook V1.0 ENbriceagcosminPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.difference Between String and Stringbuilder S.No String StringbuilderDocument8 pages1.difference Between String and Stringbuilder S.No String StringbuilderUmar AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Remote Instrumentation and Virtual Laboratories - Service Architecture and Networking-SprinDocument519 pagesRemote Instrumentation and Virtual Laboratories - Service Architecture and Networking-SprinHardy77Pas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Selection Guide - 3Document46 pagesDigital Selection Guide - 3Akash YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- NetMaster Installation GuideDocument97 pagesNetMaster Installation GuideSteve Alain Onana DangPas encore d'évaluation
- Analyze Ad Budget DatasetDocument4 pagesAnalyze Ad Budget DatasetSrikanth100% (1)
- Viruses, Worms, Hoaxes, Trojan HorsesDocument35 pagesViruses, Worms, Hoaxes, Trojan HorsesRubick TakahashiPas encore d'évaluation
- Vari Flex Drive BroDocument7 pagesVari Flex Drive Brohicham plastPas encore d'évaluation
- Savitribai Phule Pune UniversityDocument2 pagesSavitribai Phule Pune UniversityTushar ShelakePas encore d'évaluation
- Java Inheritance. Possible Questions and AnswersDocument8 pagesJava Inheritance. Possible Questions and AnswersKartheeban KamatchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Installation and Use Instructions (Android) : PrerequisitesDocument6 pagesInstallation and Use Instructions (Android) : PrerequisitesjoshuaMcClurePas encore d'évaluation
- Report Assignment TIS3151 (The Nanobots)Document21 pagesReport Assignment TIS3151 (The Nanobots)Faizal AzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Institute of Technology Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering (Computer Focus Area) Online Voting System of Ethiopian GovernmentDocument16 pagesInstitute of Technology Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering (Computer Focus Area) Online Voting System of Ethiopian GovernmentAschalePas encore d'évaluation
- Bubble SortDocument6 pagesBubble SortRollin ReviePas encore d'évaluation
- What Is InternetDocument1 pageWhat Is InternetPiyush AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- EFIT Manual (Student)Document2 pagesEFIT Manual (Student)Bogdan HoanceaPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Communicate Through BLE Using FlutterDocument20 pagesHow To Communicate Through BLE Using FlutterJulioPas encore d'évaluation
- Subject - Diagnostic Software For Delphi TVS Make Ref NoDocument5 pagesSubject - Diagnostic Software For Delphi TVS Make Ref NoTabitha BoonePas encore d'évaluation
- Installation Guide For Solaris Cluster 3.2 Software and Oracle® 10g Release 2 Real Application ClustersDocument30 pagesInstallation Guide For Solaris Cluster 3.2 Software and Oracle® 10g Release 2 Real Application Clustersdean-stiPas encore d'évaluation
- TRIDENT 9000 Video Card Settings and ConfigurationDocument3 pagesTRIDENT 9000 Video Card Settings and Configurationfabioretrotv6 retrotv6Pas encore d'évaluation
- Android Model Compare - Urovo I6300 and Cipherlab RS31Document1 pageAndroid Model Compare - Urovo I6300 and Cipherlab RS31yashavanta shettyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ni6hant Lenovo Laptop PricesDocument2 pagesNi6hant Lenovo Laptop PricesRevanth BodagalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Q1. The Following SAS Program Is SubmittedDocument23 pagesQ1. The Following SAS Program Is SubmittedrcpascPas encore d'évaluation