Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Co-Teaching Notesheet
Transféré par
lolaing0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
15 vues4 pageslevel of proficiency
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentlevel of proficiency
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
15 vues4 pagesTypes of Co-Teaching Notesheet
Transféré par
lolainglevel of proficiency
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
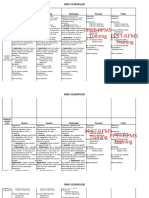
Types of Co-Teaching Models
Model When To Use Planning time Applications Comments
One Teach, One
Observe-more
detailed observation
of one or more
students-decide
hat types of
information and
meet to analy!e data
When "uestions
arise about students
Chec# student
progress
Compare target
students to others in
class
$o Which students
initiate
conversations in
cooperative groups
%tudent or# pace
%pecific student&s
attention
'o students
problem solve
Use carbon or (C)
paper for copies to
share
Use it to get
coaching feedbac#-
*o + call on some
students more than
others,
One Teach, One
*rift-one person
primary
responsibility for
teaching other
circulates the room-
provide unobtrusive
assistance to
struggling students
When lesson lends
itself to delivery by
one teacher
When one teacher
has a particular
e-pertise
+n ne situations
for teachers
When lesson
stresses processing-
students need close
monitoring
$o Teachers favorite
topic
'o ell do the
students understand
the steps
to..multiplication
%tudents learning
ho to ta#e notes
(ot helpful in
focusing student
attention-can
distract students
/ach teacher should
have the opportunity
to lead the class and
drift if this is used
Parallel Teaching-
both teachers are
teaching the same
information 0divide
the class and
conduct the lesson
simultaneously
When loer adult
student teacher ratio
is needed to improve
instructional
efficiency
Medium 1oster student
participation in
discussions
Activities such as
drill and practice-
re-teach-test and
revie
2ives teacher active
but separate
instructional role in
the classroom
Topic ith multiple
dimensions can be
presented and
groups brought
together at the end
%tudents can
strategically be
placed in the to
groups
%tation Teaching-
teachers divide
content and students
%tudents rotate from
one teacher to the
other-also use an
independent station
%tudents access
each teacher
Content is comple-
but not hierarchical
When part of
instruction is revie
When several topics
comprise instruction
Medium *uring $A one
station address
comprehension, one
focus on editing a
recent assignment,
one revie a s#ill
being taught
%% e-amine
geography, economy
and culture of a
region or country
May be more
appropriate in
higher level classes
+f students cannot
or# independently-
to groups can be
formed
Alternative
Teaching-%mall
group needs or#
and the group as a
hole can move
forard
Alternative lesson
could be taught at a
different level
Could be for a fe
minutes or entire
lesson
Where students
mastery varies
greatly
Where high levels of
mastery are
e-pected
Where some
students are
or#ing in parallel
curriculum
'igh $arge group
completes the
assignment, small
group receives
additional
instruction
One group chec#s
homeor# and
small group is pre-
taught lesson
$arge group
or#ing on pro3ects
small group being
assessed
%mall group
membership should
vary
Team Teaching-both
teachers are
delivering the same
instruction at the
same time-/ach
spea#s freely-
instruction becomes
a conversation
Teachers e-perience
is comparable and
complimentary
Teachers have a
high sense of
comfort and
compatibility
When the goal is to
demonstrate some
type of interaction to
students
'igh +n science one
demonstrates use of
materials and one
conducts the
e-periment
%ocial %tudies-
debater foreign
policy
Math one e-plains
the other does a
thin# aloud
One tal#s and the
other demonstrates
note ta#ing of the
topic
Affected by teachers
personalities and
teaching styles
Most interpersonally
comple- co teaching
approach
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Reflection MathDocument1 pageReflection MathlolaingPas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Past Tense Board GameDocument1 pagePast Tense Board GamelolaingPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (894)
- Each Scrambled Word Is The Name of An InsectDocument1 pageEach Scrambled Word Is The Name of An InsectlolaingPas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Effective Classroom ManagementDocument22 pagesEffective Classroom ManagementNanthini Subramaniam100% (1)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Akueke's Uri Ceremony and Okonkwo's Social StandingDocument1 pageAkueke's Uri Ceremony and Okonkwo's Social StandinglolaingPas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Underline The Correct Answer and Fill in The BlanksDocument1 pageUnderline The Correct Answer and Fill in The BlankslolaingPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Paperstrips ButterflyDocument4 pagesPaperstrips ButterflylolaingPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Lecture 8Document3 pagesLecture 8Lmay PhangPas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Dear TeacherDocument1 pageDear TeacherlolaingPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Learning Environment and Chapter 2Document5 pagesChapter 1 Learning Environment and Chapter 2lolaingPas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Amir and Ratna discuss fishing and shopping for dinnerDocument1 pageAmir and Ratna discuss fishing and shopping for dinnerlolaingPas encore d'évaluation
- Designing Classroom Activity - Task 1a (Group Work) (20 Marks)Document1 pageDesigning Classroom Activity - Task 1a (Group Work) (20 Marks)lolaingPas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Erik Erikson, Bandura & MarieDocument9 pagesErik Erikson, Bandura & MarielolaingPas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Teaching & Learning ActivitiesDocument1 pageTeaching & Learning ActivitieslolaingPas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- Accuracy and FluencyDocument5 pagesAccuracy and FluencylolaingPas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- What are Friends For Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesWhat are Friends For Lesson PlanlolaingPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- ExcerciseDocument3 pagesExcerciselolaingPas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- Possessive Nouns Multiple WsDocument9 pagesPossessive Nouns Multiple WsRaisa Binte HudaPas encore d'évaluation
- To Study Design Effectiveness & Role of Visual Merchandising in Creating Customer AppealDocument3 pagesTo Study Design Effectiveness & Role of Visual Merchandising in Creating Customer AppealAdeel AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Orgs Open Systems PDFDocument3 pagesOrgs Open Systems PDFYàshí ZaPas encore d'évaluation
- Format and Question - ESEM5553 ASSIG 2 UNITARDocument3 pagesFormat and Question - ESEM5553 ASSIG 2 UNITARMiz TatyPas encore d'évaluation
- Language shapes identity and reflects powerDocument2 pagesLanguage shapes identity and reflects powerMida SalisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Leadership Research ProposalDocument11 pagesLeadership Research Proposalarulit04100% (4)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- PSU TOU 442 - Đề CươngDocument17 pagesPSU TOU 442 - Đề CươngThanh Thảng Phan ThịPas encore d'évaluation
- Falsafa e HayatDocument11 pagesFalsafa e HayatKhalil-Ur Rehman0% (1)
- Lecture 7 Horizontal CirculationDocument26 pagesLecture 7 Horizontal CirculationArun Ahlawat100% (3)
- Unraveling Relatively Unclear Stories: A Narrative Analysis of Student-Teachers' Identity WorkDocument12 pagesUnraveling Relatively Unclear Stories: A Narrative Analysis of Student-Teachers' Identity WorkFadly M100% (1)
- Do You Coach Heavy or Light - ChecklistDocument1 pageDo You Coach Heavy or Light - Checklistpnichols2297Pas encore d'évaluation
- LCP Interpretation Manual VIRTUAL v2022.1Document48 pagesLCP Interpretation Manual VIRTUAL v2022.1Khurram ShahzadPas encore d'évaluation
- Education Cover LetterDocument1 pageEducation Cover Letterapi-301539657Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Early Learning Standards IllinoisDocument134 pagesThe Early Learning Standards Illinoisapi-317387547Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Knowledge Assistant: by Lumos LearningDocument23 pagesKnowledge Assistant: by Lumos LearningJasvinder SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Mastering Organizational Behavior 14th Edition Cooper Test BankDocument23 pagesMastering Organizational Behavior 14th Edition Cooper Test Bankgadsmanoutfitqcs100% (31)
- Level2 English Syllabus 002Document5 pagesLevel2 English Syllabus 002Jefferson DavidPas encore d'évaluation
- 0457 Teacher GuideDocument19 pages0457 Teacher GuideBipin Shah100% (2)
- Teaching Reading with PoetryDocument13 pagesTeaching Reading with PoetryEidda Abdul RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- TDCCBCSArabic Syllabus 2017Document24 pagesTDCCBCSArabic Syllabus 2017Januhu ZakaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person 3Document1 pageIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person 3Vergel TorrizoPas encore d'évaluation
- Daily Lesson Log 2018-2019Document21 pagesDaily Lesson Log 2018-2019Anonymous pHooz5aH6VPas encore d'évaluation
- Training TermsDocument21 pagesTraining TermsbattwomanPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Summary Lesson Plan Harmer. How To TeachDocument8 pagesSummary Lesson Plan Harmer. How To TeachGii Gamarra100% (2)
- Queen Mary College, Lahore: Submitted To: Miss Shazia Submitted By: Saba Farooq Rimsha KhalidDocument5 pagesQueen Mary College, Lahore: Submitted To: Miss Shazia Submitted By: Saba Farooq Rimsha KhalidMomna AliPas encore d'évaluation
- COMM201 - Lecture 5 - Language and DeliveryDocument18 pagesCOMM201 - Lecture 5 - Language and DeliveryCarla KingPas encore d'évaluation
- Tcallp ReviewerDocument15 pagesTcallp ReviewerCamela SorianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Use Commas in Lists SentenceDocument5 pagesUse Commas in Lists Sentenceapi-339749711Pas encore d'évaluation
- 88 Present-Perfect-Progressive US Student PDFDocument15 pages88 Present-Perfect-Progressive US Student PDFLeonel Prz Mrtz100% (1)
- Research and TeacherDocument385 pagesResearch and TeacherKiboman CompPas encore d'évaluation
- Jane Burry and Mark Burry The New Mathematics of ArchitectureDocument3 pagesJane Burry and Mark Burry The New Mathematics of Architectureccamiloo moraPas encore d'évaluation