Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Stats Chapter 14 Tools
Transféré par
Sean CallahanDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Stats Chapter 14 Tools
Transféré par
Sean CallahanDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
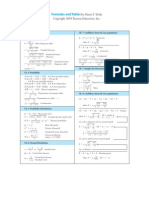
CHAPTER 14 TOOLS
14.2
Correlation Coefficient
n 8
r 0.869374114 y x
r =CORREL(array 1, array 2) 0.869374114
Starting
Salary
GPA
2,700 3.2
2,800 3.4
2,200 2.6
2,700 3.4
3,200 3.7
2,900 3.9
2,100 2.5
2,300 3.3
y x
20,900 26
Significance of the Correlation Coefficient - Hypothesis Testing When the Correlation Coefficient is equal to zero, there is no realtionship between x and y.
(Correlation Coefficient)
0.01
r -0.68377
n (number of ordered pairs) 11
t (Test Statistic for ) = r / (1-r
2
)/(n -2)] -2.81117822
degrees of freedom 9
t
/2
(critical t score)(see table 5 in appendix) 2.353
14.3
Regression Line Equation and Slope
^
y = a + bx
n 8
b 1.815730337
a 2.905617978
x
Temperat
ure
Total Sum of Squares 21
SST (equal to SSE + SSR) 730 13
21
SSE (Sum of Squares Error) 179.8337079 20
8
SSR (Sum of Squares Regression) 550.1662921 14
19
Sample Coefficient of Determination (
2
is the population coefficient of determination)> 21
R
2
= SSR / SST 0.753652455
F Test Statistic
F = SSR / (SSE/(n-2)) 18.35583435
x
Critical F Score 137
D
1
(SSR Degrees of Freedom always equals 1) 1
D
2
(SSE Degrees of Freedom is n-2) 6
USE THE RIGHT TABLE FOR THE RIGHT
14.4
Confidence Interval and Prediction Interval Construction
Use phStat on the data provided Year GPA
INCLUDE THE DATA COLUMN NAMES 1 3.07
2 2.88
3 2.96
4 2.85
5 2.98
6 3.05
7 3.07
8 2.99
9 3.19
10 3.14
11 3.16
14.5 CI = b t
/2
* s
b
x
a= 17.54340071 Minutes
b= -0.562425684 3
8
n= 10 0
SSE= 30.29726516 6
s
e
= 1.946062215 6
s
b
= 0.21220652 1
= 4.7 9
0.05 2
df(n-2)= 8 7
t
/2
= 2.306 5
UCL= -0.07307745
LCL= -1.051773918
SST= 56.9
SSR= 26.60273484 x
47
If actual value isn't specified for the
confidence and prediction interval x value,
insert the last value of x if the data on the x
axis is chronological. You can use the ANOVA
table to find the P value and other fun stuff!
R
2
= SSR / SST 0.467534883
F = SSR / (SSE/(n-2)) 7.024458399
t= (b-) / s
b
(assuming = 0 ) -2.650369483
Cumulative Probabilities for standard normal distribution tables are on page 858 and 859
WORKING ZONE-------------------------------------------
Minutes Rating
xy y
2
x
2
3 14
8 13
8640 7,290,000 10.24 0 17
9520 7,840,000 11.56 6 11
5720 4,840,000 6.76 6 15
9180 7,290,000 11.56 1 17
11840 10,240,000 13.69 9 14
11310 8,410,000 15.21 2 20
5250 4,410,000 6.25 7 14
7590 5,290,000 10.89 5 14
xy y
2
x
2
-0.68377
69050 55,610,000 86.16
When the Correlation Coefficient is equal to zero, there is no realtionship between x and y.
y xy x
2
y
2
Demand
47 987 441 2209
30 390 169 900
36 756 441 1296
40 800 400 1600
16 128 64 256
25 350 196 625
44 836 361 1936
34 714 441 1156
>
2
measures the percentage of the dependent
variable's total variation that can be explained by an
independent variable
y xy x
2
y
2
272 4961 2513 9978
(see cumulative probabilities for sandard normal distribution table)
In the two tail test, the yielded p is multiplied by two.
y xy
x
2
y
2
Rating 16.98098
14 42 9 196 16.41855 0.562426
13 104 64 169
17 0 0 289
11 66 36 121
15 90 36 225
17 17 1 289
14 126 81 196
20 40 4 400
14 98 49 196
14 70 25 196
y xy x
2
y
2
149 653 305 2277
>
2
measures the percentage of the dependent
variable's total variation that can be explained by an
independent variable
When
2
is equal to zero, that means that variation in y
outcomes is not explained by x data values; which
indicates that there is no relationship between x and y.
The p value is the probability of observing a sample mean at least as extreme as the one
selected for the hypothesis test, assuming the null hypothesis is true.
>
2
measures the percentage of the dependent
variable's total variation that can be explained by an
independent variable
>
2
measures the percentage of the dependent
variable's total variation that can be explained by an
independent variable
When
2
is equal to zero, that means that variation in y
outcomes is not explained by x data values; which
indicates that there is no relationship between x and y.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex ArgumentD'EverandMathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex ArgumentPas encore d'évaluation
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesD'EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesPas encore d'évaluation
- Stat11t - Formulas-Triola 11th Ed.Document8 pagesStat11t - Formulas-Triola 11th Ed.survivorfan2000Pas encore d'évaluation
- QM II Formula SheetDocument2 pagesQM II Formula Sheetphanindra sairamPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 12Document47 pagesLecture 12traceynguyen1205Pas encore d'évaluation
- Formula Sheet (1) Descriptive Statistics: Quartiles (n+1) /4 (n+1) /2 (The Median) 3 (n+1) /4Document13 pagesFormula Sheet (1) Descriptive Statistics: Quartiles (n+1) /4 (n+1) /2 (The Median) 3 (n+1) /4Tom AfaPas encore d'évaluation
- Exa Eco II Reevaluacion 2013 Javi ENGLISH DEFINITIVO SOLUZIONIDocument3 pagesExa Eco II Reevaluacion 2013 Javi ENGLISH DEFINITIVO SOLUZIONIdamian camargoPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Statistics and Probability For Engineers, 5th EditionDocument23 pagesApplied Statistics and Probability For Engineers, 5th EditionMuhammadHazmiMokhtar75% (4)
- Analyze The E-Views Report: R Var ( Y) Var (Y) Ess Tss Var (E) Var (Y) Rss Nvar (Y) R RDocument5 pagesAnalyze The E-Views Report: R Var ( Y) Var (Y) Ess Tss Var (E) Var (Y) Rss Nvar (Y) R REmiraslan MhrrovPas encore d'évaluation
- Polynomial Curve FittingDocument44 pagesPolynomial Curve FittingHector Ledesma IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- List MF9: MATHEMATICS (8709, 9709) Higher Mathematics (8719) STATISTICS (0390)Document8 pagesList MF9: MATHEMATICS (8709, 9709) Higher Mathematics (8719) STATISTICS (0390)Muhammad FarhanPas encore d'évaluation
- A Level - Maths - List of FormulaeDocument10 pagesA Level - Maths - List of Formulaesherlyn may lolPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Regression and Correlation: - 0 Positive Association - 0 Negative Association - 0 No AssociationDocument31 pagesLinear Regression and Correlation: - 0 Positive Association - 0 Negative Association - 0 No AssociationSodhi NirdeepPas encore d'évaluation
- Formula Sheet For StatisticsDocument43 pagesFormula Sheet For StatisticsmibuhariPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9 Tools: Z Test Statistic for a Hypothesis Test of the Population Mean (when σ is known)Document5 pagesChapter 9 Tools: Z Test Statistic for a Hypothesis Test of the Population Mean (when σ is known)Sean CallahanPas encore d'évaluation
- Improved Exponential Estimator For Population Variance Using Two Auxiliary VariablesDocument8 pagesImproved Exponential Estimator For Population Variance Using Two Auxiliary VariablesIlieCraciunPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 CDocument27 pagesChapter 7 CMahip Singh PathaniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bivariate AnalysisDocument19 pagesBivariate AnalysisMukteshwar Mishra100% (2)
- 7.1 Two Phase SamplingDocument5 pages7.1 Two Phase SamplingKEEME MOTSWAKAEPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5: Regression and Correlation: Bivariate Data) and Relationship Between The Two VariablesDocument5 pagesChapter 5: Regression and Correlation: Bivariate Data) and Relationship Between The Two VariablesSrinyanavel ஸ்ரீஞானவேல்Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mean, Variance, Moments and Characteristic Functions: PillaiDocument50 pagesMean, Variance, Moments and Characteristic Functions: PillaiShraddha SaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistics FormulasDocument8 pagesStatistics Formulascem9066100% (3)
- Linier RegressionDocument19 pagesLinier RegressionAriful RamadhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Regression: Major: All Engineering Majors Authors: Autar Kaw, Luke SnyderDocument25 pagesLinear Regression: Major: All Engineering Majors Authors: Autar Kaw, Luke Snydergunawan refiadi100% (1)
- Ch02 - Coulomb's Law and Electric Field IntensityDocument26 pagesCh02 - Coulomb's Law and Electric Field Intensityjp ednapilPas encore d'évaluation
- MF9 Formula Sheet - List of FormulasDocument9 pagesMF9 Formula Sheet - List of FormulasBrendon Nyabinde75% (4)
- Homework: Ideal FlowsDocument15 pagesHomework: Ideal Flowsgaldo2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Formula Sheet and Statistical TablesDocument11 pagesFormula Sheet and Statistical TablesdonatchangePas encore d'évaluation
- Stability of Nuclear Reactor: Point Model Analysis: K. Bu Cys, D. ŠvitraDocument13 pagesStability of Nuclear Reactor: Point Model Analysis: K. Bu Cys, D. ŠvitraUmair FarooqPas encore d'évaluation
- PowerDocument29 pagesPowerAbhijit WankhedePas encore d'évaluation
- AugustineDocument4 pagesAugustineAshley LauretaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch17 Curve FittingDocument44 pagesCh17 Curve Fittingvarunsingh214761Pas encore d'évaluation
- Effective Action and Renormalization Group Flow of Anisotropic SuperconductorsDocument19 pagesEffective Action and Renormalization Group Flow of Anisotropic SuperconductorssatyabashaPas encore d'évaluation
- STAT 266 - Lecture 2Document45 pagesSTAT 266 - Lecture 2Essumang Castro FrankPas encore d'évaluation
- SCM Session 6 Correlation and Regression AnalysisDocument63 pagesSCM Session 6 Correlation and Regression AnalysisANKITA LUTHRA EPGDIB 2018-20Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Econometrics HealthDocument183 pagesBasic Econometrics HealthAmin HaleebPas encore d'évaluation
- Elastic Scattering of A Quantum Particle by A Central PotentialDocument16 pagesElastic Scattering of A Quantum Particle by A Central PotentialJoaquin Montes FernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Correlation Between Interval and Any Nominal VariablesDocument30 pagesCorrelation Between Interval and Any Nominal VariablesolpotPas encore d'évaluation
- Assign4 SolDocument5 pagesAssign4 Solmorteza2885Pas encore d'évaluation
- Coulombic Interaction in Magnetic Field: 1 Traditional Electronic SystemDocument5 pagesCoulombic Interaction in Magnetic Field: 1 Traditional Electronic SystemRaymond AdamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework 1 Solutions: 1 Jackson 1.3Document5 pagesHomework 1 Solutions: 1 Jackson 1.3ahsanqauPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 5Document31 pagesCH 5probability2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Statistics For Management and Economics, Eighth Edition FormulasDocument16 pagesStatistics For Management and Economics, Eighth Edition FormulasLeyu WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Regression EquationDocument56 pagesRegression EquationMuhammad TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- MC0074 - Statistical and Numerical Methods Using C++Document14 pagesMC0074 - Statistical and Numerical Methods Using C++Ravish RavindranPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical Papers 47, 471-479 (2006)Document9 pagesStatistical Papers 47, 471-479 (2006)أبن الرماديPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions Advanced Econometrics 1 Midterm 2013Document3 pagesSolutions Advanced Econometrics 1 Midterm 2013Esmée WinnubstPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Fall 2007 Exam PDFDocument7 pages3 Fall 2007 Exam PDFAchilles 777Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ch17 Curve FittingDocument44 pagesCh17 Curve FittingSandip GaikwadPas encore d'évaluation
- The Academy of Aerospace Quality (Aaq) : Prepared by Edgardo J. Escalante, PH.DDocument79 pagesThe Academy of Aerospace Quality (Aaq) : Prepared by Edgardo J. Escalante, PH.DaaqipaperPas encore d'évaluation
- Semi Classic A Electron OpticsDocument15 pagesSemi Classic A Electron Opticslenc46Pas encore d'évaluation
- ElectromagneticsDocument10 pagesElectromagneticsLencie Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- STAT2201 - Ch. 14 Excel Files - UpdatedDocument41 pagesSTAT2201 - Ch. 14 Excel Files - UpdatedGurjot SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- A Simple Test For Heteroscedasticity and Random Coefficient Variation (Breusch y Pagan)Document9 pagesA Simple Test For Heteroscedasticity and Random Coefficient Variation (Breusch y Pagan)Andrés JiménezPas encore d'évaluation
- Formula CardDocument13 pagesFormula CardDasaraaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes 1Document23 pagesNotes 1Daniel Fortes ManoelPas encore d'évaluation
- An A RegDocument3 pagesAn A RegHilda AprinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsD'EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- GridDataReport KEL 2Document7 pagesGridDataReport KEL 2Anisa Noor HidayahPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Analysis ProblemsDocument12 pagesData Analysis Problems陈凯华Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pampers CaseDocument7 pagesPampers CaseUbaid Salahuddin MoorooPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Machine Learning IIT KGP Week 2Document14 pagesIntroduction To Machine Learning IIT KGP Week 2Akash barapatrePas encore d'évaluation
- Keboleh PercayaanDocument8 pagesKeboleh PercayaanAiez DisenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Residual AnalysisDocument6 pagesResidual AnalysisGagandeep SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- (Libro) Arellano - Panel Data Econometrics 2003Document244 pages(Libro) Arellano - Panel Data Econometrics 2003Federico Vallejo MondragónPas encore d'évaluation
- Slide 12 - Dimentionality Reduction - PCADocument26 pagesSlide 12 - Dimentionality Reduction - PCALôny NêzPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of Logistic Regression To People-AnalyticsDocument30 pagesApplication of Logistic Regression To People-AnalyticsSravan KrPas encore d'évaluation
- Categorical Dependent Variable Regression Models Using STATA, SAS, and SPSSDocument32 pagesCategorical Dependent Variable Regression Models Using STATA, SAS, and SPSSyuva rajPas encore d'évaluation
- Price Impact of Order Flow Imbalance: Multi-Level, Cross-Sectional and ForecastingDocument40 pagesPrice Impact of Order Flow Imbalance: Multi-Level, Cross-Sectional and Forecastingicosahedron_manPas encore d'évaluation
- Stat Lab 2Document1 pageStat Lab 2docbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Jurnal PemasaranDocument12 pagesJurnal PemasaranGloria LengkeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Machine Learning Mindmap PDFDocument5 pagesMachine Learning Mindmap PDFWences Villegas100% (1)
- 3.2 LSRL Worksheet Parts I 1-4Document2 pages3.2 LSRL Worksheet Parts I 1-4Fausto SosaPas encore d'évaluation
- MTGW6107 6112 Presetation13 14Document6 pagesMTGW6107 6112 Presetation13 14Deena Clare ThomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions To Problems 11.1 Because of Covariance StationarityDocument7 pagesSolutions To Problems 11.1 Because of Covariance StationaritySema GençPas encore d'évaluation
- DirichletReg VigDocument13 pagesDirichletReg VigLucas GallindoPas encore d'évaluation
- Andrew Rosenberg - Lecture 14: Neural NetworksDocument50 pagesAndrew Rosenberg - Lecture 14: Neural NetworksRoots999Pas encore d'évaluation
- SMSPDocument39 pagesSMSPzulaiha rahasiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Self-Interaction Matrix (SSIM)Document28 pagesStructural Self-Interaction Matrix (SSIM)Subroto SarkerPas encore d'évaluation
- Neural Network Toolbox Command ListDocument4 pagesNeural Network Toolbox Command ListAditya ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Data Analysis For Managers (MBA561E) Cia 1 Data Analysis AssignmentDocument16 pagesAdvanced Data Analysis For Managers (MBA561E) Cia 1 Data Analysis AssignmentSujith VichuPas encore d'évaluation
- K-Nearest Neighbors AlgorithmDocument11 pagesK-Nearest Neighbors Algorithmwatson191Pas encore d'évaluation
- 11-Logistic RegressionDocument27 pages11-Logistic RegressionNaitik TyagiPas encore d'évaluation
- Stats2 - qn2Document2 pagesStats2 - qn2cyrusPas encore d'évaluation
- ArimaDocument12 pagesArimaDr. Priya Iyer K BPas encore d'évaluation
- 1Document16 pages1procasinator procasinatorPas encore d'évaluation
- Wollo University Kiot Department of Industrial Engineering Worksheet On ForecastingDocument3 pagesWollo University Kiot Department of Industrial Engineering Worksheet On ForecastingTalema100% (1)
- 251-Article Text-537-2-10-20210202Document8 pages251-Article Text-537-2-10-20210202Nauffan MuftiPas encore d'évaluation
![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1714993295?v=1)