Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
ISO 9001 Lead Auditor Course Charts
Transféré par
Pili ColoradaDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ISO 9001 Lead Auditor Course Charts
Transféré par
Pili ColoradaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ISO 9001 Lead Auditor Course
The following diagrams supplement the ISO 9001 Lead Auditor Course.
Read these diagrams in conjunction with the relevant section (numbers) in
the course.
Figure 1.3
Quality Management
The definition of Quality Management is coordinated activities to direct and control an
organization with regard to quality. The coordinated activities (quality management tools)
identified in the ISO 9000:2000 standard are as depicted in the following diagram:
Quality Management System
To manage
- Policies - Proactive - Reactive - Effectiveness
- Objectives - Preventive - Detective - Efficiency
- Processes - Confidence - Conformity - Capability
- Resources
- Controls
Conformity
Consistency
Assurance
Processes
ISO 9001
Standard
QMS
Principles
Quality
Management
System
Quality
Improvement
Quality
Control
Quality
Assurance
Quality
Planning
Figure 2.2
A typical documentation structure is depicted in the following
pyramid diagram:
Procedures
(who, what, when, where)
Operational
documentation
(how)
Quality
Records
Quality Manual Policy
4. 2.2
Procedures
4.2. 3, 4.2.4, 8. 2.2,
8.3, 8.5.2, and 8. 5. 3
(plus optional procedures)
Documents needed to plan, operate
and control processes
Evidence of results achieved
& activities performed
(see Control of Records: 4.2.4)
Level 1
Describes company policy relating
to each ISO 9001 requirement
Level 2
Level 3
Level 4
QMS Documentation
TYPICAL HEIRARCHY
Figure 3.9
RAB/QSA ACCREDITATION PROGRAM
ACCREDITING
AUTHORITY
REGISTRARS
REGISTERED
ORGANIZATIONS
CUSTOMERS
NATIONAL GOVERNMENT/ TRADE ASSOCIATIONS
3
RD
PARTY
AUDITORS
INTERNAL
AUDITORS
RAB
TRAINING
ORGANIZATIONS
INDEPENDENT
AUDITORS
LEAD AUDITOR
TRAINING
TRAINING REGISTRATION
RAB
RAB
Figure 4.1
Managing an audit program
Managing an Audit Program Process Flow
PLAN DO CHECK ACT
- Objectives - Schedule audits - Monitor
- Extent - Evaluate auditors - Review
- Responsibilities - Select teams - Identify need for
- Resources - Direct activities for corrective action
- Procedures - Maintain records - Identify opportunities
to improve
AUTHORIZE
PROGRAM
IMPLEMENT
MONITOR
and
REVIEW
ESTABLISH
AUDIT
ACTIVITIES
IMPROVE
AUDITOR
COMPETENCE
Figure 4.2.2.3
Internal Audit Planning and Preparation
Departments Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec
Sales P A A
Management P
Technical P A A
Planning P A
Logistics A P A
Purchasing A P A
Warehouse 1 A A P
Warehouse 2 A P
Process 1 A A P
Process 2 A A P
Calibration A P
Key: P = Audits planned to be conducted once a year
A = Additional audits considering STATUS, IMPORTANCE, and prior AUDITS
Figure 5.3.2.1
Audit Plan - ABC, Inc.
Auditors: Group 1 - Mr. M. Damon (Team Leader); Mr. R. Moore
Group 2 - Ms. A. Jolie; Mr. R. Anderson
Audit Date: Month / Day(s) / Year
DAY 1 TIME GROUP 1 GROUP 2
08.30-09.00 Opening Meeting Opening Meeting
09.00-09.30 Plant Tour Plant Tour
09.30-10.30 Quality Manual Quality Manual
10.30-12.00 Contract Engineering Warehouse
12.00-12.30 Audit Team Prep Audit Team Prep
12.30-13.00 Lunch Lunch
13.00-14.30 Sales/Customer Support Purchasing
14.30-16.00 Design Engineering Production Scheduling
16.00-18.00 Product Development Manufacturing Engineering
18.00-18.30 Review Review
DAY 2
TIME
GROUP 1
GROUP 2
08.30-10.30 Software Systems Assembly
10.30-12.00 Calibration - Lab Assembly/Test
12.00-12.30 Audit Team Prep Audit Team Prep
12.30-13.00 Lunch Lunch
13.00-14.30 Industrial Engineering Test/Calibration - Mfg
14.30-16.00 Quality Assurance Final Inspection/Packaging
16.00-17.00 Audit Team Meeting Audit Team Meeting
17.00- Closing Meeting Closing Meeting
Figure 5.6.1
Audit Checklist
Area audited: Document Control Procedure DC-05
Look at: Procedure DC-05
Look for: Conformity of procedure to policies and ISO 9001 standard
Control of all document types, including external documents
Look at: Document Approvals
Look for: Approvals by authorized persons prior to document issue
Evidence of approvals, e.g., signature or electronic proof
Look at: Document Changes
Look for: Documents reviewed, updated as necessary, and re-approved
Current revision status identified along with nature of changes
Look at: Document Usage
Look for: Legible and identifiable versions available at points of use
No obsolete documents in use; retained documents identified
Figure 6.1.4
Collecting and verifying information
Process for collecting information to reaching audit conclusions
Audit evidence
Audit findings
Sources of
information
Evaluate against audit
criteria
Collect by appropriate
sampling and verifying
Reviewing
Audit conclusions
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- ISO 9001-2015 IA ExamDocument7 pagesISO 9001-2015 IA ExamOoi Jun Lin80% (20)
- Iso 9001 Audit Trail: A Practical Guide to Process Auditing Following an Audit TrailD'EverandIso 9001 Audit Trail: A Practical Guide to Process Auditing Following an Audit TrailÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Case Study For ISO9001 (2015)Document2 pagesCase Study For ISO9001 (2015)Jun Ooi80% (10)
- Quality Management Iso9001:2015 Changes: A Guide to ImplementationD'EverandQuality Management Iso9001:2015 Changes: A Guide to ImplementationÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Internal Audit Guidance ExampleDocument2 pagesInternal Audit Guidance Examplesunderrajan100% (1)
- Cracking the Case of ISO 9001:2015 for Manufacturing: A Simple Guide to Implementing Quality Management in ManufacturingD'EverandCracking the Case of ISO 9001:2015 for Manufacturing: A Simple Guide to Implementing Quality Management in ManufacturingPas encore d'évaluation
- Lead Auditor Workbook Updated To 2008 VerDocument116 pagesLead Auditor Workbook Updated To 2008 VerSaaidAgasi50% (2)
- QMS LA Course MaterialDocument161 pagesQMS LA Course MaterialRamesh mudunuri85% (13)
- QMS 9001-2015 Internal Auditor Training Presentation PDFDocument17 pagesQMS 9001-2015 Internal Auditor Training Presentation PDFNader Shdeed67% (9)
- LOYDS QMS Pre-Course WorkDocument48 pagesLOYDS QMS Pre-Course WorkDenzil D'Souza100% (3)
- ISO9001 The Ultimate GuideDocument20 pagesISO9001 The Ultimate GuideAymen Badreddine BouderbalaPas encore d'évaluation
- ISO 9001-2015 Mandatory Documents RequiredDocument1 pageISO 9001-2015 Mandatory Documents RequiredAnonymous GWDhNTOKO100% (5)
- Iso 9001 2015 Gap QuestionsDocument6 pagesIso 9001 2015 Gap QuestionsL100% (5)
- Iso 9001 2015 Documented InformationDocument7 pagesIso 9001 2015 Documented InformationSyed Mahmud Habibur RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 4 - Casestdudies 1 Iso 9001-2015Document2 pagesAssignment 4 - Casestdudies 1 Iso 9001-2015Iena Marlyssa Jaffar33% (3)
- Internal Audit ChecklistDocument74 pagesInternal Audit Checklistinternationalindustrialsprings100% (1)
- ISO 9001 2015 TrainingDocument26 pagesISO 9001 2015 TrainingPraveen Sharma100% (2)
- ISO 9001 Lead Auditor Course BrochureDocument4 pagesISO 9001 Lead Auditor Course Brochurerasimc94750% (1)
- 9001LA MockExam-KeyDocument17 pages9001LA MockExam-KeyAamir Sirohi92% (26)
- ISO 9001 Auditor Training Q&ADocument10 pagesISO 9001 Auditor Training Q&AAli Zafar71% (7)
- Clause by Clause Explanation of ISO 9001 2015 enDocument21 pagesClause by Clause Explanation of ISO 9001 2015 enMisael100% (16)
- ISO 9001 QuizDocument4 pagesISO 9001 QuizGVS Rao0% (1)
- Iso 9001 2015Document54 pagesIso 9001 2015qajjepl100% (13)
- ISO 9001-2015 Presentation - InfomasysDocument25 pagesISO 9001-2015 Presentation - Infomasysrasimc9475100% (5)
- Audit Plan - ISO 9001 - ISO 14001 - 2015Document8 pagesAudit Plan - ISO 9001 - ISO 14001 - 2015Corrosion Factory100% (2)
- Lead Auditor TS 16949Document95 pagesLead Auditor TS 16949tran huytrungPas encore d'évaluation
- Certified ISO 9001 Lead Auditor - Two Page BrochureDocument2 pagesCertified ISO 9001 Lead Auditor - Two Page BrochurePECBCERTIFICATIONPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution Section 1 and 2 IRQA ExamDocument5 pagesSolution Section 1 and 2 IRQA Examroswan100% (4)
- QMS Auditor / Lead Auditor CourseDocument13 pagesQMS Auditor / Lead Auditor Courserevival195Pas encore d'évaluation
- Auditor TesDocument19 pagesAuditor TesRinto Erwiansa PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- Audit Plan: Order No. Customer NoDocument2 pagesAudit Plan: Order No. Customer NofaradayPas encore d'évaluation
- Iso Lead Auditor Exam Questions and AnswersDocument7 pagesIso Lead Auditor Exam Questions and Answersjack forest8% (12)
- Iso 9001 2015 Quality Objectives and DefinitionsDocument20 pagesIso 9001 2015 Quality Objectives and Definitionsvenkata chowdary83% (12)
- ISO 9001-2015 ChecklistDocument28 pagesISO 9001-2015 Checklisthesham_tm3658100% (3)
- Checklist - Audit - ISO 9001-2015Document144 pagesChecklist - Audit - ISO 9001-2015pratomo E T100% (1)
- ISO 9001-2015 CluasesDocument1 pageISO 9001-2015 Cluasesmanuprbr100% (10)
- ISO 9001 2015 Internal Audit Checklist SampleDocument9 pagesISO 9001 2015 Internal Audit Checklist Samplemocharara65% (17)
- NCR Vs EvidenceDocument2 pagesNCR Vs EvidenceMAT-LION100% (1)
- Full IssueDocument76 pagesFull IssueAbdelmutalab Ibrahim Abdelrasul81% (16)
- Lead AuditorDocument13 pagesLead Auditorravimanas100% (3)
- 0.2 Precourse Assignment-Understanding ISO 9001Document10 pages0.2 Precourse Assignment-Understanding ISO 9001sidath thiranjayaPas encore d'évaluation
- ISO 9001-2015 Presentation PDFDocument92 pagesISO 9001-2015 Presentation PDFDaniel Tan100% (3)
- IQA Auditor TrainingDocument112 pagesIQA Auditor Trainingpapplion100% (5)
- ISO TC 176 Quality Management and Quality AssuranceDocument7 pagesISO TC 176 Quality Management and Quality AssuranceJMauricio SalgadoPas encore d'évaluation
- F103-12-QMS-2015 ISO 9001 2015 Checklist GuidanceDocument42 pagesF103-12-QMS-2015 ISO 9001 2015 Checklist GuidanceAnand Dubey96% (25)
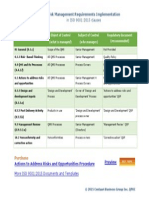
- Risk Management Requirements Implementation in ISO 9001:2015 ClausesDocument5 pagesRisk Management Requirements Implementation in ISO 9001:2015 ClausesCentauri Business Group Inc.86% (7)
- ISO 9001 Internal Audit (Training Material)Document11 pagesISO 9001 Internal Audit (Training Material)Luis Gustavo Pacheco67% (6)
- ISO 9001 Training SeriesDocument16 pagesISO 9001 Training SeriesSiva Kumar25% (4)
- Print Version Lead Auditor ModuleDocument90 pagesPrint Version Lead Auditor Modulekevinmathew27Pas encore d'évaluation
- Risk Management Requirements Implementation in ISO 9001 2015 ClausesDocument1 pageRisk Management Requirements Implementation in ISO 9001 2015 ClausesCentauri Business Group Inc.50% (2)
- ISO 9001 Training PresentationDocument9 pagesISO 9001 Training Presentationkunalkp88Pas encore d'évaluation
- ISO 9001:2015 Quality Management Systems Requirements Part 1Document33 pagesISO 9001:2015 Quality Management Systems Requirements Part 1ofusandeepPas encore d'évaluation
- ISO 9001 Training MaterialDocument249 pagesISO 9001 Training MaterialAnil Kumar100% (2)
- Pecb Iso 9001 Lead Auditorexam Preparation GuideDocument15 pagesPecb Iso 9001 Lead Auditorexam Preparation GuidefaizanAkhtar100% (1)
- Lead Auditor 9001 Self AssessmentDocument5 pagesLead Auditor 9001 Self AssessmentArshad Mahmood76% (50)
- ISO 9001 Internal Lead AuditoDocument9 pagesISO 9001 Internal Lead AuditoLedo HoussienPas encore d'évaluation
- Iso9001 NotesDocument10 pagesIso9001 NotesDEVINA GURRIAHPas encore d'évaluation
- ISO 9001-2015 ChangesDocument15 pagesISO 9001-2015 Changesmukundiso88% (8)
- ISO 9001:2015 QMS Implementation Program (Presentation)Document16 pagesISO 9001:2015 QMS Implementation Program (Presentation)Centauri Business Group Inc.96% (46)
- Arkitektonisk Betong Concrete-Formwork2 PDFDocument88 pagesArkitektonisk Betong Concrete-Formwork2 PDFJohn Nueva EspanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Berenberg European AerospaceDefence Sector Report Jun 17 2014 330pgs (Initiations)Document330 pagesBerenberg European AerospaceDefence Sector Report Jun 17 2014 330pgs (Initiations)angadsawhneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Fault-Tolerant Control of An Octorotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Under Actuators FailuresDocument175 pagesFault-Tolerant Control of An Octorotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Under Actuators FailuresMPas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum Vitae: Industrial ExperienceDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Industrial ExperienceSheikh NasiruddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Shaper Machine DefinitionDocument3 pagesShaper Machine DefinitionMuhammad AbubakarPas encore d'évaluation
- Market Drivers, Supply and Demand For PVC: IHS ChemicalDocument22 pagesMarket Drivers, Supply and Demand For PVC: IHS ChemicalGawang PamungkasPas encore d'évaluation
- Hardox in My BodyDocument2 pagesHardox in My BodyEhab Attia SelimPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Management Methodologies: A Comparative Analysis: October 2012Document14 pagesProject Management Methodologies: A Comparative Analysis: October 2012ibPas encore d'évaluation
- Atkins Analysis Design Modern Roundabout 4052013Document2 pagesAtkins Analysis Design Modern Roundabout 4052013kim suarezPas encore d'évaluation
- Bonita BPM and Aura Portal ComparisonDocument9 pagesBonita BPM and Aura Portal ComparisonYuvraj KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Four Cavity Foil Container Making Machine PDFDocument12 pagesFour Cavity Foil Container Making Machine PDFBijayShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Welcome To The Ministry of Roads and Highways - Docx - 0Document12 pagesWelcome To The Ministry of Roads and Highways - Docx - 0STP DesignPas encore d'évaluation
- Mil STD 29aDocument137 pagesMil STD 29aPablo J. González MoraPas encore d'évaluation
- Locating DevicesDocument7 pagesLocating DevicesRavi Arjun KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Installing Pacific Fighters (PF)Document8 pagesInstalling Pacific Fighters (PF)Αγγελος ΚαρλεςPas encore d'évaluation
- Actix Analyzer Getting Started GuideDocument68 pagesActix Analyzer Getting Started GuideBeliever100% (2)
- Sa Residence Fee ProposalDocument6 pagesSa Residence Fee Proposalapi-245735583Pas encore d'évaluation
- Business Process Summary May 09Document10 pagesBusiness Process Summary May 09ahza hanifPas encore d'évaluation
- CDP Model of Purchasing A Bike in Current Indian Scenario.Document46 pagesCDP Model of Purchasing A Bike in Current Indian Scenario.mukabbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Chevron Policy StatementDocument3 pagesChevron Policy StatementRahmat Budi HartantoPas encore d'évaluation
- QA-000-AA-5013 ITP For Structure Steel Erection Works Rev1 (APPROVED)Document10 pagesQA-000-AA-5013 ITP For Structure Steel Erection Works Rev1 (APPROVED)miaicarba100% (2)
- History of Lean ManufacturingDocument14 pagesHistory of Lean ManufacturingVan Michael100% (2)
- KPLC DistributionDocument598 pagesKPLC DistributionRahabGathoni50% (2)
- Silo - Tips - Industrial Services StrategiesDocument62 pagesSilo - Tips - Industrial Services StrategiesRr.Annisa BudiutamiPas encore d'évaluation
- 4230 405 PVI M 402 03 InstrumentationCable Technicalspecification C2Document9 pages4230 405 PVI M 402 03 InstrumentationCable Technicalspecification C2ajju1378Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basketball Court ProposalDocument8 pagesBasketball Court ProposalMd. NazmulPas encore d'évaluation
- Kashan Aziz CV SBPDocument4 pagesKashan Aziz CV SBPSohail MohdPas encore d'évaluation
- CT-6B Flysky Manual InstructionDocument72 pagesCT-6B Flysky Manual InstructionBo ĐỗPas encore d'évaluation
- Oomd BasicsDocument18 pagesOomd BasicsVignesh KarthiPas encore d'évaluation
- InterDocument5 pagesInterChoon Zhe ShyiPas encore d'évaluation
- University of Chicago Press Fall 2009 CatalogueD'EverandUniversity of Chicago Press Fall 2009 CatalogueÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- University of Chicago Press Fall 2009 Distributed TitlesD'EverandUniversity of Chicago Press Fall 2009 Distributed TitlesÉvaluation : 1 sur 5 étoiles1/5 (1)