Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
01 The Human Skeleton
Transféré par
Annabelle Poniente Hertez0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
155 vues2 pages01 the Human Skeleton
Titre original
01 the Human Skeleton
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce document01 the Human Skeleton
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
155 vues2 pages01 The Human Skeleton
Transféré par
Annabelle Poniente Hertez01 the Human Skeleton
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
Interactive and Integrative Lesson Plan
The Human Skeleton
(Date)
I. Objectives
Cognitive : Describe the structure and function of the skeletal system.
Describe some bones that make up the skeletal system.
Identify the bones that protect body parts.
Psychomotor : Observe the structure of bones and relate the structure to its function.
Affective : Recognize that the strength of a nation depends on the strength of its individuals, just as the
strength of the skeleton depends upon the strength of its individual bones.
II. Integration
A. Values: elf!preservation and protecting your body.
. !akaba"an: "ivic duty and #ation building
III. Subject !atter
1. #nit : $uman keletal and %uscular ystem
To$ic : &he $uman keleton
Sub%to$ic : 'ones that protect
&e'erence : i&e(tbook ), cience and $ealth ) by *essie +. ,illegas, pages -!.
!aterials : model or picture of a skeleton, pictures of houses, umbrella
2. (once$ts)&elated Ideas
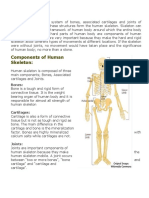
1. &he human skeleton is the frame/ork of the body. It is a to/er of bones put together by hinges and joints. It is
light/eight but strong. It is made up of -01 different bones that are designed to
a2 support the body,
b2 enable movement, and
c2 protect some body parts.
-. %an is a vertebrate animal. +ll vertebrates have an internal skeletal system, called endoskeleton.
3. &he human skeletal system is made up of t/o parts:
a2 +(ial skeleton. It is made of the bones of the skull, ribs, and the vertebrae. &he vertebrae, /hich make up
the backbone, hold the body upright
b2 +ppendicular skeleton. It includes all the bones attached to the a(ial skeleton, such as the bones of the
arms and legs, collarbones, hipbones, and shoulder bones. &he femur, fibula and tibia make up the legs4
the humerus, radius and ulna make up the arms.
). &he human skeletal system is a real masterpiece of structural design, /ith each part tailored to do a particular
job. One major function of the bones is to protect the body5s organ or a number of organs.
a2 &he vertebrae protect the spinal cord4
b2 the skull protects the brain4
c2 the rib cage protects the heart and lungs4
d2 the pelvic bones guard the kidneys and other organs of the abdomen.
3. Process Skills
Observing, inferring
IV. Procedure
A. Pre$arator" Activities
6reetings
"hecking of attendance
"hecking of assignments
1. !otivation
(Show pictures of different types of houses and buildings) All houses and buildings have practically the same parts like
roof, wall, floor, and rooms. And yet one house is different from another. What makes them different from one another
2. Presentation
!ou all must have seen how houses were built before the roofs and walls were assembled. "irst, the posts, beams and
trusses were constructed to give the house its framework upon which the walls and roofs were laid. #he final shape of a house
depends on the structural layout of these posts, beams and trusses.
$very structure has a framework. (%pen an umbrella) #his umbrella, for e&le, has these steel rods and 'oints for its
framework. (mbrellas may vary in form and shape depending on how these rods are 'oined together.
#he human body is no different. )t also has a framework, called skeleton, so magnificently designed and balanced that he
can run, 'ump, dance, bend, and do a great variety of movements in spite of his small feet. #ogether with muscles, man*s skeleton
is a masterpiece of structural form that functions with great efficiency and incredible fle&ibility.
3. (once$t *ormation
1. #he human skeleton is the framework of the body. )t is a tower of bones put together by hinges and 'oints. +ow many
bones make up the skeletal system
,. What are the functions of the human skeleton
-. .an is a vertebrate animal. What do all vertebrates have in common
/. What are the two main parts of the human skeletal system
0. Which principal bones make up the a&ial skeleton
1. Which of the a&ial bones hold the body erect or in an upright position
2. )n general, what bones make up the appendicular skeleton
3. 4ame some appendicular bones.
5. )n activity 1 on page ,6-, you will the identify parts of the human skeletal system. !ou will match the given names to the
corresponding labels of the figure. (Allow 17610 minutes for the activity.)
17. #he human skeletal system is a real masterpiece of structural design, with each part tailored to do a particular 'ob. %ne
ma'or function of the bones is to protect the body8s organ or a number of organs. )n activity , on page /60, there are four
types of bones that provide protection for the body. !ou will identify the bones and the organs they protect. (Allow 0617
minutes for the activity).
11. What is 9a: and what body organ does it protect
1,. What is 9b: and what does it protect
1-. What is 9c: and what does it guard
1/. 9d: is the backbone of the human body. )t is made up of bones connected one after another. What do you call these bones
10. #he singular form of vertebrae is vertebra. What do the vertebrae protect
4. +nhancement Activities
What are the parts of the human skeleton pages ,6-
What do bones protect pages /60
5. ,enerali-ations
What is a skeleton
What are the functions of the human skeleton
What are the two ma'or parts of the human skeletal system 4ame some bones of each part.
What do bones protect
6. A$$lication)Integration
The skeleton is the framework of the human body in the same way as population is the framework of a nation. hen the
framework is weak! the nation is weak. "ust as the skeleton is made of individual bones! the population is made up of individual
persons who contribute to the strength of the nation. #t is important that each individual must be strong. As a young pupil and an
individual citi$en! how will you contribute to the strength of your country%
The human body is protected by tough and strong bones. &ou must! in return! protect your bones by regular e'ercise and
by eating calcium(rich food. Do not be a victim of such diseases as rickets! scoliosis! osteoporosis! and later on! arthritis.
7. +valuation
!ulti$le (hoice Test. "hoose the correct ans/er.
). All vertebrates have one structure in common* they all have an endoskeleton. An endoskeleton is made up of bones inside
the body. The arrangement of the endoskeleton in the human body is simply referred to as the skeletal system. #t is made up
of +,- bones designed to do all of the following functions e'cept
a) to support the body. c) to protect body parts.
b) to enable movement. d) to receive messages from the brain.
+. The human skeletal system is made up of two ma.or parts. The first part is called the a'ial skeleton! which is made up of
the skull! ribs! and the vertebrae. The vertebrae are the small bones that make up the
a) appendages. c) backbone.
b) immovable 'oints. d) phalanges.
/. The second ma.or part of the human skeletal system is the appendicular skeleton! which is made up of bones in the arms
and legs! including the collarbones! hipbones! and shoulder bones. hich of the following is not a legbone%
a) femur b) ulna c) fibula d) tibia
0. 1ones have shapes and structural designs tailored to do a particular .ob. #f needed for protection! the bone is flat! such as
the ribs! shoulder bones! breastbone! and pelvic bone. hat do pelvic bones protect%
a) lungs b) heart c) kidneys d) cerebrum
8. Assignment
1. ;abel the other parts of the human skeleton on page ,.
,. +ow are bones classified
-. Why are leg bones hollow
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Practical Guide to Drawing Anatomy: [Artist's Workbook]D'EverandThe Practical Guide to Drawing Anatomy: [Artist's Workbook]Évaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (3)
- Parts and Function of Musculo-Skeletal SystemDocument52 pagesParts and Function of Musculo-Skeletal SystemJane Ilagan VizcoPas encore d'évaluation
- 4th Report SkeletonDocument14 pages4th Report SkeletonAndi NurhidayahPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Human Skeletal System:: Components of Human SkeletonDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Human Skeletal System:: Components of Human SkeletonElyka Alivan Valdez PolonioPas encore d'évaluation
- Module Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesModule Skeletal SystemEMEM QUENPas encore d'évaluation
- Downloadfile 5Document50 pagesDownloadfile 5Charisse Mae Berco - MaribongPas encore d'évaluation
- P - 7 Science Lesson NotesDocument104 pagesP - 7 Science Lesson Notesmichaelopi63Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Skeletal System of The FrogDocument3 pagesThe Skeletal System of The FrogLuther Abaya MolinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch-8. Body Movements (Notes)Document4 pagesCh-8. Body Movements (Notes)JAINAM SHAHPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.1 Support and Locomotion in Humans and AnimalsDocument2 pages2.1 Support and Locomotion in Humans and AnimalsBalpreet KaurPas encore d'évaluation
- P.7 Best Science Notes Term One - Teacher - AcDocument105 pagesP.7 Best Science Notes Term One - Teacher - AcMonydit SantinoPas encore d'évaluation
- ANATOMY I Lecture 02, GENERAL ANATOMY 2, Skeletal System, BonesDocument42 pagesANATOMY I Lecture 02, GENERAL ANATOMY 2, Skeletal System, BonesHalima NazarPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Biology - Zoology Quarter 4 - Module 1 The Skeletal SystemDocument13 pagesAdvanced Biology - Zoology Quarter 4 - Module 1 The Skeletal SystemKyth ClomaPas encore d'évaluation
- Movement and LocomotionDocument8 pagesMovement and LocomotionRonnith NandyPas encore d'évaluation
- Task 2. Answer The Following QuestionsDocument2 pagesTask 2. Answer The Following QuestionsAndi Resky AisyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 5 Biology Chapter 2 Locomotion SupportDocument15 pagesForm 5 Biology Chapter 2 Locomotion SupportElizabeth ThomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Ebook Biology ShazwaniDocument20 pagesEbook Biology ShazwaniNurul shazwaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Ud1 - Tema2 - READING - Skeleton and Its Functions 2021Document3 pagesUd1 - Tema2 - READING - Skeleton and Its Functions 2021Tady BenavidesPas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal System: Prepared By: GENER R. RODELASDocument31 pagesSkeletal System: Prepared By: GENER R. RODELASgener r. rodelasPas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Lesson Plan - Skeletal SystemDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan - Skeletal SystemMaria Danica89% (36)
- Muscular and Skeletal SystemsDocument18 pagesMuscular and Skeletal Systemsmanuela_ursache28Pas encore d'évaluation
- 02 SkeletalsystemDocument18 pages02 SkeletalsystemhorozukaPas encore d'évaluation
- Science and Health IV 1st RatingDocument78 pagesScience and Health IV 1st RatingDjenela MabagosPas encore d'évaluation
- St. Xavier's High School: Sector 49, GurgaonDocument4 pagesSt. Xavier's High School: Sector 49, GurgaonJsjn NPas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanAngelica MontereyPas encore d'évaluation
- SCIENCE - 6 - TG - Q2.docx Filename - UTF-8''SCIENCE 6 TG Q2Document103 pagesSCIENCE - 6 - TG - Q2.docx Filename - UTF-8''SCIENCE 6 TG Q2אנג' ליקהPas encore d'évaluation
- Major Bones and Bone Groups: Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesMajor Bones and Bone Groups: Skeletal Systemtupe salcedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscular and Skeletal Systems (Noura)Document12 pagesMuscular and Skeletal Systems (Noura)Laya ShrbagiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsDocument59 pages2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 6 TG q2Document112 pagesScience 6 TG q2Pinaka ShungaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2020-2021 AP 1 Lecture 7 Skeletal System 2Document41 pages2020-2021 AP 1 Lecture 7 Skeletal System 2OscarJaiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument7 pagesThe Musculoskeletal SystemxoxogeloPas encore d'évaluation
- Cat Quiz Ana AnsDocument4 pagesCat Quiz Ana AnsDaniel WachiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesSkeletal SystemmikePas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology Module 8aDocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Module 8aJayR MendonesPas encore d'évaluation
- L 8 - Body MovementsDocument29 pagesL 8 - Body MovementsChaitra KamuriPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy 1Document69 pagesAnatomy 1ravinder malwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy Lecture Notes Unit 5-1 Skeletal System OverviewDocument2 pagesAnatomy Lecture Notes Unit 5-1 Skeletal System Overviewrapunzel777Pas encore d'évaluation
- Serve: '.L'he Skelet - Al System The inDocument7 pagesServe: '.L'he Skelet - Al System The inVero GómezPas encore d'évaluation
- SkeletalsystemDocument43 pagesSkeletalsystemSamantha EllainePas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal SystemDocument23 pagesSkeletal Systemgame challengingPas encore d'évaluation
- ch-8 Our SkeletalDocument8 pagesch-8 Our Skeletalxhtk3em03zPas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal SystemDocument23 pagesSkeletal SystemNickmor OamlinPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 3 Skeletal SystemDocument41 pagesGrade 3 Skeletal SystemVanny Gimotea BaluyutPas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal SystemDocument12 pagesSkeletal SystemRojan V Min KookPas encore d'évaluation
- 38.1 Types of Skeletal SystemsDocument14 pages38.1 Types of Skeletal Systemsmoodapk34Pas encore d'évaluation
- Human Support SystemDocument9 pagesHuman Support Systemkiongoc100% (1)
- Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesSkeletal SystemavinmanzanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of Bone and JointDocument48 pagesAnatomy of Bone and JointKamalia Bint MuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- A Quick Representation of Body MovementsDocument16 pagesA Quick Representation of Body MovementsAkshainee SenPas encore d'évaluation
- The Main Functions of The Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesThe Main Functions of The Skeletal SystemLaura EslavaPas encore d'évaluation
- N104 ORTHO LectureDocument62 pagesN104 ORTHO LectureHarley Justiniani Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Science LPDocument2 pagesScience LPBizmates WenaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Musculoskeletal System-21805Document11 pages3 Musculoskeletal System-21805Dan ZagoreanuPas encore d'évaluation
- Science6 Q2 W1 2Document13 pagesScience6 Q2 W1 2Matt The idkPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Skeleton SystemDocument6 pagesHuman Skeleton SystemSridevi NadipalliPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Assignment (Skeletal System)Document4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lecture Assignment (Skeletal System)Destined UbaldoPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Education: School Head'S Technical Assistance Plan MAY 2021Document8 pagesDepartment of Education: School Head'S Technical Assistance Plan MAY 2021Annabelle Poniente HertezPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Education: School Head'S Technical Assistance Plan JUNE 2021Document7 pagesDepartment of Education: School Head'S Technical Assistance Plan JUNE 2021Annabelle Poniente HertezPas encore d'évaluation
- Tle Agri - NurseryDocument52 pagesTle Agri - NurserylizPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Education: School Head'S Technical Assistance Reporting Log APRIL 2021Document18 pagesDepartment of Education: School Head'S Technical Assistance Reporting Log APRIL 2021Annabelle Poniente HertezPas encore d'évaluation
- The Use of Organic FertilizerDocument15 pagesThe Use of Organic FertilizerAnnabelle Poniente HertezPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Education: School Head'S Technical Assistance Plan MAY 2021Document8 pagesDepartment of Education: School Head'S Technical Assistance Plan MAY 2021Annabelle Poniente HertezPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Education: School Head'S Technical Assistance Reporting Log APRIL 2021Document18 pagesDepartment of Education: School Head'S Technical Assistance Reporting Log APRIL 2021Annabelle Poniente HertezPas encore d'évaluation
- Reporter: Nove Joy L. Deleña Bsed-Bio - Sci. IiiDocument7 pagesReporter: Nove Joy L. Deleña Bsed-Bio - Sci. IiiAnnabelle Poniente HertezPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Education: Monthly Supervisory Accomplishment Report November 2020Document4 pagesDepartment of Education: Monthly Supervisory Accomplishment Report November 2020Annabelle Poniente HertezPas encore d'évaluation
- PFR Assignment Parental AuthorityDocument14 pagesPFR Assignment Parental AuthorityAnnabelle Poniente HertezPas encore d'évaluation
- Principle of AssessmentDocument43 pagesPrinciple of AssessmentAnnabelle Poniente HertezPas encore d'évaluation
- Template Business PlanDocument5 pagesTemplate Business PlanAnnabelle Poniente HertezPas encore d'évaluation
- Gad Legal Mandate1Document87 pagesGad Legal Mandate1LGU PadadaPas encore d'évaluation
- BSP Plastic Container PlantersDocument5 pagesBSP Plastic Container PlantersAnnabelle Poniente HertezPas encore d'évaluation
- Effects of The Environment On The Life Cycle of Organisms: Worksheet in Science IvDocument2 pagesEffects of The Environment On The Life Cycle of Organisms: Worksheet in Science IvAnnabelle Poniente Hertez100% (1)
- PFR Assignment Parental AuthorityDocument14 pagesPFR Assignment Parental AuthorityAnnabelle Poniente HertezPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Plan DETAILDocument4 pagesBusiness Plan DETAILAnnabelle Poniente HertezPas encore d'évaluation
- Cookies (100pcs) Quantity Price/Quantity Total AmountDocument3 pagesCookies (100pcs) Quantity Price/Quantity Total AmountAnnabelle Poniente HertezPas encore d'évaluation
- Body Structures That Help Animals Adapt and Survive: Worksheet in Science IvDocument2 pagesBody Structures That Help Animals Adapt and Survive: Worksheet in Science IvAnnabelle Poniente HertezPas encore d'évaluation
- Cookies (100pcs) Quantity Price/Quantity Total AmountDocument3 pagesCookies (100pcs) Quantity Price/Quantity Total AmountAnnabelle Poniente HertezPas encore d'évaluation
- Template Business PlanDocument5 pagesTemplate Business PlanAnnabelle Poniente HertezPas encore d'évaluation
- Stages in The Life Cycle of Organisms: Worksheet in Science IvDocument2 pagesStages in The Life Cycle of Organisms: Worksheet in Science IvAnnabelle Poniente Hertez0% (1)
- DLL - Science 4 - Q4 - W1Document4 pagesDLL - Science 4 - Q4 - W1Nie EbarlePas encore d'évaluation
- Body Structures That Help Animals Adapt and Survive: Worksheet in Science IvDocument2 pagesBody Structures That Help Animals Adapt and Survive: Worksheet in Science IvAnnabelle Poniente HertezPas encore d'évaluation
- Affidavit 2016Document5 pagesAffidavit 2016Annabelle Poniente HertezPas encore d'évaluation
- MedicalCertificate For Boxing 2Document1 pageMedicalCertificate For Boxing 2Annabelle Poniente HertezPas encore d'évaluation
- Ghies Teachers Study Notebook LDM Module Course 2Document45 pagesGhies Teachers Study Notebook LDM Module Course 2Annabelle Poniente Hertez100% (1)
- Las Science4 q2w2Document2 pagesLas Science4 q2w2Annabelle Poniente HertezPas encore d'évaluation
- Sworn Statement - 2016Document1 pageSworn Statement - 2016Annabelle Poniente HertezPas encore d'évaluation
- Sworn Statement ERFDocument4 pagesSworn Statement ERFAnnabelle Poniente Hertez100% (1)
- Principles of Selection and Mating SystemsDocument29 pagesPrinciples of Selection and Mating SystemsUnknown StudentPas encore d'évaluation
- DR Mushtaq Amna Ashraf Aqsa Bashir Ayesha Bibi Hira Nisar Iqra HabibDocument5 pagesDR Mushtaq Amna Ashraf Aqsa Bashir Ayesha Bibi Hira Nisar Iqra HabibtaibiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mayan Zodiac Symbols and NamesDocument7 pagesMayan Zodiac Symbols and Namescstocksg150% (2)
- Sarnat Scoring Tool: Normal/Mild Moderate HIE Severe HIEDocument1 pageSarnat Scoring Tool: Normal/Mild Moderate HIE Severe HIEBilly WijayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Surgery EmergencyDocument48 pagesPediatric Surgery EmergencyputraPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Diversity 7th Edition Hickman Test Bank 1Document9 pagesAnimal Diversity 7th Edition Hickman Test Bank 1gregoryPas encore d'évaluation
- Artificial Salmon SpawningDocument28 pagesArtificial Salmon SpawningjimborenoPas encore d'évaluation
- OrionpptDocument20 pagesOrionpptJoggie Mae MagarzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Three Faces of Hecate - Ritual PDFDocument3 pagesThree Faces of Hecate - Ritual PDFEric TuckerPas encore d'évaluation
- The Mystery of Metamorphosis - Foreword by Lynn Margulis and Dorion SaganDocument5 pagesThe Mystery of Metamorphosis - Foreword by Lynn Margulis and Dorion SaganChelsea Green Publishing100% (1)
- Fairy TaleDocument7 pagesFairy TaleMiguel Lugia-ZengPas encore d'évaluation
- Listening - Compare Animal and Human Behavior 2 - Mode - Report - Unit 6 - Lesson 3 - Vantage B2 - MyEnglishLabDocument1 pageListening - Compare Animal and Human Behavior 2 - Mode - Report - Unit 6 - Lesson 3 - Vantage B2 - MyEnglishLabAnnuar Florez100% (1)
- Csec Agriculture Science Sba (Crop Analysis)Document6 pagesCsec Agriculture Science Sba (Crop Analysis)Redso Lall67% (3)
- Lord of The Flies Final 2010Document5 pagesLord of The Flies Final 2010dagrizz2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Inbo 2009Document42 pagesInbo 2009BenjaminVasileniucPas encore d'évaluation
- CASE PRE (Intrapartum)Document6 pagesCASE PRE (Intrapartum)teuuuuPas encore d'évaluation
- Creatures & Constructs A Monster Manual Supplement For EberronDocument74 pagesCreatures & Constructs A Monster Manual Supplement For EberronJason BryantPas encore d'évaluation
- Student WorkDocument7 pagesStudent Workapi-316130138Pas encore d'évaluation
- Generic Dungeon WOTCDocument9 pagesGeneric Dungeon WOTCMark YfjPas encore d'évaluation
- Radiographic Positioning SummaryDocument10 pagesRadiographic Positioning SummaryCindy100% (1)
- Basic Spinal KriyaDocument2 pagesBasic Spinal KriyaGabriel C100% (3)
- Img 3212Document2 pagesImg 3212Douglas JoynerPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychophysiological Detection of Deception Analysis Ii - Course #503Document67 pagesPsychophysiological Detection of Deception Analysis Ii - Course #503John PrasetioPas encore d'évaluation
- Algeria Country PaperDocument9 pagesAlgeria Country PaperSandeep MahantaPas encore d'évaluation
- Eat Not This Flesh (Simoons, Frederick)Document249 pagesEat Not This Flesh (Simoons, Frederick)alvaronairaPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 3 BirdsDocument11 pagesClass 3 BirdsKrithik Koneru100% (1)
- IGCSE Biology Disease Transmission AnswersDocument2 pagesIGCSE Biology Disease Transmission Answersngole_96Pas encore d'évaluation
- WF 2Document4 pagesWF 2Mario TrPas encore d'évaluation
- OSCE - Chest PainDocument2 pagesOSCE - Chest PaincgalongPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardio VascularDocument42 pagesCardio VascularMamta ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
![The Practical Guide to Drawing Anatomy: [Artist's Workbook]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/238627287/149x198/b1987107b7/1617237212?v=1)