Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Technical Description Steam Engines
Transféré par
carzanteDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Technical Description Steam Engines
Transféré par
carzanteDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Steam Engines
technichal Description
Technical Description Steam Engine
Seite
Page 2
von
of 6
Applications of the Spilling steam
engine:
The Spilling steam engine can be used most
efficiently for driving generators, pumps and
other machines, wherever thermal steam is
required for production processes of any kind.
Combined heat and power cogeneration
with the Spilling steam engine
Combined heat and power cogeneration or
purely backpressure operation is an excellent
means for increasing efficiency in all steam
utilising plants. The available heat drop between
the steam boiler and heat consumers heating,
drying apparatus, boiling apparatus, exhaust
steam refrigerating machines and similar can
be converted into mechanical or electrical energy
with a Spilling steam engine. The Spilling steam
engine replaces the inefficient reducing valve,
which supplies heating systems and thermal
processes with steam of a specific pressure and
temperature, but eliminates the available
pressure drop without utilising the same. This
continuous elimination of valuable and utilisable
energy is no longer viable today in rationally
managed plants.
For new planning measures, it should also be
ensured that the greatest possible pressure and
heat drop is present between the boiler and heat
consumers, from which the total power demand
of the plant can be covered with a Spilling steam
engine. However, even if this objective cannot
be fully achieved, partial in-plant power
generation in backpressure operation is also
efficient.
Owing to the high primary energy utilisation in
combined heat and power cogeneration, this also
contributes towards the reduction of CO2
emissions.
The modular system offering a diverse
range of configuration options
It is recommended to process small pressure
drops in a single expansion engine and large
pressure drops in a multiple expansion engine in
order to achieve optimal steam consumptions. If
several exhaust steam systems are available, the
individual cylinders can either work against
various backpressures or a double expansion
engine can be designed as an extraction back-
pressure engine or an extraction condensation
engine to enable the extraction of production
steam from the receiver.
Use of biomass and local fuels
Highly efficient use of the Spilling steam engine
is also given where inexpensive fuels are
available for the boiler furnace, the further use of
which would otherwise be unprofitable and
elimination or removal would be difficult or incur
additional costs. In such cases, it is usually more
economical to use these residual materials for
steam generation and in turn for power
generation. This applies similarly to local fuels
such with low calorific value, which cannot be
transported and so must be used locally.
In such cases, power generation is also possible
using the Spilling steam engine in condensation
and even atmospheric exhaust operation.
Technical Description Steam Engine
Seite
Page 3
von
of 6
Waste heat utilisation
In a number of production processes in
glassworks, cement factories, gas works and in
the ceramic industry substantial amounts of
heat are also contained in the exhaust gases of
the furnace, which are not utilised. It is possible
to use these hot exhaust gases produced in a
waste heat boiler for steam generation and to
connect a Spilling steam engine downstream for
in-plant power generation.
THE SPILLING STEAM ENGINE
The SPILLING steam engine is a modular piston
expander that has been designed for use in small
and medium-sized steam power plants (up to
2000 kW) being operated primarily as combined
heat and power cogeneration plants.
The SPILLING steam engine combines the
excellent thermodynamic characteristics of the
classic steam engine and decisive features of
modern diesel engine construction. Based on
the successful synthesis of these two different
engine concepts, the Spilling engine today is a
steam engine that ranks as one of the best in its
class in terms of performance, operating
characteristics, ruggedness, easy maintenance
and low steam consumption. Particularly for
operation with alternating loads, this piston
expander is unexcelled in terms of efficiency and
performance.
The success of the Spilling engine in the area of
medium and small-sized steam engines becomes
apparent when looking at the thermodynamic and
design features of the expander.
High speeds, compact design
The rated speeds of Spilling engines are 750,
900, 1000 and 1500 rpm. As a result of these
high speeds, the Spilling engine is compact and
so requires a minimum of space using small,
inexpensive foundations, due to its favourable
mass balance. In addition, these speeds, which
are simultaneously normal rotary current speeds,
enable direct coupling with inexpensive
generators, blowers, pumps and other machines.
These high speeds also make the Spilling steam
engine suitable for sensitive operation with
precision control tasks and harsh operation with
heavy load surges.
Optimal efficiency due to volumetric
control
For the Spilling steam engine, the piston valve
control proven in continuous operation in steam
engines was retained, however combined with a
rotating control shaft as is customary in diesel
engine construction. The Spilling volumetric
control in conjunction with the optimised steam
passages is one of the decisive factors
responsible for the good thermodynamic
efficiency of the engine.
Minor mechanical wear in consequence
of low piston speed
Due to an optimal relation of engine speed and
piston stroke the Spilling steam engine is
operated with low piston speeds of 3,5 to 4,2
m/s. Resultant of this matters a minor mechanical
wear, which allows a continuous operation of the
engine.
Technical Description Steam Engine
Seite
Page 4
von
of 6
Twin shaft system with excellent mass
balance
This system offers the possibility of installation on
vibration absorbing foundations enabling oper-
ation in cellar rooms and on floors as well as in
the vicinity of residential buildings, offices or
other rooms sensitive to vibration.
Controls for any application
The electrohydraulic control for Spilling engines
can be adapted to diverse controlled variables
(e.g. exhaust steam pressure, supply steam
pressure, temperature, power, speed). Division
of the control shaft enables independent control
of two cylinder groups of an engine for controlling
two exhaust steam systems, for example.
Flexibility due to modular system
The modular design of Spilling engines enables
optimal adaptation of the engine to existing or
planned operating conditions during the design
phase and also subsequently as required. The
standardised modular system enables
replacement and spare parts to be provided for
all engine types ex works within the shortest
time.
Please contact us:
Werftstrasse 5
DE 20457 Hamburg
Fon: +49 (0)40 789 175 0
Fax: +49 (0)40 789 28 36
www.spilling.de
info@spilling.de
Technical Description Steam Engine
Seite
Page 5
von
of 6
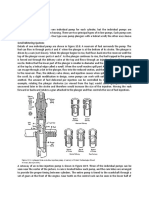
120
0200055 WT 23.07.02
Schutzvermerk nach DIN 34beachten
A
B
Oil Discharge
Oil Temperatur Measuring
Entleerung l
Messung ltemperatur
A
Draufsicht
B
Top View Geprft
Gezeichnet
Generator
n
d
e
r
u
n
g
e
n
1
Oil Supply Duct
lverteilerleitungen
Oil Sump
lsumpf
Coupling Shaft
Koppelstange
6
Excentric
Exzenter
6
Reglerfedern
6
Excenter Rod
Touthed Rim
Governor Spring
Exzenterstange
7
Zahnkranz
6
Crank Case Ventilation
Cross Head Liner
Sliding Valve Rod
Triebwerksentlftung
G-Einsatz
Schieberstange
8
Blatt 2/2
Dateiname:
w1806023.dgn
Format: A2
Steam Engine Section A-A Name Datum
Wt
27.06.02
27.06.02
Fi
Ersatz fr:
Zeichnungs-Nr.:
Ersetzt durch:
B 00
1:10 / A4
1:5 / A2
Mastab:
Dampf-Motorquerschnitt A-A
Bezeichnung:
z
u
r
A
t
h
m
o
s
p
f
r
e
L
a
t
e
r
n
e
o
f
f
e
n
Cross Head Bearing
15
Oil Strainer
Crank Shaft
Kurbelwelle
lsaugfilter ( Sieb )
Connecting Rod
Pleuel
4
3
Kreuzkopf
Crosshead Gudgeon
Cross Head
Gleitbahnbuchse
Kreuzkopfbolzen 4
4
labstreifring
Oil Scraper
Pisten Rod
Kolbenstange 3
C
r
a
n
k
c
a
s
e
w
i
t
h
F
o
r
c
e
d
L
u
b
r
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
T
r
i
e
b
w
e
r
k
m
i
t
D
r
u
c
k
u
m
l
a
u
f
-
S
c
h
m
i
e
r
u
n
g
A
t
h
m
o
s
p
h
e
r
e
L
a
t
e
r
n
o
p
e
n
t
o
Crank Shaft
Kolben
Kurbelwelle
Piston
Stuffing box (slide Valve )
Slide Valve Casing
Slide Valve Liner
Schieberkasten
Schieberlaufbuchse
Schieberstopfbuchse
9
1
Slide Valve Body
Doppelkolbenschieber
1
Cylinder
Zylinder
8
A-A
Inlet
Eintritt
Austritt
Outlet
Slide Valve
Control Shaft
Schieber
Reglerwelle
Piston with Piston Rings
Working Space
Arbeitsraum
Cylinder Liner
Zylinderlaufbuchse
Stopfbuchse ( Kolben )
Stuffing Box ( Piston )
2
1
Burst Plates FRONT
Sprengscheiben
Kolben mit Ringen 3
Burst Plate TOP
Sprengplatte
C
y
l
i
n
d
e
r
u
n
d
e
r
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
Z
y
l
i
n
d
e
r
u
n
t
e
r
D
r
u
c
k
Technical Description Steam Engine
Seite
Page 6
von
of 6
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 1977 - Wildman - Developments in Steam TurbinesDocument6 pages1977 - Wildman - Developments in Steam TurbinesManoj Kumar100% (1)
- Steam System Best Practices Ultrasound Testing Steam TrapsDocument12 pagesSteam System Best Practices Ultrasound Testing Steam TrapsJason Ng Yan FuPas encore d'évaluation
- Solar Steam GenerationDocument15 pagesSolar Steam GenerationSebastian MontecinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrualics & Hydraulic Machinery - Lecture - Notes-1 PDFDocument101 pagesHydrualics & Hydraulic Machinery - Lecture - Notes-1 PDFJitender NaiduPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Growth Estimates Reciprocating CompressorsDocument1 pageThermal Growth Estimates Reciprocating CompressorsDiego Fernando Pedroza UribePas encore d'évaluation
- Machine Design Case StudyDocument30 pagesMachine Design Case StudyJoe Felice100% (3)
- A Novel Power-Train Using Coaxial Magnetic GearDocument6 pagesA Novel Power-Train Using Coaxial Magnetic GearHuynh Thanh AnhPas encore d'évaluation
- A Manual of The Steam Engine. For Engineers and Technical Schools PDFDocument1 131 pagesA Manual of The Steam Engine. For Engineers and Technical Schools PDFbrad209Pas encore d'évaluation
- Steam Trap TesterDocument4 pagesSteam Trap TesterISMAEL RAMIREZPas encore d'évaluation
- Wankel EngineDocument15 pagesWankel EngineMuhammad Bin RiazPas encore d'évaluation
- Ball PistonDocument13 pagesBall PistonpraneethreddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar On Steam EngineDocument26 pagesSeminar On Steam EngineEr Akhilesh Singh100% (1)
- Cam DesignDocument74 pagesCam DesignMuhammad Maarij Farooq0% (1)
- Design and Structural Thermal Analysis of Gas Turbine Rotor Blade With Radial Holes Using SolidworksDocument5 pagesDesign and Structural Thermal Analysis of Gas Turbine Rotor Blade With Radial Holes Using SolidworksEditor IJTSRDPas encore d'évaluation
- 3D Modeling of Crankshaft Using Catia Software: Chapter-1Document33 pages3D Modeling of Crankshaft Using Catia Software: Chapter-1naveen mylapilli0% (1)
- The Effect of Air Inlet System Features On Automotive Turbocharger Compressor PerformanceDocument19 pagesThe Effect of Air Inlet System Features On Automotive Turbocharger Compressor Performancestefan.vince536Pas encore d'évaluation
- Innovative Turbomachinery Shaft Coupling Alignment MethodDocument8 pagesInnovative Turbomachinery Shaft Coupling Alignment Methodejzuppelli8036100% (1)
- Beam Engine Mechanism Powered Circular Sawing Machine ReportDocument34 pagesBeam Engine Mechanism Powered Circular Sawing Machine ReportSanjay CrPas encore d'évaluation
- Circular Rotor Windmill (Wind Turbine)Document105 pagesCircular Rotor Windmill (Wind Turbine)SanjaySherikarPas encore d'évaluation
- Calorific Value of HFO and MDO Comparison ReportDocument17 pagesCalorific Value of HFO and MDO Comparison Reportswapneel_kulkarni100% (3)
- Gerotor 3Document14 pagesGerotor 3Jean-Philippe GauthierPas encore d'évaluation
- Elliott Turbine-Generator ConfigurationsDocument8 pagesElliott Turbine-Generator Configurationskishwar999100% (1)
- Thermal Engineering-2 PracticalDocument35 pagesThermal Engineering-2 PracticalAlok Anand100% (1)
- 45 24985 EE328 2016 1 2 1 Lecture2allDocument51 pages45 24985 EE328 2016 1 2 1 Lecture2allHoppohigdi786 Hoppohigdi786Pas encore d'évaluation
- Components of Gas Turbine Power PlantDocument53 pagesComponents of Gas Turbine Power PlantRakesh ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Engine Crankshaft Deflection Measurement Guide - IIMSDocument9 pagesEngine Crankshaft Deflection Measurement Guide - IIMSNyan ThutaPas encore d'évaluation
- Modeling and Analysis of Steam Turbine Blade-Ijaerdv05i0451562n PDFDocument11 pagesModeling and Analysis of Steam Turbine Blade-Ijaerdv05i0451562n PDFGuruvenu KamanuruPas encore d'évaluation
- Mounting and Dismounting of Roller Bearing Project Tarek IsmaeelDocument7 pagesMounting and Dismounting of Roller Bearing Project Tarek IsmaeelhouriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Steam Turbine ModelDocument19 pagesSteam Turbine ModelRoberto ZuñigaPas encore d'évaluation
- Curtis TurbineDocument18 pagesCurtis TurbineDivya Prakash SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Growth of The STEAM-ENGINEDocument76 pagesGrowth of The STEAM-ENGINENauman KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- TT401 GearDocument45 pagesTT401 GearDurjoy Roy100% (1)
- Dony WatssDocument49 pagesDony WatssvbugaianPas encore d'évaluation
- 19 - Wartsila - Turbocharging 2 Stroke Engine - Existing & Future DemandsDocument18 pages19 - Wartsila - Turbocharging 2 Stroke Engine - Existing & Future DemandsCháu Bác HồPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Plant Part2Document80 pagesPower Plant Part2مصطفى العبادي100% (2)
- Arrow Product OverviewDocument13 pagesArrow Product OverviewRafael Zurita100% (1)
- Kaplan DesignDocument2 pagesKaplan DesignruralworldPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Energy Steam Sir Charles ParsonsDocument18 pagesThermal Energy Steam Sir Charles ParsonsgauravPas encore d'évaluation
- 4-Stroke Final ReportDocument13 pages4-Stroke Final ReportVimal YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalogo de Bombas de Caudal VariableDocument29 pagesCatalogo de Bombas de Caudal VariableRaul Rivera100% (1)
- Noble Corporation: Noble Analyst Day Singapore May 17-18, 2011Document27 pagesNoble Corporation: Noble Analyst Day Singapore May 17-18, 2011Andi ayuPas encore d'évaluation
- Helium Turbomachinery Operating Experience From Gas Turbine Power PlantsDocument35 pagesHelium Turbomachinery Operating Experience From Gas Turbine Power PlantsLarry SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- ABB - General Purpose Motors Cast Iron - GB 092003Document49 pagesABB - General Purpose Motors Cast Iron - GB 092003ivanjaviergutierrezoPas encore d'évaluation
- Biodiesel: Vegetable Oil Refining Biomass To Liquid Vegetable Oil Used As FuelDocument38 pagesBiodiesel: Vegetable Oil Refining Biomass To Liquid Vegetable Oil Used As FuelKyada RadhikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Turbines For BFP Drive PDFDocument10 pagesTurbines For BFP Drive PDFShameer Majeed100% (1)
- Steam Turbines: Prepared by Venkat Chintala Asst. Prof. S.G. Mechanical Engg. Deptt., UPESDocument85 pagesSteam Turbines: Prepared by Venkat Chintala Asst. Prof. S.G. Mechanical Engg. Deptt., UPESRaj NarayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotary Valve Steam EngineDocument13 pagesRotary Valve Steam EnginedeckyPas encore d'évaluation
- Injector Pumps In-Line Injection Pumps: Scroll-Metering SystemsDocument10 pagesInjector Pumps In-Line Injection Pumps: Scroll-Metering SystemsCate Sitati100% (1)
- Balancing Basic Part IIDocument6 pagesBalancing Basic Part IIAbdul KurniadiPas encore d'évaluation
- 08 CH-6, Fluid Motion Within Combustion ChamberDocument24 pages08 CH-6, Fluid Motion Within Combustion ChamberAhsan AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Permanent Magnet Motors GB 05-2004Document72 pagesPermanent Magnet Motors GB 05-2004David Lopez Rebollo100% (1)
- Siemens FactSheet ORC ModuleDocument2 pagesSiemens FactSheet ORC ModuleHimanshu1712Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sulzer Turbocharging 00Document18 pagesSulzer Turbocharging 00ozakyusPas encore d'évaluation
- Considerations in Greasing Electric Motor Anti Friction BearingsDocument5 pagesConsiderations in Greasing Electric Motor Anti Friction BearingsSam ChengPas encore d'évaluation
- Triangle Multi Drill HolderDocument43 pagesTriangle Multi Drill HolderSendhilNathan100% (1)
- Gas Turbine Thermal Power PlantDocument7 pagesGas Turbine Thermal Power PlantAkshay ManzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Coupling NotesDocument20 pagesFluid Coupling NotesSagar PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationD'EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationÉvaluation : 1 sur 5 étoiles1/5 (1)
- Manual Cost Analysis Tool V1.0Document54 pagesManual Cost Analysis Tool V1.0carzantePas encore d'évaluation
- Maintenance and Overhaul of Steam TurbinesDocument46 pagesMaintenance and Overhaul of Steam Turbinessubbusenthil78% (9)
- Solar400 AlgeriaDocument7 pagesSolar400 AlgeriacarzantePas encore d'évaluation
- Tabla Disponibilidad (Alternativa OREDA)Document18 pagesTabla Disponibilidad (Alternativa OREDA)carzantePas encore d'évaluation
- Tiempos de Arranque Segun Tipos de PlantasDocument17 pagesTiempos de Arranque Segun Tipos de PlantascarzantePas encore d'évaluation
- H2 Storage - CostDocument26 pagesH2 Storage - CostcarzantePas encore d'évaluation
- Costos ISCCDocument35 pagesCostos ISCCcarzantePas encore d'évaluation
- Lahmeyer - Costes de O&MDocument225 pagesLahmeyer - Costes de O&McarzantePas encore d'évaluation
- Fog Cooling Wet Compression and Droplet Dynamics in Gas Turbine PDFDocument247 pagesFog Cooling Wet Compression and Droplet Dynamics in Gas Turbine PDFcarzantePas encore d'évaluation
- ET150 y Prototipo PSA PDFDocument5 pagesET150 y Prototipo PSA PDFcarzantePas encore d'évaluation
- Vaccum Pump Vs Steam Ejector AdvantagesDocument6 pagesVaccum Pump Vs Steam Ejector AdvantagescarzantePas encore d'évaluation
- Wittmann Some Aspects On Parabolic Trough Field Operation PDFDocument9 pagesWittmann Some Aspects On Parabolic Trough Field Operation PDFcarzantePas encore d'évaluation
- Quality of Natural Gas Burnt in Combustion TurbinesDocument20 pagesQuality of Natural Gas Burnt in Combustion TurbinescarzantePas encore d'évaluation
- Task 2 Final Report PDFDocument94 pagesTask 2 Final Report PDFcarzantePas encore d'évaluation
- Aerosols en SolarGISDocument4 pagesAerosols en SolarGIScarzantePas encore d'évaluation
- Simulation Test Loop PDFDocument8 pagesSimulation Test Loop PDFcarzantePas encore d'évaluation
- Ciclo CombinadoDocument9 pagesCiclo CombinadocarzantePas encore d'évaluation
- Integrated Solar Power Plants (ISCC)Document13 pagesIntegrated Solar Power Plants (ISCC)carzantePas encore d'évaluation
- Datos Satelite Vs Datos GroundDocument8 pagesDatos Satelite Vs Datos GroundcarzantePas encore d'évaluation
- Compressor SpecificationDocument9 pagesCompressor Specificationcarzante100% (1)
- Thermal and Optical Study of Parabolic Trough Collectors of Shiraz Solar Power PlantDocument6 pagesThermal and Optical Study of Parabolic Trough Collectors of Shiraz Solar Power PlantmridupavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cimentaciones CSP PDFDocument12 pagesCimentaciones CSP PDFcarzantePas encore d'évaluation
- Roos PresentationDocument86 pagesRoos PresentationJignesh ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Solar Radiation in AfricaDocument12 pagesSolar Radiation in AfricacarzantePas encore d'évaluation
- Viabilidad CSP GreciaDocument15 pagesViabilidad CSP GreciacarzantePas encore d'évaluation
- Little ChangesDocument1 pageLittle ChangescarzantePas encore d'évaluation
- HTF Venting System - MojaveDocument29 pagesHTF Venting System - MojavecarzantePas encore d'évaluation
- Truncation of The Secondary Concentrator As Means To Cost Effective Beam-Down SystemDocument4 pagesTruncation of The Secondary Concentrator As Means To Cost Effective Beam-Down SystemcarzantePas encore d'évaluation
- HTF Venting System - MojaveDocument29 pagesHTF Venting System - MojavecarzantePas encore d'évaluation
- 3PAR DISK MatrixDocument6 pages3PAR DISK MatrixShaun PhelpsPas encore d'évaluation
- DA Savitz - Interpreting Epidemiologic Evidence - Strategies For Study Design and Analysis 2003 PDFDocument329 pagesDA Savitz - Interpreting Epidemiologic Evidence - Strategies For Study Design and Analysis 2003 PDFrindy_bilhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Engine Control System Circuit Diagram: Without This Message by Purchasing NovapdfDocument3 pagesEngine Control System Circuit Diagram: Without This Message by Purchasing NovapdfJose Luis Gutierrez TamayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cleats CatalogueDocument73 pagesCleats Cataloguefire123123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Epson WorkForce Pro WF-C878-879RDocument8 pagesEpson WorkForce Pro WF-C878-879Rsales2 HARMONYSISTEMPas encore d'évaluation
- Entropy and The Second Law of Thermodynamics Disorder and The Unavailability of Energy 6Document14 pagesEntropy and The Second Law of Thermodynamics Disorder and The Unavailability of Energy 6HarishChoudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Same Virtus: Alarm ListDocument23 pagesSame Virtus: Alarm ListLacatusu Mircea100% (1)
- Final Whole PHD ThesisDocument294 pagesFinal Whole PHD ThesisLIBIO ESTEPAPas encore d'évaluation
- GMS60CSDocument6 pagesGMS60CSAustinPas encore d'évaluation
- Motionless Electromagnetic GeneratorDocument8 pagesMotionless Electromagnetic Generatorraja100% (1)
- Flexenclosure Esite Brochure PDFDocument5 pagesFlexenclosure Esite Brochure PDFajdCruisePas encore d'évaluation
- Combined Geo-Scientist (P) Examination 2020 Paper-II (Geophysics)Document25 pagesCombined Geo-Scientist (P) Examination 2020 Paper-II (Geophysics)OIL INDIAPas encore d'évaluation
- M. Fatur - H1C018040 - PETROLOGIDocument15 pagesM. Fatur - H1C018040 - PETROLOGIFaturrachmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 3.1 - Configuring and Verifying Standard ACLsDocument9 pagesLab 3.1 - Configuring and Verifying Standard ACLsRas Abel BekelePas encore d'évaluation
- Wavetek Portable RF Power Meter Model 1034A (1499-14166) Operating and Maintenance Manual, 1966.Document64 pagesWavetek Portable RF Power Meter Model 1034A (1499-14166) Operating and Maintenance Manual, 1966.Bob Laughlin, KWØRLPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanism of Muscle ContractionDocument24 pagesMechanism of Muscle Contractionfisika100% (1)
- Food Preparation, Terms and DefinitiosDocument2 pagesFood Preparation, Terms and DefinitiosLacsi, Erica Joy V.Pas encore d'évaluation
- ElutriatorDocument9 pagesElutriatoratiyorockfan9017Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pneumatic Conveying of Bulk Solids PDFDocument231 pagesPneumatic Conveying of Bulk Solids PDFCarloLopez100% (2)
- SPE-183743-MS Maintaining Injectivity of Disposal Wells: From Water Quality To Formation PermeabilityDocument19 pagesSPE-183743-MS Maintaining Injectivity of Disposal Wells: From Water Quality To Formation PermeabilityAminPas encore d'évaluation
- EI 6702-Logic and Distributed Control SystemDocument2 pagesEI 6702-Logic and Distributed Control SystemMnskSaro50% (2)
- HydrocarbonsDocument5 pagesHydrocarbonsClaire Danes Tabamo DagalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Atmel 2565 Using The Twi Module As I2c Slave - Applicationnote - Avr311Document14 pagesAtmel 2565 Using The Twi Module As I2c Slave - Applicationnote - Avr311m3y54mPas encore d'évaluation
- Allison 1,000 & 2,000 Group 21Document4 pagesAllison 1,000 & 2,000 Group 21Robert WhooleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Assignment - 2: CodeDocument8 pagesLab Assignment - 2: CodeKhushal IsraniPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Electronics Lab ManualDocument47 pagesBasic Electronics Lab ManualAlpesh ThesiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Book Review: Laser Fundamentals, 2nd Edition by William T. SilfvastDocument2 pagesBook Review: Laser Fundamentals, 2nd Edition by William T. SilfvastAbhishekPas encore d'évaluation
- EC 201 Network TheoryDocument2 pagesEC 201 Network TheoryJoseph JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- IK Gujral Punjab Technical University: 1. Electric ChargeDocument12 pagesIK Gujral Punjab Technical University: 1. Electric ChargeJashandeep KaurPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No. 2 Rockwell Hardness Test IntroductionDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 2 Rockwell Hardness Test IntroductionAhmad Abd100% (1)