Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
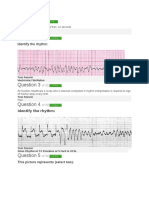
Sinus Rhythm Disturbances
Transféré par
Marcus Philip Gonzales0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
188 vues3 pagesECG INTERPRETATION
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentECG INTERPRETATION
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
188 vues3 pagesSinus Rhythm Disturbances
Transféré par
Marcus Philip GonzalesECG INTERPRETATION
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
A.
SINUS RHYTHM DISTURBANCES
1. Sinus tachycardia
Fast rates
P waves may merge with preceding T
waves
Rate: >100 bpm
2. Sinus Bradycardia
Rate: <60 bpm
3. Sinus arrhythmia
Rhythm: irregular
4. Sinus arrest/ pause
PQRST will be missing
5. Sick sinus syndrome
Combination of sinus node
dysrhythmias
Tachy-brady
Brady-tachy
B. ATRIAL ARRHYTHMIAS
1. Premature atrial contraction (PAC)
P is at opposite polarity
P will not be seen because it is lost in
the preceding T wave
P-R interval may be shorter than
normal
2. Atrial tachycardia
Rate: 160-250 bpm
P may be hidden in the previous T
wave
TYPES:
a. Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia
Four or more consecutive PACs
Rate:150-250 bpm
P waves may not be seen
b. Multifocal atrial tachycardia
Tachycardia with beat-to-beat
variation of the p wave
morphology
3. Atrial flutter
Saw-toothed F waves
Atrial Rate: 250-400 bpm
Ventricular rate: 150, 100, 75
Two for one flutter: atrial rate of 300
and ventricular arte of 150
4. Atrial fibrillation
Atrial Rate: >400 bpm
Ventricular rate: 110-180 bpm
Ventricular rhythm: irregular
C. JUNCTIONAL RHYTHMS
1. Junctional rhythm
Rate: 40-60 bpm
P wave is absent or inverted
2. Accelerated Junctional rhythm
Rate: 60-100 bpm
P wave is absent or inverted
3. Junctional Tachycardia
Rate: >100 bpm
D. ATRIOVENTRICULAR HEART BLOCKS
1. First degree heart block
Prolonged PR: >.2 secs
Constant
2. Second degree heart block
a. Mobitz type 1
Progressive lengthening of the PR
interval until a beat is dropped
Dropped beat is seen as a P wave
and not followed by QRS complex
b. Mobitz type 2
No warning before a beat is
dropped
PR interval remain constant
before the dropped beat
3. Third degree heart block / complete heart
block
P waves occur at a faster rate than
ventricular rate
QRS: <60 bpm
P waves bear no relationship to the
QRS
PR intervals: variable
QRS complex: normal/ abnormal
width
E. VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIAS
1. Premature ventricular contractions
P wave is not seen before a PVC
Aberrant in appearance
QRS: abnormally wide
T wave and QRS complex are at
opposite directions
a. Unifocal one PVC
b. Multifocal 2 or more PVC
c. Couplet 2 PVC in a row
d. Triplet 3 PVC in a row
e. Bigeminy
Every other normal beats
f. Trigemini
Every other two normal beats
g. Quadrigeminy
Every other three normal beats
2. Ventricular tachycardia
4 or more PVC: bursts and
paroxysmal
Rate: >100 bpm
3. Ventricular fibrillation
Coarse and fine rhythms
4. Idioventricular rhythm
Wide, bizarre QRS complex
Absent P wave
Rate: 20-40 bpm
Rhythm: regular
5. Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
Rate: 40-100 bpm
F. ASYSTOLE
Flat line
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ekg Full BibleDocument6 pagesEkg Full BibleTJPas encore d'évaluation
- Dysrhytmia NotesDocument11 pagesDysrhytmia NoteshannahhwolfPas encore d'évaluation
- Torsade De Pointes, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandTorsade De Pointes, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- EKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookD'EverandEKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookPas encore d'évaluation
- EKG - Assignment Without AnswersDocument10 pagesEKG - Assignment Without AnswersJon Millhollon100% (1)
- ECG Quiz Prep: Key Points for Interpreting RhythmsDocument7 pagesECG Quiz Prep: Key Points for Interpreting RhythmsAAPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam 3 Study Guide: Pain and Peripheral Vascular DiseaseDocument5 pagesExam 3 Study Guide: Pain and Peripheral Vascular DiseaseFarzanaAziziPas encore d'évaluation
- Ekg Panum or OsceDocument69 pagesEkg Panum or OsceGladish RindraPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG Guide: Anatomy, Physiology, Interpretation and AbnormalitiesDocument102 pagesECG Guide: Anatomy, Physiology, Interpretation and AbnormalitiesMustafa A. DawoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac Pacing: Terms You Will Become Familiar With in This Section of TheDocument21 pagesCardiac Pacing: Terms You Will Become Familiar With in This Section of TheClt Miskeen100% (1)
- 10 Steps To Learn ECG InterpretationDocument5 pages10 Steps To Learn ECG InterpretationIbrahem Y. NajjarPas encore d'évaluation
- EKG Clep TestDocument13 pagesEKG Clep TestElissa LafondPas encore d'évaluation
- Arrhythmia Recognition Poster Part 2Document1 pageArrhythmia Recognition Poster Part 2Gwen LylesPas encore d'évaluation
- EAR First AidDocument4 pagesEAR First Aidr_lakshmi2722Pas encore d'évaluation
- Latihan Ekg KD A III 2016Document15 pagesLatihan Ekg KD A III 2016Syamsul PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic EKG Interpretation ExamDocument13 pagesBasic EKG Interpretation Examtwdroppoint100% (1)
- EkgDocument67 pagesEkgFendi Rafif Dad'sPas encore d'évaluation
- P Waves: Identification and InterpretationDocument31 pagesP Waves: Identification and Interpretation.100% (1)
- Principles of ECGDocument11 pagesPrinciples of ECGDeinielle Magdangal RomeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Sut Ams Medical College, TVMDocument7 pagesSut Ams Medical College, TVMDIVYA R.S100% (1)
- EkgDocument94 pagesEkgCaprita LauraPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecg CookbookDocument2 pagesEcg CookbookCalin Popa100% (1)
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenDocument23 pagesELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenItsMe AJPas encore d'évaluation
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHYDocument75 pagesELECTROCARDIOGRAPHYMeliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Arrythmia AnalysisDocument60 pagesBasic Arrythmia AnalysisZakky KurniawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Right Side EcgDocument4 pagesRight Side EcgDragos CirsteaPas encore d'évaluation
- ACLS Algorithms (2011)Document6 pagesACLS Algorithms (2011)senbonsakuraPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecg Reading NotesDocument17 pagesEcg Reading NotesMarian FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- 65-Year-Old Woman With Cough and FatigueDocument7 pages65-Year-Old Woman With Cough and Fatigue최인선100% (1)
- ECG Master Class-2Document138 pagesECG Master Class-2Shohag ID Center100% (1)
- Rhythm Strip ReviewDocument8 pagesRhythm Strip ReviewDouglas Greg Cook100% (2)
- Zero Based BudgetDocument9 pagesZero Based Budgetapi-447860598Pas encore d'évaluation
- ECG Master Class-1Document132 pagesECG Master Class-1Shohag ID Center100% (1)
- Basis of ECG and Intro To ECG InterpretationDocument10 pagesBasis of ECG and Intro To ECG InterpretationKristin SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Heartbeat Irregularities ExplainedDocument5 pagesHeartbeat Irregularities ExplainedKayelyn-Rose Combate100% (1)
- EKG Quick Reference ChartDocument4 pagesEKG Quick Reference ChartMildaPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG Flashcards: Atrial ArrhythmiasDocument27 pagesECG Flashcards: Atrial ArrhythmiasDima HabanjarPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Pressure Medication ChartDocument1 pageBlood Pressure Medication CharttmlePas encore d'évaluation
- My Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesMy Cheat SheetTenzin KyizomPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Axis: Fast & Easy Ecgs - A Self-Paced Learning ProgramDocument29 pagesElectrical Axis: Fast & Easy Ecgs - A Self-Paced Learning ProgramMihaela PrisacaruPas encore d'évaluation
- DR K Chan - Ecg For SVT Made EasyDocument66 pagesDR K Chan - Ecg For SVT Made Easyapi-346486620Pas encore d'évaluation
- Practice StripsDocument9 pagesPractice StripsErica Yamamoto50% (4)
- Cardiac MedicationsDocument8 pagesCardiac Medicationsangeline totaram100% (2)
- EKG Rhythms: SVT, Atrial Fibrillation, AV Blocks (39Document10 pagesEKG Rhythms: SVT, Atrial Fibrillation, AV Blocks (39Saidel ElizondoPas encore d'évaluation
- PR-QRS-TwavesDocument3 pagesPR-QRS-TwavesKelly PrattPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG Learning ModulesDocument150 pagesECG Learning ModulesdodiPas encore d'évaluation
- Krishnan - EKG Basics Lecture NotesDocument3 pagesKrishnan - EKG Basics Lecture NotesanishdPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre - and Post Test Cardiac ArrhythmiasDocument6 pagesPre - and Post Test Cardiac ArrhythmiasEköw Santiago JavierPas encore d'évaluation
- EKG RhythmsDocument10 pagesEKG RhythmsQueenPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of MurmursDocument2 pagesClassification of MurmursNazneen SiddiquiPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic EKG Interpretation Exam AnswersDocument3 pagesBasic EKG Interpretation Exam AnswerstwdroppointPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG Interpretation and Dysrhythmias: Karen L. O'Brien MSN, RN JAN 07Document60 pagesECG Interpretation and Dysrhythmias: Karen L. O'Brien MSN, RN JAN 07ampogison08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exam 3 pathophysiology Cancer growth types and characteristicsDocument7 pagesExam 3 pathophysiology Cancer growth types and characteristicsmenickel3Pas encore d'évaluation
- DYSRHYTHMIAS (A.k.a. Arrhythmias) Disorders in TheDocument3 pagesDYSRHYTHMIAS (A.k.a. Arrhythmias) Disorders in TheDarell M. Book100% (1)
- Basics of Pacing CombinedDocument54 pagesBasics of Pacing CombinedMichael Susanto100% (1)
- ECG InterpretationDocument40 pagesECG InterpretationMuhammad BadrushshalihPas encore d'évaluation
- A Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsD'EverandA Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Lung Metabolism: Proteolysis and Antioproteolysis Biochemical Pharmacology Handling of Bioactive SubstancesD'EverandLung Metabolism: Proteolysis and Antioproteolysis Biochemical Pharmacology Handling of Bioactive SubstancesAlain JunodPas encore d'évaluation
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsD'EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Epinephrine Is The Primary Drug Used in The Cardiac Arrest AlgorithmDocument2 pagesEpinephrine Is The Primary Drug Used in The Cardiac Arrest AlgorithmMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Decreased Cardiac Output: Desired OutcomeDocument2 pagesNURSING DIAGNOSIS: Decreased Cardiac Output: Desired OutcomeMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion Fatigue Activity Intolerance Risk For Fall Imbalance Nutrition: Less Than BodyDocument1 pageIneffective Tissue Perfusion Fatigue Activity Intolerance Risk For Fall Imbalance Nutrition: Less Than BodyMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing JournalDocument7 pagesNursing JournalMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Pallia JournalDocument4 pagesPallia JournalMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Content ServerDocument13 pagesContent ServerMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Safe Handling ChemoDocument11 pagesSafe Handling ChemoMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- RRL 1Document1 pageRRL 1Marcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Communication Skills in Palliative Care A Practical GuideDocument17 pagesCommunication Skills in Palliative Care A Practical GuideMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is The Expected Date of ConfinementDocument1 pageWhat Is The Expected Date of ConfinementMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- RRL 2Document6 pagesRRL 2Marcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Crash CartDocument12 pagesCrash CartMarcus Philip Gonzales100% (1)
- Benner's 5 Stages of Nursing CompetenceDocument1 pageBenner's 5 Stages of Nursing CompetenceMagilas S. SalvacionPas encore d'évaluation
- HttpsDocument1 pageHttpsMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Surgical Knife - Is A Very Sharp Knife Used in SurgeryDocument1 pageSurgical Knife - Is A Very Sharp Knife Used in SurgeryMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing TheoriesDocument1 pageNursing TheoriesMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Breast CancerDocument1 pageBreast CancerMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Dietaty Patterns in Stroke Patients in Northwest India: (Journal Study)Document3 pagesDietaty Patterns in Stroke Patients in Northwest India: (Journal Study)Marcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Figure 1: External and Internal Components of Situational AnalysisDocument1 pageFigure 1: External and Internal Components of Situational AnalysisMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Prevention of Pressure UlcerDocument2 pagesPrevention of Pressure UlcerMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Case AnalysisDocument5 pagesCase AnalysisMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- InsulinDocument1 pageInsulinMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Needlestick InjuriesDocument6 pagesNeedlestick InjuriesMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Prevention of Pressure UlcerDocument2 pagesPrevention of Pressure UlcerMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute MIDocument13 pagesAcute MIMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- AchuhuhuDocument18 pagesAchuhuhuMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Dance Among Chinese in HongkongDocument10 pagesDance Among Chinese in HongkongMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing ElectiveDocument5 pagesNursing ElectiveMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Hemodialysis Compared To Peritoneal DialysisDocument3 pagesHemodialysis Compared To Peritoneal DialysisMarcus Philip GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Amputee Case StudyDocument2 pagesAmputee Case StudyRubilyn SumayloPas encore d'évaluation
- Consent For RhinoplastyDocument6 pagesConsent For RhinoplastyEking InPas encore d'évaluation
- Angiodroid The CO2 Injector - VascupediaDocument8 pagesAngiodroid The CO2 Injector - VascupediaArnaud TORNIERPas encore d'évaluation
- Obstetric Anal Sphincter Injury-FoudaDocument36 pagesObstetric Anal Sphincter Injury-FoudaMade DarmayasaPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaluation of Prosthetic Marginal Fit and Implant SurvivalDocument12 pagesEvaluation of Prosthetic Marginal Fit and Implant SurvivalGustavo IsmaelPas encore d'évaluation
- Intraoperative Recruitment Manoeuvres: Protective Ventilation in The ORDocument7 pagesIntraoperative Recruitment Manoeuvres: Protective Ventilation in The ORGede Eka Putra NugrahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Abdominal Wall Nerve BlocksDocument49 pagesAbdominal Wall Nerve BlocksTaupik RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalogo ColoplastDocument44 pagesCatalogo ColoplastLUIS AUGUSTO DELGADOPas encore d'évaluation
- HymenoplastyDocument11 pagesHymenoplastyAyu RahayuniPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Choice Questions: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Anaesthesia Anaesthesia For Awake CraniotomyDocument4 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Anaesthesia Anaesthesia For Awake CraniotomyEliza AmandoPas encore d'évaluation
- EmpyemaDocument12 pagesEmpyemavictoriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures (Neer Type II)Document21 pagesUnstable Distal Clavicle Fractures (Neer Type II)Orthopaedics & Trauma in YoutubePas encore d'évaluation
- L1) Oral Cavity, Palate and TongueDocument39 pagesL1) Oral Cavity, Palate and Tongue3amroooni.a.aPas encore d'évaluation
- CAT Clitoral Phimosis FINALDocument14 pagesCAT Clitoral Phimosis FINALadi130584Pas encore d'évaluation
- An Anatomic Technique For Establishing Leg Length During The Anterior Approach To Total Hip ArthroplastyDocument5 pagesAn Anatomic Technique For Establishing Leg Length During The Anterior Approach To Total Hip Arthroplasty阿欧有怪兽Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shanz - Ent 1.07 NoseDocument4 pagesShanz - Ent 1.07 NosePetrina XuPas encore d'évaluation
- Perioperative Preparation and Management: Pre-OperativeDocument14 pagesPerioperative Preparation and Management: Pre-OperativeRed StohlPas encore d'évaluation
- The Tamil Nadu Dr. M.G.R. Medical University - MSC Nursing Second YrDocument10 pagesThe Tamil Nadu Dr. M.G.R. Medical University - MSC Nursing Second YrNoufal100% (1)
- HA Procedures Respi Heart and PeripheralDocument10 pagesHA Procedures Respi Heart and Peripheralako at ang exoPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaluation of Sacral Dimples Clinical PathwayDocument10 pagesEvaluation of Sacral Dimples Clinical PathwayNavine NalechamiPas encore d'évaluation
- DR Form BsuDocument1 pageDR Form BsumingcatPas encore d'évaluation
- AbdomenDocument3 pagesAbdomenDale Ros CollamatPas encore d'évaluation
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Current.22Document16 pagesGestational Trophoblastic Disease Current.22nando8396100% (1)
- Use of Cement in Hip Arthroplasty-Blankstein2020Document9 pagesUse of Cement in Hip Arthroplasty-Blankstein2020Mohan DesaiPas encore d'évaluation
- KSDP TOG The Obstetric Gynaecologis - 2021 - Ekanem - Surgical Site Infection in Obstetrics and Gynaecology Prevention andDocument14 pagesKSDP TOG The Obstetric Gynaecologis - 2021 - Ekanem - Surgical Site Infection in Obstetrics and Gynaecology Prevention andVu AnPas encore d'évaluation
- MedOne MicroDose SF Injection KitDocument1 pageMedOne MicroDose SF Injection KitHaag-Streit UK (HS-UK)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tooth Movement & Dental Implants: Oral Physiology Dent 207Document14 pagesTooth Movement & Dental Implants: Oral Physiology Dent 207Ali Al-QudsiPas encore d'évaluation
- Biphasic DefbrillationDocument16 pagesBiphasic DefbrillationchanlalPas encore d'évaluation
- Radiologic Management of Thoracic Nodules and MassesDocument14 pagesRadiologic Management of Thoracic Nodules and MassesVianney OlveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Employee Mediclaim Policy - Future Generali 2023-24Document61 pagesEmployee Mediclaim Policy - Future Generali 2023-24Hunny Nihalani LycanPas encore d'évaluation