Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Warehouse
Transféré par
kapildreamsCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Warehouse
Transféré par
kapildreamsDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Stores & Warehouse
Management
Production and Material Management
Amit Naik
Stores & Warehouse
Management
Production and Material Management
Amit Naik
Introduction
store is a place where excess material is kept
which will be used as and when required.
Loss of items, deterioration, obsolescence
and inadequacy [of what is stored to what is
needed] are treated as part of life.
Introduction
store is a place where excess material is kept
which will be used as and when required.
Loss of items, deterioration, obsolescence
and inadequacy [of what is stored to what is
needed] are treated as part of life.
Objectives of store
In the chain of internal customers and suppliers,
stores has several internal customers. As a matter of
fact all functions of management are internal
customers to stores. Customers as usual expect
Quality Cost and Delivery fromevery supplier.
Stores also have to deliver these customer
expectations. In the process of discharging this
obligation Stores performsome activities that are
functions of Stores.
Objectives of store
In the chain of internal customers and suppliers,
stores has several internal customers. As a matter of
fact all functions of management are internal
customers to stores. Customers as usual expect
Quality Cost and Delivery fromevery supplier.
Stores also have to deliver these customer
expectations. In the process of discharging this
obligation Stores performsome activities that are
functions of Stores.
Functions of Stores
1. Receipt
2. Storage
3. Retrieval
4. Issue
5. Records
6. Housekeeping
7. Control
8. Surplus management
9. Verification
10. Interaction & coordination
Functions of Stores
1. Receipt
2. Storage
3. Retrieval
4. Issue
5. Records
6. Housekeeping
7. Control
8. Surplus management
9. Verification
10. Interaction & coordination
Receipt
Any itemof goods or material that enters the
organization always enters through the stores.
Similarly, every itemunless specifically excluded, has
to leave through the store. Stores is the final account
keeper of all materials.
Material sent by any supplier after the security
clearance comes to the stores. Stores check the
document carried by the carrier, known as Delivery
Challan, against the copy of the Purchase Order placed
on the supplier by the organization.
Receipt
Any itemof goods or material that enters the
organization always enters through the stores.
Similarly, every itemunless specifically excluded, has
to leave through the store. Stores is the final account
keeper of all materials.
Material sent by any supplier after the security
clearance comes to the stores. Stores check the
document carried by the carrier, known as Delivery
Challan, against the copy of the Purchase Order placed
on the supplier by the organization.
Receipt
Once the adequacy is established and quantity is verified
the material is sent for testing for quality parameters.
Some times quality control tests are elaborate and time
consuming. If the policy of receipt is to unload the
material subject to quality control acceptance, it is
cleared for unloading.
Unloaded material is kept on the hold if it not yet
cleared by quality control department. If the material is
rejected it is sent back to the supplier after clear
documentation.
Receipt
Once the adequacy is established and quantity is verified
the material is sent for testing for quality parameters.
Some times quality control tests are elaborate and time
consuming. If the policy of receipt is to unload the
material subject to quality control acceptance, it is
cleared for unloading.
Unloaded material is kept on the hold if it not yet
cleared by quality control department. If the material is
rejected it is sent back to the supplier after clear
documentation.
Issue
Fulfilling customer demand for the itemin
minimum time, keeping quality high and cost
minimum is issue.
An internal customer doesnt pay the price but he
has to fulfill requirement of authorization for the
demand.
A duly authorized indent or requisition for the item
is the key
Issue
Fulfilling customer demand for the itemin
minimum time, keeping quality high and cost
minimum is issue.
An internal customer doesnt pay the price but he
has to fulfill requirement of authorization for the
demand.
A duly authorized indent or requisition for the item
is the key
Storage
Once the unloaded material is approved by the
quality control department, as per the quality plan in
the quality system, it is moved to a specific place in
the stores layout.
The material is so stored that it becomes easy to
retrieve and issue subsequently.
Storage should also ensure protection against
deterioration, damage and pilferage.
Storage
Once the unloaded material is approved by the
quality control department, as per the quality plan in
the quality system, it is moved to a specific place in
the stores layout.
The material is so stored that it becomes easy to
retrieve and issue subsequently.
Storage should also ensure protection against
deterioration, damage and pilferage.
Storage
Detailed systemis adopted for location and labeling
of items while in storage. Storage plan is made
keeping in mind,
1. nature of the product- physical state, toxicity,
inflammability and other hazards
2. volume and weight- heavy or light
3. movement frequency- fast moving or slow moving
4. point of use
Storage
Detailed systemis adopted for location and labeling
of items while in storage. Storage plan is made
keeping in mind,
1. nature of the product- physical state, toxicity,
inflammability and other hazards
2. volume and weight- heavy or light
3. movement frequency- fast moving or slow moving
4. point of use
Retrieval
Easy and quick retrievability of items that are
demanded by the internal customers.
Easy identification, maximum space utilization and
minimum handling are key factors to retrieval
functions.
It is common knowledge in many of the companies
that after hours of searching for the itemis declared
to be out of stock. This causes hold up of production
process and avoidable urgent purchase of out of
stock material. This function takes place as per
established retrieval system.
Retrieval
Easy and quick retrievability of items that are
demanded by the internal customers.
Easy identification, maximum space utilization and
minimum handling are key factors to retrieval
functions.
It is common knowledge in many of the companies
that after hours of searching for the itemis declared
to be out of stock. This causes hold up of production
process and avoidable urgent purchase of out of
stock material. This function takes place as per
established retrieval system.
Records
Maintaining records of receipt and issue.
Updating the stock levels as per movement of
materials.
Basic records of store are bin card and stock
register.
Bin card is placed on the bin in which items are stored.
This gives information about receipt, issue and balance.
stock register gives all the information in the bin card
and also the value.
Records
Maintaining records of receipt and issue.
Updating the stock levels as per movement of
materials.
Basic records of store are bin card and stock
register.
Bin card is placed on the bin in which items are stored.
This gives information about receipt, issue and balance.
stock register gives all the information in the bin card
and also the value.
Housekeeping
Maintenance, cleanliness in the store and
ensuring principle of Place for Everything and
Everything in its place is fully implemented.
Good housekeeping ensures satisfactory work
practices
Housekeeping
Maintenance, cleanliness in the store and
ensuring principle of Place for Everything and
Everything in its place is fully implemented.
Good housekeeping ensures satisfactory work
practices
Verification
Stock verification to eliminate gap between
information and physical stock. In stores some items
are maintained as stock items. The stores triggers the
procurement cycle for such items when a
predetermined reorder level is reached. Hence
correct stock position through verification is critical
to ensure no shortage and no excess for the item.
Verification
Stock verification to eliminate gap between
information and physical stock. In stores some items
are maintained as stock items. The stores triggers the
procurement cycle for such items when a
predetermined reorder level is reached. Hence
correct stock position through verification is critical
to ensure no shortage and no excess for the item.
Surplus management
Surplus items are those that have accumulated due to
faulty planning, forecasting and purchasing. Hence a
usage value is associated with these items.
Scrap is wastage generated due to processes like
turning, boring drilling etc. and also due to bad
manufacturing. it is said that in India nearly Rs. 2500
crores are tied up as obsolete, surplus and scrap
items.
Surplus management
Surplus items are those that have accumulated due to
faulty planning, forecasting and purchasing. Hence a
usage value is associated with these items.
Scrap is wastage generated due to processes like
turning, boring drilling etc. and also due to bad
manufacturing. it is said that in India nearly Rs. 2500
crores are tied up as obsolete, surplus and scrap
items.
Surplus management
Effective disposal system for unneeded
material to reduce inventory cost and
proactive measures to eliminate deterioration
and obsolescence.
Obsolete items are good in all respect but
have no useful role in the company due to
changes that have occurred in the course of
time.
Surplus management
Effective disposal system for unneeded
material to reduce inventory cost and
proactive measures to eliminate deterioration
and obsolescence.
Obsolete items are good in all respect but
have no useful role in the company due to
changes that have occurred in the course of
time.
Control
Taking measures to ensure material plan is being
adhered to.
Any changes in consumption pattern or
replenishment pattern are closely monitored for
corrective action.
Material movement is watched to identify
nonmoving material for disposal. Effective control
puts into effect management objective of no
shortage and no excess.
Control
Taking measures to ensure material plan is being
adhered to.
Any changes in consumption pattern or
replenishment pattern are closely monitored for
corrective action.
Material movement is watched to identify
nonmoving material for disposal. Effective control
puts into effect management objective of no
shortage and no excess.
Causes for generation
1. Changes in product design obsoletion
2. Rationalization initiative for variety reduction
leads to surplus or obsolete items
3. Cannibalization parts of one idle machine are
fitted on another machine needed urgently during
maintenance, results into obsoletion of parts and at
times even scrap
Causes for generation
1. Changes in product design obsoletion
2. Rationalization initiative for variety reduction
leads to surplus or obsolete items
3. Cannibalization parts of one idle machine are
fitted on another machine needed urgently during
maintenance, results into obsoletion of parts and at
times even scrap
Causes for generation
Faulty planning and forecasting leads to excess
procurement, surplus generation.
Faulty purchase practices sub-optimization in
buying to utilize available discounts and
transportation economy, surplus and obsolete stocks
are generated.
Other causes parts kept aside for insurance claims,
bad storage system, bad material handling, bad
manufacturing and badly maintained machines are
other causes for spoilage and scrap.
Causes for generation
Faulty planning and forecasting leads to excess
procurement, surplus generation.
Faulty purchase practices sub-optimization in
buying to utilize available discounts and
transportation economy, surplus and obsolete stocks
are generated.
Other causes parts kept aside for insurance claims,
bad storage system, bad material handling, bad
manufacturing and badly maintained machines are
other causes for spoilage and scrap.
Interaction & coordination
Very close interaction between Purchasing,
production, quality control and engineering
functions is obviously needed in the discharge of the
functions discussed so far. It also becomes necessary
to coordinate the flow of material samples and
information through a network of departments for
performance of stores functions. Besides, every
management function being an internal customer
interaction is very important.
Interaction & coordination
Very close interaction between Purchasing,
production, quality control and engineering
functions is obviously needed in the discharge of the
functions discussed so far. It also becomes necessary
to coordinate the flow of material samples and
information through a network of departments for
performance of stores functions. Besides, every
management function being an internal customer
interaction is very important.
Stores organization
Store is a function of materials management
in an organization. Hence it is generally found
that stores function reports to the materials
manager.
But in some situations stores function reports
to the production function.
Stores organization
Store is a function of materials management
in an organization. Hence it is generally found
that stores function reports to the materials
manager.
But in some situations stores function reports
to the production function.
Stores organization
The earlier type of arrangement is based on the concept that
stores along with other functions of materials management
can be integrated into the materials organization. This will
streamline all materials management functions effectively.
The other arrangement is leaning on the fact that production
function is very closely linked to stores. And a common
command can reduce cost and increase effectiveness. And
also keep material accounting outside the scope of
procurement function.
Stores organization
The earlier type of arrangement is based on the concept that
stores along with other functions of materials management
can be integrated into the materials organization. This will
streamline all materials management functions effectively.
The other arrangement is leaning on the fact that production
function is very closely linked to stores. And a common
command can reduce cost and increase effectiveness. And
also keep material accounting outside the scope of
procurement function.
Centralized or decentralized stores
organization
Centralized stores concept is to store all items
at a central place and control materials
movement from this central place. Whereas
decentralization concept is moving the
material to the respective consumer function
or directly to the points of use.
Centralized or decentralized stores
organization
Centralized stores concept is to store all items
at a central place and control materials
movement from this central place. Whereas
decentralization concept is moving the
material to the respective consumer function
or directly to the points of use.
Features of centralized stores
organization
1. Effective supervision and control.
2. Issue at single point reduces cost of
issue
3. Reduced personnel requirement
4. Efficient layout for stores
5. Better handling technology
6. Better inventory checks
7. Maintenance of optimum stores
8. Fewer redundant and obsolete items
9. Elaborate documentation
Features of centralized stores
organization
1. Effective supervision and control.
2. Issue at single point reduces cost of
issue
3. Reduced personnel requirement
4. Efficient layout for stores
5. Better handling technology
6. Better inventory checks
7. Maintenance of optimum stores
8. Fewer redundant and obsolete items
9. Elaborate documentation
Features of decentralized stores
organization
1. Reduced handling
2. Customer friendly
3. Diluted risk of fire
4. Fewer production stoppages
5. Visual management is easier
Features of decentralized stores
organization
1. Reduced handling
2. Customer friendly
3. Diluted risk of fire
4. Fewer production stoppages
5. Visual management is easier
Stores Systems and Procedures
The systemshould take care of physical flow of
materials and flow of information.
Identification system: When one deals with large number of
items depending on physical description of the itembecomes
unreliable. Hence we need a systemwhich provides a unique
identification for each itemin the stores. Materials suppliers to
stores follow their own numbering systemfor identification.
But the systems being unique to their companies they are not
unique to the stores of the buying organization. Hence it is
primary responsibility of stores management to develop a
unique identification systemto facilitate clear communication
internally.
Stores Systems and Procedures
The systemshould take care of physical flow of
materials and flow of information.
Identification system: When one deals with large number of
items depending on physical description of the itembecomes
unreliable. Hence we need a systemwhich provides a unique
identification for each itemin the stores. Materials suppliers to
stores follow their own numbering systemfor identification.
But the systems being unique to their companies they are not
unique to the stores of the buying organization. Hence it is
primary responsibility of stores management to develop a
unique identification systemto facilitate clear communication
internally.
Arbitrary approach
Go on assigning serial numbers in sequence to the
materials as they arrive in the stores. This is a unique
systemas every itemwill posses a unique
identification number. But it will not be possible to
identify the family of parts to which this particular
part belongs. This type of numbering will not reveal
any classification of the part.
Arbitrary approach
Go on assigning serial numbers in sequence to the
materials as they arrive in the stores. This is a unique
systemas every itemwill posses a unique
identification number. But it will not be possible to
identify the family of parts to which this particular
part belongs. This type of numbering will not reveal
any classification of the part.
The symbolic approach
This is a systemusing numerical, alphabets or a
combination of both for identifying a part or item.
Following is an example:
1 52 43 25
First digit 1, stands for general class to which this item
belongs like say, raw material.
Second two digits indicate the generic class like say, bars.
Third two digits indicate steel rounds and the last two digits
indicate the specific number.
Similarly alphabets or alphanumeric can be used in place
of numbers.
The symbolic approach
This is a systemusing numerical, alphabets or a
combination of both for identifying a part or item.
Following is an example:
1 52 43 25
First digit 1, stands for general class to which this item
belongs like say, raw material.
Second two digits indicate the generic class like say, bars.
Third two digits indicate steel rounds and the last two digits
indicate the specific number.
Similarly alphabets or alphanumeric can be used in place
of numbers.
Engineering drawing number
This is quite useful internally. But has a
serious limitation that it is applicable to
manufactured parts only
Engineering drawing number
This is quite useful internally. But has a
serious limitation that it is applicable to
manufactured parts only
Stores Systems and Procedures
Stores Systems and Procedures operate the stores
every day. Systems and procedures should undergo
continuous review to avoid redundancy and rigidity.
Continuous review in the formof PDCA should
provide the benefit experience of implementation.
Operation of stores is made up of number of
activities involving various functions inside and
outside the organization. These activities are tied
together by procedures so that transparency comes in
and variations due to individual personalities are
limited.
Stores Systems and Procedures
Stores Systems and Procedures operate the stores
every day. Systems and procedures should undergo
continuous review to avoid redundancy and rigidity.
Continuous review in the formof PDCA should
provide the benefit experience of implementation.
Operation of stores is made up of number of
activities involving various functions inside and
outside the organization. These activities are tied
together by procedures so that transparency comes in
and variations due to individual personalities are
limited.
Receipt system
Stores receive materials fromvarious sources. Some
of themare internal and some are external. Receipt
systemis specific to the source. When materials
arrive froman external source following system
handles the receipts.
Purchase function raises a PO on the source of
supply a copy is sent to the stores. Stores are now
advised about the order.
Receipt system
Stores receive materials fromvarious sources. Some
of themare internal and some are external. Receipt
systemis specific to the source. When materials
arrive froman external source following system
handles the receipts.
Purchase function raises a PO on the source of
supply a copy is sent to the stores. Stores are now
advised about the order.
Receipt system
When the supplier on whomthe order is placed
supplies the goods he sends goods dispatch note,
giving information about carrier, value of the goods,
date of dispatch etc. to the receiving stores. The
carrier sends a document called consignment note.
These documents enable the store to make
arrangement for receipt of the
consignment.[handling equipment, space etc.]
Receipt system
When the supplier on whomthe order is placed
supplies the goods he sends goods dispatch note,
giving information about carrier, value of the goods,
date of dispatch etc. to the receiving stores. The
carrier sends a document called consignment note.
These documents enable the store to make
arrangement for receipt of the
consignment.[handling equipment, space etc.]
Receipt system
When the consignment arrives at the receiving
section it is checked against the documents already
received with respect to the consignment. General
condition of the goods also is checked.
When internal departments send material to stores a
material return note, transfer note or scrap report is
enclosed.
Receipt system
When the consignment arrives at the receiving
section it is checked against the documents already
received with respect to the consignment. General
condition of the goods also is checked.
When internal departments send material to stores a
material return note, transfer note or scrap report is
enclosed.
Types of storage
As per types of the materials stored
1. Raw Materials store
2. Components store
3. Work in process store
4. Finished goods store
5. Semi finished goods store
6. Tools store, die crib
7. Consumable materials store
Types of storage
As per types of the materials stored
1. Raw Materials store
2. Components store
3. Work in process store
4. Finished goods store
5. Semi finished goods store
6. Tools store, die crib
7. Consumable materials store
Types of storage
As per nature of the materials stored
1. LPG store
2. Chemicals store
3. Hazardous materials store
4. Refrigerated materials store
Types of storage
As per nature of the materials stored
1. LPG store
2. Chemicals store
3. Hazardous materials store
4. Refrigerated materials store
Types of storage
As per function of the storage
1. receiving store
2. central store
3. general stores
4. sub stores
Types of storage
As per function of the storage
1. receiving store
2. central store
3. general stores
4. sub stores
Storage systems
Physical systems
physical storage of material is very important
from the point of view of identification,
retrieval and issue.
Storage systems
Physical systems
physical storage of material is very important
from the point of view of identification,
retrieval and issue.
Methods adopted for physical
storage
Closed door system: the stored material is held
under lock and key. Entry into the store is restricted
authorized persons only. Physical movement of the
material is only with authorized documents only.
Maximum security and tight control on movement
are features of this system
Open stores system: In this systemmaterial is
stored near point of use and there is restriction on
consumption. Control passes on to the operations
department
Methods adopted for physical
storage
Closed door system: the stored material is held
under lock and key. Entry into the store is restricted
authorized persons only. Physical movement of the
material is only with authorized documents only.
Maximum security and tight control on movement
are features of this system
Open stores system: In this systemmaterial is
stored near point of use and there is restriction on
consumption. Control passes on to the operations
department
Methods adopted for physical
storage
Random access stores system: There is no fixed
location for an item. Itemoccupies the available
physical slot when it enters the store.
Stores address is fixed to the occupying item
electronically. For issue the itemis located by this
address. This systemfacilitates maximum space
utilization but electronic control is needed.
Methods adopted for physical
storage
Random access stores system: There is no fixed
location for an item. Itemoccupies the available
physical slot when it enters the store.
Stores address is fixed to the occupying item
electronically. For issue the itemis located by this
address. This systemfacilitates maximum space
utilization but electronic control is needed.
Stores record system
In stores management two types of records are
fundamental one is called bin card or stock card and
the other is stores ledger.
Stock card or bin card: bin card, fixed on the bin shows
the quantity received, issued and balances. Copy of this
record is maintained for reference by the stores in
charge. This record also triggers purchase activity
when ROL of an item is reached
store ledger, contains value in addition to the physical
stock which is also shown on the bin card.
Stores record system
In stores management two types of records are
fundamental one is called bin card or stock card and
the other is stores ledger.
Stock card or bin card: bin card, fixed on the bin shows
the quantity received, issued and balances. Copy of this
record is maintained for reference by the stores in
charge. This record also triggers purchase activity
when ROL of an item is reached
store ledger, contains value in addition to the physical
stock which is also shown on the bin card.
Issue system
Fromthe stores material is issued for internal
consumption and some times issued to outside parties
for processing.
Issue to consuming department: Material is issued to
consuming departments against a material requisition slip which
is duly authorized and made with reference to a work order for
production. Quantity needed for production is mentioned in the
work order and stores employees are not authorized to issue
excess quantity. Hence an automatic control is exercised on
consumption. The work order mentioned above is raised based
on the bill of materials for production.
rigid control on issue to processors outside
Issue system
Fromthe stores material is issued for internal
consumption and some times issued to outside parties
for processing.
Issue to consuming department: Material is issued to
consuming departments against a material requisition slip which
is duly authorized and made with reference to a work order for
production. Quantity needed for production is mentioned in the
work order and stores employees are not authorized to issue
excess quantity. Hence an automatic control is exercised on
consumption. The work order mentioned above is raised based
on the bill of materials for production.
rigid control on issue to processors outside
Issue to outside parties for
processing
procedure is same but a more rigid control is
exercised
Issue to outside parties for
processing
procedure is same but a more rigid control is
exercised
Stores accounting and verification
systems
Purpose of stores accounting is to know
1. cost of materials consumed in production
2. levels of wastage produced
3. value of material lying in stock
for ascertaining the above following factors are taken into
account
1. material price
2. freight charges
3. insurance
4. duties
5. tax
6. packaging charges etc.
Stores accounting and verification
systems
Purpose of stores accounting is to know
1. cost of materials consumed in production
2. levels of wastage produced
3. value of material lying in stock
for ascertaining the above following factors are taken into
account
1. material price
2. freight charges
3. insurance
4. duties
5. tax
6. packaging charges etc.
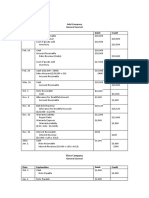
FIFO (first in, first out) and LIFO (last in, first out) are inventory management and
accounting techniques designed to add consistency to the sales and accounting
functions of business, respectively. In inventory management, FIFO and LIFO have
to do with the physical storage and movement of inventory; in accounting, the
concepts relate to how purchase costs are allocated to daily sales. The law requires
publicly traded corporations to choose and stick with a specific accounting method,
and small businesses can benefit from doing so as well.
FIFO In inventory management, FIFO means that the oldest inventory items -- the
ones purchased first -- are sold before newer items. Companies must use FIFO for
inventory if they are selling perishable goods such as food, which expires after a
certain period of time. Companies selling products with relatively short demand
cycles, such as designer fashion, also may have to pick FIFO to ensure they are not
stuck with outdated styles in inventory.
LIFO Although it is rare, there are companies that have to pick LIFO, rather than
FIFO, to manage their inventory. Sellers of homogenous commodity products such
as stone, sand and bricks usually have to take inventory from the top of large
stacks or piles, leaving the oldest batches to sit at the bottom of the piles for much
longer than newer batches. Companies such as vending machine operators also
have to choose LIFO for inventory management, as the first products they put in
their machines are sold last.
NIFO Next in, First out is an inventory valuation technique in which issues to the
production hall are valued at the current market price i.e. current cost or
replacement cost instead of the cost at which material was bought i.e. historical
cost. This valuation method attempts to keep the production cost accurate
according to the prices prevailing in the accounting period in which material was
consumed and not on the basis of the prices prevailing in the period when material
was bought. This way the measurement of production cost for internal use and cost
of goods sold for external use is more accurate and the users of information has
the figures according to latest market position and can make better decisions.
Under the 'Average Cost Method', it is assumed that the cost of inventory is
based on the average cost of the goods available for sale during the period.
The average cost is computed by dividing the total cost of goods available for sale
by the total units available for sale. This gives a weighted-average unit cost that is
applied to the units in the ending inventory. For example, if one share of Company
A's stock is purchased on June 1 for $50.00, again on June 15 for $35.00, and
again on Aug 10 for $40.00, the average-cost method assumes that three stocks
were purchased for an average cost of $41.67. This number is arrived at by adding
$50.00 + $35.00 + $40.00 and dividing the sum by 3, because there are three
stocks in the pool.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Foreign Trade Policy 2009-2014Document112 pagesForeign Trade Policy 2009-2014shruti_siPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing Management (Complete Notes)Document84 pagesMarketing Management (Complete Notes)yogita45100% (1)
- PMMDocument2 pagesPMMkapildreamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing ManagementDocument40 pagesMarketing ManagementDr Rushen SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Strategic ManagementDocument1 pageStrategic ManagementkapildreamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- AX2009 - Fact Sheet - Inventory Closing - Average Cost Price - Inventory Model Groups v1.0Document43 pagesAX2009 - Fact Sheet - Inventory Closing - Average Cost Price - Inventory Model Groups v1.0Andrew FirthPas encore d'évaluation
- TOPIC 1 Accounting For InventoryDocument9 pagesTOPIC 1 Accounting For Inventorykirah raraPas encore d'évaluation
- Kieso10eChp09 MidtermDocument30 pagesKieso10eChp09 MidtermJohn FinneyPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 03Document44 pagesCH 03Nguyen Thanh Tung (K15 HL)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tiffany and Co.'s Legacy of LuxuryDocument51 pagesTiffany and Co.'s Legacy of LuxuryawaisPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 4. InventoriesDocument77 pagesModule 4. Inventorieslord kwantoniumPas encore d'évaluation
- This Study Resource WasDocument6 pagesThis Study Resource WasLianaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2020 Mock Exam C - Morning SessionDocument21 pages2020 Mock Exam C - Morning SessionJay100% (1)
- 115 CstugDocument646 pages115 Cstugprasadv19806273Pas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting 2 DR Selim Chapter 4Document23 pagesAccounting 2 DR Selim Chapter 4Souliman MuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Inventory IllustrationDocument6 pagesInventory IllustrationVatchdemonPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 5Document22 pagesUnit 5Dr Suman RamapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 1: Conceptual FrameworkDocument16 pagesTopic 1: Conceptual FrameworkHuỳnh Như PhạmPas encore d'évaluation
- FA TableDocument8 pagesFA TableVy Duong TrieuPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamics NAV Inventory Cost Restoration WhitepaperDocument9 pagesDynamics NAV Inventory Cost Restoration WhitepaperAndrea DjunaidyPas encore d'évaluation
- Answers To QuestionsDocument17 pagesAnswers To QuestionsElie YabroudiPas encore d'évaluation
- KUIS FA 2 Anak AkunDocument4 pagesKUIS FA 2 Anak Akunelaine aureliaPas encore d'évaluation
- AUE3701 PACK ASS 2 2022 8m92akDocument38 pagesAUE3701 PACK ASS 2 2022 8m92akMonica DeetlefsPas encore d'évaluation
- IFRS SECRETS ENGLISH VERSION Complete Version PDFDocument95 pagesIFRS SECRETS ENGLISH VERSION Complete Version PDFIhab Al-AnabousiPas encore d'évaluation
- Teory NewDocument3 pagesTeory NewsanjuladasanPas encore d'évaluation
- INV.4-7Document21 pagesINV.4-7lynguyen2996Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1: Session 1 Introduction To Financial AccountingDocument161 pagesChapter 1: Session 1 Introduction To Financial AccountingHarshini Akilandan100% (1)
- CH 06Document72 pagesCH 06api-307892902Pas encore d'évaluation
- Example Lifo FifoDocument3 pagesExample Lifo FifoFaryal MughalPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Accounting 2Document3 pagesSample Accounting 2Ranen Darren P. BenitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting Standards LAQDocument4 pagesAccounting Standards LAQVinoth Kumar Kesavan (EC2352001010623)Pas encore d'évaluation
- IFRS vs GAAP Accounting Standards QuizDocument5 pagesIFRS vs GAAP Accounting Standards QuizCamilo AndrésPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Slides - Chapter 5 & 6Document102 pagesLecture Slides - Chapter 5 & 6Phan Đỗ QuỳnhPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting HandbookDocument42 pagesAccounting Handbookinfoyazid5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pertemuan 11-Ch. 22Document44 pagesPertemuan 11-Ch. 22Sarah Sarah widyanaPas encore d'évaluation