Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Partial Discharge - Open Electrical
Transféré par
BHALAJI BIRLACopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Partial Discharge - Open Electrical
Transféré par
BHALAJI BIRLADroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
9/30/2014 Partial Discharge - Open Electrical
http://www.openelectrical.org/wiki/index.php?title=Partial_Discharge 1/2
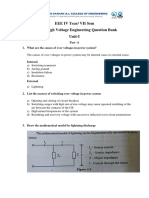
Partial discharge equivalent circuit with test circuit
Partial Discharge
From Open Electrical
A partial discharge, as defined by IEC 60270, is a "localised electrical discharges that only partially bridges
the insulation between conductors and which can or cannot occur adjacent to conductors". In other words, it
is a partial breakdown in the insulation between two active conductors.
Partial discharges can occur in any location where the local electrical field strength is sufficient to
breakdown that portion of the dielectric material (whether it be a deteriorated piece of insulation or an air
cavity). The discharges generally appear as pulses with a typical duration of less than 1us. While very short
in duration, the energy present in the discharge can interact with the surrounding dielectric material
resulting in further insulation degradation and eventually if left unchecked, insulation failure.
Partial Discharge Testing
Partial discharge testing can detect the presence and location of partial discharge activity in electrical
equipment. Suppose a piece of electrical equipment has a small air cavity in its insulation due to prolonged
degradation and the cavity is subject to partial discharge. We want to test for partial discharge and so we
connect a set of coupling capacitors in parallel to measure the charges caused by the partial discharge.
The figure right shows a simplified equivalent circuit
combined with a typical test circuit (as suggested in
IEC 60270). The circuit elements are as follows:
Vn is the voltage source
Ci is the capacitance of the insulation
system
Cp is the capacitance of an air cavity in the
insulation due to degradation
Ci' is the capacitance of the rest of the
insulation around the air cavity
Ck is the capacitance of the coupling
capacitor
M is the measuring system hooked up in series
At some inception volage, the electromagnetic field is strong enough to bridge the air cavity in the
insulation and a partial discharge occurs. After the breakdown of the air gap, the rest of the insulation
around the cavity (Ci) now sees the full voltage Vn and therefore the charge across Ci' increases.
This extra charge must be provided by all of the parallel capacitances around it (e.g. in this model Ci and
Ck) or the voltage source (though it is usually too slow to react). So in a typical situation, the capacitances
Ci and Ck discharge a short pulse into Ci' to provide the extra charge. However doing so reduces the
voltage across all the capacitances and the voltage source Vn reacts by charging all of the capacitances in
the system (including the air cavity) back to the normal voltage Vn.
9/30/2014 Partial Discharge - Open Electrical
http://www.openelectrical.org/wiki/index.php?title=Partial_Discharge 2/2
Partial discharge testing is done by directly measuring the short pulse discharged into Ci' by the coupling
capacitor Ck. In the equivalent circuit, the measuring system is represented by a single box M, but in
practice, this includes the coupling device, connecting cables, measuring device, etc.
Now it's clear that any pulse measured by the measuring system is not the actual partial discharge, but an
apparent charge caused by the real partial discharge (i.e. because the coupling capacitor Ck has to help
provide the extra charge for Ci'). It's not possible to directly measure the partial discharge, but the apparent
charges can be used to infer the level of partial discharge activity in the insulation system.
Test Circuit Calibration
Because only the apparent charges can be measured, it is important that the test circuit is properly
calibrated. During calibration, a pulse of known magnitude is delivered into the system to simulate a partial
discharge. The measuring system is then monitored to ensure that the test pulses are captured. The
calibration process is done so that pulses with magnitudes of interest (i.e. that will damage the system) are
reliably captured. A scaling factor can also be inferred based on the calibration tests.
References
[1] IEC 60270 (2000) "High Voltage Test Techniques - Partial Discharge Measurements"
[2] IEEE 400 (2001) "IEEE Guide for Field Testing and Evaluation of the Insulation of
Shielded Power Cable Systems"
[3] IEEE 1434 (2000) "IEEE Trial-Use Guide to the Measurement of Partial Discharges in
Rotating Machinery"
Retrieved from "http://www.openelectrical.org/wiki/index.php?title=Partial_Discharge"
Category: Electrical Testing
This page was last modified on 27 December 2012, at 19:12.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Impulse Generator Practical Course WorkDocument8 pagesImpulse Generator Practical Course WorkKapila Kumara100% (1)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionD'EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Curamik Design Rules DBC 20150901Document8 pagesCuramik Design Rules DBC 20150901Ale VuPas encore d'évaluation
- Technics 1998-1999Document18 pagesTechnics 1998-1999maneaxPas encore d'évaluation
- Nagashima Y.-Elementary Particle Physics Volume 1 Quantum Field Theory and ParticlesDocument9 pagesNagashima Y.-Elementary Particle Physics Volume 1 Quantum Field Theory and Particlespraveen alwisPas encore d'évaluation
- Partial DischargeDocument3 pagesPartial Dischargededy roy candra sihombingPas encore d'évaluation
- Partial Discharge - Open ElectricalDocument2 pagesPartial Discharge - Open ElectricalHerman DamanikPas encore d'évaluation
- Partial DischargeDocument5 pagesPartial DischargeAnonymous nXvsJH100% (1)
- Partial DischargedDocument3 pagesPartial DischargedNora Afzam Abd WahabPas encore d'évaluation
- Partial Discharge Overvieew Andsignal GenerationDocument7 pagesPartial Discharge Overvieew Andsignal GenerationcuntPas encore d'évaluation
- High Voltage Impulse GeneratorDocument10 pagesHigh Voltage Impulse GeneratorRoshan AkaravitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Recent Experiences With Ac Hipot & PD Commissioning Testing of Xlpe Cable Systems Rated 69Kv and Above Mark. Fenger, Mark Credland, Howard Sedding Kinectrics Inc CanadaDocument8 pagesRecent Experiences With Ac Hipot & PD Commissioning Testing of Xlpe Cable Systems Rated 69Kv and Above Mark. Fenger, Mark Credland, Howard Sedding Kinectrics Inc CanadaricPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2 Version 1 EEE 471 Switchgear and Protection - NMKHANDocument12 pagesLecture 2 Version 1 EEE 471 Switchgear and Protection - NMKHANMortuzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aspects Related To Replacing HV Lines by HV Cables On Resonant Grid BehaviorDocument6 pagesAspects Related To Replacing HV Lines by HV Cables On Resonant Grid Behaviordeepak_27Pas encore d'évaluation
- Zulu James Lab 1 4157Document7 pagesZulu James Lab 1 4157James Jimmy JahPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnostic Tests and Condition Monitoring of Electrical MachinesDocument3 pagesDiagnostic Tests and Condition Monitoring of Electrical Machineslbk50Pas encore d'évaluation
- PDDocument6 pagesPDViralBipinchandraRathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitive Reactance Experiment - LAB 7Document6 pagesCapacitive Reactance Experiment - LAB 7Mr_asad_20Pas encore d'évaluation
- Over Voltages and Insulation RequirementsDocument10 pagesOver Voltages and Insulation RequirementsPrema ElizabethPas encore d'évaluation
- E1 28 PDFDocument8 pagesE1 28 PDFSilverado01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Session 2000Document9 pagesSession 2000goluPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Blast Circuit BreakerDocument25 pagesAir Blast Circuit BreakerBhavya ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitors in DC Circuits: U Is Formed Between The Electrodes. The Subsequent Graphic Image Shows An ExampleDocument15 pagesCapacitors in DC Circuits: U Is Formed Between The Electrodes. The Subsequent Graphic Image Shows An Examplebeta akuiPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Engineering TermsDocument2 pagesElectrical Engineering TermsPalaparthy Venkata MaheshPas encore d'évaluation
- 191ee721 - Unit-1 To 5 QBDocument9 pages191ee721 - Unit-1 To 5 QBPoorani MahesPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper G 14Document5 pagesPaper G 14Dante FilhoPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 04Document55 pagesCH 04Fahad GhanyPas encore d'évaluation
- Triggered Voltage Vs Sphere Gap DistanceDocument8 pagesTriggered Voltage Vs Sphere Gap Distanceprabodh119100% (1)
- Vacuum Contactor Switching Phenomena PDFDocument9 pagesVacuum Contactor Switching Phenomena PDFjulianvillajosPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Industrial Instrumentation and Process Control (By William Dunn)Document13 pagesFundamentals of Industrial Instrumentation and Process Control (By William Dunn)Sergio AntonPas encore d'évaluation
- Partial Discharge Test With Surge Voltage in Electric Motors WindingsDocument3 pagesPartial Discharge Test With Surge Voltage in Electric Motors WindingsAgustin A.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ee8701 QBDocument8 pagesEe8701 QBNilambari BhaviniPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Utilities 1Document7 pagesEngineering Utilities 1Vanissa MontillaPas encore d'évaluation
- 022 TT Short-Circuit PDFDocument4 pages022 TT Short-Circuit PDFwwe_himanshuPas encore d'évaluation
- Direct-Current Voltage Testing by John Philip AbreoDocument27 pagesDirect-Current Voltage Testing by John Philip AbreoShiela Mae PongosPas encore d'évaluation
- ApuntesDocument28 pagesApuntesFrancisco RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- CT154 (Anglais)Document31 pagesCT154 (Anglais)kamlzPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitive Current SwitchingDocument4 pagesCapacitive Current SwitchingChandramouli RajagopalanPas encore d'évaluation
- TopicsDocument9 pagesTopicsvigneshwarannnPas encore d'évaluation
- Partial DischargeDocument5 pagesPartial DischargeAbdul AhadPas encore d'évaluation
- MPD Article What Is Partial Discharge 2020 ENUDocument2 pagesMPD Article What Is Partial Discharge 2020 ENUwellson engineerPas encore d'évaluation
- Superimposed Impulse Voltage Testing On Extruded Dc-Cables According To Iec CDV 62895Document6 pagesSuperimposed Impulse Voltage Testing On Extruded Dc-Cables According To Iec CDV 62895romany allamPas encore d'évaluation
- Theory of Static Winding Circuit AnalysisDocument13 pagesTheory of Static Winding Circuit AnalysisHoang Thanh VanPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitor: Navigation SearchDocument11 pagesCapacitor: Navigation SearchTuppada VeereshPas encore d'évaluation
- Automated Fault Clearance Using Fault Current Limiter in Primary Distribution SystemDocument6 pagesAutomated Fault Clearance Using Fault Current Limiter in Primary Distribution SystemIOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalPas encore d'évaluation
- Modelling Human BodyDocument28 pagesModelling Human BodyDhananjayPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Electronics DefinitionsDocument156 pagesBasic Electronics DefinitionsTejaswi YerraPas encore d'évaluation
- Transients in PowerDocument5 pagesTransients in Powerqais652002Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 7Document8 pagesLab 7Magdalena SimicPas encore d'évaluation
- Circuit BreakersDocument19 pagesCircuit BreakersOsama SalemPas encore d'évaluation
- 26 Most Asked Electrical Engineering Interview Questions and Answers With PDF CompressedDocument7 pages26 Most Asked Electrical Engineering Interview Questions and Answers With PDF CompressedAishwarya0% (1)
- What Are Partial Discharges On Cast Resin Transformers - EEPDocument3 pagesWhat Are Partial Discharges On Cast Resin Transformers - EEPa_mohid17Pas encore d'évaluation
- Partial DischargeDocument12 pagesPartial DischargetarsudinPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Eee Question Bank: Sub Code: Ee1004 Sub Name: Power System Transients Year: Iv SEM: ViiiDocument8 pagesDepartment of Eee Question Bank: Sub Code: Ee1004 Sub Name: Power System Transients Year: Iv SEM: Viiiqais652002Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Power Engineering - Partial Discharge - NazemiDocument31 pagesElectrical Power Engineering - Partial Discharge - NazemiDagobertortiz100% (3)
- Rosemary Ainslie. Quantum October 2002Document5 pagesRosemary Ainslie. Quantum October 2002MANNAJANELAGUNAPas encore d'évaluation
- Dry Type Transformer TestingDocument4 pagesDry Type Transformer TestingGary Martin100% (1)
- Efca 2 Lab 1vDocument8 pagesEfca 2 Lab 1vM Fa RizPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1Document32 pagesUnit 1Deadly SpyderPas encore d'évaluation
- Mitigation of Voltage Swells by Static Series Compensator: MemberDocument7 pagesMitigation of Voltage Swells by Static Series Compensator: MemberKevin MacancelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitor Switching Techniques: AbstractDocument4 pagesCapacitor Switching Techniques: AbstractMostafa MohmmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Switching A Normal' Load. Energizing A Load Begins With A Switching Device in The OpenDocument5 pagesSwitching A Normal' Load. Energizing A Load Begins With A Switching Device in The OpendenramrPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionD'EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionPas encore d'évaluation
- FileDocument12 pagesFileBHALAJI BIRLAPas encore d'évaluation
- FileDocument12 pagesFileBHALAJI BIRLAPas encore d'évaluation
- ApplicationDocument1 pageApplicationBHALAJI BIRLAPas encore d'évaluation
- ApplicationDocument1 pageApplicationBHALAJI BIRLAPas encore d'évaluation
- Industrial Training Report: ScadaDocument4 pagesIndustrial Training Report: ScadaBHALAJI BIRLAPas encore d'évaluation
- SG Industrial RepoetDocument23 pagesSG Industrial RepoetBHALAJI BIRLAPas encore d'évaluation
- IJCSE Template PDFDocument5 pagesIJCSE Template PDFBHALAJI BIRLAPas encore d'évaluation
- IJCSE Template PDFDocument5 pagesIJCSE Template PDFBHALAJI BIRLAPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Basic Electric MachinesDocument30 pages01 Basic Electric MachinesBHALAJI BIRLAPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydro-Electric Power Generation Plant: Submitted By:-Vijay Yadav Ex-Final YearDocument1 pageHydro-Electric Power Generation Plant: Submitted By:-Vijay Yadav Ex-Final YearBHALAJI BIRLAPas encore d'évaluation
- Partial Discharge - Open ElectricalDocument2 pagesPartial Discharge - Open ElectricalBHALAJI BIRLAPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Basic Electric MachinesDocument30 pages01 Basic Electric MachinesBHALAJI BIRLAPas encore d'évaluation
- Aryan NHDCDocument4 pagesAryan NHDCBHALAJI BIRLAPas encore d'évaluation
- V Ex Sy 200612042116Document11 pagesV Ex Sy 200612042116BHALAJI BIRLAPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction:-: Scalar Control of Induction MachineDocument2 pagesIntroduction:-: Scalar Control of Induction MachineBHALAJI BIRLAPas encore d'évaluation
- Aryan NHDCDocument4 pagesAryan NHDCBHALAJI BIRLAPas encore d'évaluation
- DiplomaDocument5 pagesDiplomaBHALAJI BIRLAPas encore d'évaluation
- Aryan NHDCDocument4 pagesAryan NHDCBHALAJI BIRLAPas encore d'évaluation
- Single Phase InverterDocument7 pagesSingle Phase InverterBHALAJI BIRLAPas encore d'évaluation
- GalvanometerDocument4 pagesGalvanometerBHALAJI BIRLAPas encore d'évaluation
- IntroductionDocument2 pagesIntroductionBHALAJI BIRLAPas encore d'évaluation
- Push Push VFODocument4 pagesPush Push VFOName100% (2)
- Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor With Ultrafast Soft Recovery DiodeDocument17 pagesInsulated Gate Bipolar Transistor With Ultrafast Soft Recovery DiodetaynatecPas encore d'évaluation
- Uc3843an PDFDocument16 pagesUc3843an PDFSergio Daniel BarretoPas encore d'évaluation
- BJT-CE Output Characteristics@varshi PDFDocument1 pageBJT-CE Output Characteristics@varshi PDFpriyansh jainPas encore d'évaluation
- K&H KL-720K&H KL-720.Document6 pagesK&H KL-720K&H KL-720.Gabriel SarmientoPas encore d'évaluation
- 5Holdelolw/7Hvwlqj3Urfhgxuhv: Varistor Plus Single Layer Technology Reliability Testing ProceduresDocument5 pages5Holdelolw/7Hvwlqj3Urfhgxuhv: Varistor Plus Single Layer Technology Reliability Testing ProceduresIgor PPas encore d'évaluation
- What Will Cover in This Lab?: Thevenin TheoremDocument5 pagesWhat Will Cover in This Lab?: Thevenin TheoremMuhammad AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- TMP61 ±1% 10-kΩ Linear Thermistor With 0402 and 0603 Package OptionsDocument32 pagesTMP61 ±1% 10-kΩ Linear Thermistor With 0402 and 0603 Package Optionsmauricio alfonsoPas encore d'évaluation
- Fdh5500 - F085: N-Channel Ultrafet Power Mosfet 55V, 75A, 7MDocument7 pagesFdh5500 - F085: N-Channel Ultrafet Power Mosfet 55V, 75A, 7MChristina MullinsPas encore d'évaluation
- Varlogic Nr6-Nr12 2 User ManualDocument32 pagesVarlogic Nr6-Nr12 2 User ManualDodik E. PrasetyoPas encore d'évaluation
- MG30 Generator Protection RelayDocument6 pagesMG30 Generator Protection Relaygovindappa54Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nais PLC Fp2Document39 pagesNais PLC Fp2hieutran86Pas encore d'évaluation
- EC-189191 MicroDocument88 pagesEC-189191 MicrohsuyabPas encore d'évaluation
- Wave GuidesDocument6 pagesWave GuidesEric John Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- ABB Capacitor ConstructionDocument4 pagesABB Capacitor Constructionzohaib06EE15Pas encore d'évaluation
- Noise NotesDocument89 pagesNoise NotesRaj AnPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Electronics I. HandoutDocument18 pagesApplied Electronics I. HandoutzemichaelPas encore d'évaluation
- Tripower Denso Catalog 2014 (Spark Plug Waukesha)Document7 pagesTripower Denso Catalog 2014 (Spark Plug Waukesha)FharishPutraPas encore d'évaluation
- TMS320C6713 Digital Signal ProcessorDocument4 pagesTMS320C6713 Digital Signal ProcessorAsit ParidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Silicone Rubber White PaperDocument6 pagesSilicone Rubber White PaperRahul YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Vol. 53 - No. 11: Diamond PassivesDocument184 pagesVol. 53 - No. 11: Diamond Passivesakumar_277Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1990 Seidel Aniso IIJES003626Document8 pages1990 Seidel Aniso IIJES003626Amit BiswasPas encore d'évaluation
- HW 5Document3 pagesHW 5Adarsh BasavalingappaPas encore d'évaluation
- IGBT TransistorsDocument16 pagesIGBT TransistorsMiodragPas encore d'évaluation
- Competency Based Learning Material: Sector: Electronics SectorDocument33 pagesCompetency Based Learning Material: Sector: Electronics SectorEmily Sadernas Awa100% (1)
- V1 - Multistage Amplifier N Current MirrorDocument18 pagesV1 - Multistage Amplifier N Current MirrorAshiqur Rahman ASPas encore d'évaluation
- QuizDocument5 pagesQuizSikander AzamPas encore d'évaluation