Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Computer Memories PDF
Transféré par
flobarragan90100%(1)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (1 vote)
285 vues4 pages1. The document discusses different types of computer memory storage including RAM, ROM, battery-backed RAM, hard disks, floppy disks, CD-ROMs, and RW-CDs. It describes how each type of memory functions and its advantages.
2. RAM is volatile memory used for active programs and data, while ROM stores permanent programs like the operating system. Hard disks provide large non-volatile storage and floppy disks allow portability but have smaller storage capacities. CD-ROMs and RW-CDs provide high storage capacities and durability.
3. All computer memory ultimately stores information using binary logic of 1s and 0s to represent data through different encoding schemes depending on
Description originale:
Titre original
2. Computer Memories.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce document1. The document discusses different types of computer memory storage including RAM, ROM, battery-backed RAM, hard disks, floppy disks, CD-ROMs, and RW-CDs. It describes how each type of memory functions and its advantages.
2. RAM is volatile memory used for active programs and data, while ROM stores permanent programs like the operating system. Hard disks provide large non-volatile storage and floppy disks allow portability but have smaller storage capacities. CD-ROMs and RW-CDs provide high storage capacities and durability.
3. All computer memory ultimately stores information using binary logic of 1s and 0s to represent data through different encoding schemes depending on
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
100%(1)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (1 vote)
285 vues4 pagesComputer Memories PDF
Transféré par
flobarragan901. The document discusses different types of computer memory storage including RAM, ROM, battery-backed RAM, hard disks, floppy disks, CD-ROMs, and RW-CDs. It describes how each type of memory functions and its advantages.
2. RAM is volatile memory used for active programs and data, while ROM stores permanent programs like the operating system. Hard disks provide large non-volatile storage and floppy disks allow portability but have smaller storage capacities. CD-ROMs and RW-CDs provide high storage capacities and durability.
3. All computer memory ultimately stores information using binary logic of 1s and 0s to represent data through different encoding schemes depending on
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
1 INSTITUTO SUPERIOR DEL TRADUCTORADO-DIPREGEP 5649 Calle 6 N 843 (48 y 49) TRADUCTORADO OFICIAL
THEORY AND PRACTICE OF ASSISTED TRANSLATION
INSTITUTO SUPERIOR DEL TRADUCTORADO-DIPREGEP 5649
Memory is a storage capacity that comes as either a microchip or a backing storage
device. A microchip is a minute circuit made up of a tiny silicon square that has been treated
with photosensitive lacquer and bonded with gold wires to its connections. In a
microcomputer there are two types of memory chips: the ROM and the RAM. The main
memory is RAM. RAM is a chip that can be written to and read from. It is volatile.
ROM is usually used in microcomputers for programs which it is convenient to have
available at any time, in particular when the computer has just been switched on. Normally
the Operating System is in ROM. When the computer is switched on, the Operating System in
the ROM chip runs immediately. In order to change the Operating System, the actual ROM
chip must be removed and another inserted.
Some microcomputers save the date and time on Battery Backed RAM chip. This is a
small amount of RAM memory powered by a battery. The contents of Battery Backed RAM
can be altered, but because it is powered by a battery, these contents are not lost when the
computer is switched off.
To store large amounts of data when the computer is switched off, Backing Storage
devices are used. Backing Storage is long-term storage that is non-volatile. Data stored in the
backing storage memory is kept intact when the computer is turned off. When it is needed
again it can be loaded into the memory from the backing storage device. Backing storage
could be in-built or portable. The in-built backing storage device is the computers hard disc.
It is a rigid, inflexible disc that stores the most frequently used programs and data that are
needed for the computers operation. Hard discs may be single or stacked (i.e. several platters
piled one over the other). The read/write heads of a hard disc move in unison, floating just
above the surface of the platter. There is one read/write head for each platter. When a hard
disc is switched on, the disc spins at a uniform, high speed. The read/write heads are separated
from the discs surface by a cushion of air 10 to 25 millionth of an inch deep. When in
operation, the disc spins at an average of 3,600 revolutions per minute (rpm), so fast that a
speck of dust is sufficient to cause a head crash that will destroy the disc. For this reason,
hard discs come sealed into the disc drive unit.
COMPUTER MEMORIES
2 INSTITUTO SUPERIOR DEL TRADUCTORADO-DIPREGEP 5649 Calle 6 N 843 (48 y 49) TRADUCTORADO OFICIAL
Portable backing storage devices like magnetic tapes and discs are often used as a
convenient way of storing information. The magnetic discs are portable backing storage
devices that vary considerably, depending on the size of the computer. However, they all
provide faster access than the corresponding magnetic tape which is now obsolete.
Data is stored on a magnetic disc on concentric tracks. Each track is divided into
sectors, each separated by inter-sector gaps. A sector is a unit of data read from or written to
the disc by the computer in a single read or write operation. To form the tracks and sectors,
you format a disc. This means that the disc is divided into tracks and sectors on which files
can be stored. Most discs come formatted, but when you format a disc which has already been
used, you delete any files already on the disc to create new tracks and sectors.
The most common types of portable magnetic discs are the floppy discs.
The floppy disc is a flexible, circular, re-recordable plastic disc coated with a magnetic
material. It is contained in a protective sleeve (Fig. 4). The read/write heads access the disc
through the read/write hole. The heads are actually in contact with the surface of the disc as it
spins. This reduces the life span and reliability of the floppy disc. When inserted into the disc
drive, the disc is gripped by the drive through its central hole, and spun at approximately 350
revolutions per minute (rpm).
Protective sleeve Fig. 4
The write protect mechanism is used to protect files on the floppy disc. When the write
protect mechanism in a 3 inch disc is on (i.e. the write protect hole is open), you cannot
save files on the disc, delete files saved on the disc nor alter files saved on the disc.
There used to be two types of floppy discs in the market: the 3 inch and the 5 inch
floppy discs. At the same time they came in high or low density that means the disc can store
more or less information, respectively.
A standard 5 inch floppy disc can store 320K of data (320 Kilobytes), whereas a 3
floppy disc can store 720K of data (720 Kilobytes), or more (Fig. 5). At present, the 5
inch floppy discs have disappeared and the 3 , although they used to be the most widely
Central hole
Write protect notch
Metal cover
Read/write hole
3 INSTITUTO SUPERIOR DEL TRADUCTORADO-DIPREGEP 5649 Calle 6 N 843 (48 y 49) TRADUCTORADO OFICIAL
used ones due to their larger storage capacity, smaller size and low cost, are steadily giving
way to the rewritable CD-ROM discs and pendrives.
FLOPPY DISC DENSITY STORAGE CAPACITY
5 inch
Low 320K
High 1.2M
3 inch
Low 720K
high 1.5M
Fig. 5
The CD-ROM discs are based on the use of Compact Disc (CD) technology for
backing storage for computers. CD-ROMs can be used to store very large amounts of data on
a relatively durable backing storage medium that can be accessed at speeds comparable with
magnetic discs.
An advantage of CD-ROM discs is their very high on-line storage capacity. A CD-
ROM disc can store up to 1,000M of data. This could be up to 500,000 A4 pages of text.
Another advantage of CD-ROMs is the robust nature of the discs. A CD-ROM is 12 cm in
diameter. This is a relatively compact and easy to handle way of storing such high volumes of
data.
The CD-ROM is an optical medium. It is read by a laser beam which scans tiny pits on
the surface of the disc. Consequently the risk of damage when the disc is accessed is reduced
as there is no contact between the read mechanism and the disc. The discs are coated with a
protective layer that allows them to be handled without erasing the data or damaging the disc.
The robust nature of CD-ROMs makes them suitable for the long term storage of data and for
data in frequent use. Yet the information on not all CD-ROMs can be deleted or changed.
There are Write Once Read Many (WORM) CDs that enable to save data once. The
data can then be read as many times as you like but you cannot delete or change it after the
first recording. WORM discs are recordable CDs, but not rewritable.
To be able to re-record information on CDs, special technology is needed. This type of
backing storage is called RW-CD (Rewritable Compact Disc). To the advantages of the CD-
ROM it adds the versatility of a floppy disc.
In principle, almost anything we can hear or see can be digitally converted and stored
in any form that exists in two states: as laser-readable optical pits and smooth areas (CDs and
DVDs), or as positive and negative electric charges (magnetic tapes or discs). Ultimately, all
forms of computer memory store information using binary logic. Binary logic is two-state
4 INSTITUTO SUPERIOR DEL TRADUCTORADO-DIPREGEP 5649 Calle 6 N 843 (48 y 49) TRADUCTORADO OFICIAL
logic. This means that only two states are possible. These two states are voltage levels of 5V
(on) and 0V (off). 5V is used to represent the digit 1 and 0V to represent 0.
The memory of the computer is simply a very large number of 1s and 0s that form
patterns that are recognised by the computer. In binary logic each of the 1s and 0s that form
patterns is called a binary digit. This means one digit of either two: 1 or 0. Because
everything in the memory of a computer is represented using 1s and 0s (digits), the computer
is described as being digital.
Binary digits are also known as bits that is a clipping of the original name: binary
digits. The smallest memory unit is the byte. A byte is equivalent to 8 grouped bits, e.g.
01100110, 11010111, etc. A byte is enough to store an alphanumeric character (a letter or a
number). Each different character must have a different binary code associated with it. Hence
the number of bits used determines the number of characters it is possible to code. An 8-bit
code, for example, is capable of representing 256 different characters or combinations:
00000000, 00000001, 00000011, 00000111, 00001111, 00011111, 00111111, 01111111,
11111111, 1111110, etc. Each of these 256 combinations represents a character, i.e. any sign
or symbol, like a comma, a blank space, a numeral, an asterisk, etc.
Most computers and peripherals are digital but some are not. Sensors are analogue
devices. For example, a heat sensor produces a small voltage in response to temperature
changes. This small voltage is known as an analogue signal. When the analogue signal is
input to a digital computer it must be converted from analogue to digital form. This is done
using an ADC (Analogue to Digital Convertor).
Likewise, if a digital computer outputs to an analogue device then a DAC (Digital to
Analogue Convertor) is used. This converts the digital signal from the computer to an
analogue form.
Storing information in a memory requires large numbers of bytes. For this reason,
memory sizes are measured in larger units, multiples of the byte (Fig. 6).
UNIT OF
MEMORY SIZE
EQUIVALENT
IN BYTES
Kilobyte (Kbyte or K) 1024 bytes 2
10
bytes
Megabyte (Mbyte or M) 1024 K bytes 2
20
bytes
Gigabyte (Gbyte or G) 1024 M bytes 2
30
bytes
Fig. 6
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Beginner's Guide for Cybercrime InvestigatorsD'EverandBeginner's Guide for Cybercrime InvestigatorsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Secondary Storage Devices: Units of Memory StorageDocument6 pagesSecondary Storage Devices: Units of Memory StorageRiswan BabuPas encore d'évaluation
- Secondary Storage DevicesDocument17 pagesSecondary Storage DevicesWamiq ReyazPas encore d'évaluation
- Secondary Storage DevicesDocument5 pagesSecondary Storage DevicesTauseef ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
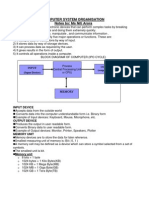
- Computer System Organisation - NotesDocument9 pagesComputer System Organisation - NotesNiti Arora0% (1)
- Project: Secondary Storage DevicesDocument10 pagesProject: Secondary Storage DevicesprasooonPas encore d'évaluation
- Secondary Storage DevicesDocument3 pagesSecondary Storage DevicesHaider Habib RanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Memory and Storage and A Little BitDocument32 pagesMemory and Storage and A Little BitWalid_Sassi_TunPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Project: Topic: Storage DevicesDocument12 pagesComputer Project: Topic: Storage DevicesPalash ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1.3. Input, Output and StorageDocument8 pages1.1.3. Input, Output and StorageEthanPas encore d'évaluation
- StorageDocument15 pagesStorageRitikPas encore d'évaluation
- Secondary Storage and MediaDocument33 pagesSecondary Storage and MediaBharti PahujaPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer HardWareDocument46 pagesComputer HardWareFrancesca AckumburPas encore d'évaluation
- Comp Activity 2Document3 pagesComp Activity 2Olsen SoqueñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Microprocessor and Microcontroller AssignmentDocument5 pagesMicroprocessor and Microcontroller AssignmentADITYA GAURAVPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Circuit Binary SystemDocument13 pagesDigital Circuit Binary SystemAlishbah Khan NiaziiPas encore d'évaluation
- Secondary MemoryDocument16 pagesSecondary Memoryeduardo acuniaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3last Components of Comp Hardware-1 Backing StoreDocument27 pages3last Components of Comp Hardware-1 Backing StoreOliver JohnsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Storage DevicesDocument3 pagesStorage DevicesKamran AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 - Hardware - Storage DevicesDocument20 pagesUnit 3 - Hardware - Storage DevicesLan HoangPas encore d'évaluation
- CA Classes-261-265Document5 pagesCA Classes-261-265SrinivasaRaoPas encore d'évaluation
- BSIT AssignmentDocument2 pagesBSIT AssignmentArchie CuyacotPas encore d'évaluation
- Ict 1Document15 pagesIct 1Noor AliPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Data Representation, Memory & Secondary Storage DevicesDocument33 pages2 Data Representation, Memory & Secondary Storage DevicesMayor ParasharPas encore d'évaluation
- Storage NotesDocument12 pagesStorage NotesJoemon JosePas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment OF ICTDocument14 pagesAssignment OF ICTArooj ArifPas encore d'évaluation
- K13-03-04 Digital Tehniques / Electronics Intrument System - Nama: NDP: Le 2: Recognize The Basic Computer StructureDocument12 pagesK13-03-04 Digital Tehniques / Electronics Intrument System - Nama: NDP: Le 2: Recognize The Basic Computer StructureGanesh Ruban AnathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Magneto Optical DrivesDocument4 pagesMagneto Optical DrivesRahul C SivadasPas encore d'évaluation
- Program No.8a: Storage Main Memory Secondary Memory Different Speeds Magnetic Media Optical Media Access ModesDocument4 pagesProgram No.8a: Storage Main Memory Secondary Memory Different Speeds Magnetic Media Optical Media Access ModesMangesh PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap6 Secondary StorageDocument21 pagesChap6 Secondary StorageVishal KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Secondary Storage DevicesDocument7 pagesSecondary Storage DevicesHanzla ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 StorageDocument15 pagesChapter 5 StorageTsepiso MohalePas encore d'évaluation
- On MemoryDocument34 pagesOn MemoryZuhair Ibne Alam8KPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Memory ? Different Types of Memory in Computer With ExamplesDocument13 pagesComputer Memory ? Different Types of Memory in Computer With Examplesgabriel chinechenduPas encore d'évaluation
- Suggest AnswersDocument10 pagesSuggest Answerssms71106Pas encore d'évaluation
- ICT NotesDocument4 pagesICT NotesMaulin Caudilla LadizaPas encore d'évaluation
- ICT 10 FIRST QUARTER Topic-8-Hardware-fundamentals-Storage-DevicesDocument53 pagesICT 10 FIRST QUARTER Topic-8-Hardware-fundamentals-Storage-DevicesDonna Joy AmahitPas encore d'évaluation
- Secondary Storage Devices 1.magnetic TapeDocument2 pagesSecondary Storage Devices 1.magnetic TapeKunal RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Cso 2Document4 pagesCso 2Mcreediocre -OWPas encore d'évaluation
- FIT Presentation NODocument23 pagesFIT Presentation NOmirzarakeekPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 Outline UneditedDocument15 pagesUnit 3 Outline UneditedEvan YEUNG [09N12]Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lec04-Auxiliary MemoryDocument32 pagesLec04-Auxiliary MemorykasunPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Computing: Date: 15 April 2019Document4 pagesIntroduction To Computing: Date: 15 April 2019Ghznfar IqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- Disks and DrivesDocument18 pagesDisks and Driveskevinkingili450Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Storage of MultimediaDocument6 pagesChapter 4 Storage of Multimediakaleb DenekePas encore d'évaluation
- Device ManagementDocument57 pagesDevice ManagementsaravanakumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Bca1 Fit Unit3Document14 pagesBca1 Fit Unit3Sunny RanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Memory: Computer Data StorageDocument15 pagesMemory: Computer Data StorageLucky SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cs 2 Assignment 2Document5 pagesCs 2 Assignment 2Rajnikhanth123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Name: - Russell D'souza F.Y.BMS Roll No.: - 17 Introduction To Computers Submitted To: - Miss Vileena 2013-2014 SignDocument17 pagesName: - Russell D'souza F.Y.BMS Roll No.: - 17 Introduction To Computers Submitted To: - Miss Vileena 2013-2014 SignRussell D'souza100% (1)
- Notes Unit 5 OSDocument16 pagesNotes Unit 5 OSSahil PahwaPas encore d'évaluation
- Optical Storage DevicesDocument5 pagesOptical Storage DevicesAbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter EightDocument27 pagesChapter EightMohamed FarahPas encore d'évaluation
- COA ProjectDocument11 pagesCOA ProjecthafeezPas encore d'évaluation
- Hard DrivesDocument69 pagesHard Drivesprerana shetePas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 08 Storage DevicesDocument28 pagesUnit 08 Storage DevicesPrakash DangolPas encore d'évaluation
- Magnetic MemoryDocument4 pagesMagnetic MemoryMohit BerryPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic: 1.3.5 Memory, Storage Devices and Media: Two Types Primary Memory Secondary MemoryDocument13 pagesTopic: 1.3.5 Memory, Storage Devices and Media: Two Types Primary Memory Secondary MemoryAthuai DoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6Document45 pagesChapter 6Yd ManPas encore d'évaluation
- COC 1 Computer Systems Servicing Presentation by Horacio N. Aceveda JRDocument92 pagesCOC 1 Computer Systems Servicing Presentation by Horacio N. Aceveda JRAriane Pearl Cuevas IslaPas encore d'évaluation
- PIC16f877A Microcontrollers and Embedded SystemsDocument43 pagesPIC16f877A Microcontrollers and Embedded SystemsTarek BarhoumPas encore d'évaluation
- Pham MASc ThesisDocument146 pagesPham MASc ThesisMunaf Hussain ShaikPas encore d'évaluation
- ACRONIME CalculatoareDocument260 pagesACRONIME CalculatoarecgabriellePas encore d'évaluation
- Ee316 4Document25 pagesEe316 4bigirimwPas encore d'évaluation
- Mealy SolutionsDocument265 pagesMealy SolutionsDasibPas encore d'évaluation
- ADE7953 EnergyMeterDocument2 pagesADE7953 EnergyMeterKram Nhoj TabatabPas encore d'évaluation
- Wiring Diagrams of PLC and DCS Systems - DI, DO, AI, AODocument1 pageWiring Diagrams of PLC and DCS Systems - DI, DO, AI, AODani FayçalPas encore d'évaluation
- Week7 IOsDocument23 pagesWeek7 IOsMuhammad Usama IbrarPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Management in Islanded DC Microgrid Using Fuzzy Controller To Improve Battery PerformanceDocument6 pagesEnergy Management in Islanded DC Microgrid Using Fuzzy Controller To Improve Battery PerformanceVelid ÇelikPas encore d'évaluation
- Circuit DescriptionDocument15 pagesCircuit DescriptionmohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultrasonic Velocity Test System 65Document4 pagesUltrasonic Velocity Test System 65Sergio CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Mozzi Interactive Sound Synthesis On The Open Source ArduinoDocument7 pagesMozzi Interactive Sound Synthesis On The Open Source ArduinojfkPas encore d'évaluation
- RP1D060D4Document2 pagesRP1D060D4Eraldo HofelmannPas encore d'évaluation
- IcaDocument2 pagesIcaapi-279049687Pas encore d'évaluation
- HEXIWEAR Hands-On Online TrainingDocument77 pagesHEXIWEAR Hands-On Online Trainingmeroka2000Pas encore d'évaluation
- User Manual: SRV02 Rotary Servo Base UnitDocument25 pagesUser Manual: SRV02 Rotary Servo Base UnitSeyhaSunPas encore d'évaluation
- Clarion Pu-2294a Pu-2325a Pu-2294b PDFDocument16 pagesClarion Pu-2294a Pu-2325a Pu-2294b PDFseotut0% (1)
- Pce 210sme 503Document79 pagesPce 210sme 503info_71071376689% (18)
- Pic12f683Document225 pagesPic12f683Yo CretzuPas encore d'évaluation
- Datasheet: Kit Contents - NI 9229 - NI 9229 Getting Started GuideDocument14 pagesDatasheet: Kit Contents - NI 9229 - NI 9229 Getting Started GuideChecho260493Pas encore d'évaluation
- CMX7164FI 2 4 2dsDocument91 pagesCMX7164FI 2 4 2dsbilou57Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit I DC Corrected Version-LibDocument32 pagesUnit I DC Corrected Version-LibpanthamangalamPas encore d'évaluation
- Bp30 - Operation - Maintenance - Final Manual 1-12-07Document145 pagesBp30 - Operation - Maintenance - Final Manual 1-12-07suresh kPas encore d'évaluation
- Embedded System For Hazardous Gas Detection and AlertingDocument14 pagesEmbedded System For Hazardous Gas Detection and AlertingijdpsPas encore d'évaluation
- M68HC08 To HCS08 TransitionDocument26 pagesM68HC08 To HCS08 TransitionRoman CorreaPas encore d'évaluation
- 623 2320 1 PBDocument4 pages623 2320 1 PBbatuhanPas encore d'évaluation
- ZSC31014Document65 pagesZSC31014William RobinsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Flyer - ibaPADU 8 HI I - EN PDFDocument2 pagesFlyer - ibaPADU 8 HI I - EN PDFc.a.g.p.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Spartan 3 BoardDocument22 pagesSpartan 3 Boardsureshfm1Pas encore d'évaluation
- iPhone 14 Guide for Seniors: Unlocking Seamless Simplicity for the Golden Generation with Step-by-Step ScreenshotsD'EverandiPhone 14 Guide for Seniors: Unlocking Seamless Simplicity for the Golden Generation with Step-by-Step ScreenshotsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Chip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyD'EverandChip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (82)
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyD'EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (229)
- CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Ninth EditionD'EverandCISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Ninth EditionÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Cyber-Physical Systems: Foundations, Principles and ApplicationsD'EverandCyber-Physical Systems: Foundations, Principles and ApplicationsHoubing H. SongPas encore d'évaluation
- CompTIA A+ Certification All-in-One Exam Guide, Eleventh Edition (Exams 220-1101 & 220-1102)D'EverandCompTIA A+ Certification All-in-One Exam Guide, Eleventh Edition (Exams 220-1101 & 220-1102)Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra User Guide For Beginners: The Complete User Manual For Getting Started And Mastering The Galaxy S22 Ultra Android PhoneD'EverandSamsung Galaxy S22 Ultra User Guide For Beginners: The Complete User Manual For Getting Started And Mastering The Galaxy S22 Ultra Android PhonePas encore d'évaluation
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102D'EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- iPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]D'EverandiPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002D'EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Practice Tests: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102D'EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Practice Tests: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Pas encore d'évaluation
- iPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XD'EverandiPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- Computer Science: A Concise IntroductionD'EverandComputer Science: A Concise IntroductionÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (14)
- Cancer and EMF Radiation: How to Protect Yourself from the Silent Carcinogen of ElectropollutionD'EverandCancer and EMF Radiation: How to Protect Yourself from the Silent Carcinogen of ElectropollutionÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Jensen Huang's Nvidia: Processing the Mind of Artificial IntelligenceD'EverandJensen Huang's Nvidia: Processing the Mind of Artificial IntelligencePas encore d'évaluation
- Raspberry PI: Learn Rasberry Pi Programming the Easy Way, A Beginner Friendly User GuideD'EverandRaspberry PI: Learn Rasberry Pi Programming the Easy Way, A Beginner Friendly User GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- Arduino and Raspberry Pi Sensor Projects for the Evil GeniusD'EverandArduino and Raspberry Pi Sensor Projects for the Evil GeniusPas encore d'évaluation
- A Beginner's Guide To IPhone 14 Pro Max Mastering: The Comprehensive User Guide And Illustrated Owner's Manual With Tips And Advanced Tricks For New BeD'EverandA Beginner's Guide To IPhone 14 Pro Max Mastering: The Comprehensive User Guide And Illustrated Owner's Manual With Tips And Advanced Tricks For New BePas encore d'évaluation
- The comprehensive guide to build Raspberry Pi 5 RoboticsD'EverandThe comprehensive guide to build Raspberry Pi 5 RoboticsPas encore d'évaluation
- iPhone Photography: A Ridiculously Simple Guide To Taking Photos With Your iPhoneD'EverandiPhone Photography: A Ridiculously Simple Guide To Taking Photos With Your iPhonePas encore d'évaluation
- Debugging Embedded and Real-Time Systems: The Art, Science, Technology, and Tools of Real-Time System DebuggingD'EverandDebugging Embedded and Real-Time Systems: The Art, Science, Technology, and Tools of Real-Time System DebuggingÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- The User's Directory of Computer NetworksD'EverandThe User's Directory of Computer NetworksTracy LaqueyPas encore d'évaluation
































































































![iPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/audiobook_square_badge/728318688/198x198/f3385cbfef/1715193157?v=1)