Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Computer Basics Vocabulary
Transféré par
Mamen CañoCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Computer Basics Vocabulary
Transféré par
Mamen CañoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Computer Technology Vocabulary
1
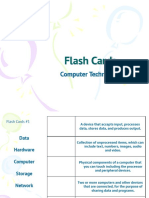
COMPUTER BASICS VOCABULARY
Types of Computers
1. Desktop Microcomputer: A personal computer based on a
microprocessor.
2. WorkStation: A desktop computer that is conventionally
considered to be more powerful than a microcomputer.
(Minicomputer)
3. Laptop or Notebook: A portable computer small enough to use on
ones lap.
4. Mainframe: A large, powerful, expensive computer system capable
of accommodating hundreds of users doing different computing
tasks.
5. Server: A computer and its associated storage devices that are
accessed remotely over a network by users.
6. Handheld: Compact enough to be used or operated while being held
in the hand or hands: a hand-held video camera
Computer Performance and Processing
1. Boot Process: Bootstrapping is the process of starting up a
computer from a halted or powered-down condition
2. Input: Information that is created or collected and fed into the
system.
3. Base 2 binary code: A numbering system with only two digits
numbers are 0 and 1. All numbers are comprised of only these two
digits.
4. Data: Facts used by a computer.
5. Information: Processed, stored or transmitted data.
6. Output: Useful information that leaves the system; i.e. processed
information.
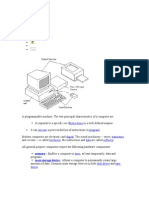
Computer Components: Hardware
1. System Unit: The main body of a computer, consisting of a plastic
or metal enclosure, the motherboard, and (typically) internal disk
drives, or power supply, cooling fans, and whatever circuit boards
plugged into the motherboard, such as a video card. The system
Computer Technology Vocabulary
2
unit is occasionally referred to as the CPU, though this really
means central processing unit.
2. CPU: Central processing unit. The brains of the computer. The
CPU is housed on a tiny silicon chip that contains millions of
switches and pathways that help your computer interpret and
execute instructions. This is where the mathematical calculations
and logical comparisons are done.
3. Circuits: (a)A closed path followed or capable of being followed by
an electric current. (b) A configuration of electrically or electro
magnetically connected components or devises.
4. Silicon chip: a small crystal of silicon semiconductor fabricated to
carry out a number of electronic functions in an integrated circuit.
5. MHz: Millions of cycles per second, a unit used to measure clock
speed in computers.
6. Pentium: The name given to Intels P5 chip, the successor to the
80486. The name was chosen because of difficulties Intel had in
trade marking a number. It suggests the number five (implying
586) while (according to Intel) conveying a meaning of strength
like titanium. Among hackers, the plural is frequently pentia.
7. RAM: Random Access Memory. It is the main memory and stores
data and programs while the computer is running. When the
computer is turned off anything in main memory disappears.
Computer can read from and write to this memory.
8. ROM: Read Only Memory. A computer chip that stores specific
instructions to manage the computers operation. Unlike main
memory, this type of memory is non-volatilethe instructions
remain permanently on the chip and cannot be changed.
9. Bit: A fundamental unit of information having just two possible
values, either 0 or 1.
10. Byte: A sequence of adjacent bits, usually eight, operated on as a
unit by a computer.
11. Kilobyte: A unit of computer memory or data storage capacity
equal to 1,024 bytes.
12. Megabyte: A unit of computer memory or data storage capacity
equal to 1,024 kilobytes.
13. Gigabyte: A unit of computer memory or data storage capacity
equal to 1,024 megabytes
Computer Technology Vocabulary
3
14. Terabyte: A unit of computer memory or data storage capacity
equal to 1,024 gigabytes.
15. Storage devices: A hardware device, such as a hard disk or floppy
disk, used to record and store data.
16. Magnetic storage: Storage device where data is saved (before
disks). Much like a reel to reel.
17. Optical Storage: Use of laser technology to read and write data on
silver platters.
18. Laser: High quality and faster. Uses the same technology as copier
machines.
19. Hard Disk: A rigid magnetic disk mounted permanently in a drive
unit.
20. Floppy Disk: A small plastic magnetic disk enclosed in a stiff
envelope with a radial slit; used to store data or programs for a
microcomputer. Floppy disks are noted for their relatively slow
speed and small capacity and low price.
21. Write-protected: To modify (a file or disk) so that its data cannot
be edited or erased.
22. Format: Prepares a disk for use on a specific type of drive by
imprinting the disk with the information it needs to work in that
particular kind of drive. Also the ability to control the appearance
and layout of data in a file.
23. Zip Disk: Magnetic disk storage device that has more capacity that
floppy disk.
24. Digital Audio tape: A format for storing music on magnetic tape.
25. CD-ROM: A compact disk that functions as read-only memory.
26. CD-R: Compact disc on which you can write only once and
thereafter is read-only.
27. CD-RW: Compact disk-rewritable.
28. DVD-ROM: Digital video disk, better capabilities.
29. Input devices: Any device used to input data into the computer
(keyboard, mouse, scanner, etc).
30. Output Devices: Device used when reading/looking at output
printer, screen.
31. Resolution: Amount of pixels on the screen. More pixels the better
resolution.
32. Pixels: The basic unit of the composition of an image on a television
screen, computer monitor, or similar display.
Computer Technology Vocabulary
4
33. Peripheral devices: Devices connected by cable to the CPU of a
computer; disk drives and printers are important peripherals.
Computer Components: Software
1. Program: A series of commands and executable files that produce
an expected result.
2. Operating System software: A type of software that provides an
interface between the user or application software and the
computer hardware.
3. Folder: A way to organize files into logical and manageable groups
4. Multitasking: The ability of an operating system to run more than
one software program at a time.
5. GUI (Graphical User Interface): A computer interface that
enables a user to control the computer and launch commands by
pointing and clicking at graphical objects such as windows, icons,
and menu items.
6. Platform: Compatible computers from one or more manufacturers;
the two popular platforms for personal computers are PCs and
Macintoshes.
7. Icons: An image that represents an executable file.
8. Menus: A list or table of executable options.
9. Application software: A program that performs a specific function.
Viruses and Destructive Programs
1. Computer Virus: Programming code created as a prank or as a
malicious action that secretly affects other programs and causes
unwanted consequences.
2. Boot Sector Virus: A virus that infects the start-up files.
3. File virus: A file that infects the files and programs that are on
the hard drive.
4. Trojan Horse: A virus that can sneak inside of another file, that
can be executed at a specific time, or under specific
circumstances.
5. Time Bomb: Computer virus that does not cause its damage until a
certain date or until the system has been booted a certain number
of times.
Computer Technology Vocabulary
5
6. Worm: A computer virus that makes many copies of itself resulting
in the consumption of system resources, thus slowing down or
actually halting tasks.
7. Logic Bomb: Computer virus that is triggered by the appearance or
disappearance of specified data.
8. Attachments: A file that is attached to another file.
Networks
1. File server: A computer that is dedicated to running applications
and storing data, which can be shared with other work-stations.
2. LAN Intranetwork: Local Area Network. A method by which
multiple computers and other devices such as printers or scanners
are connected within a confined space such as an office building.
3. WAN Internetwork: Wide Area Network by which computers over
larger geographical areas can be connected.
4. IP Address: A unique address assigned to a computer so it may be
located across the web.
History
1. Charles Babbage invented the difference machine.
2. Grace Hopper coined the term debugging.
3. Bill Gates system and application software is what made him rich.
4. Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak were two creators of Apple
Corporation.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Information Technology (Aland)Document6 pagesInformation Technology (Aland)Namo SlimanyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 (Module 6) 1. Describe The Hardware Referred To by The Terms, System Unit and ChassisDocument21 pagesChapter 2 (Module 6) 1. Describe The Hardware Referred To by The Terms, System Unit and ChassisniklynPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of Information and Communication Technology: Name: Roll No: Assignment Topic: Submitted To: Subject: DateDocument101 pagesApplication of Information and Communication Technology: Name: Roll No: Assignment Topic: Submitted To: Subject: Dateawaisiqbal132453Pas encore d'évaluation
- Computer FundamentalDocument19 pagesComputer Fundamentalredcard53Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1: Computers & Basic TerminologyDocument7 pagesLesson 1: Computers & Basic TerminologyIdham Aji WiranataPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1-Introduction To ComputersDocument8 pagesWeek 1-Introduction To ComputersJontex 254Pas encore d'évaluation
- P1 Glossari InformàticDocument6 pagesP1 Glossari InformàticjosePas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Computer?Document17 pagesWhat Is Computer?Narender SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Smcsxi PDFDocument92 pagesSmcsxi PDFsrenathPas encore d'évaluation
- Task 4Document3 pagesTask 4nadiya saputriPas encore d'évaluation
- Flash Cards: Computer TechnologyDocument13 pagesFlash Cards: Computer TechnologyKhulood Al GhailaniPas encore d'évaluation
- 2nd Quarter - Review - INSTALLING AND CONFIGURING COMPUTER SYSTEMSDocument21 pages2nd Quarter - Review - INSTALLING AND CONFIGURING COMPUTER SYSTEMSAlyzzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer BasicDocument2 pagesComputer BasicketchheroPas encore d'évaluation
- MODULE123Document71 pagesMODULE123AnalizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Material XI Comp Final CkeckedDocument12 pagesStudy Material XI Comp Final CkeckedrosePas encore d'évaluation
- CHM All NotesDocument28 pagesCHM All Notesabhishek.kunduPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 3-5 CSS 3Document15 pagesModule 3-5 CSS 3Princess Joy SarmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer LiteracyDocument13 pagesComputer LiteracyAb hamidPas encore d'évaluation
- Hardware Part 1 Defenitions PDFDocument1 pageHardware Part 1 Defenitions PDFpearl042008Pas encore d'évaluation
- Modern Computers Defined: Instructions Execute ProgramDocument2 pagesModern Computers Defined: Instructions Execute ProgramNajeeb Muhammad HasniPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer 1: (Introduction To Computer Concepts and Software)Document32 pagesComputer 1: (Introduction To Computer Concepts and Software)Cristin Porcadilla ArantePas encore d'évaluation
- 1) Computer Concepts NotesDocument6 pages1) Computer Concepts NotesVenus Leilani Villanueva-Granado100% (2)
- A Balanced Introduction To Computer Science, 2/EDocument21 pagesA Balanced Introduction To Computer Science, 2/EmainakroniPas encore d'évaluation
- TLE-ICT-CHS - Operating System (July 27,2018)Document2 pagesTLE-ICT-CHS - Operating System (July 27,2018)Marvin GoPas encore d'évaluation
- 41 PDFDocument135 pages41 PDFyPas encore d'évaluation
- Gns 312 Summary by DiamondDocument20 pagesGns 312 Summary by DiamondToheeb BadmusPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A ComputerDocument19 pagesWhat Is A ComputerFuad TalPas encore d'évaluation
- AssignmentDocument6 pagesAssignmentapi-257167729Pas encore d'évaluation
- Girma Ict AssignmentDocument5 pagesGirma Ict AssignmentGemechuPas encore d'évaluation
- The Defferent Types of Computers and ClassificationsDocument9 pagesThe Defferent Types of Computers and ClassificationsKrishza Jane NacionalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To ComputersDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Computersᗬᗴᐻ ᔤᗩᕼᕢᖆᘍPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Awareness NotesDocument10 pagesComputer Awareness NotesArihantSinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Basics of Information Technology - Activity Sheet - Chapter 1Document3 pagesBasics of Information Technology - Activity Sheet - Chapter 1you & me with zkPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer: Modern Computers DefinedDocument4 pagesComputer: Modern Computers DefinedAle AoPas encore d'évaluation
- Objective:: Computer FundamentalsDocument14 pagesObjective:: Computer FundamentalsRamana ParameswaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer: Computer System Servicing / CiscoDocument43 pagesComputer: Computer System Servicing / CiscoAhmad-Fahem IndingPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 Modmit1 StairDocument14 pagesUnit 2 Modmit1 StairJCPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Critical Thinking AnswersDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Critical Thinking Answersapi-347135684Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reading - Material - On ITDocument37 pagesReading - Material - On ITKISHORETPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Basic DefinitionDocument2 pagesComputer Basic DefinitionamuljunePas encore d'évaluation
- Computer OrganisationDocument110 pagesComputer Organisationjasneet kaurPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer SkillsDocument12 pagesComputer SkillsVincent CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Hardware SoftwareDocument41 pagesComputer Hardware SoftwareKatheryn Rose QuilapioPas encore d'évaluation
- CONCEPTSDocument8 pagesCONCEPTSfirstmancomputersPas encore d'évaluation
- NEW BASIC OF COM KulDocument13 pagesNEW BASIC OF COM KulPawan KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer FundamentalsDocument19 pagesComputer FundamentalsPaneendra KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is ComputerDocument2 pagesWhat Is Computertisya0918Pas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Devices Digital Versus AnalogDocument10 pagesTypes of Devices Digital Versus AnalogNami PatniPas encore d'évaluation
- Act 3Document3 pagesAct 3Adrian MelendezPas encore d'évaluation
- Building Simple NetworkDocument47 pagesBuilding Simple NetworkSameer PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A ComputerDocument1 pageWhat Is A ComputerMazhar ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To ComputerDocument16 pagesIntroduction To ComputerEwunetu DejenePas encore d'évaluation
- Teknologi Sistem Komputer Dan Rangkaian Semester 5 Tahun 1Dvm 2017Document20 pagesTeknologi Sistem Komputer Dan Rangkaian Semester 5 Tahun 1Dvm 2017SyahmiSyaNizarPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To ComputerDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Computerrohan gargPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To HardwareDocument14 pagesIntroduction To HardwarePriya AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Application in Management Bba 2NDDocument22 pagesComputer Application in Management Bba 2NDFariha AbdulselamPas encore d'évaluation
- ComputerDocument40 pagesComputeramermuhammad160Pas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Classification, by Size and Power: Display Screen PrinterDocument1 pageComputer Classification, by Size and Power: Display Screen PrinterpartcamillePas encore d'évaluation
- PSP FullNotes Backbencher - ClubDocument99 pagesPSP FullNotes Backbencher - Clubkaranphutane2254Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tema 1 Oposición Secundaria InglésDocument18 pagesTema 1 Oposición Secundaria InglésMamen Caño100% (1)
- Computer Basics Vocabulary: Types of ComputersDocument5 pagesComputer Basics Vocabulary: Types of ComputersMamen CañoPas encore d'évaluation
- Make or DoDocument1 pageMake or DoMamen CañoPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 4 - Listenig ScriptsDocument2 pagesUnit 4 - Listenig ScriptsMamen CañoPas encore d'évaluation
- Immigration OfficeDocument1 pageImmigration OfficeMamen CañoPas encore d'évaluation
- Conversation at CheckDocument1 pageConversation at CheckMamen CañoPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Basics Vocabulary: Types of ComputersDocument5 pagesComputer Basics Vocabulary: Types of ComputersMamen CañoPas encore d'évaluation
- To Be and Have GotDocument1 pageTo Be and Have GotMamen CañoPas encore d'évaluation
- TelephoneDocument3 pagesTelephonestereoladPas encore d'évaluation
- Tenses Table PDFDocument5 pagesTenses Table PDFAlejandra Neira GonzálezPas encore d'évaluation
- Defining and Non-Defining ClausesDocument12 pagesDefining and Non-Defining ClausesMamen Caño100% (1)
- Structure Presente Simple by ALSDocument1 pageStructure Presente Simple by ALSMamen CañoPas encore d'évaluation
- Do or Make ExerciseDocument2 pagesDo or Make ExerciseMamen Caño100% (1)
- Tenses Table PDFDocument5 pagesTenses Table PDFAlejandra Neira GonzálezPas encore d'évaluation
- Messages1 01Document1 pageMessages1 01Mamen CañoPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercises Verbal Tenses by ALSDocument11 pagesExercises Verbal Tenses by ALSMamen CañoPas encore d'évaluation
- Adverbsfrequency PDFDocument6 pagesAdverbsfrequency PDFBiljana GavriloskaPas encore d'évaluation
- Spelling Rules Past SimpleDocument1 pageSpelling Rules Past SimpleMamen CañoPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb List: Present Past Past Participle MeaningsDocument6 pagesVerb List: Present Past Past Participle MeaningsMamen CañoPas encore d'évaluation