Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 12 - Introducing Evaluation
Transféré par
yayee03Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Chapter 12 - Introducing Evaluation
Transféré par
yayee03Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
2011 1 www.id-book.
com
Introducing Evaluation
Chapter 12
2011 2 www.id-book.com
The aims
Explain the key concepts used in evaluation.
Introduce different evaluation methods.
Show how different methods are used for
different purposes at different stages of the
design process and in different contexts.
Show how evaluators mix and modify
methods.
Discuss the practical challenges
Illustrate how methods discussed in
Chapters 7 and 8 are used in evaluation and
describe some methods that are specific to
evaluation.
2011 3 www.id-book.com
Why, what, where and when to
evaluate
Iterative design & evaluation is a continuous
process that examines:
Why: to check users requirements and that
users can use the product and they like it.
What: a conceptual model, early prototypes
of a new system and later, more complete
prototypes.
Where: in natural and laboratory settings.
When: throughout design; finished products
can be evaluated to collect information to
inform new products.
2011 4 www.id-book.com
Bruce Tognazzini tells you why
you need to evaluate
Iterative design, with its repeating cycle
of design and testing, is the only validated
methodology in existence that will
consistently produce successful results. If
you dont have user-testing as an integral
part of your design process you are going
to throw buckets of money down the
drain.
See AskTog.com for topical discussions
about design and evaluation.
2011 5 www.id-book.com
Types of evaluation
Controlled settings involving users,
eg usability testing & experiments
in laboratories and living labs.
Natural settings involving users, eg
field studies to see how the product
is used in the real world.
Any settings not involving users, eg
consultants critique; to predict,
analyze & model aspects of the
interface analytics.
2011 6 www.id-book.com
Usability lab
http://iat.ubalt.edu/usability_lab/
2011 7 www.id-book.com
Living labs
Peoples use of technology in their
everyday lives can be evaluated in
living labs.
Such evaluations are too difficult to
do in a usability lab.
Eg the Aware Home was embedded
with a complex network of sensors
and audio/video recording devices
(Abowd et al., 2000).
2011 8 www.id-book.com
Usability testing & field studies
can compliment
2011 9 www.id-book.com
Evaluation case studies
Experiment to investigate a computer
game
In the wild field study of skiers
Crowdsourcing
2011 10 www.id-book.com
Challenge & engagement in a
collaborative immersive game
Physiological measures
were used.
Players were more
engaged when playing
against another person
than when playing
against a computer.
What precautionary
measures did the
evaluators take?
2011 11 www.id-book.com
What does this data tell you?
high values indicate more variation
Playing against
computer
Playing against
friend
Mean St. Dev. Mean St. Dev.
Boring 2.3 0.949 1.7 0.949
Challenging 3.6 1.08 3.9 0.994
Easy 2.7 0.823 2.5 0.850
Engaging 3.8 0.422 4.3 0.675
Exciting 3.5 0.527 4.1 0.568
Frustrating 2.8 1.14 2.5 0.850
Fun 3.9 0.738 4.6 0.699
Source: Mandryk and Inkpen (2004).
2011 12 www.id-book.com
Why study skiers in the wild ?
Jambon et al. (2009) User experience in the wild. In: Proceedings of CHI 09, ACM Press, New York,
p. 4070-4071.
2011 13 www.id-book.com
e-skiing system components
Jambon et al. (2009) User experience in the wild. In: Proceedings of CHI 09, ACM Press, New York,
p. 4072.
2011 14 www.id-book.com
Crowdsourcing-when might
you use it?
2011 15 www.id-book.com
Evaluating an ambient system
The Hello Wall is a
new kind of system
that is designed to
explore how people
react to its
presence.
What are the
challenges of
evaluating systems
like this?
2011 16 www.id-book.com
Evaluation methods
Method Controlled
settings
Natural
settings
Without
users
Observing
x x
Asking
users
x x
Asking
experts
x x
Testing
x
Modeling
x
2011 17 www.id-book.com
The language of evaluation
Analytics
Analytical
evaluation
Controlled
experiment
Expert review or crit
Field study
Formative
evaluation
Heuristic evaluation
In the wild
evaluation
Living laboratory
Predictive evaluation
Summative
evaluation
Usability laboratory
User studies
Usability testing
Users or participants
2011 18 www.id-book.com
Key points
Evaluation & design are closely integrated in user-centered
design.
Some of the same techniques are used in evaluation as for
establishing requirements but they are used differently
(e.g. observation interviews & questionnaires).
Three types of evaluation: laboratory based with users, in
the field with users, studies that do not involve users
The main methods are: observing, asking users, asking
experts, user testing, inspection, and modeling users task
performance, analytics.
Dealing with constraints is an important skill for evaluators
to develop.
2011 19 www.id-book.com
A project for you
The Butterfly Ballot: Anatomy of
disaster was written by Bruce
Tognazzini, and you can find it by
going to AskTog.com and looking
through the 2001 column.
Alternatively go directly to:
http://www.asktog.com/columns/04
2ButterflyBallot.html
2011 20 www.id-book.com
A project for you continued
Read Togs account and look at the
picture of the ballot card.
Make a similar ballot card for a class
election and ask 10 of your friends to
vote using the card. After each person
has voted ask who they intended to
vote for and whether the card was
confusing. Note down their comments.
Redesign the card and perform the
same test with 10 different people.
Report your findings.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Lecture 10 - 2020Document20 pagesLecture 10 - 2020Shahroze Kamran SahotraPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 14 5eDocument22 pagesChapter 14 5esinanahmedofficalPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter14 ID5eDocument22 pagesChapter14 ID5eH. Al-MahmoudPas encore d'évaluation
- W11 - Introducing EvaluationDocument27 pagesW11 - Introducing Evaluationmarriyam nadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 12 - EvaluationDocument45 pagesLecture 12 - EvaluationRed ArmaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 2001 8eDocument23 pagesLec 2001 8edwi krisbiantoroPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter15 - Evaluation - Inspections, Analytics, and Models 2019Document20 pagesChapter15 - Evaluation - Inspections, Analytics, and Models 2019Tefo ModukePas encore d'évaluation
- Review Ii: Course: COMP6176 / Human - Computer Interaction Year: 2015Document19 pagesReview Ii: Course: COMP6176 / Human - Computer Interaction Year: 2015Agus Sasmito HPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaluation: Inspections, Analytics & ModelsDocument19 pagesEvaluation: Inspections, Analytics & ModelsCristi PopaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ambo University Woliso Campus: School of Technology and InformaticsDocument11 pagesAmbo University Woliso Campus: School of Technology and InformaticsDagim Fekadu AmenuPas encore d'évaluation
- Ambo University Woliso Campus: School of Technology and InformaticsDocument11 pagesAmbo University Woliso Campus: School of Technology and InformaticsDagim Fekadu AmenuPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 16 5eDocument27 pagesChapter 16 5esinanahmedofficalPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 7 - Behaviour and AnalyticsDocument47 pagesWeek 7 - Behaviour and AnalyticsChui BiPas encore d'évaluation
- HCI Individual AssagnmentDocument8 pagesHCI Individual AssagnmentDagim Fekadu AmenuPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 15 5eDocument26 pagesChapter 15 5esinanahmedofficalPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 11 - EvaluationDocument64 pagesLec 11 - EvaluationFRankPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaluation Techniques and Universal DesignDocument64 pagesEvaluation Techniques and Universal DesignEbisa EdessaPas encore d'évaluation
- UsabilityDocument76 pagesUsabilityManikantan PillaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Week - 10 EvaluationDocument30 pagesWeek - 10 EvaluationJosh 14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter14 - Evaluation Studies From Controlled To Natural Settings - 2019Document19 pagesChapter14 - Evaluation Studies From Controlled To Natural Settings - 2019Tefo ModukePas encore d'évaluation
- Week 2: Design: o Introduction To Usability o The Design o Design: Defining Goals and Personas O CSCW o MobileDocument53 pagesWeek 2: Design: o Introduction To Usability o The Design o Design: Defining Goals and Personas O CSCW o MobilekickthekidsPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 15 ID2e SlidesDocument21 pagesChapter 15 ID2e SlidesAmi HabibahPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 5: Universiti Teknologi MalaysiaDocument8 pagesAssignment 5: Universiti Teknologi MalaysiaArshad ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Computer InteractionDocument12 pagesHuman Computer InteractionUsmanHaiderPas encore d'évaluation
- Human - Factors - Option - E - PPT 2Document74 pagesHuman - Factors - Option - E - PPT 2rosiemogPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 11Document23 pagesChap 11DriaAnbariasPas encore d'évaluation
- W13 - Evaluation Studies - From Controlled To Natural SettingsDocument40 pagesW13 - Evaluation Studies - From Controlled To Natural Settingsmarriyam nadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Design 2 (Chapter 5) : - Conceptual Design - Physical DesignDocument21 pagesDesign 2 (Chapter 5) : - Conceptual Design - Physical DesignDanial RajputPas encore d'évaluation
- Got Data, Now What? Analyzing Usability Study Results: Lynn Silipigni Connaway June 26, 2005Document40 pagesGot Data, Now What? Analyzing Usability Study Results: Lynn Silipigni Connaway June 26, 2005lunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Identifying Needs and Establishing RequirementsDocument33 pagesIdentifying Needs and Establishing RequirementsAsad SultanPas encore d'évaluation
- Measuring the User Experience: Collecting, Analyzing, and Presenting Usability MetricsD'EverandMeasuring the User Experience: Collecting, Analyzing, and Presenting Usability MetricsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (11)
- ch15 HciDocument28 pagesch15 Hciharleensomal28Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hci - 16Document36 pagesHci - 16Usama AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- LN IT 312 02 Human Computer InteractionDocument21 pagesLN IT 312 02 Human Computer InteractionJay ChalanagPas encore d'évaluation
- Usability Testing Workshop March2020Document89 pagesUsability Testing Workshop March2020jijiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter11 ID5eDocument33 pagesChapter11 ID5eRimsha KanwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 12Document28 pagesChapter 12bensu0603Pas encore d'évaluation
- Usability TestingDocument32 pagesUsability TestingEmmanuel larbiPas encore d'évaluation
- Midterm Lecture 3 REQS GATHERING STORYBOARDDocument29 pagesMidterm Lecture 3 REQS GATHERING STORYBOARDderek pelegrinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 HCIDocument32 pagesChapter 2 HCIyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Six: Evaluation Techniques and Universal DesignDocument27 pagesChapter Six: Evaluation Techniques and Universal DesignSun Love NewPas encore d'évaluation
- Usability EngineeringDocument2 pagesUsability EngineeringEley CuetoPas encore d'évaluation
- Portfolio HF ResearcherDocument32 pagesPortfolio HF ResearcherDan ChiushunPas encore d'évaluation
- HCI-5 Evaluation TechniquesDocument40 pagesHCI-5 Evaluation TechniquesMuhammad Hashim63% (8)
- Chapter 14 IDDocument21 pagesChapter 14 IDdivya kalyaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 11 IDDocument22 pagesChapter 11 IDyasirlatif321360Pas encore d'évaluation
- HCI SummaryDocument43 pagesHCI SummaryNelkon EugenePas encore d'évaluation
- Human Computer Interaction Introduction and OverviewDocument27 pagesHuman Computer Interaction Introduction and OverviewAdika Dwi Ananda PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- Delhi Technological University Project Proposal: Book Recommendation SystemDocument6 pagesDelhi Technological University Project Proposal: Book Recommendation SystemANIMIXPas encore d'évaluation
- Web Design UsabilityDocument17 pagesWeb Design UsabilityfariPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Computer Interaction: Lecture - 2Document24 pagesHuman Computer Interaction: Lecture - 2Meran XoranyPas encore d'évaluation
- w2 Usability Engineering 2017Document26 pagesw2 Usability Engineering 2017fentyemaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 18 Prototyping 08012024 095433amDocument18 pagesLecture 18 Prototyping 08012024 095433ampc6185.hiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Usability Testing (Kuantitatif)Document43 pagesUsability Testing (Kuantitatif)Furqan MaulanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6Document24 pagesChapter 6Youssef KabbouchPas encore d'évaluation
- User Interface Design: Definitions, Processes and PrinciplesDocument66 pagesUser Interface Design: Definitions, Processes and PrinciplesErmin SehicPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 Evaluation Again s08 p1Document24 pages11 Evaluation Again s08 p1Hasna Hena MunniPas encore d'évaluation
- The UX Five-Second Rules: Guidelines for User Experience Design's Simplest Testing TechniqueD'EverandThe UX Five-Second Rules: Guidelines for User Experience Design's Simplest Testing TechniquePas encore d'évaluation
- Design, Prototyping and Construction: ReadingsDocument35 pagesDesign, Prototyping and Construction: ReadingsZcsalweemnharr BandahalaPas encore d'évaluation
- w2 Usability EngineeringDocument8 pagesw2 Usability EngineeringfentyemaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3VA System Manual Communication en en-USDocument278 pages3VA System Manual Communication en en-UScraigjsandersonPas encore d'évaluation
- Hemu Kharel Kafle Paper On Drought in Mid and Far Western Nepal NASTDocument12 pagesHemu Kharel Kafle Paper On Drought in Mid and Far Western Nepal NASTArbind ShresthaPas encore d'évaluation
- CLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Phy Study Package 5 SET 1 Chapter 2Document24 pagesCLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Phy Study Package 5 SET 1 Chapter 2Ûdây RäjpütPas encore d'évaluation
- Interntional Audit WorkbookDocument133 pagesInterntional Audit WorkbookReynelle Cata-alPas encore d'évaluation
- Oracle Retail Invoice Matching 12.0 Defect Report: Bug Number: Severity: Functional Areas: Cross-Product ImpactDocument4 pagesOracle Retail Invoice Matching 12.0 Defect Report: Bug Number: Severity: Functional Areas: Cross-Product ImpactBali BalisPas encore d'évaluation
- X16 42552VS2010UltimTrial1Document2 pagesX16 42552VS2010UltimTrial1An LcPas encore d'évaluation
- Entrepreneurship 1 Burt S BeesDocument5 pagesEntrepreneurship 1 Burt S BeesAly BhamaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Stochastic ProgrammingDocument315 pagesStochastic Programmingfeiying1980100% (1)
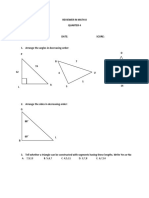
- Reviewer in Math 8Document13 pagesReviewer in Math 8Cañeda AlejanioPas encore d'évaluation
- Hibernate Search ReferenceDocument118 pagesHibernate Search ReferenceSiarhei SakovichPas encore d'évaluation
- Amazon Web ServicesDocument85 pagesAmazon Web ServicesSrinivasa Reddy KarriPas encore d'évaluation
- Erickson - 1981 - Secret Societies and Social StructureDocument24 pagesErickson - 1981 - Secret Societies and Social StructureRene PlascenciaPas encore d'évaluation
- 26 Rules To Becoming A Successful SpeakerDocument46 pages26 Rules To Becoming A Successful SpeakerSpeakerMatch100% (23)
- 7 ODE 2nd Order v2Document3 pages7 ODE 2nd Order v2Agung GuskaPas encore d'évaluation
- En VocabDocument251 pagesEn Vocabmadmis01999Pas encore d'évaluation
- Univariate Homework 2 (1) CompletedDocument6 pagesUnivariate Homework 2 (1) CompletedNytaijah McAuleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Media ART: Course: History of Media Art Instructor: Zeib JahangirDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Media ART: Course: History of Media Art Instructor: Zeib JahangirLiaqat AleePas encore d'évaluation
- Trainer Competency ModelDocument4 pagesTrainer Competency ModelpattapuPas encore d'évaluation
- z80 LH0080 Tech ManualDocument25 pagesz80 LH0080 Tech ManualAnonymous 8rb48tZSPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Companion Earth's Changing Surface Virtual Field TripDocument90 pagesScience Companion Earth's Changing Surface Virtual Field TripScience Companion100% (2)
- Ei GSM IcbDocument11 pagesEi GSM IcbwimaxaaabglPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 Task Performance 1 - ARG - MMW - RelevoDocument4 pages03 Task Performance 1 - ARG - MMW - Relevocessarine relevoPas encore d'évaluation
- 22 Oktober 2019 - EP UNPARDocument73 pages22 Oktober 2019 - EP UNPARGina AnindithaPas encore d'évaluation
- 07 Test ADocument24 pages07 Test ARashmin ShetPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry 12 - Unit 3 - Solubility (M.C.)Document34 pagesChemistry 12 - Unit 3 - Solubility (M.C.)julyfriskaPas encore d'évaluation
- Koala 20161128Document1 pageKoala 20161128Ale VuPas encore d'évaluation
- Words N Expressions To AvoidDocument3 pagesWords N Expressions To AvoidLina Marie BesaPas encore d'évaluation
- Shape Memory Alloy - SeminarDocument15 pagesShape Memory Alloy - SeminarGeorgeMThomas33% (3)
- Types of EconomyDocument2 pagesTypes of EconomyAyush GargPas encore d'évaluation
- Release Notes: 2288H V5&1288H V5&2288C V5&5288 V5 CPLD V212Document6 pagesRelease Notes: 2288H V5&1288H V5&2288C V5&5288 V5 CPLD V212LTI MaintenancePas encore d'évaluation