Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
PPMP Cost Management
Transféré par
bkumar1979Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
PPMP Cost Management
Transféré par
bkumar1979Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Date 8
th
Sep 2014
Plan Cost Management: To make sure our project doesnt cost more than weve budgeted.
Estimate Costs: Develop estimated costs for each scheduled activity.
Determine Budget: Aggregate activity costs into an approved project budget.
Control Costs: Monitor, manage, and control costs.
Cost management plan includes:
what types of indirect costs, if any, will be posted against the project
units of currency to be used
precision level/acceptable rounding for costs
currency conversion issues
acceptable thresholds for cost variances
the general ledger or control accounts for expenses and costs
the performance measurement formulas that will be used
at what points in the project performance measurements will be made
Plan Costs Management
# The Plan Cost Management process is where we plan out all the work well do to make sure our
project doesnt cost more than youve budgeted.
Inputs
1. Risk Management Plan
2. Project Charter
3. Enterprise Enviromental factor
4. Organization Process Assest
Tools & Techniques
1. Expert Judgment
2. Analytical Techniques
3. Meeting
Outputs
1. Cost Management Plan
Estimate Costs
Estimate Costs: The process of developing an approximation of the monetary resources needed to
complete project activities. It is performed after Define Scope, Create WBS, Define Activities, Estimate
Activity Resources, and Estimate Activity Durations. Estimations must be done based on a WBS to
improve accuracy.
# Cost of quality: Cost that is incurred to achieve required quality
# Stranded/Sunk Costs: costs incurred that cannot be reversed irrespective to future events
# Value Engineering/ Analysis: finding less costly way to do the same work. E.g. outsourcing
# Marginal analysis: Spend time on improvement if it improves revenues or productivity.
# Order of Magnitude Estimate: Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM): -50% to +50% (at Initiation) as the
project moves, estimates should become more accurate, Conceptual Est: -30% to + 50%, Preliminary Est:
-20% to +30%, Definitive Est: -15% to +20%, Control Est: -10% to +15% (for Activities with relatively few
unknowns).
Inputs
1. Cost management plan
2. HR management plan: to know labor rates.
3. Scope baseline: We need to whos doing what work, and how long itll take, so we can figure out
how much it will cost.
4. Project schedule
5. Risk register
6. Enterprise Environmental factor
7. Organization Process Assets
Tools & Techniques
1. Expert Judgments
2. Analogous estimating (Gross Value Estimating approaches) Top-down estimates are the least
accurate and it gives Project Manager an idea of the level of Management's expectations.
3. Parametric estimating (Uses Statistical relationship)
4. Bottom-up estimating
5. three-point estimating
6. Reserve analysis Reserve analysis evaluates risks by making financial allowances for them in the
projects funding requirements.# Budget reserve # Contingency reserves (for known risks) # Mgmts.
reserves (for unknown risks)
7. Cost of quality
8. Project Management Software
9. Vendor bid analysis
10. Group decision-making techniques
Outputs
1. Activity Cost estimates
2. Basis of estimates is the supporting detail that provides supplementary information about the
activity estimates, such as any assumptions made, constraints, how the estimate was derived, the
confidence level in the estimate, and any risk factors that were considered.
3. Project Documents updates
Important Points
"There are a few numbers that will appear on the test as definitions. You wont need to calculate these,
but you should know what each term means.
Benefit cost ratio (BCR): This is the amount of money a project is going to make versus how much it will
cost to build it. Generally, if the benefit is higher than the cost, the project is a good investment.
Net present value (NPV): This is the actual value at a given time of the project minus all of the costs
associated with it. This includes the time it takes to build it and labor as well as materials. People
calculate this number to see if its worth doing a project.
Opportunity cost: When an organization has to choose between two projects, they are always giving up
the money they would have made on the one they dont do. Thats called opportunity cost. Its the
money you dont get because you chose not to do a project.
Example -- If a project will make your company $150,000, then the opportunity cost of selecting another
project instead is $150,000 because thats how much your companys missing out on by not doing the
project.
Internal rate of return: This is the amount of money the project will return to the company that is
funding it. Its how much money a project is making the company. Its usually expressed as a percentage
of the funding that has been allocated to it.
Depreciation: This is the rate at which your project loses value over time. So, if you are building a
project that will only be marketable at a high price for a short period of time, the product loses value as
time goes on.
Lifecycle costing: Before you get started on a project, its really useful to figure out how much you
expect it to costnot just to develop, but to support the product once its in place and being used by
the customer."
Types of costs:
Direct cost: include dedicated labor, material, supplies, equipment, licenses, fees, training, travel, or
professional service fees
Indirect cost: Example, if a color printer is shared by several project teams, its difficult to definitively
determine what percentage of costs each should share.
Variable cost: fluctuate and can't be predicted with absolute certainty. For example, travel or
transportation costs that can change depending upon the cost of fuel or certain commodities and types
of raw materials. Variable cost change with the amount produced
Fixed cost: are static throughout the project or have only a small likelihood of fluctuation. Fixed costs
are usually for items such as rents, leases, licenses, salaries, and fixed fees. Fixed cost do not vary with
the amount produced
# Direct cost and variable costs that are directly attributable to the project or that vary with amount of
work accomplished
Factors affecting costs:
-Risks: During early phases, the greatest risk to budget accuracy is usually that the scope, activity, and
constraints arent fully known
-Total Cost of Ownership/Life-Cycle:
-Cost of Quality: Cost that is incurred to achieve required quality
-Marketplace Conditions:
Accuracy of Estimates:
Rough order of magnitude estimate ROM: this type of estimate is made during initiating process.
Typical range is +/-50 percent from actual.
Budget estimate: this type of estimate is made during planning phase. Typical range is -10 to +25
percent from actual.
Definitive estimate: Later during the project estimates will become more refined, some PMs use the
range of -5 to +10 or -/+10
Determine Budget
Determine Budget (Cost Performance Baseline): The process of aggregating the estimated costs of
individual activities or work packages to establish an authorized cost baseline. Budget, is time-phased
(WHAT costs will be incurred and WHEN they will be incurred). The Cost Baseline describes a detailed
budget that shows costs and timelines for each work package or activity. It is performed after Define
Activities, Estimate Activity Resources, Estimate Activity Durations, Develop Schedule and Estimate
Costs.
# Larger projects may be divided into multiple Cost Baselines.
The entire estimated cost of the budget, including any contingency or management reserves, is the
project funding requirements.
Project funding requirements = Project Budget (Project Base Cost + Risk response cost [ planned])
+ Reserve ( contingency reserve [known unknowns]
+ Mgmt. reserve [unknowns] )
Cost Aggregation:
1.Activity Estimates ->2.Work Package Estimates ->3. Control Account Estimates ->4. Project Estimates -
>5.Contingency Reserves ->6.Cost Baseline ->7.Mgmt Reserves ->8. Cost Budget.
Inputs
1. Cost management plan
2. Scope baseline
3. Activity cost estimate
4. Basis of estimates
5. Project Schedule
7. Risk register
8. Agreements
9. Organization Process Assets
Tools & Techniques
1. Cost aggregation
2. Reserve analysis
3. Expert Judgement
4. Historical Relationships
5. Funding limit reconciliation
Outputs
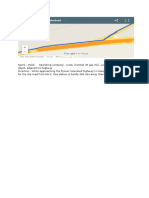
1. Cost baseline (S curve): Time phased funding requirements - the performing organization needs to
know when the project will need money
# A cost baseline must include a contingency reserve for risks. It does not include a management
reserve.
2. Project funding requirements (Dotted Steps) (Expenditure, Liabilities and Reserves)
3. Project Documents updates
"At a broad level, the budgetary classifications are generally:
Reserves Labor/Personnel Professional, Contracted, or Outside Services Supplies, Materials
Equipment, Hardware, and Software Training, Travel Licenses, fees Indirect Costs
we will get questions on the EXAM asking you to select between projects using Net Present Value (NPV)
or Benefit Cost Ratio(BCR). Always choose the project with the BIGGEST NPV or BCR.
A Management Reserve is money set aside to cover unplanned, unexpected costs.
Our projects funding requirements need to cover both the budget in the Cost Performance Baseline and
the management reserve."
# Parametric estimation is used in Estimate Costs and Determine Budget.
# Cost aggregation is rolling up costs from the work package level to the control account level so that
the numbers can be followed down through the WBS hierarchy.
# Control accounts are high level WBS items that are used to track cost estimates. They do not
represent activities or work packages. They represent the cost of the work packages and activities that
appear under them in the WBS.
# The main outputs of Estimate Costs are the activity cost estimate and the basis of estimates. The
main outputs of Determine Budget are the cost baseline and project funding requirements.
# Lifecycle costing means estimating the money it will take to support your product or service
when it has been released.
# A management reserve is money set aside to cover unplanned, unexpected costs. Your projects
funding requirements need to cover both the budget in the cost baseline and the management
reserve.
# Estimate Costs is just like Estimate Activity Durations. You get the cost estimate and the basis of the
cost estimate, updates to the plan, and requested changes when you are done.
Control Cost
Control Costs: The process of monitoring the status of the project to update the project budget and
managing changes to the cost baseline.
# To-Complete Performance Index (TCPI): performance needed in order to achieve earned value targets
(either financial or schedule). Two forms, TCPIC and TCPIS.
# TCPI (Based on BAC) = Work Remaining i.e, (BAC-EV) / Remaining Funds i.e., (BAC-AC) (lower than 1 is
good)
# TCPI (Based on EAC) = Work Remaining i.e, (BAC-EV) / Remaining Funds i.e., (EAC-AC) (lower than 1 is
good)
# TCPI calculation is based on a specified management goal. If the cumulative CPI falls below the
baseline plan, all future work of the project will need to immediately be performed in the range of the
TCPI (BAC) to stay within the authorized BAC. Once management acknowledges that the BAC is no
longer attainable, the PM will prepare a new EAC for the work, and one approved the project will work
to the new EAC value and it supersedes the BAC.
# EVM is a way to discover trends or indications of the way the project is going.
# The EVM method works well in conjunction with manual forecasts of the required EAC costs. The most
common EAC forecasting approach is a MANUAL, BOTTOM-UP SUMMATION by the PM and Project
Team.
# Project Manager monitor EV, both incrementally to determine CURRENT STATUS and cumulatively to
determine long-term PERFORMANCE TRENDS.
Input
1. Project management Plan
2. Project funding requirement
3. Work performance data
4. Organization Process Assets
Tools & Techniques
1. Earned value management (Variances and Trends)
2. Forecasting (EAC and ETC)
3. To-complete performance index (TCPI)
4. Performance reviews
5. Project Management software
6. Reserve analysis
Outputs
1. Work performance information
2. Cost forecast
3. Change request
4. Project management plan update
5. Project documents updates
6. Organizational process assets update
# The Scope Statement provides the Product Description, Acceptance Criteria, Key Deliverables, Project
Boundaries, Assumptions, and Constraints about the Project.
"# Project Cost Control includes:
1) Influencing the factors that create changes to the authorized cost baseline,
2) Ensuring that all change requests are acted on in a timely manner,
3) Managing the actual changes when and as they occur,
4) Ensuring that cost expenditures do not exceed the authorized funding, by period and in total for the
project,
5) Monitoring cost performance to isolate and understand variances from the approved cost baseline,
6) Monitoring work performance against funds expended,
7) Preventing unapproved changes from being included in the reported cost or resource usage,
8) Informing appropriate stakeholders of all approved changes and associated cost, and
9) Acting to bring expected cost overruns within acceptable limits."
BAC * Planned % complete = PV
BAC * Actual % complete=EV
EV-PV = SV
EV/PV=SPI
EV-AC=CV
EV/AC=CPI
# Lower is loser
(BAC-EV)/(BAC-AC)=TCPI
(BAC-EV)/(EAC-AC)=TCPI
BAC/CPI=EAC
EAC-AC=ETC
BAC-EAC=VAC
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Somatic Symptom DisorderDocument26 pagesSomatic Symptom DisorderGAYATHRI NARAYANAN100% (1)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- SAP Check ListDocument34 pagesSAP Check Listbkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- SOD GuideDocument26 pagesSOD Guidebkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- MOH Formulary Drug List 2014Document115 pagesMOH Formulary Drug List 2014mahmud000Pas encore d'évaluation
- GDPR in ChartsDocument13 pagesGDPR in ChartsImageking0% (2)
- Antenna Tilt GuidelinesDocument24 pagesAntenna Tilt GuidelinesJorge Romeo Gaitan Rivera100% (5)
- SAP PRESS Implementing SAP Business Suite On SAP HANADocument34 pagesSAP PRESS Implementing SAP Business Suite On SAP HANAbkumar197933% (3)
- SAP PRESS Implementing SAP Business Suite On SAP HANADocument34 pagesSAP PRESS Implementing SAP Business Suite On SAP HANAbkumar197933% (3)
- SAP PRESS Implementing SAP Business Suite On SAP HANADocument34 pagesSAP PRESS Implementing SAP Business Suite On SAP HANAbkumar197933% (3)
- Italian Renaissance Art: Prepared by Ms. Susan PojerDocument46 pagesItalian Renaissance Art: Prepared by Ms. Susan Pojerragusaka100% (12)
- Wamit V6.4: Diffraction-Radiation ComputationDocument66 pagesWamit V6.4: Diffraction-Radiation ComputationAnonymous JEe6LWPPas encore d'évaluation
- SBX SandBox ChecksDocument192 pagesSBX SandBox Checksbkumar1979100% (1)
- 4 Supplier Invoice: S.No APPDocument11 pages4 Supplier Invoice: S.No APPbkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- Project Excecution and DeliverableDocument7 pagesProject Excecution and DeliverableHari PrashannaPas encore d'évaluation
- IntreDocument1 pageIntrebkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- FP - TEST - 00 FP - Check - Destination - Service FP - TEST - IA - 01 FP - PDF - TEST - 00Document1 pageFP - TEST - 00 FP - Check - Destination - Service FP - TEST - IA - 01 FP - PDF - TEST - 00bkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- Idioms Tio Phrases: English For Competitive Exam. by Dharmendra Kumar (ADVOCATE)Document1 pageIdioms Tio Phrases: English For Competitive Exam. by Dharmendra Kumar (ADVOCATE)bkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- GERA IT Service: Invoice of Tax On MRPDocument4 pagesGERA IT Service: Invoice of Tax On MRPbkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- CbseDocument10 pagesCbsedarshanraghuPas encore d'évaluation
- Try 123Document1 pageTry 123bkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- CNGDocument1 pageCNGbkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- Book 1Document3 pagesBook 1bkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- Activities 140216Document3 pagesActivities 140216bkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 5 Architecture and ScenariosDocument6 pagesUnit 5 Architecture and Scenariosbkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 5 Architecture and ScenariosDocument6 pagesUnit 5 Architecture and Scenariosbkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- Project Plan - SoH Migration - PI Industries 1 Aug 15Document4 pagesProject Plan - SoH Migration - PI Industries 1 Aug 15bkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- of NewsDocument1 pageof Newsbkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- SAP PI For BeginnersDocument16 pagesSAP PI For Beginnersdeathead1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Less SionDocument6 pagesLess Sionbkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- Upload 1 Doc for Every 1 Downloaded on ScribdDocument1 pageUpload 1 Doc for Every 1 Downloaded on Scribdbkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- Brajesh Kumar's Resume: SAP Basis Experience and Career ProfileDocument5 pagesBrajesh Kumar's Resume: SAP Basis Experience and Career Profilebkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- SAP WalkInDrive 23may2015Document13 pagesSAP WalkInDrive 23may2015bkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- CommandDocument10 pagesCommandbkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- Remotelogin 192.168.1.120 User ID Admin Password Omax@123 Open HANA StudioDocument5 pagesRemotelogin 192.168.1.120 User ID Admin Password Omax@123 Open HANA Studiobkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- Abap With NetweaverDocument1 pageAbap With Netweaverbkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- DevDocument12 pagesDevbkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- ABAP Workbench - Mod: Contribute To Scribd To Access This DocumentDocument9 pagesABAP Workbench - Mod: Contribute To Scribd To Access This Documentbkumar1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- MKTG10001Document38 pagesMKTG10001Jessica KokPas encore d'évaluation
- Sanjay Chandra Vs Cbi On 23 November, 2011Document21 pagesSanjay Chandra Vs Cbi On 23 November, 2011SaiBharathPas encore d'évaluation
- Francis Asbury Revival Study PDFDocument10 pagesFrancis Asbury Revival Study PDFLauRa Segura VerasteguiPas encore d'évaluation
- Fiber006 SorDocument1 pageFiber006 SormbuitragoPas encore d'évaluation
- QP ScriptDocument57 pagesQP ScriptRitesh SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Culture, Society, and Politics - IntroductionDocument55 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society, and Politics - IntroductionTeacher DennisPas encore d'évaluation
- MSO 1st Year Assignments 2017-18 (English) PDFDocument7 pagesMSO 1st Year Assignments 2017-18 (English) PDFAmritpal BhagatPas encore d'évaluation
- Memorial On Behalf of PetitionerDocument35 pagesMemorial On Behalf of PetitionerAjitabhGoel67% (3)
- DIWADocument64 pagesDIWADyanWahyu NMibhye SygSmuaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 03 02 Iep and Lesson Plan Development Handbook - Schoolhouse DocumentDocument42 pages4 03 02 Iep and Lesson Plan Development Handbook - Schoolhouse Documentapi-252552726Pas encore d'évaluation
- Advocacy Plan Final Edec 435Document11 pagesAdvocacy Plan Final Edec 435api-375034422Pas encore d'évaluation
- Creating A Seasonal Greeting Card RubricDocument3 pagesCreating A Seasonal Greeting Card Rubricapi-244997750Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mughals in IndiaDocument4 pagesMughals in IndiaSalony RoongtaPas encore d'évaluation
- VC3 TranslationDocument313 pagesVC3 TranslationFuyuki Maxwell ArashiPas encore d'évaluation
- Coursework of Signals and Systems: Moh. Kamalul Wafi December 6, 2018Document2 pagesCoursework of Signals and Systems: Moh. Kamalul Wafi December 6, 2018kartiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Reading at the BeachDocument3 pagesReading at the BeachhihiijklkoPas encore d'évaluation
- Maintain Records and Bond EmployeesDocument5 pagesMaintain Records and Bond EmployeesAngel Frankie RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- 50 Sets of Puzzles and Seating Arrangement For IBPS PO Mains 2017 SolutionsDocument23 pages50 Sets of Puzzles and Seating Arrangement For IBPS PO Mains 2017 SolutionssaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ds Mini ProjectDocument12 pagesDs Mini ProjectHarsh VartakPas encore d'évaluation
- Outlook Business The Boss July 2015Document14 pagesOutlook Business The Boss July 2015Nibedita MahatoPas encore d'évaluation
- A Legacy of Female Autonomy During The Crusades: Queen Melisende of Jerusalem by Danielle MikaelianDocument25 pagesA Legacy of Female Autonomy During The Crusades: Queen Melisende of Jerusalem by Danielle MikaelianDanielle MikaelianPas encore d'évaluation
- History of English - IntroductionDocument58 pagesHistory of English - IntroductionPaul Edward GuevarraPas encore d'évaluation
- CPS 101 424424Document3 pagesCPS 101 424424Ayesha RafiqPas encore d'évaluation