Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Deliverable 2 Assignment
Transféré par
alishadns0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
32 vues10 pagesDeliverable Assignment Two
INFOSYS S2 2014 Group 94
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDeliverable Assignment Two
INFOSYS S2 2014 Group 94
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
32 vues10 pagesDeliverable 2 Assignment
Transféré par
alishadnsDeliverable Assignment Two
INFOSYS S2 2014 Group 94
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 10
1
INFOSYS.110 BUSINESS SYSTEMS:
DELIVERABLE 2: BUSINESS SECTION
2014
Name Alisha Sharma
NetID asha584
Group Number: 094
Website Link: http://infosys1102014s2group94.blogspot.co.nz/
Tutorial Details
Tutor: Day: Time:
Khushbu Tilvawala Tuesday 2pm
Time Spent on
Assignment:
32 hours Word Count:
1647 (excluding
references)
2
2
THE TAKE AWAY APP
INTRODUCTION
University students often skip meals due to hectic schedules, being unable to make time to
stop and buy food, or because waiting in long queues to buy food is undesirable. This
problem can be solved by the creation of The Take Away App, an app for smartphones
that links up all the food providers on the campus of the University of Auckland and allows
students to purchase and pay for their food and drinks in advance, and pick their food up on
the go. This solves the problem of university students skipping meals, which can have
adverse health effects such as malnutrition, or the development of high blood pressure and
diabetes in the future (Spicer, 2012).
3. BUSINESS SECTION
3.1 Vision
To provide university students the means of obtaining food in a manner that is both timely
and convenient and to provide businesses on-campus with more revenue.
3.2 Industry Analysis: Food Ordering Technologies Industry
Industry: Food Ordering Technologies Industry.
Force: High/Low: Justification:
Buyer power: Low While there are many apps that allow customers
to order food while on the go, these apps tend to
be for specific food providers or companies, such
as Menulog (Menulog, 2014). There are none that
link all the various food providers on a University
Campus, so buyer power is low.
3
3
Supplier power: Low There are many firms to choose from who
specialize in creating apps. Therefore supplier
power is low. (Top 50 Custom Mobile Application
Development Companies A Curated List from
Quora, 2013)
Threat of new entrants: Low While finding the resources to create an app may
not be difficult and time consuming, creating
partnerships with different restaurants and banks
will be diffcult. Thus there are high barriers to
entry in this industry.
Threat of substitutes: High There are many substitutes for this app in the
form of other apps that allow you to order coffee
on the go (Stewart, 2013), or apps such as the
Dominos app that allows you to order from one
shop only. Students could also call and place
orders, or physically go to the shop and buy food.
Rivalry among existing
competitors:
High Menulog would be our closest competitor,
allowing you to order food online. However as
they offer discounts and special deals, which are
a form of price competition, it could be said that
rivarly among existing competitors would be high.
Overall attractiveness of the industry: The Food Ordering Technologies Industry is
therefore an attractive industry due to its low buyer and supplier power, and low threat of
new entrants.
4
4
3.3 Customers and Thei r Needs
The primary users of this product will be students at the University of Auckland, who have a
busy timetable, non-stop classes, or would like the convenience of ordering food while on
the go. However this is by no means a limiting criteria; any student at the University of
Auckland can be a user of the app. Students would need a way to order food in a timely,
convenient manner, and the freedom of choosing when to pick up their food.
3.4 The Product and Service
Research shows that the popularity of mobile apps is increasing exponentially, with
predictions that mobile application downloads will number 185 billion in 2014 (Anthes,
2011). Therefore a convienient solution to the aforementioned problem would be on an app
on a students phone, which would be available on both the Apple and Android operating
systems and requires internet access to work. The app contains a list of all the food
providers on campus. The student chooses a place, chooses what to order, and can either
pay immediately, as their account is linked directly to their bank account, debit/credit card,
or when they pick up their food. They can also arrange a time for pick up. The student gets
instant confirmation of their order via a text with their order number which they show to
the food provider to receive their food.
3.5 Suppliers and Partners
One of our suppliers would be a company that creates the app for us. They would supply us
with the systems needed to make the app work across both Android and Apple operating
systems, as well as providing us the compatibility with a bank account or debit/credit card.
Our second supplier would be an IT services provider to provide us with the systems
required to link the app with the management systems in place in the food providers
currently in the University of Auckland.
Our partners with this app would be all the food providers on the campus of the University
of Auckland. They would provide us with their menus, which we would use to show students
using the app. Together we would create a system to link the app itself to the systems used
by the food providers, to register incoming orders and payments via the app. We would also
5
5
be partnered with the major banks in Auckland, as we would require a way to securely
access the students linked bank account or debit/credit cards to register payments going
through to the food providers.
3.6 Strategy: Focused Market at Low Cost
The app will target mainly students at the University of Auckland, a segmented target
market. We are tailoring the app to this specialised market by linking all food providers on
the campus and creating a timely, convenient way for students to order food while on the
go, thus meeting the needs of our target market.
Therefore the stategy used is that of Focused Market at Low Cost.
3.7 Value Chain Activity: Technology Development and R&D
The most important value chain activity for this business is Technology Development and
R&D.
The market for applications is constantly changing and updating (Hernandez, 2010). A lot of
time, effort and money would be put into constantly upgrading the app to meet the
constantly upgrading technology systems. Ensuring that the app remains technologically up
to date is not a competitive advantage but rather a competitive necessity (Mobile Apps Help
Drive Business Success, 2012), as if the app becomes outdated and we do not upgrade it in
time or at all, students will stop using the app and we will lose customers.
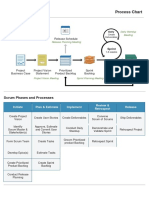
3.8 Business Processes
3.8.1. ORDER MANAGEMENT PROCESS - The Order Management Process is used to ensure
that each order has been correctly processed by the system. This is a key process for our
value chain activity, Technology and Development and R&D, as we rely on the systems
implemented in the app to correctly interpret each order placed by a student, and send it to
the correct food provider. If this process did not work, then students would not receive the
correct orders, or food providers may not receive the correct food/drinks order, thus
leading to a lot of confusion and irritation on both the student and the businesss part.
6
6
Therefore this process is required to ensure that each order is processed correctly, and that
all the relevant parties that are required to be involved, are involved.
7
7
3.8.2. APP IMPROVEMENT PROCESS The App Improvement Process is used to check that the
app is running smoothly, and to see if there are any areas that require improvement. This
process is a part of our key value chain activity, Technology and Development and R&D, as it
provides us with data on if the app is operating as intended. If the app does not operate as
intended due to a bug or a glitch, then our customers will be unhappy and will not use the
app. Therefore this process is required to ensure that the app runs smoothly and to the
correct standard.
8
8
3.9 Functionalities
3.9.1. ORDER MANAGEMENT PROCESS
Process the Order
Checking that the Student Paid for the Order
3.9.2. APP IMPROVEMENT PROCESS
Doing a Required Systems Check
Fixing the System if it does not pass the Systems Check
3.10 Systems
3.10. 1. ORDER PROCESSI NG SYSTEM This system will be used to ensure that orders are
correctly linked to the relevant food providers, and that there are no mix ups in the system.
The Order Processing System will run through the Order Management System for each
individual order. This system is vital to ensuring that customers receive the correct items
from the correct shop from where they ordered.
3.10. 2. SALES PROCESSING SYSTEM This system will work in conjunction with the Order
Processing System to help manage payments made via the app. The Sales Processing System
is used to check whether the student has paid or not, and it also houses the information
about the students bank details or debit/credit card, should they choose to use this method
of payment. This system ensures that transactions are procesed correctly and that
confidential information is kept private and safe.
3.10. 3. DATA MANAGEMENT SYSTEM This system will be used to manage the numerous
student accounts on the app. It houses all the information about student accounts and thus
works in conjunction with the Sales Processing System. It ensures that each account is kept
private and that students can access their accounts with the correct information in each
account.
9
9
3.11. Summary Table: Value Chain to Systems
Value Chain
Activity
Processes Functionalities Specific Information
System(s)
Broad Information
System(s)
Technology
Development
and R&D
Order
Management
Process
1. Process the Order
2. Has the Student Paid for the Order?
Order Processing System
Sales Processing System
Transaction Processing
System
App
Improvement
Process
1. Doing a Required Systems Check
2. Fixing the System if it does not pass the
Systems Check
Data Management System
Sales Processing System
Customer Relationship
Management
10
10
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, the Take Away App will solve the problem of University of Auckland students
skipping meals by providing a timely, convenient way for students to buy food. Information
systems will be utilized to make the app as efficient and easy-to-use as possible. This app
will create an innovative solution to a problem that has adverse health effects in the long
run.
REFERENCES
1. Spicer, E. (2012). College Students May be Prone to Malnutrition. Retrieved from
http://college.usatoday.com/2012/10/31/college-students-may-be-prone-to-
malnutrition/
2. Menulog. (2014). About Us. Retrieved from
http://www.menulog.co.nz/about_menulog
3. Top 50 Custom Mobile Application Development Companies A Curated List from
Quora. (2013). Retrieved from http://blog.contractiq.com/top-50-custom-mobile-
application-development-companies-a-curated-list-from-quora/
4. Stewart, T. (2013). Get Your Fix Quicker With This Handy App. Retrieved from
http://www.stuff.co.nz/the-press/business/8973574/Get-your-fix-quicker-with-this-
handy-app
5. Anthes, G. (2011). Invasion of the Mobile Apps. Communications Of the ACM, 54(9),
16-18. doi: 10.1145/1995376.1995383
6. Mobile Apps Help Drive Business Success. (2012). CIO Insight, 1. Retrieved from
http://www.cioinsight.com/
7. Hernandez, G.M. (2010). Mobile Apps: A Revenue Playground for Developers and
Advertising. Carribbean Business, 38(38), 42-43. Retrieved from
http://www.caribbeanbusiness.pr/
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Watergems - How To Design A Water Distribution SystemDocument3 pagesWatergems - How To Design A Water Distribution SystemhiyogsPas encore d'évaluation
- RISC Vs CISCDocument13 pagesRISC Vs CISCBehin SamPas encore d'évaluation
- Explosion WeldingDocument22 pagesExplosion WeldingLesther Alexander CorreaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mooring SystemsDocument6 pagesMooring SystemsVinicius PessottiPas encore d'évaluation
- Safety in The Kitchen - 1Document36 pagesSafety in The Kitchen - 1Roxanne OquendoPas encore d'évaluation
- Continuous Thread Stud Double End Stud ADocument11 pagesContinuous Thread Stud Double End Stud AMarius Mihai Buzduga0% (1)
- 01 40 00 - Quality RequirementsDocument27 pages01 40 00 - Quality RequirementsshauhramPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulic Home ElevatorDocument38 pagesHydraulic Home ElevatorPatrisha SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structures NotesDocument9 pagesData Structures NotesMohammed JeelanPas encore d'évaluation
- LSV-08-2 NCPDocument2 pagesLSV-08-2 NCPishtiaqPas encore d'évaluation
- Vol Damper (Smacna)Document9 pagesVol Damper (Smacna)MohamedOmar83Pas encore d'évaluation
- Procesos SCRUMDocument2 pagesProcesos SCRUMRosePas encore d'évaluation
- Differential Calculus Assignment No.3Document20 pagesDifferential Calculus Assignment No.3Agerico FunelasPas encore d'évaluation
- Bomet CountyDocument1 pageBomet CountyPrince AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Asida Distance Relay Adr-239aDocument27 pagesAsida Distance Relay Adr-239aRitesh JaiswalPas encore d'évaluation
- ICE Annex A Methodologies For RecyclingDocument17 pagesICE Annex A Methodologies For RecyclingChai Lin NyokPas encore d'évaluation
- Elmer TutorialsDocument65 pagesElmer TutorialsmariomatoPas encore d'évaluation
- D Praveen Kumar ChaubeyDocument2 pagesD Praveen Kumar ChaubeyyouvsyouPas encore d'évaluation
- Refrigerator: Service ManualDocument44 pagesRefrigerator: Service ManualBetileno QuadAlexPas encore d'évaluation
- Datasheet 783Document2 pagesDatasheet 783veertulPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulation of Immediate Release Dosage Form of Ranitidine HCL Tabletsusing HPMC and Starch Acetate Film FormerDocument11 pagesFormulation of Immediate Release Dosage Form of Ranitidine HCL Tabletsusing HPMC and Starch Acetate Film Formersunaina agarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Castrol - Iceomatic SW 68Document7 pagesCastrol - Iceomatic SW 68advantage025Pas encore d'évaluation
- Catalogo CMCDocument145 pagesCatalogo CMCalyboscanPas encore d'évaluation
- CAG Report On Antrix-Devas DealDocument76 pagesCAG Report On Antrix-Devas DealCanary Trap100% (1)
- Battery CatalogueDocument6 pagesBattery CataloguerantaroPas encore d'évaluation
- Spirex": Onepiece Spiral Flexible CouplingDocument1 pageSpirex": Onepiece Spiral Flexible CouplingHazim HazimPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-1 - Spur Gears - Lecture - 6 - Problems Spur Gear - Mahesh GaikwadDocument13 pagesUnit-1 - Spur Gears - Lecture - 6 - Problems Spur Gear - Mahesh GaikwadNikhil JadhavPas encore d'évaluation
- ABM Chain HoistDocument14 pagesABM Chain HoistZuwairi NawawiPas encore d'évaluation
- Demineralization Mechanism and Influence of Parameters On High Ash Indian Coal by Chemical Leaching of Acid and Alkali SolutionDocument1 pageDemineralization Mechanism and Influence of Parameters On High Ash Indian Coal by Chemical Leaching of Acid and Alkali SolutionSushanta Kumar BeheraPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument107 pagesUntitledniko_seppanenPas encore d'évaluation