Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Natural Logarithm Notes
Transféré par
katycwi0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
11K vues3 pagesThe document defines the natural logarithm (ln) as the logarithm to base e of a number. It provides the definition of the natural logarithm, lists some of its key rules and properties, and gives examples of applying the product rule, quotient rule, power rule, and derivatives and integrals of the natural logarithm function. Some key properties covered are that the natural logarithm is the inverse function of the exponential function e^x, its derivative is 1/x, and its integral is x(ln(x)-1)+C.
Description originale:
RULES OF NATURAL LOGARITHMS FOR CALCULUS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThe document defines the natural logarithm (ln) as the logarithm to base e of a number. It provides the definition of the natural logarithm, lists some of its key rules and properties, and gives examples of applying the product rule, quotient rule, power rule, and derivatives and integrals of the natural logarithm function. Some key properties covered are that the natural logarithm is the inverse function of the exponential function e^x, its derivative is 1/x, and its integral is x(ln(x)-1)+C.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
11K vues3 pagesNatural Logarithm Notes
Transféré par
katycwiThe document defines the natural logarithm (ln) as the logarithm to base e of a number. It provides the definition of the natural logarithm, lists some of its key rules and properties, and gives examples of applying the product rule, quotient rule, power rule, and derivatives and integrals of the natural logarithm function. Some key properties covered are that the natural logarithm is the inverse function of the exponential function e^x, its derivative is 1/x, and its integral is x(ln(x)-1)+C.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
Natural Logarithm - ln(x)
Natural logarithm is the logarithm to the base e of a number.
Natural logarithm (ln) definition
Natural logarithm (ln) rules & properties
o Derivative of natural logarithm (ln)
o Integral of natural logarithm (ln)
Graph of ln(x)
Natural logarithms (ln) table
Natural logarithm calculator
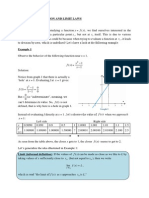
Definition of natural logarithm
When
e
y
= x
Then base e logarithm of x is
ln(x) = log
e
(x) = y
The e constant or Euler's number is:
e 2.71828183
Ln as inverse function of exponential function
The natural logarithm function ln(x) is the inverse function of the exponential function e
x
.
For x>0,
f (f
-1
(x)) = e
ln(x)
= x
Or
f
-1
(f (x)) = ln(e
x
) = x
Natural logarithm rules and properties
Rule name Rule Example
Product rule
ln(x y) = ln(x) + ln(y) ln(3 7) = ln(3) + ln(7)
Quotient rule
ln(x / y) = ln(x) - ln(y) ln(3 / 7) = ln(3) - ln(7)
Power rule
ln(x
y
) = y ln(x) ln(2
8
) = 8 ln(2)
ln derivative
f (x) = ln(x) f ' (x) = 1
/ x
ln integral
ln(x)dx = x (ln(x) - 1)
+ C
ln of negative
number
ln(x) is undefined when x
0
ln of zero
ln(0) is undefined
ln of one
ln(1) = 0
ln of infinity
lim ln(x) = ,when x
Logarithm product rule
The logarithm of the multiplication of x and y is the sum of logarithm of x and logarithm of y.
log
b
(x y) = log
b
(x) + log
b
(y)
For example:
log
10
(3 7) = log
10
(3) + log
10
(7)
Logarithm quotient rule
The logarithm of the division of x and y is the difference of logarithm of x and logarithm of y.
log
b
(x / y) = log
b
(x) - log
b
(y)
For example:
log
10
(3 / 7) = log
10
(3) - log
10
(7)
Logarithm power rule
The logarithm of x raised to the power of y is y times the logarithm of x.
log
b
(x
y
) = y log
b
(x)
For example:
log
10
(2
8
) = 8 log
10
(2)
Derivative of natural logarithm
The derivative of the natural logarithm function is the reciprocal function.
When
f (x) = ln(x)
The derivative of f(x) is:
f ' (x) = 1 / x
Integral of natural logarithm
The integral of the natural logarithm function is given by:
When
f (x) = ln(x)
The integral of f(x) is:
f (x)dx = ln(x)dx = x (ln(x) - 1) + C
Ln of 0
The natural logarithm of zero is undefined:
ln(0) is undefined
The limit near 0 of the natural logarithm of x, when x approaches zero, is minus infinity:
Ln of 1
The natural logarithm of one is zero:
ln(1) = 0
Ln of infinity
The limit of natural logarithm of infinity, when x approaches infinity is equal to infinity:
lim ln(x) = , when x
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsD'EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Logarithm Power Rule: F (X) LN (X)Document2 pagesLogarithm Power Rule: F (X) LN (X)ddongchimPas encore d'évaluation
- Facts About e - ScribdDocument2 pagesFacts About e - ScribdddongchimPas encore d'évaluation
- Definition of Natural LogarithmDocument6 pagesDefinition of Natural LogarithmWidiya ALam SUrPas encore d'évaluation
- Rules of LogarithmsDocument9 pagesRules of LogarithmsVon ChristianPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics-Limits CalculusDocument2 pagesMathematics-Limits CalculusKartik PurwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus Cheat Sheet LimitsDocument2 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet LimitsDavid IvekovićPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus Cheat Sheet LimitsDocument2 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet LimitsJuan Carlos BetancurPas encore d'évaluation
- Limits: Calculus Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesLimits: Calculus Cheat SheetPratiksh PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Derivative of Logarithmic and Exponential FunctionDocument3 pagesDerivative of Logarithmic and Exponential FunctionPrincessdy CocadizPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 4Document8 pagesGroup 4Katerina TaglePas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics CalculusDocument11 pagesMathematics CalculusAnish NaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 12. Derivatives of Log - FunctionsDocument5 pagesLecture 12. Derivatives of Log - FunctionsBeshoy AdelPas encore d'évaluation
- MTHS111 Lesson2 2024Document34 pagesMTHS111 Lesson2 2024pearphelokazi45Pas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus I - Lecture 11 - Derivatives of General Exponential and Inverse FunctionsDocument15 pagesCalculus I - Lecture 11 - Derivatives of General Exponential and Inverse FunctionsTanaka DoporaPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 152, Section 55 (Vipul Naik) : X 1 R X 0 XDocument12 pagesMath 152, Section 55 (Vipul Naik) : X 1 R X 0 XnawramiPas encore d'évaluation
- MTHS111 Lesson2 2024Document23 pagesMTHS111 Lesson2 2024pearphelokazi45Pas encore d'évaluation
- GT1 W01 TT02 PDFDocument67 pagesGT1 W01 TT02 PDFTrọng HiếuPas encore d'évaluation
- EE101 Calculus and Analytical Geometry 2: Ngcy@ucsiuniversity - Edu.myDocument48 pagesEE101 Calculus and Analytical Geometry 2: Ngcy@ucsiuniversity - Edu.myYao SsengssPas encore d'évaluation
- Differentiation FormulaeDocument3 pagesDifferentiation FormulaeknoxmathsPas encore d'évaluation
- MATH 31B - Week 1 Exponential, Inverse Functions, and Logarithmic Functions (I)Document3 pagesMATH 31B - Week 1 Exponential, Inverse Functions, and Logarithmic Functions (I)Agus LeonardiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mlelectures PDFDocument24 pagesMlelectures PDFAhly Zamalek MasryPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus Cheat Sheet LimitsDocument2 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Limitstasos_rex3139Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit I Mathematical ToolsDocument16 pagesUnit I Mathematical ToolsparveezPas encore d'évaluation
- A Functional Determinant Expression For The Riemann Xi FunctionDocument13 pagesA Functional Determinant Expression For The Riemann Xi FunctionJose Javier Garcia MoretaPas encore d'évaluation
- X X X F X F X F X: Likelihood FunctionDocument12 pagesX X X F X F X F X: Likelihood FunctiondPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Handout Maths First YearDocument39 pages01 Handout Maths First YearAnuj DhorajiwalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4: Derivatives of Logarithmic Function Logarithmic FunctionsDocument19 pagesChapter 4: Derivatives of Logarithmic Function Logarithmic Functionsathia solehahPas encore d'évaluation
- PDF Presentation3Document29 pagesPDF Presentation3Ferdian Rafa FirdausPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuovo Text DocumentDocument4 pagesNuovo Text Documentgiuseppe21112006Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Mathematics: Introduction To LogarithmDocument9 pagesFundamentals of Mathematics: Introduction To LogarithmGURUMARUTHI KUMARPas encore d'évaluation
- Rules of Differentiation of Functions in CalculusDocument7 pagesRules of Differentiation of Functions in CalculusOyedotun TundePas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus BookletDocument6 pagesCalculus Bookletangie81Pas encore d'évaluation
- Formulas Calculo Integral (By Carrascal)Document4 pagesFormulas Calculo Integral (By Carrascal)IñakiPas encore d'évaluation
- Logarithm Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesLogarithm Cheat SheetM J Rhoades82% (11)
- 3 Random ProcessesDocument24 pages3 Random ProcessesSamson ImmanuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Differentiation of Logarithmic FunctionDocument11 pagesDifferentiation of Logarithmic FunctionMaria AndresPas encore d'évaluation
- Guc 2029 61 37611 2023-10-29T18 28 36Document22 pagesGuc 2029 61 37611 2023-10-29T18 28 36Marley EssamPas encore d'évaluation
- Algebra+2 FormulasDocument8 pagesAlgebra+2 FormulasYuan AcostaPas encore d'évaluation
- Intro To Fourier Integral: Xu-Yan ChenDocument10 pagesIntro To Fourier Integral: Xu-Yan ChenpietzdeoPas encore d'évaluation
- Slides L4Document15 pagesSlides L4Nyan LinnPas encore d'évaluation
- Cramer RaoDocument11 pagesCramer Raoshahilshah1919Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter1 Limits Continuity RevisedDocument12 pagesChapter1 Limits Continuity Reviseddiktatorimhotep8800Pas encore d'évaluation
- Page - 1Document5 pagesPage - 1RexTheKingPas encore d'évaluation
- Logs and Exponentials - Review PDFDocument12 pagesLogs and Exponentials - Review PDFPoopy PantsPas encore d'évaluation
- PChem HelpDocument27 pagesPChem HelpJillPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculating LyapunovDocument5 pagesCalculating LyapunovNeelima SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Logarithm Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesLogarithm Cheat SheetAnupam PathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Derivative of The Natural Log Function PDFDocument10 pagesDerivative of The Natural Log Function PDFLazar MihaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Definition of Natural Logarithm Function: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus F.T.CDocument5 pagesDefinition of Natural Logarithm Function: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus F.T.CChirag JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Tables of Laguerre Polynomials and Functions: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 39D'EverandTables of Laguerre Polynomials and Functions: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 39Pas encore d'évaluation
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)D'EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)D'EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)Pas encore d'évaluation
- API 510 Recert Test GuideDocument2 pagesAPI 510 Recert Test Guidekatycwi100% (1)
- Trig DerivativesDocument1 pageTrig DerivativeskatycwiPas encore d'évaluation
- Phase 1: Induction - Acceptable Foods List Most Fish, PoultryDocument4 pagesPhase 1: Induction - Acceptable Foods List Most Fish, PoultryRacheal0% (1)
- QC Surveillance Report FormDocument1 pageQC Surveillance Report FormkatycwiPas encore d'évaluation
- UT Shearwave Level II Indication Plotting ExerciseDocument8 pagesUT Shearwave Level II Indication Plotting ExercisekatycwiPas encore d'évaluation
- Iso Iec 25030 2007 eDocument44 pagesIso Iec 25030 2007 eAngélica100% (1)
- GR 9 Eng CodebDocument6 pagesGR 9 Eng CodebSharmista WalterPas encore d'évaluation
- Support Vector Machine Master ThesisDocument7 pagesSupport Vector Machine Master Thesistammymajorsclarksville100% (2)
- Final Quiz 2 - Attempt ReviewDocument6 pagesFinal Quiz 2 - Attempt Reviewkoraijohnson7Pas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Urban PlanningDocument33 pagesWhat Is Urban PlanningDivine Grace FernandoPas encore d'évaluation
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentAditya ShanbhagPas encore d'évaluation
- Royal British College Dancesport TeamDocument10 pagesRoyal British College Dancesport TeamAnna rose CabatinganPas encore d'évaluation
- Swot Analysis of Indian EconomyDocument2 pagesSwot Analysis of Indian EconomymyeyesrbeautPas encore d'évaluation
- Adolescents' Gender and Their Social Adjustment The Role of The Counsellor in NigeriaDocument20 pagesAdolescents' Gender and Their Social Adjustment The Role of The Counsellor in NigeriaEfosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Yu ZbornikDocument511 pagesYu ZbornikВладимирРакоњацPas encore d'évaluation
- Coating Resins Technical Data SYNOCURE 867S - 60Document1 pageCoating Resins Technical Data SYNOCURE 867S - 60Heramb TrifaleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION TO LITERATUREDocument4 pagesChapter 1 INTRODUCTION TO LITERATUREDominique TurlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Effective TeachingDocument94 pagesEffective Teaching小曼Pas encore d'évaluation
- Coal Mining Technology and SafetyDocument313 pagesCoal Mining Technology and Safetymuratandac3357Pas encore d'évaluation
- DC Generator - Construction, Working Principle, Types, and Applications PDFDocument1 pageDC Generator - Construction, Working Principle, Types, and Applications PDFGokul GokulPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 7 - Friction - NptelDocument18 pagesLecture 7 - Friction - Nptels_murugan02Pas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Logarithm Approximate FloatingDocument6 pages12 Logarithm Approximate FloatingPhilippe Englert VelhaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progression (Ex 5.1) Exercise 5.1Document8 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progression (Ex 5.1) Exercise 5.1Akash DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Kingroon ConfiguracoesDocument3 pagesKingroon ConfiguracoesanafrancaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2021 Individual 20546 (Lawrence, Stephen R. and Bette F.) ClientDocument18 pages2021 Individual 20546 (Lawrence, Stephen R. and Bette F.) ClientVANDA MOOREPas encore d'évaluation
- Final LUS EvaluationDocument36 pagesFinal LUS EvaluationNextgenPas encore d'évaluation
- The Perception of Luxury Cars MA Thesis 25 03Document60 pagesThe Perception of Luxury Cars MA Thesis 25 03Quaxi1954Pas encore d'évaluation
- Uniden PowerMax 5.8Ghz-DSS5865 - 5855 User Manual PDFDocument64 pagesUniden PowerMax 5.8Ghz-DSS5865 - 5855 User Manual PDFtradosevic4091Pas encore d'évaluation
- Group Members: - Muhamad Sahli B Muda - Nurul Hana Balqis Baharom - Napsiah Abdul RahmanDocument18 pagesGroup Members: - Muhamad Sahli B Muda - Nurul Hana Balqis Baharom - Napsiah Abdul RahmanNurul Hana BalqisPas encore d'évaluation
- 835 (Health Care Claim PaymentAdvice) - HIPAA TR3 GuideDocument306 pages835 (Health Care Claim PaymentAdvice) - HIPAA TR3 Guideअरूण शर्माPas encore d'évaluation
- 3-A Y 3-B Brenda Franco DíazDocument4 pages3-A Y 3-B Brenda Franco DíazBRENDA FRANCO DIAZPas encore d'évaluation
- Exemption in Experience & Turnover CriteriaDocument4 pagesExemption in Experience & Turnover CriteriaVivek KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Charter of The New UrbanismDocument4 pagesCharter of The New UrbanismBarabas SandraPas encore d'évaluation
- UserProvisioningLabKit 200330 093526Document10 pagesUserProvisioningLabKit 200330 093526Vivian BiryomumaishoPas encore d'évaluation