Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Sac 3
Transféré par
sbmiller87Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Sac 3
Transféré par
sbmiller87Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
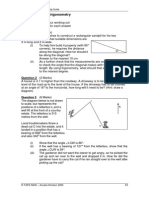
Module 2 Trigonometry Extended Response SAC Flying High
For the purposes of this SAC, the curvature of the earth has been taken into account and lines can be considered as
straight. Due to the curvature of the earth some diagrams do not appear to be drawn to scale.
This SAC explores flights between and within Australia and New Zealand made by two airlines Gondwana Air and Haka
Airlines.
Question 1
A plane flies from Melbourne to Hobart to Auckland and back to Melbourne as shown in the diagram below. The plane
flies in a straight line on each leg of the journey and turns through an angle of 90 at Hobart.
a) The distance between Melbourne and Hobart is 601 km to the nearest km and from Hobart to Auckland the
distance is 2427 km to the nearest km. Show that the direct distance from Auckland to Melbourne is 2500 km to the
nearest km. (3 marks)
b) Calculate the angle between the flight in to Auckland and the flight out of Auckland correct to one decimal
place. (2 marks)
Question 2
Thylacine Airport is located in Tasmania. A map of the airport is shown below:
a) Calculate the length of the edge labelled x km correct to one decimal place. (2 marks)
b) Calculate the land area in square kilometres of the airport. Give your answer correct to two decimal places.
(3 marks)
( )
c) Convert your answer to hectares. (1 mark)
Thylacine Airport is undergoing an upgrade on the existing site, so a scale model of the site has been constructed. The
scale model uses a 1:5000 scale.
d) Calculate the length of the side that is 13.2 km on the scale model in centimetres. (2 marks)
13.2 100 000 = 1 320 000 cm
1 320 000 5000 = 264 cm
e) Calculate the area of the scale model in metres squared correct to 2 decimal places. (2 marks)
96.42 1 000 000 = 96 420 000 m
2
96 420 000 5000
2
= 3.8568 3.86 m
2
The control tower at Thylacine Airport is cylindrical with a radius of 35 metres and a height of 120 metres as shown
below:
f) Calculate the volume of the control tower at Thylacine Airport in cubic metres correct to the nearest whole
metre. (2 marks)
g) Calculate the volume of the control tower in the scale model in cubic centimetres correct to 2 decimal places.
(3 marks)
Question 3
A plane flies over a hiker at a height of 5 kilometres above his head. The hiker first sees the plane at point A when it is
on an angle of elevation of 75. A short time later the plane is at an angle of elevation of 48. The plane has maintained
its altitude during this time.
a) Calculate the horizontal distance of the plane from the hiker when it is at point A, correct to the nearest metre.
(2 marks)
b) Calculate the distance flown between points A and B correct to the nearest metre. (2 marks)
c) When the plane is at point B the pilot looks down at a monument directly in line with the plane and the hiker.
The monument rises 180 metres above the hikers head. If the pilot is looking down on an angle of elevation of 32, how
far is the monument horizontally from the hiker (correct to the nearest metre)? (2 marks)
Total distance is 7714 + 4502 = 12216 m
Question 4
Gondwana Airlines flies direct from Melbourne to Sydney to Brisbane, then returning to Melbourne, as shown in the
diagram below.
The distance flown from Melbourne to Sydney is 703 km, from Sydney to Brisbane the distance flown is 742 km and the
distance from Brisbane to Melbourne is 1373 km.
a) Given the distances as stated, use the cosine rule to show that the angle between the flight into Sydney and the
flight out of Sydney is 143.7 correct to one decimal place. (2 marks)
b) Calculate the size of the angle between the flight into Brisbane and the flight out of Brisbane using the sine rule.
Demonstrate the equation that you used to obtain your answer. Give your answer correct to one decimal place.
(2 marks)
c) Use any appropriate method calculate the size of the remaining angle in the triangle correct to the nearest
degree. (1 mark)
180 17.5 143.7 = 18.8
Question 5
Haka Airlines flies daily from Wellington to Christchurch and return. The bearing that the plane needs to take from
Christchurch to Wellington is 034.
a) Draw a diagram showing the relative position of Wellington and Christchurch and any relevant angles. (1 mark)
b) What is the bearing from Wellington to Christchurch? (2 marks)
180 +34 = 214
c) The direct flight between Wellington and Christchurch is 307 km. How far north of Christchurch is Wellington?
Give your answer correct to the nearest kilometre. (2 marks)
Question 6
Gondwana Airlines flies from Sydney to Auckland and then from Auckland to Christchurch. The plane flies 2167 km on a
bearing of 105 to get to Auckland and then flies 767 km on a bearing of 192 to get to Christchurch.
a) Draw a diagram representing these flights, showing all angles. (1 mark)
b) Use this information to calculate the distance from Sydney to Christchurch, correct to the nearest kilometre.
(3 marks)
c) What bearing would the plane need to take to return to Sydney from Christchurch? (3 marks)
Angle ACS is 67.9 68
Bearing is 360 (68 12) = 304
Question 7
The Tasman Sea can be considered to be roughly bounded by the cities of Hobart, Brisbane, Auckland and Christchurch.
This is shown in the diagram below along with the distances between these cities.
The bearing from Hobart to Brisbane is 018 and the bearing from Hobart to Christchurch is 100. Use this information
to estimate the area of the Tasman Sea to the nearest 1000 square kilometres. (5 marks)
( )
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- DGCA Question For January Attempt 2019Document19 pagesDGCA Question For January Attempt 2019YADWINDER SINGH100% (4)
- Study Guide - Air NavDocument298 pagesStudy Guide - Air NavIvan ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 6147751028545554443Document19 pages5 6147751028545554443Vatsal WadhwaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen Nav BFCDocument12 pagesGen Nav BFCTushar MantriPas encore d'évaluation
- MATH 1720 Final Exam ReviewDocument12 pagesMATH 1720 Final Exam ReviewRafael Pati Liggayu IIPas encore d'évaluation
- Navigation Final Exam 227 228 04Document22 pagesNavigation Final Exam 227 228 04Khalil KallangodanPas encore d'évaluation
- Air NavigationDocument9 pagesAir NavigationAkshay MaheshwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Algebra and TrigonometryDocument3 pagesAlgebra and TrigonometryReam MairPas encore d'évaluation
- Questions Air NavigationDocument14 pagesQuestions Air NavigationRavi Bali100% (4)
- 5 PaperDocument14 pages5 PaperVivek Chandra100% (2)
- Distance Formula WorksheetDocument7 pagesDistance Formula Worksheetapi-735539036Pas encore d'évaluation
- CPL by GODFATHER (ANSWER2) - 1Document65 pagesCPL by GODFATHER (ANSWER2) - 1bcbddtzhzgPas encore d'évaluation
- Nav Final 1Document17 pagesNav Final 1lee.georgee6204Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bearings Group AssignmentDocument7 pagesBearings Group AssignmentSkyla DavisPas encore d'évaluation
- 1303 FT RetestDocument6 pages1303 FT RetestAkshay MaheshwariPas encore d'évaluation
- General Navigation Exam 3Document19 pagesGeneral Navigation Exam 3momanbhPas encore d'évaluation
- Math2412 LocDocument5 pagesMath2412 LocKautilPas encore d'évaluation
- Word Problems in Oblique Triangles (Cosine Law)Document1 pageWord Problems in Oblique Triangles (Cosine Law)Chelsea RubioPas encore d'évaluation
- Remedial Test (Just The Answers)Document13 pagesRemedial Test (Just The Answers)lornehessPas encore d'évaluation
- Me Diag 2 - DummyDocument3 pagesMe Diag 2 - DummyKrizia SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- 1303 FT (Retest)Document6 pages1303 FT (Retest)Akshay MaheshwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Class4 SurveyingQuestions PDFDocument66 pagesClass4 SurveyingQuestions PDFJay PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Test 50 Ans Trigonometry Appnv of TrigonometryDocument14 pagesTest 50 Ans Trigonometry Appnv of TrigonometrysghkkPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 O Level Pure 1964 Paper 1Document5 pages01 O Level Pure 1964 Paper 1badamsmithPas encore d'évaluation
- CPL Review 03Document6 pagesCPL Review 03Plane driverPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Aircraft NavigationDocument3 pages1 Aircraft Navigationmike_cjPas encore d'évaluation
- GenNav Unsolved QPaper GEDocument17 pagesGenNav Unsolved QPaper GEDharmendraPas encore d'évaluation
- HSC Exam Questions (Trigonometric Ratios)Document9 pagesHSC Exam Questions (Trigonometric Ratios)Eva100% (1)
- Review For Part 1Document5 pagesReview For Part 1joeramon1997Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Surveying 15Cv34Document23 pagesBasic Surveying 15Cv34Ajeeth BPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of Trigonometry Solved Board Q Paper-2Document8 pagesApplication of Trigonometry Solved Board Q Paper-2Kunal SagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Atpl 6Document22 pagesAtpl 6Vatsal WadhwaPas encore d'évaluation
- QB General Navigation 20CBAR33Document7 pagesQB General Navigation 20CBAR33farry100% (1)
- Fuselage and Tail Sizing - 5 Topics: Example 6.2 (Part I)Document12 pagesFuselage and Tail Sizing - 5 Topics: Example 6.2 (Part I)Ajay YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Aptitude Old PaperDocument35 pagesAptitude Old PaperMayank SagarPas encore d'évaluation
- NAVY Question PapersDocument35 pagesNAVY Question PapersRajan Raju IndukuriPas encore d'évaluation
- Quantitative Aptitude Question Answers PDFDocument35 pagesQuantitative Aptitude Question Answers PDFKirañ M R CfcPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus Test For Wedensday 003Document7 pagesCalculus Test For Wedensday 003Prisha ShettyPas encore d'évaluation
- Online Class Test On Math D 15.9.2020 PDFDocument7 pagesOnline Class Test On Math D 15.9.2020 PDFFaiyad 091 class IX sdPas encore d'évaluation
- 3-10 Trigonometry AssignmentDocument2 pages3-10 Trigonometry Assignmentapi-261651658Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1108.1201 FT Final (Retest)Document36 pages1108.1201 FT Final (Retest)Akshay MaheshwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Quantitative Aptitude Question & AnswersDocument35 pagesQuantitative Aptitude Question & AnswersNAVEEN SAI SINGHPas encore d'évaluation
- Quantitative Aptitude Question & AnswersDocument35 pagesQuantitative Aptitude Question & AnswersNAVEEN SAI SINGHPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometry ReviewDocument6 pagesTrigonometry Reviewwarlito floresPas encore d'évaluation
- Navigation Question Bank: The EarthDocument237 pagesNavigation Question Bank: The Earthreethu reddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Airport Engineering 2 - KaviyarsanDocument55 pagesAirport Engineering 2 - KaviyarsanAbishek KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- GNAV Key FactsDocument2 pagesGNAV Key FactsRapsakPas encore d'évaluation
- Year 9 Revision Trigonometry and Non Linear Curve Sketching HW HandoutDocument9 pagesYear 9 Revision Trigonometry and Non Linear Curve Sketching HW HandoutMusab AlbarbariPas encore d'évaluation
- Indigo PaperDocument5 pagesIndigo Papersummum14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gnav Test-2Document7 pagesGnav Test-2Harshit dubeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Navigation Questionnaire CPL PatternDocument18 pagesAir Navigation Questionnaire CPL Patternnodynaren100% (1)
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics 12 May Chapter 2 Units and MeasurementsDocument18 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics 12 May Chapter 2 Units and Measurementsnithya M.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nav Test For CPL CandidatesDocument8 pagesNav Test For CPL CandidatesVivek BaskarPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 2 Cosmos CollegeDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 Cosmos CollegeBollywood RetroPas encore d'évaluation
- September 21 (Test 3)Document11 pagesSeptember 21 (Test 3)Karun SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- FINAL COACHING 7 - MATHEMATICS LooksfamDocument50 pagesFINAL COACHING 7 - MATHEMATICS LooksfamAlan Je MusketerPas encore d'évaluation
- General Navigation: Exam 1, 70 Questions Time Allowed 2 HoursDocument96 pagesGeneral Navigation: Exam 1, 70 Questions Time Allowed 2 HoursRishabhYadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Extended Response/Problem Networks & Directed GraphsDocument6 pagesExtended Response/Problem Networks & Directed Graphssbmiller87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Extended Response/Problem Business-Related Mathematics Session OneDocument2 pagesExtended Response/Problem Business-Related Mathematics Session Onesbmiller87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 - Outcome 3 - Collaboratively Solve An Information Problem For A ClientDocument4 pagesUnit 2 - Outcome 3 - Collaboratively Solve An Information Problem For A Clientsbmiller87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Building The Torch: What Your Doing : You Will Be Creating Your Own SwitchDocument4 pagesBuilding The Torch: What Your Doing : You Will Be Creating Your Own Switchsbmiller87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exam 2 SolutionsDocument12 pagesExam 2 Solutionssbmiller87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Critical Path AnalysisDocument2 pagesCritical Path Analysissbmiller87Pas encore d'évaluation
- A History of PhotographyDocument49 pagesA History of PhotographyderghalPas encore d'évaluation
- Models - Rf.plasmonic Wire Grating PDFDocument26 pagesModels - Rf.plasmonic Wire Grating PDFrak999Pas encore d'évaluation
- ClimateDocument30 pagesClimateSujitnkbpsPas encore d'évaluation
- Appendix B Laplace Transform: Time Domain, E.G. If We Have A Voltage V Which Is ADocument6 pagesAppendix B Laplace Transform: Time Domain, E.G. If We Have A Voltage V Which Is AulaganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Section 133123Document11 pagesSection 133123Dian Aplimon JohannisPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 4 Chemistry Yearly Plan 2019Document2 pagesForm 4 Chemistry Yearly Plan 2019Jenny WeePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Four: Fig.12.a. Flow Diagram of Simple Vapour Compression SystemDocument15 pagesChapter Four: Fig.12.a. Flow Diagram of Simple Vapour Compression SystemAnonymous 5HYsyrddpPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculating MagnificaitonDocument3 pagesCalculating MagnificaitonShruthi Yalamalli ArunPas encore d'évaluation
- Logistic Regression EBayDocument10 pagesLogistic Regression EBayPrateek ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- GATE 2014 Examination CE: Civil Engineering: Read The Following Instructions CarefullyDocument33 pagesGATE 2014 Examination CE: Civil Engineering: Read The Following Instructions CarefullySai KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Stiffness Analysis of FramesDocument37 pagesStiffness Analysis of FramesCarolina VacaPas encore d'évaluation
- Materials and Approaches For On Body Energy HarvestingDocument8 pagesMaterials and Approaches For On Body Energy HarvestingShotech EngineeringPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 8 Ee ReportDocument10 pagesLab 8 Ee Reportshikazi ziki100% (1)
- CHM 2045 Lab ReportDocument11 pagesCHM 2045 Lab ReportlexilocoPas encore d'évaluation
- Signals & Systems (Solved Problems)Document7 pagesSignals & Systems (Solved Problems)Lohith CoreelPas encore d'évaluation
- Report WritingDocument24 pagesReport WritingVasudevanPas encore d'évaluation
- Self Assessment ASPDocument104 pagesSelf Assessment ASPTarek San100% (1)
- LNG Receiving Terminals: BY CH - Satvika 16021A2545Document24 pagesLNG Receiving Terminals: BY CH - Satvika 16021A2545Ram Charan Konidela100% (1)
- t9 PDFDocument21 pagest9 PDFselvaganapathy1992Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nortje Desiree 2002 PDFDocument328 pagesNortje Desiree 2002 PDFAtul KulkarniPas encore d'évaluation
- High Efficiency Coalescers For Gas Processing OperationsDocument9 pagesHigh Efficiency Coalescers For Gas Processing OperationsAndri SaputraPas encore d'évaluation
- 7UT51x Manual UsDocument232 pages7UT51x Manual UsMtdb Psd100% (1)
- Connecting and Interpreting Limit SwitchesDocument6 pagesConnecting and Interpreting Limit SwitchesbangunprayogiPas encore d'évaluation
- ECE 371JB Lecture 3Document38 pagesECE 371JB Lecture 3yassinebouazziPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 IntroductionDocument5 pages3 IntroductionKhamvanh PhengnaonePas encore d'évaluation
- Ee 1002Document108 pagesEe 1002Akhilesh Kumar MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- B Tech ECE Courses NBADocument4 pagesB Tech ECE Courses NBAPratyush ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Volumetric Efficiency: Object: To TheoryDocument3 pagesVolumetric Efficiency: Object: To Theoryahmad shaheenPas encore d'évaluation
- RC2Document92 pagesRC2Chrisneil DelosreyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Review of Cement Clinker ChemistryDocument14 pagesResearch Review of Cement Clinker ChemistryAman SahadeoPas encore d'évaluation