Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Defects in Dyeing With Reactive Dyes
Transféré par
vinayakasisDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Defects in Dyeing With Reactive Dyes
Transféré par
vinayakasisDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Defects in Dyeing with Reactive Dyes
Defect: Colors are not fast to washing, Abrasion;Staining in the fabric when transporting
from place to the other, water marks on the fabric
Remedy : Wash the fabric with soap and soda ash at right temperature. Adding sequestering
agent will yield good results. Treating with Ammonia will also give good results.
Defects in the fabric due to Printing- Need to take out full color
Remedy: Treat the dyed fabric with Sodium Hydrosuphite with 5-10 gm Sodium Hydrosulphite
at 75 deg C for 30-45 minutes. Add 5-7 gms Caustic Soda for even removal of colors. The color
becomes light yellow or brown after removal. Wash it thoroughly with soap.
The color can also be removed by solution of Sodium Hypochlorite. Treat the fabric with a
sodium hypochlorite solution ( 3-5 gms Chlorine) for 20-30 minutes. Keep the pH between 9-10.
The fabric is treated with Acetic acid after removal of color to remove chlorine and to neutralise
the fabric.
The fabric can be redyed after removal of color
Defect: Bleeding in colors during washing, abrasion
Remedy: Boil the fabric with caustic, Treat the fabric with Hydrogen Peroxide ( 5-10 gpl, 60-70
deg C) to make the color fast.
Defect: The fabric has been dyed in darker shade, uneven dyeing
Remedy: To take out color from the fabric treat it with caustic for 45-60 min at 70 deg C.
Thereafter treat the fabric with 10-20 gpl Acetic Acid for 40-60 min at 80-85 deg C.
Defect: Uneven dyeing, marks of water, marks of colors
Remedy: Wash the fabric in soap and redye in a darker shade
Defect : The fabric has become stiff and rough after dyeing
Remedy: Finish after adding right softner
Defect: Color staining of fabric, uneven dyeing
Remedy: Redye the fabric in darker shade.
Defect: Color staining in fabrics of darker shade, uneven undyeing
Remedy: Dye the fabric in Sulphur black
Caution: Please treat a small length fabric to check the effectiveness and any harmful
effects before commencing a full treatment.
About these ads
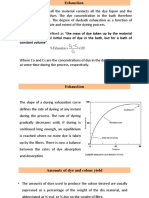
Common Causes of Dyeing Defects:
It is important that the general precautions should be followed while dyeing a textile material. It is always helpful
to keep a record of all the conditions (including temperature, time, conc of color, chemicals, material to liquor
ratio) in order to get an even shade in each batch. In general the following are the common causes of dyeing
defects across all the categories of dyes:
1. The material is not well prepared for dyeing and printing
a. Material having dead fibres or other defective fibres
b. Left over of Chemicals after bleaching etc.
c. Material not properly desized
d. Material not properly mercerised.
e. Absorbancy of the fabric not proper
f. Sticking of insoluble material on the fibres
g. Impurities are not removed properly
h. Uneven heat treatment.
2.Water Quality not Proper
a. More Hardness of water
b. Water has metal ions such as iron.
c. pH of water not proper
d. Water having more chlorine
3. Due to Shortcomings in making Dyeing Solution
a. Improper weight ratio of colors, material and chemicals.
b. Improper material to water ratio
3. Improper filtering of concentrated colors.
4. Due to Shortcomings in the dye machinery
a. Coming out of Dye liquor during dyeing
b. Defective instruments controlling temperature, pressure speed etc.
fJIGGER DYEING
thE Fabric is wound around one of the rollers; during dyeing the fabric is passed through the dye
bath and rewind on to the second roller.
When all First the fabric is passed through the dye bath the direction of movement is reversed,
this would be repeated until the dyeing is completed. During dyeing tension is imparted in
length of the fabric.
Suitable for delicate fabrics & light wt. Fabric.
Low liquors ratios (1:2 to 1:6) the consumption of chemicals and energy is low.
Knitted and stretch woven fabrics cannot be used
Machine Details
Machine make: Swastik (India)
Number of operator: 1 operator per 2 machines
Total number of machines: 13
Production: 20,000 m/ 13 machines/ day
Speed of the machine: 60 m/min
Roller pressure: 70 75 Kg/cm
Maximum Temperature: 80 C
SCM Textile Processing Mills in Erode.
PROCESS FLOW
SAMPLING (COMPUTER ART DESIGN)
STRIKE OFF FOR SAMPLING (SMALL SCREEN DEVELOPMENT)
PARTY SAMPLE APPROVAL
BLD (BRIGHT LIGHT DUPLICATE)
ROTARY SCREEN EXPOSING
PRINTING
SCREEN PRINTING
The respective screens are mounted on the roROTARY tary heads
Selected squeegees are inserted and connected to the respective colour pumps
The fabric to be printed is fed to the blanket and gets printed by the respective screens in
continuous manner
The printed fabric is conveyed through dryer and plaited
Machine details:
Machine make: Stomac
Machine width: 70 inch
Numbers of colours possible: 12
Numbers of operators: 1 operator and 4 assistants per machine
Printing speed: up to 80 meters/minute
PRINTING
Pigment printing is one of the simplest direct styles, which is applicable to all class fibres
Since the pigments are insoluble colouring PIGMENT matters, they are physically applied by
means of binders.
DISCHARGE PRINTING
Discharge prints are fabrics that are dyed a solid colour prior to printing.
The design is applied by screen or roller with a chemical a reducing agent which removes the
colour of the originally dyed fabric.
Cotton Dyeing:
Temperature: 60-80 degrees
Pressure: atmospheric pressure
pH: 10.8 11.4
Dye: Reactive dyes
Time: 45-75 min
Polyester Dyeing:
Temperature: 130 degrees
Pressure: 2kg/cm2
pH: 4 - 5
Dye: disperse dye
Time: 2 hours
Bleaching
Checking pH (process before pH =5.5-6)
Dyeing (pH = 7-9)
Shade checking
Soaping (95 degree Celsius for 15-30 minutes)
pH stabilization + finishing
Machine Details
Machine make: THIES
Number of operator: 1operator and 1 assistant per machine
Total number of machines: 7
Capacity: 1080 kg/batch
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Tie-Dye 101: How to Make Over 20 Fabulous PatternsD'EverandTie-Dye 101: How to Make Over 20 Fabulous PatternsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (3)
- Printing DefectsDocument4 pagesPrinting DefectsShrishti GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Apparel DyeingDocument21 pagesApparel DyeingUmme Hafsa OpurbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Report On: Dip Dyeing Process On Twill FabricDocument6 pagesLab Report On: Dip Dyeing Process On Twill FabricIMAMA HOSSAIN SOBUJPas encore d'évaluation
- Pad Steam MachineDocument27 pagesPad Steam MachineJuan CubasPas encore d'évaluation
- Application Methods of Reactive Dyeing - Textile LearnerDocument12 pagesApplication Methods of Reactive Dyeing - Textile LearnerAnas ZidanePas encore d'évaluation
- Dyeing of Polyester and Cotton BlendDocument50 pagesDyeing of Polyester and Cotton BlendarafathosainPas encore d'évaluation
- National Textile University Faculty of Engineering & TechnologyDocument8 pagesNational Textile University Faculty of Engineering & TechnologyShahan AkhtarPas encore d'évaluation
- Continuous Dyeing MachineDocument18 pagesContinuous Dyeing Machinebigstar42Pas encore d'évaluation
- Application of Disperse Dyes Application Methods of Disperse Dyes Factors Considered For SelectionDocument1 pageApplication of Disperse Dyes Application Methods of Disperse Dyes Factors Considered For SelectionrashidtexPas encore d'évaluation
- Dyeing Process of Cotton Fabric With Reactive DyesDocument6 pagesDyeing Process of Cotton Fabric With Reactive DyesShaheen Monir HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Garment Wet WashingDocument32 pagesGarment Wet WashingMdJulkarNaimPas encore d'évaluation
- 11.5 Dyeing of Polyester Fibre Using Disperse DyesDocument8 pages11.5 Dyeing of Polyester Fibre Using Disperse DyesPriya GhoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Dyeing of Knitted Fabrics PDFDocument7 pagesDyeing of Knitted Fabrics PDFAhmed AksarPas encore d'évaluation
- Discharge Printing On Cotton FabricDocument2 pagesDischarge Printing On Cotton FabricMd. Sazzad Hossen100% (2)
- Methods of ColorationDocument11 pagesMethods of ColorationFerdous Khan RubelPas encore d'évaluation
- TRI 3004 Garment Dyeing With PigmentsDocument9 pagesTRI 3004 Garment Dyeing With PigmentsAyman sebaeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Final PPT - LeninDocument34 pagesFinal PPT - LeninAman AnshuPas encore d'évaluation
- Dyeing With Polyester Using HTHP BEAM DYEING MACHINEDocument4 pagesDyeing With Polyester Using HTHP BEAM DYEING MACHINESivakumar KPas encore d'évaluation
- Disperse DyesDocument23 pagesDisperse DyesPratik Minj100% (3)
- Dyeing Unit 3Document69 pagesDyeing Unit 3HAMSA LEKHAPas encore d'évaluation
- Textile Dyeing Document For Lab Matching With Various Dyes. (Exhaust Process)Document89 pagesTextile Dyeing Document For Lab Matching With Various Dyes. (Exhaust Process)Khandaker Sakib FarhadPas encore d'évaluation
- Volumnia SlidesCarnivalDocument21 pagesVolumnia SlidesCarnivalDhanraj SutharPas encore d'évaluation
- Fabric Dyeing ProcessDocument8 pagesFabric Dyeing ProcessNikita JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Semi Continuous Dyeing ProcessDocument3 pagesSemi Continuous Dyeing ProcessMonjur MorshedPas encore d'évaluation
- TD Assignment 2Document20 pagesTD Assignment 2palakPas encore d'évaluation
- Study On Different Types of Dyeing Faults PDFDocument10 pagesStudy On Different Types of Dyeing Faults PDF呂仲書Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dyeing Flowchart/wet Processing TechnologyDocument15 pagesDyeing Flowchart/wet Processing Technologyreezwan_mgl100% (1)
- PrintingDocument56 pagesPrintingNikithaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Printing of P.F VTH Vat& Sulphur DyesDocument4 pagesPrinting of P.F VTH Vat& Sulphur DyesMuhammad Asad NawazPas encore d'évaluation
- Jigger and Winch Dyeing MachineDocument10 pagesJigger and Winch Dyeing MachineSajid arPas encore d'évaluation
- Wpt-III Lab Report 1Document4 pagesWpt-III Lab Report 1Rafid RatulPas encore d'évaluation
- Dyeing-Pad Batch AssignmentDocument22 pagesDyeing-Pad Batch AssignmentTooba Anum100% (1)
- Dyeing Machines and MethodsDocument20 pagesDyeing Machines and MethodsAnonymous UoRu4s100% (3)
- Pad Steam MachineDocument27 pagesPad Steam Machineahmer adnan88% (8)
- Problems & Solutions in Polyester ProcessingDocument4 pagesProblems & Solutions in Polyester ProcessingRezaul Karim TutulPas encore d'évaluation
- Batchwise Processing Vis - A-Vis Continuous Wet Processing India'S Strength &weaknessDocument15 pagesBatchwise Processing Vis - A-Vis Continuous Wet Processing India'S Strength &weaknessSunil SonigaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Dyeing & PrintingDocument13 pagesDyeing & PrintingshponPas encore d'évaluation
- Normal Wash, Pigment Wash, Caustic WashDocument9 pagesNormal Wash, Pigment Wash, Caustic WashTauhidurRChowdhuryPas encore d'évaluation
- Different Dyieng MethodsDocument46 pagesDifferent Dyieng MethodsDeepali Choudhary100% (1)
- Dyeing Process of Cotton Fabric With Reactive DyesDocument6 pagesDyeing Process of Cotton Fabric With Reactive DyesMianAbrarAnjumPas encore d'évaluation
- PolyesterDocument15 pagesPolyesterRITIKPas encore d'évaluation
- Colour FastnessDocument37 pagesColour FastnessSivakumar K100% (1)
- 4.1.04 Application of A Vat Dye PDFDocument5 pages4.1.04 Application of A Vat Dye PDFAhmad Samer100% (1)
- Batch Dyeing Process, Batch Dyeing Process For Textiles, Process of Batch DyeingDocument3 pagesBatch Dyeing Process, Batch Dyeing Process For Textiles, Process of Batch DyeingVipin Singh KandholPas encore d'évaluation
- Dying and Printing PresentationDocument22 pagesDying and Printing PresentationMamta BamniyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 11.1 Dyeing of Cotton With Vat DyesDocument10 pages11.1 Dyeing of Cotton With Vat DyesPraveen NagarajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Precaution Manual For Colour Blooming Auxiliaries Applications On Textiles.Document12 pagesPrecaution Manual For Colour Blooming Auxiliaries Applications On Textiles.L.N.CHEMICAL INDUSTRY100% (1)
- Green University of Bangladesh: Department of Textile EngineeringDocument9 pagesGreen University of Bangladesh: Department of Textile EngineeringGreen University TextilePas encore d'évaluation
- 2nd Lab ReportDocument13 pages2nd Lab Reportali hasan100% (1)
- Printing Styles and MethodsDocument27 pagesPrinting Styles and MethodsRoja JayaramPas encore d'évaluation
- Session 11-Methods of PrintingDocument33 pagesSession 11-Methods of PrintingAneesha PandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pigment Dyeing: "Wash-Down" ColorantDocument8 pagesPigment Dyeing: "Wash-Down" ColorantLeo ChoePas encore d'évaluation
- Jigger Dyeing Machine:: Fabric PreparationDocument2 pagesJigger Dyeing Machine:: Fabric PreparationnaaomaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Denim ProcessingDocument14 pagesDenim ProcessingPrem SidharthPas encore d'évaluation
- Dyeing TheoryDocument11 pagesDyeing TheoryaliPas encore d'évaluation
- University of Management and Technology: Textile Labs Wet Processing Lab Manual TX-232Document16 pagesUniversity of Management and Technology: Textile Labs Wet Processing Lab Manual TX-232Safdar ZafarPas encore d'évaluation
- Methods of Printing: Session 11Document33 pagesMethods of Printing: Session 11Vaisistha BalPas encore d'évaluation
- Weaving, Processing and Finishingin Texttile IndustriesDocument2 pagesWeaving, Processing and Finishingin Texttile IndustriesShivam AgnihotriPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Classification of PigmentsDocument6 pagesChemical Classification of PigmentsPoison EmuPas encore d'évaluation
- Levocol HCF - NLDocument3 pagesLevocol HCF - NLvinayakasis100% (1)
- Grey Scale For Assessing Change in ShadeDocument2 pagesGrey Scale For Assessing Change in ShadevinayakasisPas encore d'évaluation
- Process Control and Safety in Chemical Processing PDFDocument44 pagesProcess Control and Safety in Chemical Processing PDFvinayakasisPas encore d'évaluation
- A Guide To Understanding FabricsDocument28 pagesA Guide To Understanding FabricsGarmentLearnerPas encore d'évaluation
- Silk Industry Cental Silk Board PDFDocument26 pagesSilk Industry Cental Silk Board PDFvinayakasisPas encore d'évaluation
- Brochure Substante ClariantDocument29 pagesBrochure Substante Clariantleva_misa100% (2)
- Acceptable Quality Levels in The Textile Sector and Their Effect On The Level of CompetitionDocument8 pagesAcceptable Quality Levels in The Textile Sector and Their Effect On The Level of CompetitionvinayakasisPas encore d'évaluation
- Open Access Scientific Reports: Optimization of Caustic Soda Concentration For Causticization of CottonDocument6 pagesOpen Access Scientific Reports: Optimization of Caustic Soda Concentration For Causticization of CottonvinayakasisPas encore d'évaluation
- Albatex: LD Leveling AgentDocument4 pagesAlbatex: LD Leveling AgentvinayakasisPas encore d'évaluation
- Mercerization of Cotton: - John Mercer 1791-1866 British Chemist - Expts On Measurement of Viscosity of Solutions ofDocument20 pagesMercerization of Cotton: - John Mercer 1791-1866 British Chemist - Expts On Measurement of Viscosity of Solutions ofvinayakasisPas encore d'évaluation
- Best Practice For Fabric InspectionDocument3 pagesBest Practice For Fabric InspectionvinayakasisPas encore d'évaluation
- GA5 Pre S1 T5Document2 pagesGA5 Pre S1 T5xugiantsPas encore d'évaluation
- 110 WS Solutions KeyDocument2 pages110 WS Solutions Keyshanmugam karthickPas encore d'évaluation
- F324Jan11 25761Document16 pagesF324Jan11 25761Lexy Lawton-BoweringPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Synthesis TEMPLATEDocument30 pagesOrganic Synthesis TEMPLATEKyle HallPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-4 Water TechnologyDocument22 pagesUnit-4 Water TechnologymaheshkancherlajobPas encore d'évaluation
- Provisional List of Additives Used in Plastics: 1 Publication Date: 10/04/2008 11 Update 28/10/2011Document4 pagesProvisional List of Additives Used in Plastics: 1 Publication Date: 10/04/2008 11 Update 28/10/2011Rim BdidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3Document51 pagesChapter 3Ngọc Hà NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytical Chemistry Basics 43pDocument43 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Basics 43pOmairPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Resistance of Epoxy To Common ProductsDocument4 pagesChemical Resistance of Epoxy To Common ProductsBoro TerakolPas encore d'évaluation
- The Process of Manufacture of Urea in A Naphtha Based PlantDocument4 pagesThe Process of Manufacture of Urea in A Naphtha Based PlantahmedkhidryagoubPas encore d'évaluation
- Alkane and AlkeneDocument40 pagesAlkane and AlkenePawankumar Gupta91% (11)
- A New Method For The Esterification of Sulfonic AcidsDocument3 pagesA New Method For The Esterification of Sulfonic AcidsLuis angel NarvaezPas encore d'évaluation
- Request For Proposal Water Well Drilling v2Document9 pagesRequest For Proposal Water Well Drilling v2elnaqa176Pas encore d'évaluation
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument2 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentShridevi RaviPas encore d'évaluation
- Emf Values of Organic CompoundsDocument34 pagesEmf Values of Organic CompoundsPrabir SahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Alcohol Final 114806Document5 pagesAlcohol Final 114806Aditya Singh ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 With Notes PDFDocument2 pages5 With Notes PDFKimberley Anne SeePas encore d'évaluation
- Che 021 - Q1 - Worksheet #1Document3 pagesChe 021 - Q1 - Worksheet #1elliPas encore d'évaluation
- 20 Types of Reactions Lab (Simple Format)Document1 page20 Types of Reactions Lab (Simple Format)Victor BPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 14 ElementsDocument10 pagesGroup 14 ElementsWorld of SciencePas encore d'évaluation
- Chia Seed PolysaccharideDocument6 pagesChia Seed PolysaccharideRal T. BerensPas encore d'évaluation
- Stoichiometry ModuleDocument8 pagesStoichiometry ModuleKaye NicolasPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmaceutico Analytical Study of Lokanatha RasaDocument6 pagesPharmaceutico Analytical Study of Lokanatha RasaEditor IJTSRDPas encore d'évaluation
- TDS of Maleic Anhydride.Document1 pageTDS of Maleic Anhydride.Mudassar HussainiPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Practical Test 1Document2 pagesScience Practical Test 1Rodgers PrinciplePas encore d'évaluation
- Edexcel Chemistry Unit 2 Revision NotesDocument10 pagesEdexcel Chemistry Unit 2 Revision NotesMohammad Izaz MahmudPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 Acid-Base ReactionDocument111 pagesChapter 7 Acid-Base ReactionUMMU MARDHIAH ABDUL HALIMPas encore d'évaluation
- ShowTechnicalDataSheet SF 1642Document4 pagesShowTechnicalDataSheet SF 1642Trần Yến NhiPas encore d'évaluation
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument6 pagesNew Microsoft Word Documentlubna84Pas encore d'évaluation