Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Hydatidiform Mole
Transféré par
Krisna Augustian0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
67 vues4 pagesMola hidatidosa cases
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentMola hidatidosa cases
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
67 vues4 pagesHydatidiform Mole
Transféré par
Krisna AugustianMola hidatidosa cases
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
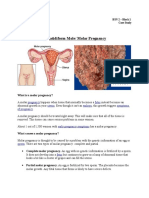
Hydatidiform mole
Share on facebook Share on twitter Bookmark & Share Printer-friendly version
Hydatidiform mole is a rare mass or growth that forms inside the womb (uterus) at the
beginning of a pregnancy !t is a type of gestational trophoblastic disease ("#$) % cancerous
form of "#$ is called choriocarcinoma
Causes
Hydatidiform mole& or molar pregnancy& results from over-production of the tissue that is
supposed to develop into the placenta #he placenta feeds the fetus during pregnancy 'ith a
molar pregnancy& the tissues develop into an abnormal growth& called a mass
#here are two types(
Partial molar pregnancy( #here is an abnormal placenta and some fetal development
)omplete molar pregnancy( #here is an abnormal placenta but no fetus
Both forms are due to problems during fertili*ation #he e+act cause of fertili*ation
problems is unknown % diet low in protein& animal fat& and vitamin % may play a role
Symptoms
%bnormal growth of the womb (uterus)
o ,+cessive growth in about half of cases
o Smaller-than-e+pected growth in about a third of cases
-ausea and vomiting that may be severe enough to re.uire a hospital stay
/aginal bleeding in pregnancy during the first 0 months of pregnancy
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism
o Heat intolerance
o 1oose stools
o 2apid heart rate
o 2estlessness& nervousness
o Skin warmer and more moist than usual
o #rembling hands
o 3ne+plained weight loss
Symptoms similar to preeclampsia that occur in the 4st trimester or early 5nd
trimester -- this is almost always a sign of a hydatidiform mole& because preeclampsia
is e+tremely rare this early in a normal pregnancy
o High blood pressure
o Swelling in feet& ankles& legs
Exams and Tests
% pelvic e+amination may show signs similar to a normal pregnancy& but the si*e of the
womb may be abnormal and the baby6s heart sounds are absent #here may be some vaginal
bleeding
% pregnancy ultrasound will show an abnormal placenta with or without some development
of a baby
#ests may include(
H)" blood test
)hest +-ray
)# or 72! of the abdomen
)omplete blood count
Blood clotting tests
8idney and liver function tests
Treatment
!f your doctor suspects a molar pregnancy& a suction curettage ($ and )) may be performed
% hysterectomy may be an option for older women who do not wish to become pregnant in
the future
%fter treatment& serum H)" level will be followed !t is important to avoid pregnancy and to
use a reliable contraceptive for 9 - 45 months after treatment for a molar pregnancy #his
allows for accurate testing to be sure that the abnormal tissue does not grow back 'omen
who get pregnant too soon after a molar pregnancy have a high risk of having another molar
pregnancy
Outlook (Prognosis)
7ore than :;< of hydatidiform moles are benign (noncancerous) #reatment is usually
successful )lose follow-up by your doctor is important %fter treatment& use effective
contraception for at least 9 - 45 months to avoid pregnancy
!n some cases& hydatidiform moles develop into invasive moles #hese can grow deep into the
uterine wall and cause bleeding or other complications
!n a few cases& a hydatidiform mole develops into a choriocarcinoma #his is a fast-growing
cancerous form of gestational trophoblastic disease
Possible Complications
1ung problems may occur after a $ and ) if the mother6s uterus is larger than 49 weeks
gestational si*e
)omplications of molar pregnancy include(
Preeclampsia
#hyroid problems
7olar pregnancy that continues or comes back
)omplications related to the surgery to remove a molar pregnancy include(
,+cessive bleeding
Side effects of anesthesia
Alternatie !ames
Hydatid mole= 7olar pregnancy
"eferences
)opeland 1>& 1andon 7B 7alignant diseases and pregnancy !n( "abbe S"& -iebyl >2&
Simpson >1& eds Obstetrics - Normal and Problem Pregnancies 9th ed Philadelphia& Pa(
,lsevier Saunders= 5;45(chap ?@
"oldstein $P& Berkowit* 2S "estational trophoblastic disease !n( %beloff 7$& %rmitage
>A& -iederhuber >,& 8astan 7B& 7c8enna '"& eds Abeloffs Clinical Oncology ?th ed
Philadelphia& Pa( ,lsevier )hurchill 1ivingstone= 5;;:(chap B?
8avanagh >>& "ershenson $7 "estational trophoblastic disease( hydatidiform mole&
nonmetastatic and metastatic gestational trophoblastic tumor( diagnosis and management !n(
8at* /1& 1ent* "7& 1obo 2%& "ershenson $7& eds Comprehensive Gynecology 9th ed
Philadelphia& Pa( ,lsevier 7osby= 5;45(chap 0C
#pdate $ate% &&'(')*&)
3pdated by( Susan Storck& 7$& D%)A"& )hief& ,astside $epartment of Abstetrics and
"ynecology& "roup Health )ooperative of Puget Sound& Bellevue& 'ashington= )linical
#eaching Daculty& $epartment of Abstetrics and "ynecology& 3niversity of 'ashington
School of 7edicine %lso reviewed by %$%7 Health Solutions& ,bi+& !nc& ,ditorial
#eam( $avid Eieve& 7$& 7H%& $avid 2 ,lt*& Stephanie Slon& and -issi 'ang
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ectopic Pregnancy1Document4 pagesEctopic Pregnancy1Arumtyas Cahyaning WijanartiPas encore d'évaluation
- Causes: Gestational Trophoblastic Disease ChoriocarcinomaDocument7 pagesCauses: Gestational Trophoblastic Disease ChoriocarcinomajudssalangsangPas encore d'évaluation
- Final H MoleDocument4 pagesFinal H MoleJewelyn BrondaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydatidiform MoleDocument2 pagesHydatidiform MolePaola AgustinPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydatidiform MoleDocument10 pagesHydatidiform MoleLisa TurnerPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydatidiform MoleDocument15 pagesHydatidiform MoleRegine Mae Morales EncinadaPas encore d'évaluation
- O o o o o O: Hydatidiform MoleDocument5 pagesO o o o o O: Hydatidiform MoleArniefah RegaroPas encore d'évaluation
- Abruptio Placentae Case StudyDocument4 pagesAbruptio Placentae Case StudyMonchee YusonPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple PregnancyDocument52 pagesMultiple Pregnancyazida90100% (4)
- Antepartum HeamorrhageDocument34 pagesAntepartum HeamorrhageSHOWMAN DEEPAKPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Read MoreDocument15 pagesEctopic Pregnancy: Read MoreVanessa Santos100% (1)
- Hydatidiform MoleDocument3 pagesHydatidiform MoleJny SherpaPas encore d'évaluation
- Miscarriage Early Pregnancy LossDocument10 pagesMiscarriage Early Pregnancy LossiwenniePas encore d'évaluation
- P ('t':'3', 'I':'3054201308') D '' Var B Location Settimeout (Function ( If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') ( B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Document13 pagesP ('t':'3', 'I':'3054201308') D '' Var B Location Settimeout (Function ( If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') ( B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Arumtyas Cahyaning WijanartiPas encore d'évaluation
- Molar PregnancyDocument4 pagesMolar PregnancyBeyonce SkekelPas encore d'évaluation
- Uterus: Signs and SymptomsDocument11 pagesUterus: Signs and SymptomsJoy Parallag - BautoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument6 pagesHyperemesis GravidarumMary Ann YumulPas encore d'évaluation
- Gestational Trophoblastic DiseasesDocument76 pagesGestational Trophoblastic DiseasesJhon NegessePas encore d'évaluation
- Hydatidiform MoleDocument3 pagesHydatidiform Molelanilyn aquinoPas encore d'évaluation
- TBL (Miscarrriage)Document36 pagesTBL (Miscarrriage)hitsugayat_7100% (1)
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument9 pagesEctopic PregnancyCatherine ZamoraPas encore d'évaluation
- MK Disorders in Early Pregnancy (OBGY)Document26 pagesMK Disorders in Early Pregnancy (OBGY)Moses Jr KazevuPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic Pregnanc Y Ectopic Pregnanc YDocument26 pagesEctopic Pregnanc Y Ectopic Pregnanc Ybladimer_riaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bleeding in Early PregnancyDocument40 pagesBleeding in Early PregnancyOmar mohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple PregnancyDocument55 pagesMultiple PregnancyNathaniel YeriPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 High Risk PregnancyDocument103 pages3 High Risk PregnancyKaguraPas encore d'évaluation
- Complications During Pregnancy - Chapt 5 - 1Document40 pagesComplications During Pregnancy - Chapt 5 - 1Bob IrsanPas encore d'évaluation
- Molar Pregnancy: Women's HealthDocument8 pagesMolar Pregnancy: Women's HealthAnonymous SeK7brdMc4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Abortion: Mohamed Sinan Govt Medical College, CalicutDocument60 pagesAbortion: Mohamed Sinan Govt Medical College, CalicutYash SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- JhoanneDocument4 pagesJhoanneShena_Borgo_os_7245Pas encore d'évaluation
- First Trimester BleedingDocument48 pagesFirst Trimester BleedingEliana ArshidPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydatidiform Mole Study GuideDocument4 pagesHydatidiform Mole Study GuideCarl Elexer Cuyugan AnoPas encore d'évaluation
- Miscarriage (Abortion) : (Adhesions Inside The Uterine Cavity)Document10 pagesMiscarriage (Abortion) : (Adhesions Inside The Uterine Cavity)Rashed Shatnawi100% (1)
- Abruptio PlacentaeDocument18 pagesAbruptio PlacentaeRitamariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument16 pagesAbruptio Placentaim_anjeh100% (2)
- Antepartum HemorrhageDocument43 pagesAntepartum HemorrhageashwiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Bleeding From The Genital Tract in Early Pregnancy (Before 28 Weeks)Document76 pagesBleeding From The Genital Tract in Early Pregnancy (Before 28 Weeks)Tiondi francisPas encore d'évaluation
- APH DR DaudDocument56 pagesAPH DR DaudMohd Daud Che YusofPas encore d'évaluation
- Early Pregnancy ComplicationsDocument101 pagesEarly Pregnancy ComplicationsDerian IrawanPas encore d'évaluation
- MiscarriageDocument38 pagesMiscarriagezianab aliPas encore d'évaluation
- Miscarriage & Early Pregnancy LossDocument38 pagesMiscarriage & Early Pregnancy LossLuqman OsmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Abortion: Mohamed Sinan Govt Medical College, CalicutDocument60 pagesAbortion: Mohamed Sinan Govt Medical College, CalicutMhr AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study #1: AbortionDocument42 pagesCase Study #1: AbortionJhoanne DelloroPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 5: Prencess Pango Ember Pastor Denise Po Justine Ramirez Rizalia Ramos Kaye Rile Joebert RomeroDocument77 pagesGroup 5: Prencess Pango Ember Pastor Denise Po Justine Ramirez Rizalia Ramos Kaye Rile Joebert RomeroDenise Louise PoPas encore d'évaluation
- Gestational DisordersDocument30 pagesGestational DisordersGwyneth GuintuPas encore d'évaluation
- Multimedia: - Chorionic Villus SamplingDocument8 pagesMultimedia: - Chorionic Villus SamplingsomeonebelerPas encore d'évaluation
- Aminotic Fluid DisordersDocument34 pagesAminotic Fluid DisordersCheru DugasePas encore d'évaluation
- Identifying Clients at RiskDocument57 pagesIdentifying Clients at Riskcoosa liquors100% (1)
- Hydatidiform MoleDocument4 pagesHydatidiform MoleKristine CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Wo Repro Week 2Document25 pagesWo Repro Week 2Naina Karamina SakinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument6 pagesAbruptio PlacentaIkAw NajUd PArt'xPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 20Document21 pagesChapter 20M Rama Anshorie100% (1)
- Jurnal Mola HidatidosaDocument8 pagesJurnal Mola HidatidosaDebby SofianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Molar PregnancyDocument13 pagesMolar PregnancyShalynurPas encore d'évaluation
- OB Review Sheet FinalDocument22 pagesOB Review Sheet FinalEmma KnoxPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic Pregnancy Kehamilan Luar RahimDocument5 pagesEctopic Pregnancy Kehamilan Luar RahimMuhamad Aminuddin Abu BakarPas encore d'évaluation
- Preterm BreechDocument38 pagesPreterm Breechorin78Pas encore d'évaluation
- 64 GTD LectureDocument53 pages64 GTD Lecturecollinsmag0% (1)
- 1 MiscarriageDocument34 pages1 Miscarriagezxcvbzaki123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ovarian Cysts, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandOvarian Cysts, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- Featured Grand RoundsDocument3 pagesFeatured Grand RoundsChin Edward ChandraPas encore d'évaluation
- Indonesia Vaccine Update October 2015Document15 pagesIndonesia Vaccine Update October 2015Krisna AugustianPas encore d'évaluation
- Otitis MediaDocument84 pagesOtitis MediaAlex MatthewPas encore d'évaluation
- Indonesia Vaccine Update October 2015Document15 pagesIndonesia Vaccine Update October 2015Krisna AugustianPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Malignant MelanomaDocument3 pagesOral Malignant MelanomaKrisna AugustianPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydatidiform MoleDocument4 pagesHydatidiform MoleKrisna AugustianPas encore d'évaluation
- Wonderkid FM 13Document1 pageWonderkid FM 13Krisna AugustianPas encore d'évaluation
- Abstrak English Modals Verbs EtcDocument1 pageAbstrak English Modals Verbs EtcKrisna AugustianPas encore d'évaluation
- Toksikologi: Tinjauan PustakaDocument2 pagesToksikologi: Tinjauan PustakaRahmat IkhwaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Pico CpapDocument4 pagesPico CpapAbc DefPas encore d'évaluation
- OB Final Exam Study GuideDocument14 pagesOB Final Exam Study GuideMarissa SolanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Routine Antenatal Fetal AuscultationDocument4 pagesRoutine Antenatal Fetal AuscultationiisPas encore d'évaluation
- Obstetrical Procedures 72Document3 pagesObstetrical Procedures 72Rosnalia HariyantoPas encore d'évaluation
- CHN Part 2 - Vital StatisticsDocument2 pagesCHN Part 2 - Vital StatisticsMichelle Gambol100% (1)
- Bahirdar UniversityDocument43 pagesBahirdar Universityseid negash100% (1)
- MATERI 2 CPD DR - GALA Materi CPDDocument28 pagesMATERI 2 CPD DR - GALA Materi CPDNaura NazifahPas encore d'évaluation
- Stages of Labor Nursing Intervention: First StageDocument3 pagesStages of Labor Nursing Intervention: First StageJhanniel IreneaPas encore d'évaluation
- Roleplay MCNDocument7 pagesRoleplay MCNJoshua AysonPas encore d'évaluation
- Operative DeliveryDocument19 pagesOperative DeliveryMtwe ZakayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pregnant Woman Emergency Clinical CaseDocument210 pagesPregnant Woman Emergency Clinical CaseAillenne AlambraPas encore d'évaluation
- Zerihun FigaDocument46 pagesZerihun FigaMoges desalePas encore d'évaluation
- Exam Labor ProcessDocument4 pagesExam Labor ProcessAileen A. Monares0% (1)
- OB NotesDocument2 pagesOB NotesJudy Ann CristePas encore d'évaluation
- MCN 1stweekDocument4 pagesMCN 1stweekCrystal MaidenPas encore d'évaluation
- Pengaruh Edukasi Online Berbasis Family Centered Dalam Pemberian Asi EksklusifDocument9 pagesPengaruh Edukasi Online Berbasis Family Centered Dalam Pemberian Asi EksklusifrisdawatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Hubungan Usia Dengan EmesisDocument7 pagesHubungan Usia Dengan EmesisNahar RuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre EclampsiaDocument27 pagesPre EclampsiaBRI KUPas encore d'évaluation
- Sexual and Reproductive Health and Rights: UNFPA Asia Pacific Regional PrioritiesDocument12 pagesSexual and Reproductive Health and Rights: UNFPA Asia Pacific Regional PrioritiesADBI EventsPas encore d'évaluation
- Health 10: 3 Quarter Week 7Document10 pagesHealth 10: 3 Quarter Week 7Maria Rose Tariga Aquino50% (2)
- MCN Test 2 AnswerDocument3 pagesMCN Test 2 AnswerJhessel CelosoPas encore d'évaluation
- International Journal of Scientific Research: Obstetrics & GynaecologyDocument3 pagesInternational Journal of Scientific Research: Obstetrics & Gynaecologyxasan kaamilPas encore d'évaluation
- Antepartum HaemorrhageDocument9 pagesAntepartum Haemorrhageareeb khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy and AssociatedDocument10 pagesHypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy and AssociatedMedrechEditorialPas encore d'évaluation
- A Rare Case Report - Syncephalus Conjoint TwinsDocument3 pagesA Rare Case Report - Syncephalus Conjoint Twinsalifa9393Pas encore d'évaluation
- In Vitro FertilizationDocument4 pagesIn Vitro FertilizationFrances Kaye Sta. CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundic HeightDocument37 pagesFundic HeightJanel PinuelaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - Overview of Maternal and Newborn Care - 08022014 - PHA RHMPP and NDPsDocument25 pages1 - Overview of Maternal and Newborn Care - 08022014 - PHA RHMPP and NDPsBoj OdejarPas encore d'évaluation
- First Trimester Bleeding and Pregnancy OutcomeDocument4 pagesFirst Trimester Bleeding and Pregnancy OutcomeShania BaraqbahPas encore d'évaluation
- Fetal DeathDocument12 pagesFetal DeathMerty Gonzales ٿPas encore d'évaluation