Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Measurement Igcse
Transféré par
boltu0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
278 vues8 pages1. A student is determining the density of a metre rule by measuring its mass using a balancing experiment and measuring its dimensions to calculate volume.
2. The student then determines the mass of an unknown load attached to the metre rule using a similar balancing method and measurements.
3. The document provides background on the experiments and measurements performed by the student to calculate density, including diagrams of the setup and calculations.
Description originale:
igcse
Titre original
Measurement igcse
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce document1. A student is determining the density of a metre rule by measuring its mass using a balancing experiment and measuring its dimensions to calculate volume.
2. The student then determines the mass of an unknown load attached to the metre rule using a similar balancing method and measurements.
3. The document provides background on the experiments and measurements performed by the student to calculate density, including diagrams of the setup and calculations.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
278 vues8 pagesMeasurement Igcse
Transféré par
boltu1. A student is determining the density of a metre rule by measuring its mass using a balancing experiment and measuring its dimensions to calculate volume.
2. The student then determines the mass of an unknown load attached to the metre rule using a similar balancing method and measurements.
3. The document provides background on the experiments and measurements performed by the student to calculate density, including diagrams of the setup and calculations.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 8
Scientia Academy Measurement Test Marks :80 Time :1:30 Hrs
1. An IGCSE student is determining the density of the material of a metre rule.
Fig. 1.1 shows the balancing experiment used to determine the mass of the rule.
Fig. 1.1
(a) (i) On Fig. 1.1, measure the distance a from the centre of the load X to the pivot.
a = ................................................. cm
(ii) On Fig. 1.1, measure the distance b from the pivot to the 50.0 cm mark on the rule.
b = ................................................. cm
(a) The diagram is drawn one tenth of actual size.
(i) Calculate the actual distance x from the centre of the load X to the pivot.
x = ................................................. cm
(ii) Calculate the actual distance y from the pivot to the 50.0 cm mark on the rule.
y = ................................................. cm
(iii) Calculate the mass m of metre ruler using equation
where k = 100
(b) Figs. 1.2 and 1.3 show part of the metre rule drawn actual size
Take and record measurements from Fig. 1.2 to determine the average width w of
the metre rule.
w = ................................................. cm
(ii) Take and record measurements from Fig. 1.3 to determine the average thickness t
of the metre rule.
t = ................................................. cm
(iii) Calculate the volume V of the metre rule using the equation V = lwt where l is the
length of the metre rule (100.0 cm).
V = ..................................................
(iv) Calculate the density of the metre rule using the equation = m/V
(d) State the assumption that the student has made about the position of the centre of
mass of the metre rule.
2. The IGCSE class is determining the mass of a load using a balancing method.
The load X has been taped to the metre rule so that its centre is exactly over the 90.0 cm
mark. It is not moved during the experiment. A mass m of 40 g is placed on the rule and its
position adjusted so that the rule is as near as possible to being balanced with the 50.0 cm
mark exactly over the pivot. This is repeated using a range of masses. The readings are
shown in Table 2.1
(c) For each value of d, calculate 1/d and record it in the table
(d) Determine the mass Mof the load X using the equation M= G/k where k = 40.0 cm.
3.Fig shows part of a measuring instruments
(a) State the name of this instrument
(b) Record the reading shown in figure
(c) Describe how you would find the thickness of a sheet of paper used in magazine
4. The list below gives the approximate densities of various metals
At an antique market, a collector buys what is advertised as small ancient gold statue .When the
collector tests it in the laboratory ,he finds its mass is 600 g and its volume is 65 cm
3
.
(a) In a space below ,describe how the volume of statue could be measured .You may draw a
diagrams if you wish [3]
(b) Use the figures given above to decide whether the statue was really made of gold. Show
your working[3]
(c) Was the statue made of Gold? [1] [Total:7]
5.An engineering machine has a piston which is going up and down approximately 75 times per
minute. Describe carefully how stop watch may be used to find accurately the time for one up and
down cycle of the piston [Total:4]
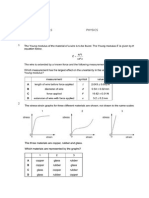
6. . Table 6.1 shows some measurements taken by three IGCSE students. The second column shows
the values recorded by the three students. For each quantity, underline the value most likely to be
correct. The first one is done for you.
7.Complete the table shown below
Measurement Unit Symbol
length
Kilogram
s
8.How many grams there in 1 kilogram ?
9. What is the S I Unit of time ?
10.Aluminium has a density of 2700 Kg/m
3
. What is the density in g/cm
3
?
11.
Which of the above are
a. Units of mass?
b. Units of length?
c. Units of volume ?
d. Units of time ?.
e. Units of density? [5]
12. (a) Define density. [1]
(b) The density of aluminium is 2.70 g / cm
3
. The thickness of a rectangular sheet of
aluminium foil varies, but is much less than 1 mm.
A student wishes to find the average thickness. She obtains the following measurements.
mass of sheet = 60.7 g
length of sheet = 50.0 cm
width of sheet = 30.0 cm
Calculate the students values for
(i) the volume of the sheet,
volume = .................................................. [2]
(ii) the average thickness of the sheet.
thickness = .................................................. [2]
(c) Another student, provided with a means of cutting the sheet, decides to find its average
thickness using a single measuring instrument. Assume the surfaces of the sheet are perfectly
smooth.
(i) Name a measuring instrument she could use.[1]
(ii) Describe the procedure she should follow to obtain an accurate value of the
average thickness of the sheet.
Details of how to read the instrument are not required. [3][Total: 9]
13. The period of the vertical oscillations of a mass hanging from a spring is known to be constant.
(a) A student times single oscillations with a stopwatch. In 10 separate measurements,
The stopwatch readings were:
1.8 s, 1.9 s, 1.7 s, 1.9 s, 1.8 s, 1.8 s, 1.9 s, 1.7 s, 1.8 s, 1.8 s.
What is the best value obtainable from these readings for the time of one oscillation?
Explain how you arrive at your answer.
best value =
explanation
(b) Describe how, using the same stopwatch, the student can find the period of oscillation more
accurately.
[Total: 5]
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Paper 1Document32 pagesPaper 1naamashirPas encore d'évaluation
- GCSE Exam Topic - HCF, LCM, Product of Prime Factors - Questions - Grade CDocument8 pagesGCSE Exam Topic - HCF, LCM, Product of Prime Factors - Questions - Grade CJoel GrayPas encore d'évaluation
- 97 Upper and Lower BoundsDocument8 pages97 Upper and Lower BoundsJoel GrayPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 12 - Shape: Answer All QuestionsDocument9 pagesUnit 12 - Shape: Answer All QuestionsAnonymous wgrNJjAPas encore d'évaluation
- Metals Non Metals ActivityDocument2 pagesMetals Non Metals ActivityIkeNovalinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 6 Volume Surface Area 3d Shapes DDocument2 pagesGrade 6 Volume Surface Area 3d Shapes DjadenjedidiahPas encore d'évaluation
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Human NutritionD'EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Human NutritionPas encore d'évaluation
- Primary 6 FractionsDocument3 pagesPrimary 6 FractionsAbinaya AyyakannuPas encore d'évaluation
- Secondary School ‘KS4 (Key Stage 4) - Maths – Algebra– Ages 14-16’ eBookD'EverandSecondary School ‘KS4 (Key Stage 4) - Maths – Algebra– Ages 14-16’ eBookPas encore d'évaluation
- Integer Word ProblemsDocument2 pagesInteger Word ProblemsuhasiniPas encore d'évaluation
- GCSE Foundation Exam QuestionsDocument46 pagesGCSE Foundation Exam QuestionsBecca RickwoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 24 Further Volume and Surface AreaDocument14 pagesTopic 24 Further Volume and Surface AreaSherluck John ErasmoPas encore d'évaluation
- Biological Molecules - Food Test - DNA - Cambridge IGCSE Biology - 0610-0970 (Chapter4)Document19 pagesBiological Molecules - Food Test - DNA - Cambridge IGCSE Biology - 0610-0970 (Chapter4)Malak KhalilPas encore d'évaluation
- Covalent Bonding 1Document2 pagesCovalent Bonding 1Vina Octavia AzzahraPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Pri WB Math P5 PDFDocument10 pages12 Pri WB Math P5 PDFteerapong onogkPas encore d'évaluation
- 8th Science Work WorksheetDocument2 pages8th Science Work WorksheetJR Cupid ShooterPas encore d'évaluation
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Reproduction In PlantsD'EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Reproduction In PlantsÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- Ratio and ProportionDocument3 pagesRatio and ProportionLai Kee KongPas encore d'évaluation
- PseudocodeDocument9 pagesPseudocodePallavi GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Corresponding Angles and Alternate Angles Questions MMEDocument7 pagesCorresponding Angles and Alternate Angles Questions MMEumar tariqPas encore d'évaluation
- AQA GCSE Physics Unit 1 Higher Question June 12Document20 pagesAQA GCSE Physics Unit 1 Higher Question June 12John Flores0% (1)
- Square Roots and Cube RootsDocument11 pagesSquare Roots and Cube RootsSushobhan SanyalPas encore d'évaluation
- GCSE Maths Practice Paper - TransformationsDocument18 pagesGCSE Maths Practice Paper - TransformationsTishefunmi Ogunmoye100% (1)
- Elements Compounds and MixturesDocument10 pagesElements Compounds and MixturesthaboPas encore d'évaluation
- "Full Coverage": Ratio: (Edexcel GCSE (9-1) Mock Set 2 Spring 2017 1F Q13)Document14 pages"Full Coverage": Ratio: (Edexcel GCSE (9-1) Mock Set 2 Spring 2017 1F Q13)fg ddfgdgfPas encore d'évaluation
- P5 Average1 WSDocument20 pagesP5 Average1 WSAyu Nur PrajantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Balanced Unbalanced Forces HandoutDocument4 pagesBalanced Unbalanced Forces Handoutapi-258720550Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42afy100% (1)
- 8 Magnetism Worksheet PDFDocument3 pages8 Magnetism Worksheet PDFfreanchiePas encore d'évaluation
- 1 The Diagram Shows A Kettle of Boiling Water.: SublimationDocument13 pages1 The Diagram Shows A Kettle of Boiling Water.: SublimationNethuni KumarasinghePas encore d'évaluation
- Chemisty Yr 10 Sep-2022 MSDocument10 pagesChemisty Yr 10 Sep-2022 MSFredrick OmbungaPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Machine AssignmentDocument4 pagesSimple Machine AssignmentVinod KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic - 17 TransformationsDocument88 pagesTopic - 17 TransformationsJorifPas encore d'évaluation
- 13 Pri WB Math P5 PDFDocument11 pages13 Pri WB Math P5 PDFteerapong onogk0% (1)
- Class 6 Maths Knowing Our NumbersDocument2 pagesClass 6 Maths Knowing Our Numbersaayush619_com3918Pas encore d'évaluation
- Year 6 End of Term 3 Exams - 2023 (Mathematics)Document10 pagesYear 6 End of Term 3 Exams - 2023 (Mathematics)MUKONKA MULEYAPas encore d'évaluation
- Distance Time Graphs WorksheetDocument5 pagesDistance Time Graphs WorksheetMaridjan WiwahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Accuracy and Bounds - Past Paper Questions: Year Series Paper NumberDocument18 pagesAccuracy and Bounds - Past Paper Questions: Year Series Paper Numberislam2059Pas encore d'évaluation
- Forces and Pressure 3.1 Understanding Pressure ( / 8 X 100 % %)Document21 pagesForces and Pressure 3.1 Understanding Pressure ( / 8 X 100 % %)mangimanPas encore d'évaluation
- Circle Word ProblemsDocument2 pagesCircle Word ProblemsRizky HermawanPas encore d'évaluation
- WORKSHEET 13.2 Formation of Male Gametes (Spermatogenesis)Document2 pagesWORKSHEET 13.2 Formation of Male Gametes (Spermatogenesis)HUSNA 83100% (1)
- Worksheet States of Matter Ks3Document3 pagesWorksheet States of Matter Ks3Animesh RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- IGCSE Maths Paper 3 Model AnswersDocument22 pagesIGCSE Maths Paper 3 Model AnswersDON-thegreat100% (7)
- Pre-Final Igcse Physics Grade 10 Sem 1 2014 Soal - RevisiDocument22 pagesPre-Final Igcse Physics Grade 10 Sem 1 2014 Soal - RevisiJoshuaUntungPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/41Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/41CindirllaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1 Physical Quantities and Measurement Techniques-P1Document17 pages1.1 Physical Quantities and Measurement Techniques-P1Nahiyan kamalPas encore d'évaluation
- SL - MathDocument2 pagesSL - MathastargroupPas encore d'évaluation
- Circle Theorems IGCSEDocument12 pagesCircle Theorems IGCSEWaseem AminPas encore d'évaluation
- Upper & Lower Bounds Worksheet #01, Approximation, Number From GCSE Maths TutorDocument2 pagesUpper & Lower Bounds Worksheet #01, Approximation, Number From GCSE Maths TutorgcsemathstutorPas encore d'évaluation
- Find The Actual DistanceDocument4 pagesFind The Actual DistanceMinna NashydPas encore d'évaluation
- Oak 2021 Secondary ks3 ks4 ScienceDocument142 pagesOak 2021 Secondary ks3 ks4 ScienceГоар МкртичянPas encore d'évaluation
- Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures ClozeDocument4 pagesElements, Compounds, and Mixtures ClozeIan Hatol0% (1)
- Maths WorksheetDocument4 pagesMaths Worksheetharpreet singh100% (1)
- VIII NSO MOCK TEST 3 (v3)Document9 pagesVIII NSO MOCK TEST 3 (v3)neomatrix70Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 - WorksheetDocument5 pagesChapter 1 - WorksheetAnan BarghouthyPas encore d'évaluation
- FPS U2 SS PDFDocument52 pagesFPS U2 SS PDFAnonymous 4VcUAodJ5Pas encore d'évaluation
- 170 - LTTC Grammar Sample G6Document13 pages170 - LTTC Grammar Sample G6Nihla Marikar ShafiePas encore d'évaluation
- Work With FunDocument8 pagesWork With FunnooriPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Semester WorksheetsDocument42 pages1st Semester WorksheetsMang friesPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 10 PhysicsDocument2 pagesGrade 10 PhysicsTinotenda ChatindoPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 12 Quantum Physics WorksheetDocument2 pagesClass 12 Quantum Physics WorksheetboltuPas encore d'évaluation
- Day 1 Subject LessonDocument5 pagesDay 1 Subject LessonboltuPas encore d'évaluation
- CollisionDocument7 pagesCollisionboltuPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.hooks LawDocument10 pages4.hooks LawboltuPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Worksheet LehDocument7 pagesPhysics Worksheet LehboltuPas encore d'évaluation
- QST Paper FormatDocument6 pagesQST Paper FormatboltuPas encore d'évaluation
- Slip Ring and Split RingDocument5 pagesSlip Ring and Split RingboltuPas encore d'évaluation
- Jingle Bells EasyDocument1 pageJingle Bells EasyboltuPas encore d'évaluation
- Matter and Materials Physics CLASS:11Document10 pagesMatter and Materials Physics CLASS:11boltuPas encore d'évaluation
- 100.03 #Value! 12 #Value! 30 #Value! 31Document2 pages100.03 #Value! 12 #Value! 30 #Value! 31boltuPas encore d'évaluation
- Resistivity of A WireDocument6 pagesResistivity of A WireboltuPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathrubhumi AstrologyDocument8 pagesMathrubhumi AstrologyboltuPas encore d'évaluation
- Editionname:The Times of India Pageno:201Document1 pageEditionname:The Times of India Pageno:201boltuPas encore d'évaluation
- Wbuhs PG ThesisDocument7 pagesWbuhs PG Thesisgbx272pg100% (2)
- SRM OverviewDocument37 pagesSRM Overviewbravichandra24Pas encore d'évaluation
- Case Analysis, Case 1Document2 pagesCase Analysis, Case 1Aakarsha MaharjanPas encore d'évaluation
- DP 900T00A ENU TrainerHandbookDocument288 pagesDP 900T00A ENU TrainerHandbookAndré baungatnerPas encore d'évaluation
- Consumer Behaviour ProjectDocument43 pagesConsumer Behaviour ProjectMuhammad UsmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Adsa Ka SyllabusDocument3 pagesAdsa Ka SyllabusHacker RanjanPas encore d'évaluation
- Snap-Tite75 Series-Catalog 3800 - SectionBDocument3 pagesSnap-Tite75 Series-Catalog 3800 - SectionBfrancis_15inPas encore d'évaluation
- The Logistics of Harmonious Co-LivingDocument73 pagesThe Logistics of Harmonious Co-LivingKripa SriramPas encore d'évaluation
- Kelompok CKD - Tugas Terapi Modalitas KeperawatanDocument14 pagesKelompok CKD - Tugas Terapi Modalitas KeperawatanWinda WidyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Critical and Creative ThinkingDocument26 pagesCritical and Creative Thinkingjoaquinricardo20153461Pas encore d'évaluation
- Metal, Metallurgy, Music, Husserl, Simondon Richard Pinhas: I Have Two Questions To Formulate Regarding The Last Session, Although WhatDocument13 pagesMetal, Metallurgy, Music, Husserl, Simondon Richard Pinhas: I Have Two Questions To Formulate Regarding The Last Session, Although WhatbluexpectroPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample CBAP Elicitation Scenario Based Questions Set 01Document31 pagesSample CBAP Elicitation Scenario Based Questions Set 01Rubab Javaid100% (1)
- English Action Plan 2023-2024Document5 pagesEnglish Action Plan 2023-2024Gina DaligdigPas encore d'évaluation
- NAAC 10.12.1888888 NewDocument48 pagesNAAC 10.12.1888888 Newచిమ్ముల సందీప్ రెడ్డిPas encore d'évaluation
- Maximus MHX DatasheetDocument5 pagesMaximus MHX Datasheetjulya julyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk LogDocument1 pageRisk LogOzu HedwigPas encore d'évaluation
- Tridium Europe DatasheetDocument2 pagesTridium Europe DatasheetHoàngTrầnPas encore d'évaluation
- TrapsDocument11 pagesTrapsAmandeep AroraPas encore d'évaluation
- Iphone 14 Pro Max Inspired Preset by Rey Dhen - XMPDocument3 pagesIphone 14 Pro Max Inspired Preset by Rey Dhen - XMPRizkia Raisa SafitriPas encore d'évaluation
- Problems 1Document2 pagesProblems 1Andoy Don M.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nguyen Ngoc-Phu's ResumeDocument2 pagesNguyen Ngoc-Phu's ResumeNgoc Phu NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Norm TMT PDFDocument12 pagesNorm TMT PDFGustavoPas encore d'évaluation
- Session Outline Template - English - 1 W5ADocument2 pagesSession Outline Template - English - 1 W5ARakhshanda FawadPas encore d'évaluation
- Normal DistributionDocument23 pagesNormal Distributionlemuel sardualPas encore d'évaluation
- Remote Sensing: Carbon Stocks, Species Diversity and Their Spatial Relationships in The Yucatán Peninsula, MexicoDocument18 pagesRemote Sensing: Carbon Stocks, Species Diversity and Their Spatial Relationships in The Yucatán Peninsula, MexicoSara EspinozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistema A-101 LVSDocument4 pagesSistema A-101 LVSAdministrador AngloPas encore d'évaluation
- Configuration Diagrams: Group 80ADocument24 pagesConfiguration Diagrams: Group 80ASaHdo AbdelHamid100% (1)
- Overview of Risk Based Audit ProcessDocument17 pagesOverview of Risk Based Audit ProcessAira Nhaira Mecate100% (1)
- Metascope An/Pas-6 (5855-790-6197) : Technical ManualDocument38 pagesMetascope An/Pas-6 (5855-790-6197) : Technical ManualDens VillaPas encore d'évaluation
- C1 L2D Quadratic FormulaDocument3 pagesC1 L2D Quadratic FormulaJo-Amver Valera ManzanoPas encore d'évaluation