Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Role of Steroids in Otolaryngology
Transféré par
Mohammed Sahib0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
28 vues15 pagesbook
Titre original
Steroids Ent
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
ODP, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentbook
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme ODP, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
28 vues15 pagesRole of Steroids in Otolaryngology
Transféré par
Mohammed Sahibbook
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme ODP, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 15
Role of Steroids in
otolaryngology
Dr T
Balasubramanian
Introduction
Corticosteroids are small lipophilic molecules
These molecules readily diffuse across cell
membrane into the cytoplasm
Inside the cytoplasm these molecules bind to the
corticosteroid receptors present there.
The steroid-receptor complex acts on transcription
factors
Action of steroid-receptor complex
This activated complex acts on transcription proteins
found inside the cytoplasm
Causes a reduction in the amount of inflammatory
cytokines secreted by the cell
Reduces the cells response to inflammation
Due to this complex mechanism of action there is a
time delay between the administration of the drug
and its clinical activity
Time delay of hours is common
Intravenous steroids
!seful during emergencies
"ne hour is gained when the drug is administered
intravenously
Drugs with minimal mineralocorticoid effect is
preferred
#ethylprednisolone $ Dexamethasone are preferred
as intravenous steroids
Oral steroids
!sed in patients who need long term administration
of the drug
%rednisolone is preferred to prednisone &prodrug'
%rednisone needs to be metabolised in the liver into
its active metabolites
Dexamethasone is the most potent oral steroid with
very negligible mineralocorticoid effect
Depo injections - IM
#ethyl prednisolone acetate is commonly used
Its effect on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis
lasts for weeks
!sually administered once in weeks
intramuscularly
#inimum plasma concentration after depo in(ection
lasts for -) weeks
Intranasal steroids
Intranasally adeministered steroid should be
lipophilic
*irst pass metabolism is avoided
+ery low dose is enough for local effect , reduced
systemic toxicity
"n administration -./ of the drug stays in the non
ciliated anterior part of the nose while the other -./
is in the posterior ciliated columnar portion of the
nasal cavity
Intranasal steroid (contd)
*luticasone propionate commonly used. 0ighly
lipophilic and has a large tissue distribution volume
1eclamethasone dipropionate $ budesonide are less
lipophilic and hence are rapidly absorbed into the
circulation when applied as topical spray
2pray administered in a3ueous forms are better than
aerosols.
Topical application is effective on itching and
snee4ing
2ystemic application is better for blockage $ anosmia
Nasal topical steroids indications
5llergic rhinitis
+asomotor rhinitis
6asal polyposis
#anagement of rhinitis medicamentosa
Idiopathic rhinitis
Systemic steroids
"ral
%arenteral
Depo &intramuscular'
Systemic steroids indications
5ngioneurotic oedema
5cute allergic rhinitis
Drug anaphylaxis
5cute sensorineural hearing loss &sudden deafness'
Treatment of acute hyposmia $ anosmia
5cute stridor before tracheostomy
5cute epiglottitis
Croup
Systemic steroids indications (contd)
"titis externa , to reduce external canal
inflammatory oedema
1ells palsy
6asal sarcoidosis
7egners granulomatosis
Thankyou
Steroid ear drops
!sed to treat ec4ematous conditions of the skin
lining fo external canal
!sed in the treatment of myringitis granulosa
Can be used to reduce middle ear mucosal oedema
in active middle ear infections with central
perforation
8ong term use can cause atrophy of the skin lining
of the external ear canal
Intranasal steroid (contd)
Topical steroids when used on hyper reactive nose
can cause increased snee4ing
Reassurance is a must and the drug should not be
stopped
Dry nasal mucosa $ crusts $ blood stained discharge
seen in patients on long term nasal steroid therapy
%rolonged usage may cause increased risk of
cataract and osteoporosis
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- NDDSDocument17 pagesNDDSsomesh chandraPas encore d'évaluation
- AnticholinergicsDocument33 pagesAnticholinergicspramod bhaleraoPas encore d'évaluation
- Adrenal Cortical SteroidsDocument17 pagesAdrenal Cortical SteroidsSri RamPas encore d'évaluation
- Cholinergic Antagonists: DR - Ch. Shanmukha Sai RaghavDocument12 pagesCholinergic Antagonists: DR - Ch. Shanmukha Sai RaghavShanmukh SaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Book ReadingDocument37 pagesBook Reading東廣謀Pas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency Tray PesentationDocument14 pagesEmergency Tray Pesentationgaladimawa2002Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pharma-Respiratory DrugsDocument56 pagesPharma-Respiratory DrugsZainab ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- Corticosteroids: Ghadi Mahmoud Elbarghathi Roll Number: 1950 5 Year 2021-2022Document26 pagesCorticosteroids: Ghadi Mahmoud Elbarghathi Roll Number: 1950 5 Year 2021-2022Ghadi ElbarghathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ophthalmic PreparationsDocument41 pagesOphthalmic PreparationsMuhammad TalhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cough: PHR Sangita ShakyaDocument21 pagesCough: PHR Sangita ShakyaCurex QAPas encore d'évaluation
- BNS 200 Drugs and The EyeDocument36 pagesBNS 200 Drugs and The EyeAnthony MoepengPas encore d'évaluation
- Asthma COPD DrugsDocument63 pagesAsthma COPD DrugsSimbarashe KanyeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Parasympathomimetic DrugsDocument156 pagesParasympathomimetic Drugsjunaid imranPas encore d'évaluation
- By Duy Thai, 1997: Pharmacology Semester 1 Page 1 of 4Document4 pagesBy Duy Thai, 1997: Pharmacology Semester 1 Page 1 of 4ravi2like100% (2)
- Analgesic constant rate infusions in dogs and catsDocument7 pagesAnalgesic constant rate infusions in dogs and catsOlga Lucia Duque QuijanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs Used in Critica Care SettingDocument54 pagesDrugs Used in Critica Care SettingChandan KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Cholinergic Antagonists: Prepared by: Sevan Mahmod 07512491694 يسيردتلا رجفلا دهعمDocument42 pagesCholinergic Antagonists: Prepared by: Sevan Mahmod 07512491694 يسيردتلا رجفلا دهعمAhmed MohamadPas encore d'évaluation
- Local AnesthesiaDocument63 pagesLocal AnesthesiaReda IsmaeelPas encore d'évaluation
- Top 5 Corticosteroids For Use in Emergency SettingsDocument4 pagesTop 5 Corticosteroids For Use in Emergency SettingsIulian Cătălin GrămadăPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Surgery & Pain Managment 13-14Document175 pagesOral Surgery & Pain Managment 13-14Priya SargunanPas encore d'évaluation
- Corticosteroid: Saut Samuel Simamora Department Ophthalmology Diponegoro University-Kariadi HospitalDocument21 pagesCorticosteroid: Saut Samuel Simamora Department Ophthalmology Diponegoro University-Kariadi HospitalSania NadianisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Routes of Drug AdministrationDocument39 pagesRoutes of Drug AdministrationAditya AdhikariPas encore d'évaluation
- Nitrofurantoin: Tejal Khade Assistant Professor KGRDCP & RiDocument10 pagesNitrofurantoin: Tejal Khade Assistant Professor KGRDCP & RiAkshada bhangrePas encore d'évaluation
- VACDocument39 pagesVACkarthikaPas encore d'évaluation
- AnesthesiaDocument6 pagesAnesthesiaSamyuktha NatarajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs Used in Respiratory DisordersDocument137 pagesDrugs Used in Respiratory DisordersAntonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Carbamate PoisoningDocument18 pagesCarbamate PoisoningJulie Ann TrinidadPas encore d'évaluation
- Crash Cart PresentationDocument22 pagesCrash Cart PresentationGLADYSHERBA.SPas encore d'évaluation
- Systemic Anti-Infl Ammatory AgentsDocument5 pagesSystemic Anti-Infl Ammatory Agentsbebek sakitPas encore d'évaluation
- 09 Ocular Adverse EffectsDocument14 pages09 Ocular Adverse EffectsJhonatha MoránPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory Stimulant and Nesal DecongestantDocument22 pagesRespiratory Stimulant and Nesal DecongestantAyesha AlamPas encore d'évaluation
- Speaker: DR Srikanth AlladiDocument71 pagesSpeaker: DR Srikanth AlladisrikanthalladiPas encore d'évaluation
- Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis: Intranasal Corticosteroids as First LineDocument21 pagesTreatment of Allergic Rhinitis: Intranasal Corticosteroids as First LineLee Ji MinPas encore d'évaluation
- Ocular Pharmacology PDFDocument54 pagesOcular Pharmacology PDFbenny christantoPas encore d'évaluation
- AnaesthesiaDocument69 pagesAnaesthesiahitusajnani02Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes: Introduction To Ocular Pharmacology, Ocular Route of Drug Administration, Chemotherapy, Antibiotics, Antiviral and Antifungal DrugsDocument8 pagesLecture Notes: Introduction To Ocular Pharmacology, Ocular Route of Drug Administration, Chemotherapy, Antibiotics, Antiviral and Antifungal Drugskûrñï såñskrùthîPas encore d'évaluation
- AnesthesiaDocument12 pagesAnesthesiaعلي الاسديPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology Intravenous Anesthetic Agents DissociativesDocument13 pagesPharmacology Intravenous Anesthetic Agents DissociativesInnocent MwilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology of Etimodate - 084220Document27 pagesPharmacology of Etimodate - 084220Danielle MadePas encore d'évaluation
- Asthma FinalDocument31 pagesAsthma FinalGideon Antwi BoadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Antifungal Agents: Laboratorium Farmakologi Dan Terapi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Jenderal SoedirmanDocument51 pagesAntifungal Agents: Laboratorium Farmakologi Dan Terapi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Jenderal SoedirmanprofPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory Stimulants, Bronchial Dilators-Dr - Jibachha Sah, M.V.SC, LecturerDocument23 pagesRespiratory Stimulants, Bronchial Dilators-Dr - Jibachha Sah, M.V.SC, Lecturerjibachha sahPas encore d'évaluation
- Deflazacort Training Manual OverviewDocument10 pagesDeflazacort Training Manual Overviewanupdr_cPas encore d'évaluation
- Glaucoma & ConjuctivitisDocument25 pagesGlaucoma & ConjuctivitisArifaa NovianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Adrenocortical AgentsDocument23 pagesAdrenocortical AgentsGlaiza Joves EncarnacionPas encore d'évaluation
- Local Anesthesia and Concious SedationDocument43 pagesLocal Anesthesia and Concious Sedationpawi18Pas encore d'évaluation
- SerotoninsDocument14 pagesSerotoninsRaja AffanPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument95 pagesUntitledMohan KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- THALIDOMIDE: A WONDER DRUG WITH A TRAGIC PASTDocument48 pagesTHALIDOMIDE: A WONDER DRUG WITH A TRAGIC PASTSiddharth DashPas encore d'évaluation
- Cholinergic System Model Questions & AnswersDocument45 pagesCholinergic System Model Questions & AnswersDr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHM100% (5)
- Routes of Drug AdministrationDocument34 pagesRoutes of Drug AdministrationDesmalinda Ramadhani100% (1)
- Routes of Drug AdministrationDocument34 pagesRoutes of Drug AdministrationNa SyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anticolinergic Drugs: Mechanisms and UsesDocument26 pagesAnticolinergic Drugs: Mechanisms and UsesHuzaifa KhaleeqPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs Used in EmergencyDocument7 pagesDrugs Used in EmergencyAzza DianPas encore d'évaluation
- Otiflox New Ear DropsDocument9 pagesOtiflox New Ear DropsShreyas ModiPas encore d'évaluation
- 16 Drugs Affecting RespiDocument3 pages16 Drugs Affecting RespiAdriwayne Francis GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Steroids in Dentistry: Presented By-Shibani Sarangi Postgraduate Iind Year (Dept of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery)Document67 pagesSteroids in Dentistry: Presented By-Shibani Sarangi Postgraduate Iind Year (Dept of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery)Max FaxPas encore d'évaluation
- Differentiating Anesthesia Equipment: Identify and Understand Anesthesia Equipment in 1 Hour (Including the most popular manufacturers and suppliers to buy Anesthesia Equipment)D'EverandDifferentiating Anesthesia Equipment: Identify and Understand Anesthesia Equipment in 1 Hour (Including the most popular manufacturers and suppliers to buy Anesthesia Equipment)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Local Anesthesia Made Easy: Complete Guide on How to make your Local Anesthetic Procedure a Success (Including a List of Anesthetic Equipment and their Uses)D'EverandLocal Anesthesia Made Easy: Complete Guide on How to make your Local Anesthetic Procedure a Success (Including a List of Anesthetic Equipment and their Uses)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ossicular Recon Slides 090629Document89 pagesOssicular Recon Slides 090629Mohammed Sahib100% (1)
- 39-Vocal Fold Injection Via MicrolaryngosDocument8 pages39-Vocal Fold Injection Via MicrolaryngosMohammed SahibPas encore d'évaluation
- VC Palsy TreatmentDocument6 pagesVC Palsy TreatmentMohammed SahibPas encore d'évaluation
- Disorders of Speech and LanguageDocument23 pagesDisorders of Speech and LanguageMohammed SahibPas encore d'évaluation
- TNM Staging For H&NDocument30 pagesTNM Staging For H&NkiwiamoghPas encore d'évaluation
- Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve MONITORINGDocument4 pagesRecurrent Laryngeal Nerve MONITORINGMohammed SahibPas encore d'évaluation
- Biofilms in ENT: Understanding Chronic & Recurrent InfectionsDocument10 pagesBiofilms in ENT: Understanding Chronic & Recurrent InfectionsMohammed SahibPas encore d'évaluation
- Sleep Apnea Pics 2012 0415Document44 pagesSleep Apnea Pics 2012 0415Mohammed SahibPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Exercise On HTNDocument4 pagesEffect of Exercise On HTNMohammed SahibPas encore d'évaluation
- Angioedema 2012 0425Document12 pagesAngioedema 2012 0425Mohammed SahibPas encore d'évaluation
- Integ - 2Document12 pagesInteg - 2segotierjudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Bhasa InggrisDocument23 pagesBhasa InggrisrinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Profile For Females: Conners' Parent Rating Scale-Revised (S)Document2 pagesProfile For Females: Conners' Parent Rating Scale-Revised (S)Claudya Abarca50% (8)
- Abnormal Psychology V2Document343 pagesAbnormal Psychology V2Bianca Dennise Villar Guingab100% (2)
- Alberta Stroke Program Early CT ScoreDocument15 pagesAlberta Stroke Program Early CT ScoreRainickBrenhizarNavarroPas encore d'évaluation
- High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin at Presentation To Rule Out Myocardial Infarction (Historic)Document20 pagesHigh-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin at Presentation To Rule Out Myocardial Infarction (Historic)DenisseRangelPas encore d'évaluation
- Israeli Scientists Claim To Reverse Aging ProcessDocument2 pagesIsraeli Scientists Claim To Reverse Aging ProcessKarina PolikarpovaPas encore d'évaluation
- FAMILY NURSING CARE PLAN FOR THE DALIPE FAMILYDocument22 pagesFAMILY NURSING CARE PLAN FOR THE DALIPE FAMILYAdrienne Nicole PaneloPas encore d'évaluation
- IWGDF Guidelines 2019 PDFDocument194 pagesIWGDF Guidelines 2019 PDFMara100% (2)
- 62 year old female patient hip fracture and death during surgery after late night fallDocument3 pages62 year old female patient hip fracture and death during surgery after late night fallPatient Safety MyPas encore d'évaluation
- Trauma Guidlines Primary Dentition IADT 2020Document18 pagesTrauma Guidlines Primary Dentition IADT 2020Carlos MikaelPas encore d'évaluation
- Literature ReviewDocument3 pagesLiterature Reviewapi-509948413Pas encore d'évaluation
- Laporan Kasus Rehabilitasi Medik Pada Pasien Dengan Cervical DystoniaDocument6 pagesLaporan Kasus Rehabilitasi Medik Pada Pasien Dengan Cervical DystoniaDwi Putri SariPas encore d'évaluation
- Maintenance Fluid TherapyDocument22 pagesMaintenance Fluid TherapyJonathan IngramPas encore d'évaluation
- (FINAL) Prof. Dr. Dr. Bambang Budi Siswanto, SPJP (K) - Understanding HF in IndonesiaDocument32 pages(FINAL) Prof. Dr. Dr. Bambang Budi Siswanto, SPJP (K) - Understanding HF in IndonesiaTicksPas encore d'évaluation
- Join Radiotherapy Physics TeamDocument2 pagesJoin Radiotherapy Physics TeamAlina RogojanuPas encore d'évaluation
- Core Topics in Internal MedicineDocument4 pagesCore Topics in Internal MedicineKristina Anne CoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chakra Var Thy 2018Document15 pagesChakra Var Thy 2018Vlady78Pas encore d'évaluation
- ACUTE DIARRHEAL SYNDROME CASE FORMDocument2 pagesACUTE DIARRHEAL SYNDROME CASE FORMmaria putriPas encore d'évaluation
- Simplexa C CMV Mol2250 Ifu - enDocument17 pagesSimplexa C CMV Mol2250 Ifu - enandi takwaPas encore d'évaluation
- Central Nervous System Anesthetics ExplainedDocument59 pagesCentral Nervous System Anesthetics ExplainedbrihaspathiacademyPas encore d'évaluation
- Babesia Species: - Order: Piroplasmida - Family: Babesiidae - Medically Important SpeciesDocument7 pagesBabesia Species: - Order: Piroplasmida - Family: Babesiidae - Medically Important SpeciesMegbaru100% (1)
- Crossfit Gym Membership Contract and Receipt TemplateDocument6 pagesCrossfit Gym Membership Contract and Receipt Templatemohit jPas encore d'évaluation
- Health Grades 7 LAMP4th QuarterDocument2 pagesHealth Grades 7 LAMP4th QuarterLaarni Quindoyos AntonioPas encore d'évaluation
- Regional Anesthesia Head Neck Slides 060524Document84 pagesRegional Anesthesia Head Neck Slides 060524srisaivimalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology of The Male GUTDocument108 pagesPathology of The Male GUTHoque Mohammed Newaz ShorifulPas encore d'évaluation
- Choking: What To Do If A Child Is Choking?Document3 pagesChoking: What To Do If A Child Is Choking?Jamieson TobeyPas encore d'évaluation
- FREE RANGE CHICKEN AND GOAT PRODUCTION GUIDEDocument78 pagesFREE RANGE CHICKEN AND GOAT PRODUCTION GUIDEMA DapPas encore d'évaluation
- Ukuran Hepar Lien Pada AnakDocument6 pagesUkuran Hepar Lien Pada Anakivan ekoPas encore d'évaluation
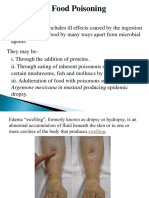
- Food Poisoning and IntoxicationsDocument26 pagesFood Poisoning and IntoxicationslakshmijayasriPas encore d'évaluation