Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
The Passive
Transféré par
mariepalm0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
85 vues3 pagesE.g.: the police arrest thieves every week. Somebody cleans the room every day. Use be + past participle to form the passive.
Description originale:
Titre original
The passive.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentE.g.: the police arrest thieves every week. Somebody cleans the room every day. Use be + past participle to form the passive.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
85 vues3 pagesThe Passive
Transféré par
mariepalmE.g.: the police arrest thieves every week. Somebody cleans the room every day. Use be + past participle to form the passive.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
The passive
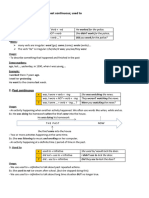
1 Forms: use be + past participle to form the passive
Active Passive
Present Simple (verb in the Present
Simple)
e.g.: * The police arrest thieves every week.
*Somebody cleans the room every day.
Present Simple (am/is/are + past
participle)
e.g.: * Thieves are arrested by the police
every week.
* The room is cleaned every day.
Present continuous (am/is/are + verb
ing)
e.g.: * The police are arresting a thief at the
moment.
* Somebody is cleaning the room at the
moment.
Present continuous (am/is/are being +
past participle)
e.g.: * A thief is being arrested by the police
at the moment.
* The room is being cleaned at the
moment.
Past Simple (verb in the Past Simple)
e.g.: * The police arrested a thief last week.
* Somebody cleaned the room
yesterday.
Past Simple (was/were + past participle)
e.g.: * A thief was arrested by the police last
week.
* The room was cleaned yesterday.
Past continuous (was/were + verb ing)
e.g.: * The police were arresting a thief when
I arrived in the shop.
* Somebody was cleaning the room
when I arrived.
Past continuous (was/were being + past
participle)
e.g.: * A thief was being arrested by the
police when I arrived in the shop.
* The room was being cleaned when I
arrived.
Present Perfect Simple (have/has + past
participle)
e.g.: * The police have just arrested a thief.
* The room looks nice. Somebody has
cleaned it.
Present Perfect Simple (have/has been +
past participle)
e.g.: * A thief has just been arrested by the
police.
* The room looks nice. It has been
cleaned.
Past Perfect Simple (had + past participle)
e.g.: * There was a crowd in front of the
shop. The police had arrested a thief.
* The room looked nice. Somebody had
cleaned it.
Past Perfect Simple (had been + past
participle)
e.g.: * There was a crowd in front of the
shop. A thief had been arrested by the police.
* The room looked nice. It had been
cleaned.
Future (will/shall + infinitive or am/is/are
going to + infinitive)
e.g.: * The police are going to arrest the thief.
* Somebody will clean the room later.
Future (will/shall be + past participle or
am/is/are going to be + past participle)
e.g.: * The thief is going to be arrested by the
police.
* The room will be cleaned later.
Modals (can/could/may/might/must/ have
to/should + infinitive)
e.g.: * The police have to arrest the thief.
* Somebody can clean the room.
* The situation is serious. We must do
something.
* You should call the doctor.
* The music was very loud. You could
hear it from a long way away.
Modals (can/could/may/might/must/ have
to/should be + past participle)
e.g.: * The thief has to be arrested by the
police.
* The room can be cleaned.
* The situation is serious. Something
must be done.
* The doctor should be called.
* The music was very loud. It could be
heard from a long way away.
Infinitives
Be + past participle
e.g.: * Please go away. I want to be left alone.
* The meat is ready to be cooked.
Present participles
Being + past participle
e.g.: * I remember being taken to the zoo when I was a child. (= I remember somebody
taking me to the zoo when I was a child.)
* Steve hates being kept waiting. (= He hates people keeping him waiting.)
* I managed to climb over the wall without being seen (= without anybody seeing me)
* I dont like being told what to do. (= I dont like people telling me what to do.)
2 USE
1. When we use an active verb, we say what the subject does.
e.g.: - My grandfather was a builder. He built this house in 1935.
- Its a big company. It employs two hundred people.
When we use a passive verb, we say what happens to the subject.
e.g.: - This house is quite old. It was built in 1935.
- Two hundred people are employed by the company.
2. When we use the passive, who or what causes the action is often unknown or
unimportant.
e.g.: - A lot of money was stolen in the robbery. (somebody stole it, but we dont know
who)
- Is this room cleaned every day? (its not important who)
If we want to say who does or what causes the action, we use by.
e.g.: - This house was built by my grandfather.
- Two hundred people are employed by the company.
3. Some verbs can have two objects, for example give:
e.g.: - Somebody gave the police the information. (= Somebody gave the information
to the police.)
So it is possible to make two passive sentences:
The police were given the information.
The information was given to the police.
Other verbs which can have two objects are: ask, offer, pay, show, teach, tell.
When we use these verbs in the passive, most often we begin with the person.
e.g.: - I was offered the job, but I refused it. (= they offered me the job)
- You will be given plenty of time to decide. (= we will give you plenty of time to
decide)
- Have you been shown the new machine? (= Has anybody shown you the new
machine?)
4. I was born. (not I am born.)
e.g.: - I was born in Chicago.
- Where were you born?
But: How many babies are born every day?
5. Get
You can use get instead of be in the passive (informal spoken English).
e.g.: - There was a fight at the party, but nobody got hurt. (= nobody was hurt)
- I dont often get invited to parties. (= Im not often invited)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Master English in 12 Topics.: Master English in 12 Topics, #1D'EverandMaster English in 12 Topics.: Master English in 12 Topics, #1Évaluation : 2.5 sur 5 étoiles2.5/5 (5)
- The Complete English Master: 36 Topics for Fluency: Master English in 12 Topics, #4D'EverandThe Complete English Master: 36 Topics for Fluency: Master English in 12 Topics, #4Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (4)
- Active & PassiveDocument9 pagesActive & PassiveCes Anne SalamanezPas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar2: 5.past Perfect Continuous: S + Had + Been + V-IngDocument4 pagesGrammar2: 5.past Perfect Continuous: S + Had + Been + V-Ingtranbichngan90Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Receiver of The ActionDocument4 pagesThe Receiver of The ActionJaavi Ravanal SandovalPas encore d'évaluation
- Other Commonly Used English Structure in BroadcastDocument24 pagesOther Commonly Used English Structure in BroadcastAviolita KartikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Voice TheoryDocument5 pagesPassive Voice TheoryaidfosPas encore d'évaluation
- PassiveDocument16 pagesPassiveByron PacaizaPas encore d'évaluation
- TensesDocument28 pagesTensesKalai ShanPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Voice - Grammar ReferenceDocument3 pagesPassive Voice - Grammar ReferencehoroaPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Past TenseDocument9 pagesSimple Past TenseSandra KundingPas encore d'évaluation
- L2 PassiveDocument2 pagesL2 PassivePatricia López RasteuPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Past Past ContinuousDocument2 pagesSimple Past Past Continuoushuong ngo thePas encore d'évaluation
- Passive VoiceDocument8 pagesPassive VoiceJoaquin ZarcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Voice-April 2020Document5 pagesPassive Voice-April 2020Daniela LozadaPas encore d'évaluation
- La Voix Passive en Anglais - ExplicationDocument2 pagesLa Voix Passive en Anglais - Explicationmayarandria2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Past TenseDocument7 pagesSimple Past TenseSanteni RamPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Voice PresentationDocument15 pagesPassive Voice PresentationRemy Artha Sari NaibahoPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Past Tens1Document5 pagesSimple Past Tens1Sandra KundingPas encore d'évaluation
- The Active and The Passive: TenseDocument4 pagesThe Active and The Passive: TenseratatecheraPas encore d'évaluation
- Les 7 Unit 15 Grammar Verb Forms 6 Had Worked, Was Working (Student Version For HUbl)Document15 pagesLes 7 Unit 15 Grammar Verb Forms 6 Had Worked, Was Working (Student Version For HUbl)MervePas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 Passive VoiceDocument16 pagesUnit 3 Passive Voicemiriam_bello_2950% (2)
- IE Grammar - Past Simple 1Document2 pagesIE Grammar - Past Simple 1cong chuot 3Pas encore d'évaluation
- PassivesDocument10 pagesPassivesSis MKesPas encore d'évaluation
- The Passive, Causative Constructions, Personal and Impersonal Passive Constructions.Document4 pagesThe Passive, Causative Constructions, Personal and Impersonal Passive Constructions.Hugo AguiarPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive and Active Voice-ConceptDocument30 pagesPassive and Active Voice-Concepthappyindriyono2402Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 4: School Education System Part E: Language Focus: Wednesday 27th, 2021Document5 pagesUnit 4: School Education System Part E: Language Focus: Wednesday 27th, 202116Kim Ngân PhạmPas encore d'évaluation
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument13 pagesActive and Passive VoiceRizky HasibuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar Unit 2Document4 pagesGrammar Unit 2Huỳnh NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- P4 Passive VoiceDocument24 pagesP4 Passive VoiceNuha HanifahPas encore d'évaluation
- General Information: PassiveDocument2 pagesGeneral Information: PassiveSandraGMPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive VoiceDocument13 pagesPassive VoiceSergiu SecrieruPas encore d'évaluation
- Cách sử dụng: Kể lại sự việc trong quá khứ. Adv: yesterday, last, ago... Ex: I did not do my homework yesterdayDocument8 pages Cách sử dụng: Kể lại sự việc trong quá khứ. Adv: yesterday, last, ago... Ex: I did not do my homework yesterdayHà Thu VânPas encore d'évaluation
- Present SimpDocument12 pagesPresent SimpJasmin UbaldoPas encore d'évaluation
- 11S2 ENG Ebook P1 Passive Voice & CausativeDocument12 pages11S2 ENG Ebook P1 Passive Voice & CausativeFathimah AqiylaPas encore d'évaluation
- PASSIVE (Edilgen) & CAUSITIVE (Ettirgen) : Tarık İnce Dilko 1Document3 pagesPASSIVE (Edilgen) & CAUSITIVE (Ettirgen) : Tarık İnce Dilko 1Yavuz Selim ArslanPas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar ReferenceDocument16 pagesGrammar Referenceluciacayetano07Pas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Form (1) This Test Comes From - The Site To Learn English (Test N°5733)Document2 pagesPassive Form (1) This Test Comes From - The Site To Learn English (Test N°5733)Maria Rajendran MPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge Grammar For IELTSDocument9 pagesCambridge Grammar For IELTSNguyễn Anh ThưPas encore d'évaluation
- 5A Grammar ExplainationDocument7 pages5A Grammar Explainationeng.hasan.91777Pas encore d'évaluation
- English 7 Past and Past Perfect PowerpointDocument16 pagesEnglish 7 Past and Past Perfect PowerpointRhea Mae TorresPas encore d'évaluation
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument13 pagesActive and Passive VoiceRizky HasibuanPas encore d'évaluation
- E1 - The Passive Voice - CDocument13 pagesE1 - The Passive Voice - CDarcy DeeaPas encore d'évaluation
- Минулий тривалий час (2 ЗАНЯТТЯ)Document18 pagesМинулий тривалий час (2 ЗАНЯТТЯ)JuliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Past Tenses 1Document47 pagesPast Tenses 1Ичинноров МягмарсүрэнPas encore d'évaluation
- Simplepastvscontinuous 131210151932 Phpapp01Document15 pagesSimplepastvscontinuous 131210151932 Phpapp01api-317398821Pas encore d'évaluation
- Self-Study 3Document11 pagesSelf-Study 3Анна МарияPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive VoiceDocument9 pagesPassive VoiceLuísa Mestre100% (1)
- Bahasa Inggris - Materi Presentasi ''Simple Present + Past Tense''Document14 pagesBahasa Inggris - Materi Presentasi ''Simple Present + Past Tense''Tyas Rahmaditia100% (3)
- Passive VoiceDocument9 pagesPassive VoiceGeorgia KleoudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre Inter Me DireDocument3 pagesPre Inter Me Diresim_opsPas encore d'évaluation
- Tense Person, Number: Is Spoke DidDocument4 pagesTense Person, Number: Is Spoke DidAyu NabillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive VoiceDocument11 pagesPassive VoiceJuan DiegoPas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar - Passive Voice Present PerfectDocument23 pagesGrammar - Passive Voice Present PerfectRahma LuttifahPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Voice: Tense TranformationsDocument6 pagesPassive Voice: Tense TranformationsStephy PunctPas encore d'évaluation
- Somebody Will Clean The Room LaterDocument6 pagesSomebody Will Clean The Room LaterBrenda Naranjo MorenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive VoiceDocument4 pagesPassive Voicetogol artPas encore d'évaluation
- Stative VerbsDocument4 pagesStative Verbsromandon waePas encore d'évaluation
- E1 - The Passive Voice - CDocument13 pagesE1 - The Passive Voice - CDarcy DeeaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 PassiveDocument7 pagesUnit 2 PassiveVăn Đại - BKHNPas encore d'évaluation
- B1 ProdE 2 PresentSimple Continuous Marie2018Document4 pagesB1 ProdE 2 PresentSimple Continuous Marie2018mariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- Poster 6Document1 pagePoster 6Ashish JosephPas encore d'évaluation
- Reading Methodology 2LG - StudentsDocument14 pagesReading Methodology 2LG - StudentsmariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- Linking Words AN4LM2 5 Themes a-C-P BisDocument2 pagesLinking Words AN4LM2 5 Themes a-C-P BismariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- Asking Questions in ENglish - GamesDocument6 pagesAsking Questions in ENglish - GamesmariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb PatternsDocument10 pagesVerb PatternsmariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- Teaching Listening MarieDocument13 pagesTeaching Listening MariemariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- Teaching Listening MarieDocument13 pagesTeaching Listening MariemariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Express The FuturDocument3 pagesHow To Express The FuturmariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- Adjectives Comparatives SuperlativesDocument1 pageAdjectives Comparatives SuperlativesmariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- B2 ReportedSpeechDocument15 pagesB2 ReportedSpeechmariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- Islcollective The Messy Room There Be Prepositions To Be 155514d4be1a75b91d3 21535558Document3 pagesIslcollective The Messy Room There Be Prepositions To Be 155514d4be1a75b91d3 21535558Ezzy ArandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus Extra Reading BAC3 Emu 2017 2018Document35 pagesSyllabus Extra Reading BAC3 Emu 2017 2018mariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- The PluralDocument1 pageThe PluralmariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- Conditionals - À Compléter Par ÉlèvesDocument1 pageConditionals - À Compléter Par ÉlèvesmariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- Adjective Lesson PlanDocument1 pageAdjective Lesson PlanmariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- Past PresentperfectDocument5 pagesPast PresentperfectmariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- Past SimpleDocument1 pagePast SimplemariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- Asking and Giving DirectionsDocument2 pagesAsking and Giving DirectionsmariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- Linking WordsDocument2 pagesLinking WordsmariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercises - Some or Any: Are There Any Chairs in Your Kitchen? Yes, There Are.Document2 pagesExercises - Some or Any: Are There Any Chairs in Your Kitchen? Yes, There Are.mariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- Irregular Verbs - Mpa 092012Document2 pagesIrregular Verbs - Mpa 092012mariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- Useful Phrases For Discussions: 1. Asking About or For An OpinionDocument4 pagesUseful Phrases For Discussions: 1. Asking About or For An OpinionMercedes Jimenez Roman100% (1)
- Present Perfect Simple or Present Perfect Continous PDFDocument2 pagesPresent Perfect Simple or Present Perfect Continous PDFmariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- Business+Benchmark+Upper+Intermediate+SB+Wordlist+NEW+VERSION FRENCH CHECKED FINALDocument36 pagesBusiness+Benchmark+Upper+Intermediate+SB+Wordlist+NEW+VERSION FRENCH CHECKED FINALmariepalm100% (1)
- Business+Benchmark+Pre-Intermediate+Wordlist FRENCH CHECKED FINALDocument48 pagesBusiness+Benchmark+Pre-Intermediate+Wordlist FRENCH CHECKED FINALmariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- BB - Unit 8 Négo - ConditionalsDocument1 pageBB - Unit 8 Négo - ConditionalsmariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- BOWLING FOR COLUMBINE DiscussionDocument1 pageBOWLING FOR COLUMBINE DiscussionmariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- IRREGULAR VERBS - MPA 4èDocument2 pagesIRREGULAR VERBS - MPA 4èmariepalmPas encore d'évaluation
- WorldEnglishInstitute 1712257877897Document5 pagesWorldEnglishInstitute 1712257877897christlovelebienheureuxPas encore d'évaluation
- Rules of Concord by FreeManDocument10 pagesRules of Concord by FreeManChika JonesPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Error Exercise - Active and Passive VoiceDocument3 pagesCommon Error Exercise - Active and Passive VoiceDard TongPas encore d'évaluation
- G1 LM English Week 8 PDFDocument15 pagesG1 LM English Week 8 PDFdhePas encore d'évaluation
- Scripps National Spelling Bee List 2018-2019Document17 pagesScripps National Spelling Bee List 2018-2019Dilip Choudhary100% (1)
- A Study of Transfer Directions in Grammatical MetaphorDocument17 pagesA Study of Transfer Directions in Grammatical Metaphorwaseemhasan85Pas encore d'évaluation
- Adverbs Rules IIDocument2 pagesAdverbs Rules IIKarina MachadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pali GrammarDocument182 pagesPali GrammarJagadeesh Lakshmanan100% (1)
- Topic Vocabulary: Change: AdaptDocument14 pagesTopic Vocabulary: Change: AdaptBach Hua HuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Theory of PrepositionsDocument2 pagesLearning Theory of Prepositionskelas satuPas encore d'évaluation
- UAM English 9 4th QuarterDocument3 pagesUAM English 9 4th QuartermikkaellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bahasa Inggris. EkonomiDocument135 pagesBahasa Inggris. EkonomiYusra MeinizarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan AdverbsDocument13 pagesLesson Plan AdverbsZirome MaePas encore d'évaluation
- Picture 1: Additional ResourcesDocument3 pagesPicture 1: Additional ResourcesJulián VegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Prepare Level 1: 0 in The ClassroomDocument28 pagesPrepare Level 1: 0 in The ClassroomАЛЕКСАНДР ИВАНОВPas encore d'évaluation
- Spark 2.1 BLERINA SPARK 2Document38 pagesSpark 2.1 BLERINA SPARK 2isliPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Notes 6Document195 pagesLesson Notes 6Cami Barn StjarnannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ben Blackwell, Immortal Glory and The Problem of Death in RM 3,23Document24 pagesBen Blackwell, Immortal Glory and The Problem of Death in RM 3,23robert guimaraesPas encore d'évaluation
- Review of A Grammar of Domari PDFDocument7 pagesReview of A Grammar of Domari PDFulisePas encore d'évaluation
- Touchstone 2 Second EditionDocument164 pagesTouchstone 2 Second EditionCristian bermudez padilla80% (41)
- American Language Hub Starter WorkbookDocument82 pagesAmerican Language Hub Starter Workbookbillhorn7793Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ingles Tarea de La ViejaDocument9 pagesIngles Tarea de La ViejaGuillermoOsorioNoboaPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of SpeechDocument37 pagesParts of SpeechIsai Garcia FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 MS - 2nd Generation Sequence 2 Me, My Personality and Experiences - All Lessons by Khelil Moudjib Arrahmane 2018-2019-ConvertiDocument64 pages4 MS - 2nd Generation Sequence 2 Me, My Personality and Experiences - All Lessons by Khelil Moudjib Arrahmane 2018-2019-ConvertiZellagui SaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Iit Indore Cse SyllabusDocument199 pagesIit Indore Cse SyllabusVenuSrivatsavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Grammar I-I-armDocument6 pagesPractical Grammar I-I-armZara GalstyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Right On! 3 Teachers BookDocument441 pagesRight On! 3 Teachers BookLevan Medoshvili74% (27)
- Parts of SpeechDocument79 pagesParts of Speechjimmy jayPas encore d'évaluation
- Daily Language Week 18Document3 pagesDaily Language Week 18Shado Usama Ebrahem Abbas BadraPas encore d'évaluation
- MarinaDocument12 pagesMarinahalil_ajaPas encore d'évaluation