Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Online Voting System
Transféré par
Arihant Pawariya83%(6)83% ont trouvé ce document utile (6 votes)
4K vues37 pagesThis document describes an online voting system project report submitted by two students. The report includes an introduction describing the purpose and scope of the project, which is to develop an online platform to enable secure electronic voting from anywhere. It discusses the goals of reducing problems with the current voting system and increasing voter turnout. The technologies used include PHP and a database. The report later covers system design aspects such as use case diagrams, activity diagrams, class diagrams, and the database design. It also includes implementation details and screenshots of the user interface.
Description originale:
OVS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThis document describes an online voting system project report submitted by two students. The report includes an introduction describing the purpose and scope of the project, which is to develop an online platform to enable secure electronic voting from anywhere. It discusses the goals of reducing problems with the current voting system and increasing voter turnout. The technologies used include PHP and a database. The report later covers system design aspects such as use case diagrams, activity diagrams, class diagrams, and the database design. It also includes implementation details and screenshots of the user interface.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
83%(6)83% ont trouvé ce document utile (6 votes)
4K vues37 pagesOnline Voting System
Transféré par
Arihant PawariyaThis document describes an online voting system project report submitted by two students. The report includes an introduction describing the purpose and scope of the project, which is to develop an online platform to enable secure electronic voting from anywhere. It discusses the goals of reducing problems with the current voting system and increasing voter turnout. The technologies used include PHP and a database. The report later covers system design aspects such as use case diagrams, activity diagrams, class diagrams, and the database design. It also includes implementation details and screenshots of the user interface.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 37
1
Online Voting System
A PROJECT REPORT
Submitted by
ARIHANT (11BCE0071)
SAMEER SAH (11BCE0257)
I n partial fulfillment for the award of the degree
Of
BACHELOR OF TECHNOLOGY
IN
COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
VIT
U N I V E R S I T Y
(Est. u/s 3 of UGC Act 1956)
Vellore - 632 014, Tamil Nadu, India
VIT UNIVERSITY
SEPTEMBER 2014
2
VIT
U N I V E R S I T Y
(Estd. u/s 3 of UGC Act 1956)
Vellore - 632 014, Tamil Nadu, India
School of Computing Science & Engineering
BONAFIDE CERTIFICATE
This is to certify that the Mini Project entitled Online Voting System
submitted by Arihant (11BCE0071) and Sameer Sah (11BCE0257) to Vellore
Institute of Technology, Vellore in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the
award of the degree of B.TECH in Computer Science and Engineering is a
record of bonafide Mini Project undertaken by them under my supervision. This
project report has not been submitted and will not be submitted for the award of
any other degree or diploma in this institute or any other institute or university.
GOVINDA K.
SUPERVISOR
Senior Assistant Professor
Date: Date:
Internal Examiner (s) External Examiner (s)
3
ABSTRACT
The word vote means to choose from a list, to elect or to determine. The main
goal of voting (in a scenario involving the citizens of a given country) is to
come up with leaders of the peoples choice. The present system of casting
votes has resulted in a number of problems such as low percentage of voting,
late results, discomfort to old aged and handicapped people etc. Voting through
EVM has not been able to address these problems completely. To overcome
these, an attempt has been made to introduce an online platform specifically
designed for electronic voting that will enable people to vote securely from
anywhere without moving to a voting machine, all they need is a computer or
mobile and internet connection. This platform will provide the desired comfort
and security to the voters which will bypass the lengthy process which claims a
significant amount of money, time and energy of all concerned. This is a small
scale project for Online voting system. The basic idea is that the citizens of the
country can vote for the candidates during election in the online. It consists of
voter details, security system, status and exits. The administrator can enter the
name and password and generate the reports and can perform operation like add
citizens, search, delete the citizens in the database. In Online voting system we
can get the result of the election based on polling.
4
CHAPTER NO. TITLE PAGE NO.
ABSTRACT 3
LIST OF TABLES 6
LIST OF FIGURES 7
LIST OF SYMBOLS 8
1. INTRODUCTION 9
1.1 PURPOSE 10
1.2 SCOPE 10
1.3 PROBLEM STATEMENT 10
1.4 DESCRIPTION OF THE SYSTEM 11
1.4.1 PROPOSED SYSTEM 11
1.4.2 GOALS OF THE SYSTEM 12
1.4.3 TECHNOLOGIES USED 13
2. LITERATURE REVIEW 14
2.1 OLD METHODS OF VOTING 14
2.2 SECURITY ISSUES 15
2.3 CURRENT SYSTEM DRAWBACKS 15
2.4 SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS 16
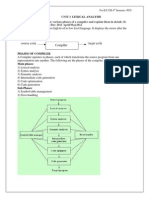
3. DESIGN
3.1 SOFTWARE REQUIREMENT SPECIFICATION 18
3.1.1 FUNCTIONAL REQUIREMENTS 18
3.1.2 NON-FUNCTIONAL REQUIREMENTS 18
3.2 SOFTWARE DESIGN 19
3.2.1 ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN 19
3.2.2 SYSTEM MODELS 20
3.2.2.1 CONTEXT MODEL 20
3.2.2.2 BEHAVOURIAL MODELS 20
3.2.2.3 STRUCTURAL MODELS 26
5
3.3 DATABSE DESIGN 30
4. IMPLEMENTATION 31
4.1 USER INTERFACE 31
5. CONCLUSION
6. REFERENCES
6
List of Tables
Table 1: Admin Table
Table 2: Voter Table
Table 3: Candidate Table
7
List of Figures
Figure 1: Architecture Diagram
Figure 2: Context Model Diagram
Figure 3, 3.1: Use Case Diagrams
Figure 4, 4.1, 4.2: Data Flow Diagrams
Figure 5, 5.1, 5.2, 5.3: Activity Diagram
Figure 6, 6.1, 6.2, 6.3: Class Diagrams
Figure 7: ER Diagram
Figure 8, 8.1: Sequence Diagram
8
List of Symbols, Abbreviations and Nomenclature
OVS Online Voting System
HTTP Hyper Text Markup Language
PHP
DBMS Database Management System
9
1. INTRODUCTION
The online voting system is the system that aims in reducing the complexity
and cost of the election process. Here the voter can vote in spite of his absence
in the particular locality. The administrators effort is much reduced by
checking the election status of all the localities individually forms a place and it
is easy for him to announce the election result. The administrator is the soul
controller of the online voting system in all process including refreshing the
votes, editing the voter details, creating new nominee and so on. Thus the online
voting system can reduce the cost and effort of election process.
In this voting system each voter will be provided with a specific voter-id and
a password through which access for the voting can be granted. If once the
access is granted for a voter-id then the access is denied for logging in till the
voting system is refreshed for the next election. Similarly the administrator will
be provided with a special id through which he can view the status of the
election.
Based on the id segregation between the voter and administrator is carried
out initially. If the user id is invalid then an error message will be displayed. If
the id entered is of type administrator then an information i.e., the election
status will be displayed which changes dynamically. Otherwise the voter
information will be displayed which changes dynamically depending on the
changes made which will proceed him to the next level in which he can cast his
vote and it is updated automatically.
The advantages of the online voting system are that the speed of information
retrieval and updating is made easy and other advantages are:
Online implementation makes it easy for voters to participate in election.
It becomes easier to conduct election.
Election expenses can be reduced.
Non-Residential citizens can also participate in the election.
10
1.1. PURPOSE
In OVS a voter can use his\her voting right online without any difficulty.
He\She has to fill a registration form to register himself\herself. All the
entries are checked by the DATABASE which has already all
information about the voter. If all the entries are correct then a USER ID
and PASSWORD is given to the voter, by using that ID and
PASSWORD he\she can cast his\her vote. If conditions are wrong then
that entry will be discarded.
1.2. SCOPE
The supplementary specification applies to online voting system. This
specification defines the non-functional requirement of the system such
as:
Functionality: Since it stand alone application, one or more user may use
it at a time.
Usability: Desktop interface (Windows XP/7/8)
Reliability: The system is available only at the Election time.
Performance: The performance depends on hardware specification.
1.3. PROBLEM STATEMENT:
The online voting system is the system implemented to make the voting
system easy for both polling and also for the administrator to view and
11
check the result for each area individually. Here the voting is done
anywhere with in spite of the area in which they reside.
The voters or the administrator can login only if they already have a user
id and password. New user can be only created by the administrator.
The voter can login with his user id only if he has not casted the vote
already. If he has already casted the vote the voter status is changed to
voted and he cannot login with that user id unless the administrator
refreshes the voting system.
The administrator controls all parts of the online voting system except
the vote casting part which is restricted to the voters only.
The voter when logs in he can view his personal details which cannot be
edited by him he can only report the changes to the administrator who
can edit the details. The voter is granted permission only to view his
personal details and vote.
The voter while voting is provided with the option of voting for one of
the candidates or he can choose none of the above.
1.4. DESCRIPTION OF THE SYSTEM
1.4.1 PROPOSED SYSTEM
The proposed system is divided into four stages: Register,
Authentication, Voting and Counting. All are based on the Client-
Server model.
Register Stage: First, all the users who want to vote in the election
ought to register in advance. Here, the user is provided with a
unique username and password that would later be used to log-in
on an election day.
12
Authentication: The registered voters will need to log-in using
access credentials provided at the registeration stage. They will be
allowed to vote once they are verfied.
Voting Stage: The voter casts his vote once he is verified. Then,
the vote is encrypted and stored.
Counting Stage: All the votes cast are decrypted and then result is
declared.
In order to encrypt and decrypt the votes, RSA algorithm is used.
This asymmetric primitive has a pair of two keys, the public key
and the private key. It involves three steps that are: key generation
(which occurs at the Registration Stage), encryption (during the
Voting Stage) and decryption (at the Counting Stage). Any
encrypted text with one key of the pair, can be decrypted with the
other one. If encryption occurs with the public key then it must be
decrypted using the private key and vice versa. The key pairs are
generated based on two large prime numbers that must be kept in
secret just as the private key. Then, AES-256 is implemented on
the system to grant the security needed to keep safe the
asymmetric cryptography keys that are being generated. The
encryption/decryption keys are stored in the Database with limited
access; however, they are encrypted using AES-256 before being
stored on the server.
1.4.2 GOALS OF THE SYSTEM
Planned approach towards working: - The working in the
organization will be well planned and organized. The data will be
stored properly in data stores which will help in retrieval of
information as well as its storage.
13
Accuracy: - The level of accuracy in the proposed system will be
higher. All operation would be done correctly and it ensures that
whatever information is coming from the center is accurate.
Reliability: - The reliability of the proposed system will be high
due to the above stated reasons. The reason for the increased
reliability of the system is that now there would be proper storage
of information.
No Redundancy: - In the proposed system utmost care would be
that no information is repeated anywhere, in storage or otherwise.
This would assure economic use of storage space and consistency
in the data stored.
Immediate retrieval of information: - The main objective of
proposed system is to provide for a quick and efficient retrieval of
information.
Immediate storage of information: - In manual system there are
many problems to store the largest amount of information.
Easy to Operate: - The system should be easy to operate and
should be such that it can be developed within a short period of
time and fit in the limited budget of the user.
1.4.3 TECHNOLOGIES USED
This project will be a Web application to be developed in PHP
having
Database Design (My SQL)
Form Design (HTML 4.0)
Coding (PHP)
Testing (WAMP SERVER)
Reporting Tool (Data Report)
14
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 OLD METHODS OF VOTING
Paper-based voting: The voter gets a blank ballot and use a pen or a
marker to indicate he want to vote for which candidate. Hand-counted
ballots is a time and labor consuming process, but it is easy to
manufacture paper ballots and the ballots can be retained for
verifying, this type is still the most common way to vote.
Lever voting machine: Lever machine is peculiar equipment, and each
lever is assigned for a corresponding candidate. The voter pulls the
lever to poll for his favorite candidate. This kind of voting machine
can count up the ballots automatically. Because its interface is not
user-friendly enough, giving some training to voters is necessary.
Direct recording electronic voting machine: This type, which is
abbreviated to DRE, integrates with keyboard; touch screen, or
buttons for the voter press to poll. Some of them lay in voting records
and counting the votes is very quickly. But the other DRE without
keep voting records are doubted about its accuracy.
Punch card: The voter uses metallic hole-punch to punch a hole on
the blank ballot. It can count votes automatically, but if the voters
perforation is incomplete, the result is probably determined
wrongfully.
Optical voting machine: After each voter fills a circle correspond to
their favorite candidate on the blank ballot, this machine selects the
darkest mark on each ballot for the vote then computes the total result.
15
This kind of machine counts up ballots rapidly. However, if the voter
fills over the circle, it will lead to the error result of optical-scan.
Recent years, a considerable number of countries has adopted E-
voting for their official elections. These countries include; America,
Belgium, Japan and Brazil.
2.2 SECURITY ISSUES
Foreign experience revealed that they are often confronted by security
issues while the online voting system is running. The origin of the
security issues was due to not only outsider (such as voters and
attackers) but also insider (such as system developers and
administrators), even just because the inheritance of some objects in the
source code are unsuitable. These errors caused the voting system to
crash. The proposed solutions were correspondingly outlined to hold
back these attacks. For example, to avoid hacker making incursion into
the voting system via network, we can design our system to transmit
data without network. Another example is to limit voter to input
particular data, so that we can prevent the command injection from
running.
2.3 CURRENT SYSTEM DRAWBACKS
The problems of the existing manual system of voting include among
others the following:
Expensive and Time consuming: The process of collecting data and
entering this data into the database takes too much time and is expensive
to conduct, for example, time and money is spent in printing data capture
16
forms, in preparing registration stations together with human resources,
and there after advertising the days set for registration process including
sensitizing voters on the need for registration, as well as time spent on
entering this data to the database.
Too much paper work: The process involves too much paper work and
paper storage which is difficult as papers become bulky with the
population size.
Errors during data entry: Errors are part of all human beings; it is very
unlikely for humans to be 100 percent efficient in data entry.
Loss of registration forms: Some times, registration forms get lost after
being filled in with voters details, in most cases these are difficult to
follow-up and therefore many remain unregistered even though they are
voting age nationals and interested in exercising their right to vote.
Short time provided to view the voter register: This is a very big problem
since not all people have free time during the given short period of time
to check and update the voter register.
Above all, a number of voters end up being locked out from voting.
2.4 SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS:
MYSQL DBMS- It allows combination, extraction, manipulation and
organization of data in the voters database. It is platform independent
and therefore can be implemented and used across several such as
Windows, Linux server and is compatible with various hardware
mainframes. It is fast in performance, stable and provides business
value at a low cost.
NetBeans IDE 7.1.2- The NetBeans IDE is an award-winning
integrated development environment available for Windows, Mac,
17
Linux, and Solaris. The NetBeans project consists of an open-source
IDE and an application platform that enable developers to rapidly
create web, enterprise, desktop, and mobile applications using the Java
platform, as well as PHP, JavaScript and Ajax, Groovy and Grails, and
C/C++. The NetBeans project is supported by a vibrant developer
community and offers extensive documentation and training resources
as well as a diverse selection of third-party plugins.
JAVA coding- This is for advanced user who find PHP codes easy to
work with.
Testing- is done via WAMPSERVER.
Web browsers: Mozilla Firefox, Google chrome, Opera and Internet
Explorer
Reporting Tool i.e. through Data Report.
HARDWARE REQUIREMENTS:
Microsoft Windows XP Professional SP3/Vista SP1/Windows 7
Professional:
Processor: 800MHz Intel Pentium III or equivalent
Memory: 512 MB
Disk space: 750 MB of free disk space
Ubuntu 9.10:
Processor: 800MHz Intel Pentium III or equivalent
Memory: 512 MB
Disk space: 650 MB of free disk space
18
3 DESIGN
3.1 SOFTWARE REQUIREMENT SPECIFICATION
FUNCTIONAL REQUIREMENTS:
Registration of the voter is done by the Administrator.
Administrator can change the information any time if required.
Registration of the Voter depends upon the information filled by
the user.
Voter is given a unique ID and Password.
Voter can give vote after login and entering the ID and
Password.
In the Database information of every voter is stored.
Database shows the information of every user to the
Administrator.
NON-FUNCTIONAL REQUIREMENTS:
Secure access of confidential data (users details). SSL can be
used.
24 X 7 availability on the voting day.
Better component design to get better performance at peak time
on the Election Day.
Flexible service based architecture will be highly desirable for
future extension.
User friendly interface for inexperienced internet users.
19
3.2 SOFTWARE DESIGN
3.2.1 ARCHITECTURE DIAGRAM
Counting
Registration
Authentication
Voting Stage
Voter
Figure 1: Architecture Diagram
20
3.2.2 SYSTEM MODELS
3.2.2.1 CONTEXT MODEL
Figure 2: Context Diagram
3.2.2.2 BEHAVIOURAL MODEL
USE CASE DIAGRAMS
Figure 3: Use Case Diagram
Online Voting
System
Voters Database
Voters
Management
System
Update Voters
details
Candidates
Database
Results
Add and
Remove
candidates
Registration
21
Figure 3.1: Use Case Diagram
DATA FLOW DIAGRAMS
DFD LEVEL 0:
Figure 4: Data Flow Diagram
User
and
Administrator
Output
System
22
DFD LEVEL 1:
Figure 4.1: Data flow Diagram
Login
Process
Voting
Process
Voter
information
checking
process
Voter
Registration
Process
Final
Report
23
DFD LEVEL 2:
Voter data Stored Data Voting Data Results
Figure 4.2: Data Flow Diagram
Administrator Voter
Final
Result
Voting
process
Voter
Registration
Informatio
n
checking
Login Process
24
ACTIVITY DIAGRAMS
LOGIN:
Figure 5: Activity Diagrams
25
VOTER DETAILS:
Figure 5.1: Activity Diagrams
CAST VOTE:
Figure 5.2: Activity Diagrams
26
The voter selects the
view to see the result
System displays the no. of vote
of each nominee & also winner
STATUS:
Figure 5.3: Activity Diagram
3.2.2.3 STRUCTURAL MODELS
CLASS DIAGRAMS
LOGIN:
Figure 6: Class Diagrams
27
REGISTRATION:
Figure 6.1: Class Diagrams
CAST VOTE:
Figure 6.2: Class Diagrams
28
STATUS:
Figure 6.3: Class Diagrams
ER DIAGRAM
Figure 7: ER Diagram
Voter Candidates
Registration
Process
Registered Voter Databas
e
Registered Candidate
Voting
ADMIN
Add
Candidates
Update Candidate
Details
Delete Candidate
Add Voters
Update Voter
Details
Check Results
29
SEQUENCE DIAGRAMS
Figure 8: Sequence Diagrams
Figure 8.1: Sequence Diagrams
30
3.3 DATABASE DESIGN
The project uses three tables:
Administrator Table
Voter Table
Candidate Table
ADMIN TABLE:
Table 1: Admin Table
VOTER TABLE:
Table 2: Voter Table
Field Name Data Type Description
Username Varchar Login id for Admin.(Primary key)
Password Varchar Password for Login
Field Name Data Type Description
VoterId Integer Login id for Voter(Primary key)
Name Varchar Name of the voter
Sex Varchar Sex of voter
Age Integer Age of voter
City Varchar City of voter
Security Varchar Security Question
Status Boolean Status of voter(he/she can vote or not)
31
CANDIDATE TABLE:
Field Name Data Type Description
Symbol Varchar Party Symbol (Primary key)
Name Varchar Name of the voter
Sex Varchar Sex of voter
Age Integer Age of voter
City Varchar City of voter
Count Integer Count the no of votes
Table 3: Candidate Table
4 IMPLEMENTATION
4.1 USER INTERFACE
HOME WINDOW
32
SIGN UP WINDOW
LOGIN WINDOW
33
REGISTRATION FORM
SELECT REGION
34
SELECT CANDIDATES
35
5 CONCLUSION
This Online Voting system will manage the Voters information by which voter
can login and use his voting rights. The system will incorporate all features of
the traditional Voting system. It provides the tools for maintaining voters vote
to every candidate and it counts total number of votes of every candidate. There
is a database which is maintained by the Administrator in which all the names
of voter with complete information is stored.
In this, user who is above 18 years registers their information on the database
and when they want to vote they have to login by their id and password and can
vote to any candidate only single time. Voting detail is stored in database and
the result is displayed by calculation. By online voting system the percentage of
voting increases. It decreases the cost and time of voting process. It is very easy
to use and it is very less time consuming. Also it is very easy to debug in case
some of technical malfunction.
36
6 REFERENCES
1. Anderson C. (2006). How to Rig a Democracy: A Timeline of
Electronic Voting in the United States. The Independent. Retrieved
November 28, 2006 from: http://www.indypendent.org/?p=608
2. Bellis, M. (2007). The History of Voting Machines. Retrieved November
9, 2006 from: http://inventors.about.com/library/weekly/aa111300b.htm
3. Cranor, L.F., & Cytron, R.K. (1996). Design and Implementation of a
Security-Conscious Electronic Polling System. Washington University
Computer Science Technical Report (WUCS). Retrieved October 9, 2006
from: http://www.acm.org/crossroads/ords2-4/voting.html
4. Electronic Voting and Counting Development of the System. (2005).
Elections ACT. Retrieved February 11, 2007 from:
http://www.elections.act.gov.au/EVACS.html http://www.iiec.or.ke/
5. Electronic Voting Systems, ACE Project The Electoral Knowledge
Network, [online] 2013, http://www.aceproject.org May 19, 2013
6. Eliver Prez Villegas, Gina Gallegos-Garca, Gualberto Aguilar Torres,
Hctor Flores Gutirrez, Implementation of Electronic Voting System in
Mobile Phones with Android Operating System, Vol. 4 No. 9 September
2013, http://www.cisjournal.org
7. Hakan Evecek, Applying MESE processes to Improve Online E-Voting
Prototype System with Paillier Threshold Cryptosystem Web Services,
University of Colorado, Spring 2007.
8. Jrg Ritter, Decentralized E-Voting on Android Devices Using
Homomorphic Tallying, Bern University of Applied Sciences
Engineering and Information Technology CH-2501 Biel, Switzerland,
February 7, 2014
37
9. Roger S. Pressman, Software Engineering- A Practitioners Approach,
McGraw-Hill International Edition, Seventh Edition, 2009.
10. Software engineering 8th edition by Ian Sommerville.
11. Simply Voting System Project https://www.simplyvoting.com/
12. Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unified_Modeling_Language
13. Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronic_voting
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Hobsbawm-The Age of EmpireDocument440 pagesHobsbawm-The Age of EmpireAnirban Paul100% (2)
- ONLINE VOTING SYSTEmDocument33 pagesONLINE VOTING SYSTEmVinoth Kumar57% (14)
- Online Voting SystemDocument31 pagesOnline Voting SystemCyrion Kinunda33% (3)
- Online Survey DocumentDocument42 pagesOnline Survey Documentmswarna100% (1)
- Online Voting SystemDocument20 pagesOnline Voting SystemMorash Khalid67% (3)
- Online Voting SystemDocument64 pagesOnline Voting SystemShaibu Suleiman Yahaya100% (1)
- Online Voting SystemDocument36 pagesOnline Voting SystemVenkatesh Hanumandla57% (7)
- Project Report of Online Voting SystemDocument22 pagesProject Report of Online Voting Systemneethu s.s89% (9)
- Online Voting System FinalDocument92 pagesOnline Voting System FinalJaldeep100% (2)
- All Autolisp CommandsDocument6 pagesAll Autolisp CommandsJay RammaPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.online Voting SystemDocument40 pages6.online Voting SystemRubilu Ruby81% (27)
- Secure Online Voting SystemDocument178 pagesSecure Online Voting SystemMichael Chinwuba92% (13)
- Airline ReservationDocument101 pagesAirline ReservationGaurav Sharma0% (1)
- Report On Attendance Management System PDFDocument62 pagesReport On Attendance Management System PDFAbhishek100% (1)
- Online Voting System Using PythonDocument48 pagesOnline Voting System Using PythonPreethu Gowda80% (5)
- Online Resume Builder OgDocument79 pagesOnline Resume Builder OgSunit PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- Documentation - Online Voting SystemDocument52 pagesDocumentation - Online Voting SystemNaren Gs75% (79)
- Online Voting SystemDocument26 pagesOnline Voting SystemVenkatesh Hanumandla96% (27)
- Online Voting System Full DocumentDocument42 pagesOnline Voting System Full DocumentShaju Afridi100% (2)
- BANCS@24Document27 pagesBANCS@24Arihant Pawariya80% (5)
- Online Voting SystemDocument59 pagesOnline Voting SystemZendax100% (1)
- E Voting Some Project ReportDocument37 pagesE Voting Some Project ReportGamini RathnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Online Voting SystemDocument27 pagesOnline Voting Systemသဲဆု100% (1)
- Online Booking System Project ReportDocument67 pagesOnline Booking System Project Reportmandeep kumar50% (4)
- Online Voting SystemDocument97 pagesOnline Voting SystemPrashant DixitPas encore d'évaluation
- 10-3 Developing Microservices With WM Microservices RuntimeDocument82 pages10-3 Developing Microservices With WM Microservices RuntimesankbdPas encore d'évaluation
- Online Smart Voting System Using Face RecognitionDocument5 pagesOnline Smart Voting System Using Face RecognitionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- "Online Voting System": A Project OnDocument104 pages"Online Voting System": A Project Ondeepak Gupta100% (1)
- Online Voting System: MD Jahirul IslamDocument31 pagesOnline Voting System: MD Jahirul IslammartPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1. Online Voting SystemDocument44 pages1.1. Online Voting SystemManvi YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Online Voting ReportDocument69 pagesOnline Voting ReportPriya Kapoor100% (1)
- Online Voting System LATESTDocument38 pagesOnline Voting System LATESTYash TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Online Voting System A ASP - Net ProjectDocument47 pagesOnline Voting System A ASP - Net ProjectParthiban Aero82% (11)
- Online Voting System ContentsDocument19 pagesOnline Voting System Contentsm.k.snigdhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Online VotingDocument11 pagesOnline VotingAyush AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Online Voting System Problem StatementDocument1 pageOnline Voting System Problem StatementAjay Ravuri100% (4)
- Online Voting SystemDocument73 pagesOnline Voting SystemselbalPas encore d'évaluation
- Online Voting SystemDocument32 pagesOnline Voting Systemanubhav0% (2)
- Voting System ReportDocument20 pagesVoting System Reportsamuel sridhar100% (1)
- Project Report On E-Polling System Using PythonDocument31 pagesProject Report On E-Polling System Using PythonSaivee AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Report: Online Voting SystemDocument34 pagesProject Report: Online Voting SystemGanesh Raj PspkPas encore d'évaluation
- Online Voting System PDFDocument3 pagesOnline Voting System PDFrollie torres100% (2)
- Title of The Project Online VotingDocument25 pagesTitle of The Project Online VotingYashuPas encore d'évaluation
- SynopsisofivotingsystemDocument10 pagesSynopsisofivotingsystemSujeet Singh83% (6)
- Online Voting System PDFDocument28 pagesOnline Voting System PDFShimaa AshrafPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Proposal For Online Voting SystemDocument3 pagesProject Proposal For Online Voting SystemAdym Aymd100% (1)
- Online Voting ReportDocument29 pagesOnline Voting ReportMugaya Kevin FrancisPas encore d'évaluation
- Online Voting System SRSDocument9 pagesOnline Voting System SRSKamal chaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Offline ExaminerDocument47 pagesOffline ExaminerDevish Wakde78% (9)
- Online SystemDocument35 pagesOnline SystemPravashSahoo100% (1)
- Bus Reservation Amit ProjectDocument28 pagesBus Reservation Amit ProjectMohitShakya100% (1)
- Project ReportDocument29 pagesProject ReportAnimesh BeheraPas encore d'évaluation
- Online Voting System SRSDocument7 pagesOnline Voting System SRSSanthosh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Shop Management System by SandipDocument31 pagesShop Management System by SandipSAPNAPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Project Report Batch 5Document50 pagesFinal Project Report Batch 537 RAJALAKSHMI RPas encore d'évaluation
- Irb OnlineshoppingsystemDocument76 pagesIrb OnlineshoppingsystemIrshad BhatPas encore d'évaluation
- University For Development Studies FaculDocument70 pagesUniversity For Development Studies FaculMary Jane PagayPas encore d'évaluation
- Nishant SinghDocument45 pagesNishant SinghNishu SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Debretabor University Technology Faculity Department of Information Technology Online Shopping SystemDocument56 pagesDebretabor University Technology Faculity Department of Information Technology Online Shopping Systemmamaru bantiePas encore d'évaluation
- IndexDocument1 pageIndexbharathimanianPas encore d'évaluation
- IMee Report (1) - MergedDocument62 pagesIMee Report (1) - MergedRaiden mathewPas encore d'évaluation
- Stay Safe Women Security Android App Project ReportDocument44 pagesStay Safe Women Security Android App Project ReportKanu KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Certificate: Amc Engineering CollegeDocument42 pagesCertificate: Amc Engineering Collegelakshmisagar S DPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter-1 Introduction To Embedded SystemDocument2 pagesChapter-1 Introduction To Embedded SystemMadhav ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Constitution of The United StatesDocument21 pagesThe Constitution of The United StatesJeff PrattPas encore d'évaluation
- Smart Home Automation Using AndroidDocument8 pagesSmart Home Automation Using Androidultimatekp144100% (1)
- Bill Summary - 121st - A - BillDocument1 pageBill Summary - 121st - A - BillShamal KamblePas encore d'évaluation
- Android Home AppliDocument5 pagesAndroid Home AppliGaurav GaikwadPas encore d'évaluation
- Smart Homes For A Better Living Using BluetoothDocument4 pagesSmart Homes For A Better Living Using BluetoothInternational Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology100% (1)
- State by State Voucher ComparisonDocument11 pagesState by State Voucher ComparisonArihant PawariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- High Capacity Colored Two Dimensional Codes: Antonio Grillo, Alessandro Lentini, Marco Querini and Giuseppe F. ItalianoDocument8 pagesHigh Capacity Colored Two Dimensional Codes: Antonio Grillo, Alessandro Lentini, Marco Querini and Giuseppe F. ItalianoArihant PawariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cs2352 PCD Unit1 NotesDocument11 pagesCs2352 PCD Unit1 NotesArihant PawariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Data StructureDocument36 pagesData Structureapi-3853475Pas encore d'évaluation
- Capital FlowDocument7 pagesCapital FlowArihant PawariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Oil CrisisDocument15 pagesOil CrisisArihant PawariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 0Document2 pagesChapter 0Arihant PawariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Constitution of The United StatesDocument21 pagesThe Constitution of The United StatesJeff PrattPas encore d'évaluation
- Forex MarketDocument8 pagesForex MarketArihant PawariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 794713132491542Document6 pages794713132491542Arihant PawariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- One Vs GroupDocument1 pageOne Vs GroupArihant PawariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparing AlgorithmsDocument38 pagesComparing AlgorithmsArihant PawariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- UPSC Civil Services Exam SyllabusDocument231 pagesUPSC Civil Services Exam Syllabusvssridhar99100% (1)
- Best of Quora - 2012Document442 pagesBest of Quora - 2012Arda KutsalPas encore d'évaluation
- The No Child Left Behind Act of 2001 and The Pathways To College Network FrameworkDocument10 pagesThe No Child Left Behind Act of 2001 and The Pathways To College Network FrameworkArihant PawariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kashmir Peace PollDocument149 pagesKashmir Peace PollArihant PawariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Members of 16 Lok SabhaDocument62 pagesMembers of 16 Lok SabhaArihant PawariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Online Voting SystemDocument20 pagesOnline Voting SystemArihant PawariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- CornellsystemDocument1 pageCornellsystemapi-253788473Pas encore d'évaluation
- UPSC Civil Services Exam SyllabusDocument231 pagesUPSC Civil Services Exam Syllabusvssridhar99100% (1)
- CornellsystemDocument1 pageCornellsystemapi-253788473Pas encore d'évaluation
- CPM and CCPM A Compare and Contrast Pinnacle Strategies PDFDocument15 pagesCPM and CCPM A Compare and Contrast Pinnacle Strategies PDFishita.brahmbhattPas encore d'évaluation
- The Magic PassportDocument7 pagesThe Magic Passportmarcelo cobiasPas encore d'évaluation
- CMME 2 ReportDocument7 pagesCMME 2 ReportMicro YuchenPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 10 Pair of Linear Equations in 2 Variables (10) - 0Document2 pagesCBSE Class 10 Pair of Linear Equations in 2 Variables (10) - 0Deepak100% (1)
- KPSC - QP - 145-15Document12 pagesKPSC - QP - 145-15M UllerPas encore d'évaluation
- CPM PertDocument31 pagesCPM PertmawandePas encore d'évaluation
- ZEBEX Industries IncDocument2 pagesZEBEX Industries IncSibusiso GamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Códigos de ErrorDocument36 pagesCódigos de ErrorGerardo MandujanoPas encore d'évaluation
- ECEN 449 Khatri WebsiteDocument6 pagesECEN 449 Khatri WebsiteThuy NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.0 - Problem Solving 1Document20 pages3.0 - Problem Solving 1princess50% (2)
- STM STM32 STM32F103RE Learning Centre MCU Application Notes STMicroelectronics - Application - Notes - 6Document19 pagesSTM STM32 STM32F103RE Learning Centre MCU Application Notes STMicroelectronics - Application - Notes - 6tiago-macedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Backbonetutorials PDFDocument55 pagesBackbonetutorials PDFAnkush SachdevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rust by ExampleDocument335 pagesRust by ExamplevictoriogaieroPas encore d'évaluation
- Crabby's Top 10 E-Mail Crabs: Crab #1: Discretion Is The Greater Part of ReplyingDocument9 pagesCrabby's Top 10 E-Mail Crabs: Crab #1: Discretion Is The Greater Part of ReplyingSarangPas encore d'évaluation
- Backdoor AndroidDocument1 pageBackdoor Androidyulika_vPas encore d'évaluation
- Boundary-Value Problems: Example 6.1-1Document4 pagesBoundary-Value Problems: Example 6.1-1Munir AslamPas encore d'évaluation
- RealviewDocument62 pagesRealviewXaxo PapoPas encore d'évaluation
- SIEM PM EnterpriseDocument2 pagesSIEM PM EnterpriseTama OlanPas encore d'évaluation
- Complex Numbers WorksheetDocument3 pagesComplex Numbers WorksheetArsalan RaisaniPas encore d'évaluation
- RSLTE020 MIMO and OFDM RSLTEDocument114 pagesRSLTE020 MIMO and OFDM RSLTEAnonymous DUua3A5Pas encore d'évaluation
- FEM PrimerDocument26 pagesFEM Primerted_kordPas encore d'évaluation
- Lovely Professional University Form/Lpuo/Ap-3Document3 pagesLovely Professional University Form/Lpuo/Ap-3Sam JindalPas encore d'évaluation
- Map 3 D 2015 InstallDocument15 pagesMap 3 D 2015 InstallHarrison HayesPas encore d'évaluation
- Microsoft Dynamics SOA WhitepaperDocument22 pagesMicrosoft Dynamics SOA WhitepapermagnumzipPas encore d'évaluation
- Installing OpenSceneGraphDocument9 pagesInstalling OpenSceneGraphfer89chopPas encore d'évaluation
- Radio Graph TheoryDocument12 pagesRadio Graph TheoryMarty NobisPas encore d'évaluation
- VisiLogic Software Manual-Getting StartedDocument220 pagesVisiLogic Software Manual-Getting StartedtomearsovskiPas encore d'évaluation