Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
SAP Time Integration-CATS
Transféré par
Singh 10Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SAP Time Integration-CATS
Transféré par
Singh 10Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
2008 Wellesley Information Services. All rights reserved.
All Roads Lead to Payroll
Best Practices to Help You
Select the Right Time
Management Strategy and
Solution
Dirk Liepold
RowSix
1
In This Session ...
Get a detailed look at all of your options, both SAP and
third-party, for evaluating and managing time in your
SAP Payroll processes
Review the seven variables that will drive your time
management strategy and your decision of which tools
to use
Compare standard SAP Time Management functionality
with third-party time management options and explore
the various processes available for tracking time
Explore how SAP Time Management integrates with
other modules and applications and understand the
impact this integration will have on the time
management strategy you choose
222
What Well Cover
Exploring time management business processes
Examining decision criteria
Introducing time management players
Understanding SAP Time Management functionality
Developing custom solutions using SAP tools
Selecting the right strategy
Implementing SAP Time Management
Wrap-up
3
Business Processes Within Time Management
Time and attendance
Sets up and tracks adherence to policies for attendance and
related elements like tardiness, discipline, and overtime
Calculates the related rates of payment and benefit accruals
Absence management
Sets up and tracks adherence to leave policies for vacation,
disability, and regulated benefits such as the U.S. Family
Medical Leave Act (FMLA)
3
4
Business Processes Within Time Management (cont.)
Scheduling and optimization
Automatically creates schedules based on business drivers
and employee constraints
Advanced applications can optimize the allocation of labor
resources across locations, times, and tasks, and based on
employee skills, attributes, and preferences
Labor forecasting
Ability to predict staffing-level requirements using historical
data inputs on business metrics such as sales or required tasks
4
5
Business Processes Within Time Management (cont.)
Budgeting
Predicts costs of labor forecasts, in most cases long-time
horizons such as quarters or years, either through top-down
allocations of funds or bottom-up aggregation of labor
requirements
Self-service
Allows frontline workers to interact with any of the modules to
clock in and out, request leaves or specific shifts, see their
schedules, etc.
For some systems, this capability may be sold as a separate
module; in others, this capability is a given of the Web-based
interface
5
666
What Well Cover
Exploring time management business processes
Examining decision criteria
Introducing time management players
Understanding SAP Time Management functionality
Developing custom solutions using SAP tools
Selecting the right strategy
Implementing SAP Time Management
Wrap-up
77
Seven Variables That Drive Your Time Management Strategy
The following seven variables are essential as part of a
decision process for selecting the right time
management strategy:
1. Data requirements
2. Input/output requirements
3. Functional requirements
4. System scalability requirements
5. Security requirements
6. Employee mix and client culture
7. Cost
88
Data Requirements
Units (minutes/hours/days/miles)
Attendance elapsed time worked
Attendance by code (regular, overtime, double time)
Exception time vs. actual time
Clock-in/clock-out/break-in/break-out
Cost objects
Cost center, order, WBS, position, project, activity type, work
center
Wage types
Direct vs. indirect labor indicator
99
Input Requirements
Centralized vs. decentralized
Corporate workstation
Kiosk
Internet/intranet
Mobile device
Swipe card reader, proximity reader, and biometric
reader (finger, hand, optical)
Interactive Voice response (IVR)
Optical Mark reader (OMR)
Paper timecard
Real-time vs. off-line (replication)
Interface
10 10
Output Requirements
Payroll system
Financial system
Project system
Plant maintenance system
Business Warehouse
11 11
Functional Requirements
All the time management business processes that
should be part of the implementation scope have to be
identified and defined in detail
This includes end-to-end processes, including non
system-supported steps as well as paper forms
12 12
Functional Requirements (cont.)
Workforce scheduling
Time entry
Time approval
Gross pay calculation
Time balance tracking
Quota accrual
Absence and attendance tracking
Time data reporting
Employee Self-Service (ESS)
13 13
Workforce Scheduling
Flexible work schedule setup
Flexible holiday calendar setup
Staff scheduling
Schedule bidding
Shift trading
Schedule compliance
Skills and competencies
14 14
Time Entry and Time Approval
Time entry
Positive vs. negative (exception reporting)
Data entry screen layout
Data entry field list
Time entry period (daily, weekly, bi-weekly)
Single point of time entry for multiple downstream systems
Multi-language front end
ESS
Time approval
One approver required vs. two approvers
Dynamic teams by supervisor (integration to HR or OM)
Approval delegation to back-up or during absence/vacation
15 15
Gross Pay Calculation and Quota Accrual
Gross pay calculation
Flexible gross-pay rule setup
Retroactive calculation capability
Integration with payroll
Integration with HR
Quota accrual
Flexible quota accrual rule setup
Retroactive calculation capability
Integration with payroll
Integration with HR
16 16
Absence and Attendance Tracking
Flexible absence/attendance code setup
Real-time checking against available balance
Permissibility of codes by employee type/location
Real-time check against work schedule
FMLA (Family Medical Leave Act) balance tracking
Absence donations to employees or absence pools
17 17
Time Data Reporting and ESS
Time data reporting
Flexible absence/attendance
Planned vs. actual hours worked
Overtime
Quota balance(s) and absence/vacation liability
Integration to data warehouse
Hours by cost object
ESS
Time entry
Quota balance overview
Time statement
Leave request
18 18
System Scalability, Security, and Employee Mix
System scalability requirements
Time entry
Time evaluation
Security requirements
Access limitation by group of employees
Access limitation by role (employee, supervisor)
Delegation of data entry/approval
Employee time entry in specific location only
Employee mix and client culture
High number of non-exempt employees
Skills
Work location(s)
19 19
Cost
License fees
Implementation cost
Hardware cost
Long-term support cost (Total Cost of Ownership [TCO])
Additional hidden cost
Additional hardware
Additional training
Integration cost (direct and indirect)
Cost for keeping compliancy
Leap-frog cost
20 20 20
What Well Cover
Exploring time management business processes
Examining decision criteria
Introducing time management players
Understanding SAP Time Management functionality
Developing custom solutions using SAP tools
Selecting the right strategy
Implementing SAP Time Management
Wrap-up
21
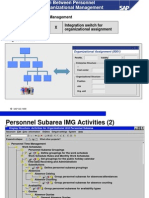
Who Are the Players in Time Management?
Workforce management software vendors can be divided
into the following camps:
Full HCM suite vendors
Kronos, Softscape, Ultimate Software
ERP providers
SAP, Infor, Oracle
Workforce specialists
CyberShift, InVision, Kaba Workforce, ScheduleSoft,
(scheduling capability only), ScheduleSource, Stromberg,
TimeLink, Workplace Systems, Workbrain (bought by Infor)
21
22
Who Are the Players in Time Management? (cont.)
Time management software vendors can be divided into
the following camps: (cont.)
Call center specialists
Aspect Software, NICE Systems, Witness Systems/Verint
Vertical market/process specialists
Deltek (project-based industries), JDA (retail), ORTEC
(planning/distribution), RedPrairie/BlueCube (warehousing
and distribution/retail), Reflexis (retail), Servigistics (field
services), Tomax (retail)
22
23
Integrating WFM into Other Areas of the Business
Companies are
expecting to
eventually integrate
Workforce
Management (WFM)
into other areas of
the business
Core HR, for payroll
purposes, seems to
be the most
important area to
integrate with WFM
23
24
Evaluating the Time Management Players
When deciding on a time management strategy, define
the to-be design and then conduct a fit/gap analysis of
SAP Time Management functionality
In order to be able to satisfy certain functional
requirements that cannot be covered by standard SAP,
evaluate other WFM vendors to analyze the fit for
eventually filling the SAP Time Management
functionality gaps
Conduct a cost analysis to compare SAP custom
development vs. a bolt-on solution
Bolt-on license cost
Bolt-on implementation cost
Cost for integrating bolt-on with SAP
24
25 25 25
What Well Cover
Exploring time management business processes
Examining decision criteria
Introducing time management players
Understanding SAP Time Management functionality
Developing custom solutions using SAP tools
Selecting the right strategy
Implementing SAP Time Management
Wrap-up
26 26
Time Input Options in SAP
Time Management Infotypes via PA30 and PA61
Time Managers Workplace (PTMW)
Cross Application Time Sheet (CATS)
Classical (CAT2) SAP ERP transaction via SAPGUI
Regular (CATW) SAP ESS Web front end
For Service Providers (CATSXT)
Notebook (remote entry via off-line application with replication
to CATS)
Instant (iView)
Calendar (iView)
Phone (Wireless Access Point [WAP])
27 27
Time Input Options in SAP (cont.)
SAP xApp Mobile Time and Travel (MTT)
Duet
(Microsoft Office integration)
Time entry
Leave request
28 28
SAP Time Entry Front-End Solutions
The current SAP time entry offerings cover a wide range
of functionality, including the evolution from SAPGUI-
based time entry via transaction PA61 to Duet
-based
time entry
The benefits of using a standard SAP time entry solution
is the tight integration with all other SAP components
The following screens show examples of SAP time entry
front-end solutions
29
SAP ERP PA61 Time Input
29
Integration
with SAP HR
Personnel
Number
Integration
with SAP
Work
Schedule
Integration
with SAP HR
Employee
Organizational
Assignment
Integration
with SAP
Cost
Objects
Integration
with SAP
Holiday
Calendar
30
SAP CATS Classic Time Entry via CAT2
30
In addition to the standard
SAP integration points, the
classic CATS time entry
solution allows flexible
design of the time entry
screen via configurable
profiles to define:
-List of entry fields
-Time period
-Number of approval steps
Worklists can be defined
to simplify data entry
31
SAP Duet
Time Entry via MS Outlook
31
This new SAP time entry
solution allows for time
entry via MS Outlook.
Office users do not need
SAPGUI to enter time.
32 32
Third-Party Time Entry with Interface to SAP
Business Application Programming Interface (BAPI) into
the CATS table (CATSDB)
Time recording via Communication Channel 1 (CC1)
Old CC1 is based on Application Link Enabling (ALE)
New CC1 is based on a BAPI
Inbound: Into Infotype 2011 Time Events
Outbound: HR mini master, quota balances, time balances
Plant data collection via Communication Channel 2 (CC2)
Integration to PP, PP/PI, PP/SM, PS
33 33
Third-Party Time Entry with Interface to SAP (cont.)
B-COMM Connection SAP-certified interface into CATS
Custom Batch-Input (Batch Data Communication [BDC]
or CALL TRANSACTION) into:
Infotype 2001 Absences
Infotype 2002 Attendances
Infotype 2010 Employee Remuneration Info
34
SAP Certified Time Management Interfaces
Examples for vendors who
can provide SAP-certified
interfaces are:
Kaba GmbH
TimeLink
Kronos
*see full list in Appendix A
34
35
Kaba Benzing B-COMM Connection to SAP
B-COMM for ERP is a communications software for
connecting Kaba Benzing terminals to SAP ERP systems
B-COMM for R/3 ERP is for SAP versions 3.1-4.7
The core of this software is a SAP-certified interface that
ensures faultless data exchange between the individual
SAP modules and the data collection devices
Supported communication
Ethernet
HTTP(s)
XML
Radio frequency
35
36
KABA Benzing B-COMM Connection to SAP (cont.)
Supported data collection methods
Badge-based magnetic stripe
Barcode (visible and infrared)
Proximity
Biometric (hand geometry/fingerprint)
Touch screen kiosk
Telephone (IVR)
Windows CE/pocket PC
Web time clock
Mobile/wireless
Badge-based
36
37 37
Time Data Processing Options with SAP
Approval
Yes/No
1-Step/2-Step
Integration to Org. Management via Structural Authorization
Time leveling
Check against scheduled hours (IT0007 - Planned Working
Time)
Integration to communication (IT0105 - Communication)
38 38
Time Data Processing Options with SAP (cont.)
Integration to other applications
Org. Management (Structural Authorization)
Human Resources (PTEX2000 and PTEX2010)
Controlling (CATSCO)
Plant Maintenance/Customer Service (CATSPM)
Project System (CATSPS)
Materials Management (CATSMM)
Workflow
Security
39 39
About SAP Time Evaluation
The heart of the overall time management functionality
encompassing all the business rules to process time
data and generate wage-types and hours per employee
Schemas and personnel calculation rules allow
configuration of the most complex business rules
Time evaluation generates:
Wage types and hours based on configurable business rules
Absence and attendance accrual based on configurable
business rules
Tightly integrated into payroll via cluster B2 table ZL
Allows positive and negative time evaluation
Supports full automatic retroactive calculation
40 40
Retroactive Calculation Capabilities
One of the core strengths of SAP Time Evaluation
Retroactive time data changes to SAP infotypes trigger
automatic recalculation of time evaluation results,
payroll results, and quota accrual balances
No manual intervention required
Typically late time entries and/or work schedule changes
cause the majority of retro scenarios
Infotypes that can trigger time management related retro
calculations
Infotype 0001 Org. Assignment
Infotype 2001 Absences
Infotype 2002 Attendances
Infotype 0007 Work Schedule
Infotype 0041 Date Types (can be configured to trigger retro)
41 41
Retroactive Calculation Capabilities (cont.)
Using bolt-on systems does not allow you to use the full
power of SAPs retro calculation capabilities
Manual calculations and adjustments are usually required to
ensure correct calculations
Let SAP do the job for you
Do not implement cumbersome manual processes to patch the
problems that are a result of lack of integration
SAP retro-calculation can minimize time investment of
your payroll support personnel to fix problems caused
by late time entry or manually-entered retro time entry
changes
42 42
Example of Retro Calculation: Variables
Employee type: Salaried exempt defined in IT0001
Hourly rate: $10 defined in IT0008
Anniversary date: 01/15/1998 defined in IT0041
Business rule configured in SAP Quota Accrual Rule
All exempt employees are eligible for vacation accrual
12 hours vacation accrual for 10+ years anniversary
Accrual rate is prorated based on worked hours per period
(80 hrs worked/80 hrs planned) = 100%
43 43
Example of Retro Calculation: Initial Time Entry
Initial time entry for bi-weekly period 01/06/08-01/19/08
Entered 80 hours of Regular Work into CATS
Period pay results generated by SAP Payroll:
$800 base pay Update payroll cluster
Period accrual generated by SAP Time Evaluation:
12 hours vacation Update Infotype 2006 (Absence Quota)
44 44
Example of Retro Calculation: Retroactive Change
Retro change for bi-weekly period 01/06/08-01/19/08
Changed 80 hours of Regular Work to 60 hours in CATS
Entered 20 hours of Unpaid Leave into CATS
Current period adjustment generated by SAP Payroll
- $200 base pay Change of payroll cluster
Accrual adjustment generated by SAP Time Evaluation
9 hours vacation Change of Infotype 2006 (Absence Quota)
45 45
Time Data Reporting Options with SAP
SAP offers a wide range of reporting alternatives
In addition to different levels of standard reporting, the
SAP development environment allows for development
of custom reports with full integration into all SAP data
objects:
Human Resource Information System (HRIS)
SAP ERP standard reports
SAP NetWeaver
BI standard reports
SAP Query
SAP custom reports
46 46
Data Output Options with SAP
If gross payroll processing does not reside within SAP,
there are several options to interface the time evaluation
data to a to third-party payroll
Depending on the scenario, there can be different flavors
of time data that are interfaced out of SAP:
Raw absences and/or attendances (either directly out of CATS
or out of Infotypes 2001/2002)
Raw employee remuneration data (either directly out of CATS or
out of Infotypes 2010)
Wage types and hours by employee after time evaluation (out of
cluster B2 table ZL after time evaluation)
47 47
Data Output Options with SAP (cont.)
Possible approaches for outbound interfaces
Custom interface using BAPIs
RPTEZL00 Supply Third-Party Payroll System
PU12 Interface Toolbox
48
SAP Time Management Integration
48
Attendances/
absences
Work
schedule
Availability
Time
events
FI and CO
Abs./Att.
quotas
Time balances
Payroll
Capacity
Planning
Activity
Allocation
CO
CATS
PM, PS,
MM-SRV
Remuneration
specification
Time
Evaluation
Time
wage types
3
rd
-Party
Payroll
PCC1
PCC2
Workflow
PA
OM
TM PY
Approval
49 49
SAP Time Management Integration (cont.)
Integration points to SAP HCM processes
Payroll All roads lead to Payroll
Personnel Administration
Organizational Management
Integration points to other SAP processes
Plant Maintenance (PM) activity, receiving order
Project System (PS) project code
External Services Management (MM-SRV) service number,
purchase order
Financials/Controlling (FI/CO) cost center, WBS, activity
50 50
SAP Time Management Integration (cont.)
SAP Infrastructure
Portal
ESS
BI/BW
SAP Security
Structural authorizations
SAP Workflow
51
Time Entry Approval Reporting Scheduling Accrual Time Evaluation SAP Integration Points
B
a
d
g
e
B
i
o
m
e
t
r
i
c
s
W
E
B
P
C
P
a
y
r
o
l
l
P
A
/
O
M
F
I
/
C
O
/
P
S
/
M
M
W
o
r
k
f
l
o
w
S
e
c
u
r
i
t
y
OI
n
f
r
a
s
t
r
u
c
t
u
r
e
SAP X X X X X X X X X X X X
Bolt-On X X X
Degree of integration
SAP Time Management Integration (cont.)
As part of your decision process to select the right strategy, do
not underestimate the power of SAP integration and consider the
downsides due to disintegration when decoupling functionality
and data from your core SAP system
52 52
Issues Due to Lack of Integration
Common payroll issues due to decoupling time
entry/time evaluation from SAP Payroll
Calculation of salaried exempt paid/unpaid absences
Regular Rate of Pay (RROP) calculation for overtime payments
Retroactive time entry changes
Retroactive organization assignment changes
Retroactive work schedule changes
53 53
Issues Due to Lack of Integration (cont.)
Common quota accrual and quota balance tracking
issues due to decoupling time entry/time evaluation from
SAP quota accrual:
Quota accrual requires worked hours for proration
Absence entries greater than scheduled hours
Absence entries on OFF days
Retroactive time entry changes
Retroactive organization assignment changes
Retroactive work schedule changes
Retroactive anniversary data changes
Accurate sick and vacation liability reporting
Accurate ESS sick and vacation balance display to employees
54 54
Issues Due to Lack of Integration (cont.)
Other common issues due to decoupling time entry/time
evaluation from SAP HR/payroll:
Time approval employees by supervisor
Qualifications for scheduling
Detailed absence/attendance reporting
Accurate labor cost reporting
Redundant data definitions (cost objects, wage types, PERNR)
Additional interfaces required
SAP HR mini master time system
Valid SAP cost objects time system
Quota balances time system
Time extract SAP Payroll
55 55 55
What Well Cover
Exploring time management business processes
Examining decision criteria
Introducing time management players
Understanding SAP Time Management functionality
Developing custom solutions using SAP tools
Selecting the right strategy
Implementing SAP Time Management
Wrap-up
56 56
Custom Solution Development with SAP Tools
ABAP Workbench
BAPIs
Standard user exits
Business Add-Ins (BAdIs)
Enhancements
SAP NetWeaver Developer Studio
SAP Visual Composer
SAP Java Connector
Test Workbench
SAP Solution Manager
SAP Correction and Transport System
57 57
Custom Solution Development with SAP Tools (cont.)
SAP HCM-Specific Tools
PM01 Maintain/Create Personnel Admin. Infotypes
PPCI Maintain/Create Personnel Planning Infotypes
PE03 Maintain Features
PE04 Maintain Functions and Operations for Time and Payroll
HRFORMS HR Forms Workplace
58 58
Custom Solution Development with SAP Tools (cont.)
Speed to market
Quickly adapt to rapidly changing business and market
conditions
Leap-frog and have a competitive advantage
Quality and upgradability
Ensure quality and protect upgradability by leveraging SAP
development methodologies
Lower risk
Be confident that your solution is synchronized with SAPs
release strategy
59 59
Custom Solution Development with SAP Tools (cont.)
Development resources
Leverage your existing SAP support resources/skills
SAP custom development
SAP consulting firms
60
Leverage What You Paid For
Development workbench
Extended Computer Aided Test Tool (eCATT)
Version control
Basis/Security/Job scheduling
Change and Transport System (CTS)
Performance monitoring
Scalability
No additional license fees
61 61 61
What Well Cover
Exploring time management business processes
Examining decision criteria
Introducing time management players
Understanding SAP Time Management functionality
Developing custom solutions using SAP tools
Selecting the right strategy
Implementing SAP Time Management
Wrap-up
62 62
Checklist for Selecting the Right Strategy
1. Define your time management scope
Organizational
Functional
Technical
2. Define process and functional requirements
3. Evaluate existing SAP TM functionality
4. Conduct detailed gap analysis and identify SAP gaps
5. Compare Solution Alternatives for gap resolution
Consult experienced SAP HCM Solution Architect
Compare SAP enhancement vs. bolt-on system
TCO = Implementation cost + license fees + support cost
Include soft benefits in your comparison
63
Methodology for Selecting the Right Strategy
Design
Define TM Scope
GAP Analysis
Learn about all SAP TM capabilities
Map SAP TM functionality to functional
requirements
Identify and document SAP TM gaps
Analyze 3
rd
-Party TM products
Analyze SAP Enhancement alternatives
Document Final list of alternatives
Conduct cost comparison:
License Cost
Implementation Cost
Support Cost
Hidden Cost
Finalize TM Strategy
Decision
64 64
Comparing SAP Enhancements to Bolt-On System Solution
Category SAP Enhancement Bolt-On
Functionality Unlimited Leap-Frog Limited
Integration
Other SAP Application data
Security
Workflow
Integration Interface(s)
Data Unification
Accurate
No duplicates
Normalized
YES NO
Development Environment Consistent Different
Skills Consistent Different
Version Management Consistent Different or N/A
Migration Pipeline Consistent Different or N/A
Security Consistent Different or N/A
License Fees No Additional Additional
Release strategy Consistent Different
Scalability Consistent Different
Testing Consistent Different
Support Consistent Different
Landscape Homogenous Heterogeneous
Standardization
Uniform reporting
Uniform codes (PERNR, chart of accounts, etc.)
Harmonization of master data
Optimization of business processes
Front-end look and feel
Consistent Different
65 65
Your Current and Future ERP Strategy
IF your current and future ERP strategy is SAP
Put on your SAP hat
Leverage your existing SAP investment
Leverage your existing SAP development and support staff and
infrastructure
Avoid rebuilding a heterogeneous IT landscape
Explore the SAP toolkit to bridge functionality gaps
ELSE
Why are you here?
66 66 66
What Well Cover
Exploring time management business processes
Examining decision criteria
Introducing time management players
Understanding SAP Time Management functionality
Developing custom solutions using SAP tools
Selecting the right strategy
Implementing SAP Time Management
Wrap-up
67 67
SAP Time Management Implementation Scenarios
With different time management system scenarios come
various issues
Interfaces and dis-integration points can be avoided
by using SAP standard wherever possible
Interfaces cause:
Increase in overall system complexity
Higher long-term support costs (TCO)
Data redundancy
Slower adaptability to business changes
68 68
SAP Time Management Implementation Scenario 1
SAP
Payroll
OnCall
(IVR)
WTE
EE-Info/
Schedule
PA/Vac
Liability
(G/L)
WTE
OT Data
PeopleSoft
Payroll
Employee
Data
Hours &
Time
Codes per
Employee
PA/Vac
Hours &
Dollars per
Employee
Bi-weekly
Hours &
Wage
Types per
Employee
Generate GPR
Transmission
File RPTEZL00
Check Hours
& Wage
Types per
Employee
Time Evaluation
RPTIME00
OMR2SAP
Interface
Schedule
Assignment
PeopleSoft
Master Data
Daily
Employee
Data
Changes
Absences,
Attendance
On Call,
Pay in Lieu
Employee
Time Data
Entry
Custom TM
WebTime Entry
Time
Data Master
Data
Shift/
Schedule
Changes
Create and
FTP Flatfile
with Time
Events
WTE
PA/VAC
Balances
PA/Vac,
Holiday
Balances
per
Employee
Custom
PA/Vacation
Accrual
Program
HR Mini
Master &
Cost
Objects
69
RROP calculation for original time entry
Hours Rate Factor Earnings
Regular 40 10 1 400.00
OT 3 10 1 30.00
Bonus 100.00
Total Base 43 530.00
RROP Rate
FLSA Rate (Total Earnings/Total Hours) 12.33
Overtime Premium
Hours Rate Factor Earnings
OT 3 12.32558 0.5 18.49
Total Compensation
Base Pay 530.00
Premium 18.49
548.49
RROP calculation after retroactive changes
Hours Rate Factor Earnings
Regular 40 10 1 400.00
OT 1 10 1 10.00
Bonus 100.00
Total Base 41 510.00
RROP Rate
FLSA Rate (Total Earnings/Total Hours) 12.44
Overtime Premium
Hours Rate Factor Earnings
OT 1 12.43902 0.5 6.22
Total Compensation
Base Pay 510.00
Premium 6.22
516.22
SAP Time Management Implementation Scenario 1 (cont.)
SAP to PeopleSoft payroll interface issue
RROP calculation for OT in payroll cannot be accurately made
based on hours worked/week because the hours are
accumulated on a bi-weekly level
Retro changes for RROP rate must be calculated manually
70
SAP Time Management Implementation Scenario 1 (cont.)
Third-party TM to SAP interface issues
Paid and unpaid absence calculations and splits for salaried
non-exempt employees
Retroactive time data changes
Absences on unscheduled days
Absences with hours greater than planned hours
71 71
SAP Time Management Implementation Scenario 2
ADP
Payroll
Hours &
Wage
Types per
Employee
Time Evaluation
RPTIME00
PA/VA Accrual
Schedule
Assignment
Weekly
Lump-sum
Absences,
Remuneration
Hrs & Wage
Types
Employee
Time Data
Entry
3
rd
-Party TM
Time Entry
Time
Data Master
Data
HR Mini
Master &
Cost
Objects
CAT2
Time Entry
HR Mini
Master &
Cost
Objects
FI/CO
Labor Cost
Distribution
CATS
FI/CO
Cost
Objects
Shift/
Schedule
Changes
72
SAP Time Management Implementation Scenario 2 (cont.)
SAP to ADP payroll interface issue
Limited retro calculation capability
ADP to SAP FI/CO interface issues
No retro calculation capability for FI postings
No detail of internal technical wage types, period balances,
QTD/YTD balances that can be tracked in SAP
Third-party TM to SAP interface issues
Paid/unpaid absence calculations and splits for salaried
non-exempt employees
Retroactive time data changes
Absences on unscheduled days
Absences with hours greater than planned hours
73 73
SAP Time Management Implementation Scenario 3
Hrs and Wage
types
Per Employee
Employee
Time Data
Entry
3
rd
-Party TM
Scheduling
Time Entry
Time Evaluation
PA/VAC Accrual
Time
Data Master
Data
Shift/
Schedule
Changes
HR Mini
Master &
Cost
Objects
CAT2
Time Entry
FI/CO
CATS
Payroll
RPCALCU0
Cost
Objects
PA/VAC
Balances
74
SAP Time Management Implementation Scenario 3 (cont.)
Absence/vacation accrual issues
Limited retro calculation capabilities for accruals
No automatic triggering of retro-calculation based on SAP
master data changes
Time evaluation issues
Limited retro calculation capability for wage types and hours
No automatic triggering of retro-calculation based on SAP
master data changes
RROP calculation and recalculation accuracy
75
SAP Time Management Implementation Scenario 3 (cont.)
Third-party TM to SAP interface issues
Paid and unpaid absence calculations and splits for salaried
non-exempt employees
Retroactive time data changes
Absences on unscheduled days
Absences with hours greater than planned hours
76 76
Dos and Donts for SAP Time Management Implementations
Push-out as much functionality as possible into SAP to
take advantage of the SAP integration effects
Challenge the need for best-of-breed front-end
functionality if you can provide a similar front-end
with SAP
Time evaluation and accrual can have a complex set
of rules
Some vendors sell easy plug & play templates that usually
require as much custom work as the set-up of time schemas
and Personnel Calculation Rules (PCRs) in SAP
SAP schemas and PCRs are very flexible and can reflect
any calculation and accrual scenario so build these
rules in SAP rather than in a bolt-on
77 77
Dos and Donts for SAP Time Management
Implementations (cont.)
If you have to build custom interfaces for time entry from
third-party systems, design a robust error log that allows
easy troubleshooting
You do not have to have a one-for-all solution and can
use different SAP time management processes for
different types of employees and/or locations
Define a proper regression test strategy to carefully test
the time evaluation and accrual processes and results
after any configuration change or enhancement to these
processes
Electronic extract and comparison tools help reduce risk
78 78
Dos and Donts for SAP Time Management
Implementations (cont.)
The main recipient of the time data is payroll: All roads
lead to payroll
Therefore the accuracy of time data has a direct impact
on your payroll accuracy
Federal and state rule compliance
Corporate rule compliance
Union contract compliance
Non-compliance can cause high cost
Manual labor required to fix payroll calculation issues
Loss of manual labor for strategic HR/payroll work
Legal claims and lawsuits
79 79 79
What Well Cover
Exploring time management business processes
Examining decision criteria
Introducing time management players
Understanding SAP Time Management functionality
Developing custom solutions using SAP tools
Selecting the right strategy
Implementing SAP Time Management
Wrap-up
80 80 80
Resources
Personnel Time Management
http://help.sap.com/saphelp_47x200/helpdata/en/8a/9868bc46c4
11d189470000e829fbbd/frameset.htm
SAP Note 897623: User exits and BAdIs in the PT area
SAP PRESS Publications
Ewald Brochhausen, Juergen Kielisch, Juergen Schnerring,
Jens Staeck, mySAP HR: Technical Principles and
Programming (SAP PRESS, 2003).
Christian Krmer, Sven Ringling, and Song Yang, Mastering HR
Management with SAP (SAP PRESS, 2006).
Martin Gillet, Integrating CATS (SAP PRESS, 2006).
Where
to
FIND it
81 81 81
7 Key Points to Take Home
Consider all variables impacting a decision for your time
management strategy
Get to know all SAP Time Management capabilities and
functions in detail
Consider bridging potential SAP TM functionality gaps
by building the missing functionality within SAP, using
SAP development tools
SAP Time Management is tightly integrated with SAP
Payroll and SAP HR
Decoupling the three causes many downstream issues
When choosing a bolt-on solution, ensure that the
vendor offers SAP-certified interface(s)
82 82 82
7 Key Points to Take Home (cont.)
Dont buy redundant functionality that you own already
SAP Time Management is complex, but very flexible
Consult an experienced SAP Time Management Solution
Architect before finalizing your time management strategy
83 83 83
Your Turn!
How to contact me:
Dirk Liepold
dirkl@rowsix.net
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Sulzer S20UDocument180 pagesSulzer S20Uhartley112100% (4)
- HR400Document14 pagesHR400SureshPas encore d'évaluation
- How Cathay Pacific Leveraged IT to Support Business GrowthDocument2 pagesHow Cathay Pacific Leveraged IT to Support Business Growthranjeeeth8569100% (1)
- Time Recording Using CatsDocument89 pagesTime Recording Using Catsrajeevmenon2003100% (3)
- SAP HR Training Course OverviewDocument2 pagesSAP HR Training Course OverviewVishal ShorgharPas encore d'évaluation
- Time Evaluation With Clock TimesDocument310 pagesTime Evaluation With Clock Timesravibabu1620100% (2)
- Sap HR/HCM: Cross Application Time SheetDocument4 pagesSap HR/HCM: Cross Application Time Sheetclaoker100% (2)
- Integration Case Study: Sap Erp 6.0Document32 pagesIntegration Case Study: Sap Erp 6.0majid DPas encore d'évaluation
- Processing Classes (SAP HCM)Document5 pagesProcessing Classes (SAP HCM)chinnipappu1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Expert Mode Organizational Units/Objects Transaction CodesDocument51 pagesExpert Mode Organizational Units/Objects Transaction CodesPradeep KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Payroll Troubleshooting Reference GuideDocument75 pagesPayroll Troubleshooting Reference Guidesenthilmask80Pas encore d'évaluation
- CATS FAQsDocument19 pagesCATS FAQsunfriendly.gy2268Pas encore d'évaluation
- Honda Sales ProjectDocument72 pagesHonda Sales Projectsurendar100% (2)
- Mark11 Spare Parts Section - REV3Document72 pagesMark11 Spare Parts Section - REV3Orlando MelipillanPas encore d'évaluation
- About Sap CatsDocument9 pagesAbout Sap CatsElena Puscu100% (1)
- Sap CatsDocument1 pageSap Catsrtelagamsetty2211Pas encore d'évaluation
- SAP Human Capital Management: Time Recording Using CATSDocument89 pagesSAP Human Capital Management: Time Recording Using CATSrajeevmenon2003Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Fundamentals of Customizing SAP Payroll With Schemas, Rules, Functions, and OperationsDocument72 pagesThe Fundamentals of Customizing SAP Payroll With Schemas, Rules, Functions, and OperationsVishalPas encore d'évaluation
- Understand SAP HR Payroll Clusters and TablesDocument7 pagesUnderstand SAP HR Payroll Clusters and TablesarunPas encore d'évaluation
- Sap HCM (Om) Configuration DocumentDocument63 pagesSap HCM (Om) Configuration DocumentBuhle Mtshweni100% (5)
- SAP HR Sample Resume 1Document8 pagesSAP HR Sample Resume 1Alok ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- Configuring SAP HR Payroll Settings For Retroactive AccountingDocument1 pageConfiguring SAP HR Payroll Settings For Retroactive Accountingravibabu1620Pas encore d'évaluation
- Integrating Personnel and Organizational Management in SAPDocument89 pagesIntegrating Personnel and Organizational Management in SAPnaren_3456Pas encore d'évaluation
- Organizational & Personnel ManagementDocument474 pagesOrganizational & Personnel ManagementSushil Makee43% (7)
- Mastering The Six SAP Payroll Building BlocksDocument73 pagesMastering The Six SAP Payroll Building BlocksPikiniso100% (1)
- Sap CatsDocument29 pagesSap CatsElena PuscuPas encore d'évaluation
- SAP HR Transaction CodesDocument17 pagesSAP HR Transaction CodesSuprasanna PradhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Interview Questions - SAP HRDocument13 pagesInterview Questions - SAP HRrajesh600Pas encore d'évaluation
- SAP Time MGMT CDocument95 pagesSAP Time MGMT CjigargandPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Absence QuotasDocument31 pagesUnderstanding Absence QuotasHan Maryani100% (1)
- SAP HR Time Management TroubleshootingDocument22 pagesSAP HR Time Management Troubleshootingemin3mfan7756100% (2)
- Sap HR Payroll Procedure Manual For End UsersDocument126 pagesSap HR Payroll Procedure Manual For End UsersRahul KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- SAP HR Time Management User Manual WWW Sapdocs PDFDocument52 pagesSAP HR Time Management User Manual WWW Sapdocs PDFpuspaoktavianiPas encore d'évaluation
- CatsDocument19 pagesCatsmfmyPas encore d'évaluation
- SAP Payroll Basics - Part 1 - Insight Consulting PartnersDocument2 pagesSAP Payroll Basics - Part 1 - Insight Consulting PartnersDionisis Panagopoulos100% (1)
- Payroll SapDocument15 pagesPayroll Sapeurofighter100% (1)
- SAP ERP HCM Wage Types, Pay Structures and Master Data MaintenanceDocument10 pagesSAP ERP HCM Wage Types, Pay Structures and Master Data Maintenanceravibabu1620100% (1)
- Reka Sap HR Pa NotesDocument24 pagesReka Sap HR Pa Notestekkie4Pas encore d'évaluation
- SAP HR Time ManagementDocument37 pagesSAP HR Time Managementsatya.patna100% (4)
- SAP HCM Study Material - PayrollDocument8 pagesSAP HCM Study Material - PayrollAditya_Vickram_540Pas encore d'évaluation
- Time Schema SAPDocument3 pagesTime Schema SAPanupthkPas encore d'évaluation
- Fesco Sap HCM BBP V1 PDFDocument177 pagesFesco Sap HCM BBP V1 PDFAsad100% (3)
- 4.1 Payroll PDFDocument19 pages4.1 Payroll PDFjfmorales100% (1)
- Sap HCMDocument4 pagesSap HCMchhabramanujPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of SAP ConfigurationDocument113 pagesOverview of SAP ConfigurationNashwa MuhammedPas encore d'évaluation
- SAP HCM Payroll Concepts and ProcessesDocument17 pagesSAP HCM Payroll Concepts and ProcessesRitu Gupta100% (2)
- Kindly Find The Complete Steps For Indian Payroll ConfigurationDocument10 pagesKindly Find The Complete Steps For Indian Payroll ConfigurationAmruta HanagandiPas encore d'évaluation
- SAP HCM - Absence Quota GenerationDocument39 pagesSAP HCM - Absence Quota Generationsainath89100% (6)
- Understanding HR Schema and PCR With An ExampleDocument7 pagesUnderstanding HR Schema and PCR With An Examplemadaxx2010100% (1)
- Guide For Overtime PCRDocument28 pagesGuide For Overtime PCRVishwanath RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- SAP HR - HCM - Personnel AdministrationDocument9 pagesSAP HR - HCM - Personnel AdministrationMrinal Kanti DasPas encore d'évaluation
- SAP interface programming with RFC and VBA: Edit SAP data with MS AccessD'EverandSAP interface programming with RFC and VBA: Edit SAP data with MS AccessPas encore d'évaluation
- Consultant Handbook For New GLDocument53 pagesConsultant Handbook For New GLPrashant SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 25 PY PayrollDocument98 pagesChap 25 PY Payrollokail72Pas encore d'évaluation
- SAP HR InfotypesDocument7 pagesSAP HR InfotypesRamPas encore d'évaluation
- FS10N-DisplayG LAccountBalanceDocument2 pagesFS10N-DisplayG LAccountBalanceSingh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Payroll & Time Test Tool (PTTT)Document1 pagePayroll & Time Test Tool (PTTT)Singh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- FB03 Display GL/AP Documents: PurposeDocument2 pagesFB03 Display GL/AP Documents: PurposeSingh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- SAP HR Config AllDocument486 pagesSAP HR Config AllSatyendra Gupta100% (1)
- HR and Finance ConfiDocument87 pagesHR and Finance ConfiSingh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mastering The Six SAP Payroll Building BlocksDocument73 pagesMastering The Six SAP Payroll Building BlocksPikiniso100% (1)
- TCodes Abap PDFDocument0 pageTCodes Abap PDFSingh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- FS10N-DisplayG LAccountBalanceDocument2 pagesFS10N-DisplayG LAccountBalanceSingh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Catc ReportDocument5 pagesCatc ReportSingh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- FK06 MarkvendorfordeletionDocument2 pagesFK06 MarkvendorfordeletionSingh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- View Vendor BalancesDocument2 pagesView Vendor BalancesSingh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- FK03 DisplayavendormasterrecordDocument6 pagesFK03 DisplayavendormasterrecordSingh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- FK04 DisplayVendorAccountChangesDocument2 pagesFK04 DisplayVendorAccountChangesSingh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- FK02 ChangeaVendorMasterRecordDocument7 pagesFK02 ChangeaVendorMasterRecordSingh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- FK05 Block UnblockVendorDocument2 pagesFK05 Block UnblockVendorSingh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- FK01 CreateaVendorMasterRecordDocument7 pagesFK01 CreateaVendorMasterRecordSingh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- FI03 Display Bank Master Data: PurposeDocument2 pagesFI03 Display Bank Master Data: PurposeSingh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- FCHN AbandonedcheckprocessDocument11 pagesFCHN AbandonedcheckprocessSingh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Change Bank Master Data DetailsDocument2 pagesChange Bank Master Data DetailsSingh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- FCH7 ReprintCheckDocument2 pagesFCH7 ReprintCheckSingh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Create Bank DataDocument2 pagesCreate Bank DataSingh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- FCH8 CancelCheckPaymentDocument2 pagesFCH8 CancelCheckPaymentSingh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- FBL3n-Display ChangeG LAccountLineItemsDocument2 pagesFBL3n-Display ChangeG LAccountLineItemsSingh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- FCHN DisplayCheckRegisterDocument3 pagesFCHN DisplayCheckRegisterSingh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- FCH2 DisplayPaymentDocumentChecksDocument2 pagesFCH2 DisplayPaymentDocumentChecksSingh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fch1 Display Check Information: PurposeDocument2 pagesFch1 Display Check Information: PurposeSingh 10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Raju - Reliability EngineerDocument2 pagesRaju - Reliability EngineerMadhuseptember2022Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Hook Sping 2002Document11 pagesThe Hook Sping 2002Larry FeldhausPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.7 Conveyor Belt Operating ProcedureDocument3 pages4.7 Conveyor Belt Operating Procedurejohnson OlubiPas encore d'évaluation
- Icmeas 2017: Local Advisory CommitteeDocument3 pagesIcmeas 2017: Local Advisory CommitteeZawad AbedinPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines For HOLES in BONDEK II SheetDocument4 pagesGuidelines For HOLES in BONDEK II SheetSK ChauPas encore d'évaluation
- The Envelopes of The Arts Centre in SingaporeDocument12 pagesThe Envelopes of The Arts Centre in SingaporeAndriPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of Sabah and Labuan Grid Code 16 June 2014Document81 pagesOverview of Sabah and Labuan Grid Code 16 June 2014kiddjoe1470100% (1)
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning: Technical DescriptionDocument27 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning: Technical DescriptionFranz CorasPas encore d'évaluation
- Jha of PaintingDocument3 pagesJha of PaintingAllan Camacho Regalado100% (1)
- DOE-0359 Hanford Site Electrical Safety ProgramDocument59 pagesDOE-0359 Hanford Site Electrical Safety Programandresboy123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Oracle Communications Billing and Revenue Management Product ReviewDocument21 pagesOracle Communications Billing and Revenue Management Product ReviewJohn SitholePas encore d'évaluation
- Crane Safety Program EssentialsDocument11 pagesCrane Safety Program Essentialssekhargm100% (1)
- Borehole Imaging Tools PDFDocument4 pagesBorehole Imaging Tools PDFshahbazmirzaPas encore d'évaluation
- List of BAPIsDocument35 pagesList of BAPIsthiago.alves.85Pas encore d'évaluation
- International GTA220Document1 pageInternational GTA220Anwar MdPas encore d'évaluation
- Double-Multiple StramtubeDocument9 pagesDouble-Multiple StramtubeTheo PopaPas encore d'évaluation
- bb9df927-5af1-44e0-ae49-d3fd10a5eb4b (1)Document6 pagesbb9df927-5af1-44e0-ae49-d3fd10a5eb4b (1)anonymphantomPas encore d'évaluation
- Brochure - FTTH Drop Cabinet For 48f & 96f Customer ConnectionsDocument8 pagesBrochure - FTTH Drop Cabinet For 48f & 96f Customer ConnectionskmalPas encore d'évaluation
- Procu Man Supple 9Document3 pagesProcu Man Supple 9ruwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Strategic Management g9 Elon Musk BetsDocument5 pagesStrategic Management g9 Elon Musk BetsJaya Neelanshi SethPas encore d'évaluation
- 2008 10 6 4R70W InterchangeDocument14 pages2008 10 6 4R70W InterchangeJon Rodriguez100% (4)
- IBM Maximo Products V7.1Document143 pagesIBM Maximo Products V7.1dayooyefugaPas encore d'évaluation
- Upper West Side Town House Construction SetDocument34 pagesUpper West Side Town House Construction SethannahchiaroniclarkePas encore d'évaluation
- CH 02Document39 pagesCH 02enamislamPas encore d'évaluation
- Written Lockout/Tagout Program University of South Carolina (Enter Department Name Here)Document13 pagesWritten Lockout/Tagout Program University of South Carolina (Enter Department Name Here)SaidPas encore d'évaluation
- UF Table For Lighting PDFDocument2 pagesUF Table For Lighting PDFperckys kabudiPas encore d'évaluation