Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
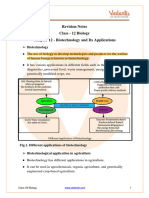
Chapter - 12: Quick Revision Notes Biotechnology and Its Applications Important Terms
Transféré par
Shaharukh NadafTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Chapter - 12: Quick Revision Notes Biotechnology and Its Applications Important Terms
Transféré par
Shaharukh NadafDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Quick Revision
67
CHAPTER 12
Quick Revision Notes
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND ITS APPLICATIONS
Important terms
1)
Transgenics The genetically modified organism that contains a foreign gene or segment
of DNA and expresses it.
2) Biopiracy - Use of bioresources by countries, multinational companies and other
organisations without proper legal authorisation.
Biotechnological applications
(1) IN AGRICULTURE
a)
Genetically Modified plants Genetic modification has
(i)
made crops more tolerant to abiotic stresses.
(ii)
reduced dependence of chemical pesticides.
(iii) helped to reduce post harvest losses.
(iv) increased efficiency of plant to use of minerals
(v)
fortification of plants with various nutrients.
b) Bt. Cotton
A bacteria Bacllus thuringiensis has cry gene which codes a toxin protein.
These genes can be incorporated in plants such as cotton which are infected
by cotton bollworm.
If these plants are eaten by the insect, the toxin which exist as inactive protoxins
in the bacteria or the genetically modified plant gets activated due to alkaline
pH of the gut.
The activated toxin binds to the surface of hindgut epithelial cells and create
pores that cause swelling and lysis and eventually death of the insect.
c) Pest Resistant Plants - Developed on the basis of RNA interference.
It takes place when mRNA of the pest in silenced i.e. not allowed to translate
due to the formation of dsRNA.
(2) BIOTECHNOLOGICAL APPLICATION IN MEDICINE (i) Genetically Engineered Insulin
Insulin from animal sources used to cause allergy and reactions in human beings so
it was genetically engineered in bacteria.
Structure of insulin
Insulin in mammals exists as pro-hormone. It has A, B, C polypeptide from which C
peptide is removed for becoming active form.
A and B chains are bridged by disulphide bonds.
68
BiologyXII
Maturation of pro-insulin into insulin
3)
Preparation of Insulin
Prepared in 1983 by Eli Lily, an American Company.
Prepared two DNA sequences corresponding to A and B chains of human insulin and
introduced them in plasmids of E. coli to produce insulin chains.
Chains A and B were produced separately and combined by disulphide bonds to
create human insulin.
Gene therapy
The diseases which are due to defect in some gene can be cured by incorporating
the correct functional gene in body cells which take over the non-functional gene.
The first clinical gene therapy was given in 1990 to a girl with adenosine deaminase
(ADA) deficiency.
It is caused due to deletion of the gene for adenosine deaminase.
Here lymphocytes from the blood of the patient are grown in a culture outside the
body.
A functional ADA cDNA is then introduced into these lymphocytes which are then
returned in the patient.
It is not a permanent cure and periodic infusion of such genetically engineered
leucocytes is required.
A permanent cure would be to isolate the gene producing ADA from marrow cells
and introducing the gene at early embryonic stage.
4) Molecular diagnosis
PCR is done to detect HIV, mutation in genes, genetic disorders and to amplify DNA
for DNA fingerprinting.
ELISA is done by which infection of pathogen can be detected by presence of antigen
or by detecting antibodies synthesised against pathogens.
Transgenic Animals Animals that have had their DNA manipulated to possess and express
a foreign gene. Transgenic rats, rabbits, pigs, sheep and cows have been produced.
Need for developing transgenic animals(i) These animals enable scientists to study the working of genes, their regulation,
Quick Revision
69
effect on normal body functions and development i.e. study normal physiology and
development.
(ii) Study of disease The role of genes in development of diseases can be studied through
transgenic animals.
(iii) Biological products Transgenic animals that produce useful biological products can be
created by introduction of the portion of DNA which codes for a particular product.
(iv) Vaccine safety Transgenic mice are being developed for use in testing the safety of
vaccines before they are used on humans.
(v) Chemical safety testing Toxicity of drugs is also tested on transgenic animals.
ETHICAL ISSUES
Genetic modification of organisms can have unpredictable results when such organisms
are introduced into the ecosystem.
Indian government has set up organisations such as GEAC Genetic Engineering
Approval Committee, which will make decisions regarding the validity of GM research
and the safety of introducing GM organisms for public services.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Structure of DnaDocument5 pagesStructure of Dnaapi-253560385Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter-10 Class 12biologyDocument4 pagesChapter-10 Class 12biologytanyaverma2729Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biotechnology ApplicationDocument5 pagesBiotechnology ApplicationSabith tvPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio ApplicationsDocument4 pagesBio ApplicationskaiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsDocument9 pagesBiotechnology and Its Applicationstamalbio7Pas encore d'évaluation
- XII-12-Biotechnology and Its ApplicationDocument33 pagesXII-12-Biotechnology and Its Applicationmy yoPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 CH 12Document4 pages12 CH 12Ring BabuPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 12. Xii Biotechnology and Its ApplicationDocument33 pagesChapter 12. Xii Biotechnology and Its ApplicationBeena PalPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 25 - EditedDocument10 pagesModule 25 - Editedrichard reyesPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 12 Biology - Biotechnology and Its Applications AssignmentDocument8 pagesCBSE Class 12 Biology - Biotechnology and Its Applications AssignmentSuresh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOTECHNOLOGY and Its Applications Class 12Document4 pagesBIOTECHNOLOGY and Its Applications Class 12Albina Zainab P.TPas encore d'évaluation
- Therapeutic Proteins: Presented By:Rafa Zubair N.V First M.Pharm Department of PharmacologyDocument28 pagesTherapeutic Proteins: Presented By:Rafa Zubair N.V First M.Pharm Department of PharmacologykhawarkhubaibPas encore d'évaluation
- Biotechnology ApplicationsDocument38 pagesBiotechnology ApplicationsTulika BholaPas encore d'évaluation
- © Ncert Not To Be Published: Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsDocument10 pages© Ncert Not To Be Published: Biotechnology and Its Applicationsaayushi24681438Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsDocument4 pagesBiotechnology and Its ApplicationsRavi RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic EngineeringDocument17 pagesGenetic EngineeringDALEY ZISSPas encore d'évaluation
- Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsDocument8 pagesBiotechnology and Its ApplicationsS SURAJPas encore d'évaluation
- Biotech ResearchDocument7 pagesBiotech Researchthekingraja2602Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biotechnology and Its Applications Chapter - 12Document5 pagesBiotechnology and Its Applications Chapter - 12Mauz KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Biology 12th Term II Ch. 4Document2 pagesCBSE Biology 12th Term II Ch. 4Abhishek GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Ch12Document7 pagesBiology Ch12Kalyan ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 12Document6 pagesChapter 12a34146525Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biotechnology and It's ApplicationsDocument19 pagesBiotechnology and It's Applicationssharmakrati762Pas encore d'évaluation
- Udaan 97,+2 Bio, 27.12.2022Document8 pagesUdaan 97,+2 Bio, 27.12.2022Mandeep KaurPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 25 Edited Pages DeletedDocument12 pagesModule 25 Edited Pages DeletedDos DosPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic Engineering Gr11Document33 pagesGenetic Engineering Gr11Ravindra Persaud 9APas encore d'évaluation
- Final AyushDocument19 pagesFinal Ayushmdgst2021Pas encore d'évaluation
- BiotechnologyDocument81 pagesBiotechnologyYvonne Dulay BarrozoPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 12 CH 12 Bio - 221015 - 211431Document27 pagesClass 12 CH 12 Bio - 221015 - 211431Anant VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 12 - Biology - Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsDocument5 pagesClass 12 - Biology - Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsMonalisa MajhiPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 12Document6 pagesCH 12Влад СуботковскийPas encore d'évaluation
- Scitech Topic 11Document14 pagesScitech Topic 11Merca Rizza SolisPas encore d'évaluation
- Biotechnology and Its Applications Short NotesDocument3 pagesBiotechnology and Its Applications Short NotesADITYA MAHECHAPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 4 (BScBT2)Document17 pagesGroup 4 (BScBT2)Debarghya DuttaPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic EngineeringDocument35 pagesGenetic EngineeringNatalie Dela Cruz OngsiakoPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 10 ReportDocument21 pagesGroup 10 ReportAileen Mae TabilePas encore d'évaluation
- Biotech and ApplicationDocument8 pagesBiotech and ApplicationrajjoPas encore d'évaluation
- Biotechnology and Its Application Class 12 Notes Biology Chapter 12 (PDF)Document8 pagesBiotechnology and Its Application Class 12 Notes Biology Chapter 12 (PDF)vinamrapawar24905Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biotechnology and Its Application Class 12 Notes Biology Chapter 12 (PDF)Document8 pagesBiotechnology and Its Application Class 12 Notes Biology Chapter 12 (PDF)Saishreeta JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- GB2 4. Producing GMOsDocument47 pagesGB2 4. Producing GMOsMehaela Pearl MendezPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic EngineeringDocument16 pagesGenetic EngineeringVinoth Rouge Rockers100% (2)
- GMOs PDFDocument32 pagesGMOs PDFShalyn ArimaoPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOTECHNOLOGY - Applications & Ethical IssuesDocument11 pagesBIOTECHNOLOGY - Applications & Ethical IssuesKorou LaikhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance PyqDocument12 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance PyqSoumya Ranjan NaikPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter-12 Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsDocument6 pagesChapter-12 Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsbpmbhamoraPas encore d'évaluation
- Biotechnology Sir LitaDocument34 pagesBiotechnology Sir LitaJulien KhalilPas encore d'évaluation
- Biotech No L Oh y ApplicationsDocument17 pagesBiotech No L Oh y Applicationsanil.04087679Pas encore d'évaluation
- MODULE 7-GeneticsDocument10 pagesMODULE 7-GeneticsDivine Grace CincoPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledRheena FelicianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Biotech RorDocument5 pagesBiotech Roramora eliPas encore d'évaluation
- PDF 20230131 204404 0000Document15 pagesPDF 20230131 204404 0000shanmugapriyamanisadhu05Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Other Potential Applications of The New TechnologyDocument20 pagesLecture Other Potential Applications of The New TechnologyMudassar IqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- STS GmoDocument31 pagesSTS GmoJulie Ann Camacho BabaPas encore d'évaluation
- TM-08 Genetically Modified Organisms (2016)Document33 pagesTM-08 Genetically Modified Organisms (2016)ZANUBA ULYA’ HAURA CELLIN 1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Module 10 P 67 76Document10 pagesModule 10 P 67 76Blessie Ysavyll SaballePas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER VII Genetically Modified OrganismDocument16 pagesCHAPTER VII Genetically Modified OrganismMaeann FernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 Bio2 Genetic EngineeringDocument42 pagesModule 1 Bio2 Genetic Engineeringjaydie domalaonPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Unit 5Document2 pagesBio Unit 5jaina4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Novapdf: Unfiled Notes Page 1Document4 pagesNovapdf: Unfiled Notes Page 1Shaharukh NadafPas encore d'évaluation
- Wednesday, January 14, 2015 2:12 PM: NovapdfDocument3 pagesWednesday, January 14, 2015 2:12 PM: NovapdfShaharukh NadafPas encore d'évaluation
- Core Java API: I/ODocument13 pagesCore Java API: I/OShaharukh NadafPas encore d'évaluation
- M18 - Case StudyDocument32 pagesM18 - Case StudyShaharukh NadafPas encore d'évaluation
- M15 - XMLDocument36 pagesM15 - XMLShaharukh NadafPas encore d'évaluation
- Software Engineering An Overview: Ranjit Raman Team Coordinator E-Gov, C-DAC, PuneDocument37 pagesSoftware Engineering An Overview: Ranjit Raman Team Coordinator E-Gov, C-DAC, PuneShaharukh NadafPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To The Spring FrameworkDocument19 pagesIntroduction To The Spring FrameworkShaharukh NadafPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter - 11: Quick Revision Notes Biotechnology - Principle and Processes Important TermsDocument4 pagesChapter - 11: Quick Revision Notes Biotechnology - Principle and Processes Important TermsShaharukh NadafPas encore d'évaluation
- Webwork in Action: An Introduction To WebworkDocument26 pagesWebwork in Action: An Introduction To WebworkShaharukh NadafPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter - 13: Quick Revision Notes Organisms and Population Important TermsDocument5 pagesChapter - 13: Quick Revision Notes Organisms and Population Important TermsShaharukh NadafPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter - 3: Quick Revision Notes Human Reproduction Important TermsDocument7 pagesChapter - 3: Quick Revision Notes Human Reproduction Important TermsShaharukh NadafPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic EngineeringDocument3 pagesGenetic EngineeringseshatcallingPas encore d'évaluation
- DBT-JRF BET Part B Agricultural Biotechnology PDFDocument3 pagesDBT-JRF BET Part B Agricultural Biotechnology PDFambu100% (2)
- Introduction To Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsSiddhesh YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Transgene SLIENCINGDocument35 pagesTransgene SLIENCINGRajaram Krishnasamy100% (1)
- TrangenesisVs SelectiveBreedingDocument11 pagesTrangenesisVs SelectiveBreedingTomasLiefferingPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 - Genetic Engineering 1Document20 pagesModule 2 - Genetic Engineering 1Ash MiPas encore d'évaluation
- Transgenic Animals: Submitted by Pratham Varshney Xii A 23Document16 pagesTransgenic Animals: Submitted by Pratham Varshney Xii A 23PappuPas encore d'évaluation
- Long Term Follow Up After Admin Human GT Products - Jan - 2020Document37 pagesLong Term Follow Up After Admin Human GT Products - Jan - 2020DPas encore d'évaluation
- Gate 2010 PDFDocument8 pagesGate 2010 PDFKedar SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab and Zoo Animal Management: Dr. Arbab SikandarDocument15 pagesLab and Zoo Animal Management: Dr. Arbab SikandarMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal BioTechnologyDocument2 pagesAnimal BioTechnologyHồ Thanh MaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Transgenic AnimalsDocument13 pagesTransgenic AnimalsSamunderSinghSinghraPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloning Human BeingsDocument310 pagesCloning Human BeingsThe Hastings CenterPas encore d'évaluation
- 928 12 Bio Botany Sliptest Questions emDocument10 pages928 12 Bio Botany Sliptest Questions emYazer ArafathPas encore d'évaluation
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsDocument20 pages© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsMehul JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Extra Yds Deneme Sinavi 5Document20 pagesExtra Yds Deneme Sinavi 5atalikaciPas encore d'évaluation
- Dunaliella Salina As A Novel Host For The Production of Recombinant ProteinsDocument9 pagesDunaliella Salina As A Novel Host For The Production of Recombinant ProteinsMarcusPas encore d'évaluation
- Beda GMO Dan LMODocument8 pagesBeda GMO Dan LMOHollie PorterPas encore d'évaluation
- The Cloning Sourcebook - A. Klotzko (Oxford, 2001) WWDocument373 pagesThe Cloning Sourcebook - A. Klotzko (Oxford, 2001) WWAlin DumiPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Genetics and Society 2Nd Edition Yashon Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument30 pagesHuman Genetics and Society 2Nd Edition Yashon Test Bank Full Chapter PDFmagdalavicemanocgp100% (11)
- Lecture 18Document36 pagesLecture 18MOHAMMED ELNAGGARPas encore d'évaluation
- Biopharming TrainingDocument97 pagesBiopharming TrainingBalakrishnan NatarajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic ManipulationDocument51 pagesGenetic ManipulationMandre DynaPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 - Pharmaceutical Biotechnology (PCS521) - Lecture Six.Document36 pages6 - Pharmaceutical Biotechnology (PCS521) - Lecture Six.habiba nafeaPas encore d'évaluation
- Role of Plant Biotechnology in The Advancement of Classical AgricultureDocument10 pagesRole of Plant Biotechnology in The Advancement of Classical AgricultureInternational Journal of Chemical & Biological Sciences100% (2)
- Ethical Issues in Genetic Engineering and TransgenicsDocument13 pagesEthical Issues in Genetic Engineering and TransgenicsBakhtawar ShafiquePas encore d'évaluation
- Transgenic Animal 2Document47 pagesTransgenic Animal 2Dr-Rafaa EssoknePas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To CassavaDocument43 pagesIntroduction To Cassavajames agboPas encore d'évaluation
- The Process of Genetic EngineeringDocument21 pagesThe Process of Genetic EngineeringJam Gumanoy NavarroPas encore d'évaluation
- LECTURE 9-Transgenic Technology in Marine Organisms PDFDocument26 pagesLECTURE 9-Transgenic Technology in Marine Organisms PDFIntan Lestari DewiPas encore d'évaluation
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessD'Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (33)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceD'EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (517)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityD'EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceD'EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (18)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseD'EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (52)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedD'EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (11)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerD'EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (393)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionD'EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (812)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesD'EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (397)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsD'EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (6)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeD'EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifePas encore d'évaluation
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveD'EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (66)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainD'EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (110)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomD'EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (216)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainD'EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (65)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorD'EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorPas encore d'évaluation
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindD'EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (93)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)D'EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (411)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildD'EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (44)
- Darwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignD'EverandDarwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (39)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldD'EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (597)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemD'EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (115)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueD'EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (38)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperD'EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (16)