Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Drilling and Completions - 3
Transféré par
2014481102Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Drilling and Completions - 3
Transféré par
2014481102Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Drilling and Completions
Drilling techniques
Vertical drilling straight down into reservoir (in early days)
Horizontal drilling horizontally to reach the target zone e.g.
drill to penetrate the reservoir at a very shallow angle or to
expose more of low permeability reservoir to the wellbore so
that production rate is increased
Directional drilling the process of directing a wellbore along
some trajectory to a predetermined target
Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Drilling and Completions
Drilling techniques
Wellhead
Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Drilling and Completions
Application of directional drilling
Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Drilling and Completions
Application of directional drilling
Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Drilling and Completions
Application of directional drilling
Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Drilling and Completions
Application of directional drilling
Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Drilling and Completions
Application of directional drilling
Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Drilling and Completions
Application of directional drilling
Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Drilling and Completions
Application of directional drilling
Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Drilling and Completions
Drilling techniques
Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Drilling and Completions
Casing and cementing
What is casing?
Large-diameter steel pipe lowered into a borehole and
cemented in place
Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Drilling and Completions
Casing and cementing
Purpose of casing:
To prevent contamination of fresh water sands
To enhanced the probability of drilling to total depth (TD)
To seal off weak, fractured and unconsolidated
formations
To control pressure during drilling
To meet production requirements
To confine production to the wellbore
To protect the hole from the mud
To prevent water migration(from mud) to producing
formation e.g. shale tends to draw water out of the
mud causing them to swell
Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Drilling and Completions
Casing and cementing
Casing program
Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Drilling and Completions
Casing and cementing
Casing program
Surface casing
Drilling operation begins by drilling the large-diameter
surface hole to penetrate unconsolidated
formation(near to surface) and any potable water
zones
Normally a few hundred feet deep (300 5000ft)
depending on local conditions encountered
Surface casing is usually cemented to the surface
Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Drilling and Completions
Casing and cementing
Casing program
Function of surface casing
Prevent fresh-water aquifer from being contaminated
with drilling mud, gas, oil or salt water
State and federal regulations for the protection of
underground fresh-waters reservoirs are usually quite
specific about the setting depth of surface casing
Maintain hole integrity by preventing cave-in and
washout of loose formations
Minimize lost circulation into shallow, permeable zone
Provide a mean for attaching the BOPs
Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Drilling and Completions
Casing and cementing
Casing program
Function of Intermediate casing
Main application of intermediate casing is to case off
the troublesome formations that prevent the well from
being drilled to the target depth e.g. shallower weak
zones (rupture, lost circulation or stuck pipe)
Occasionally, intermediate casing is used to isolate salt
or anhydrite (calcium sulphate)formations, which may
cause drilling fluid contamination, or perhaps leak out
to such an extent as to cause pipe sticking
Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Drilling and Completions
Casing and cementing
Casing program
Production casing this string is set at a depth slight above
midway through or below the pay zone
Function isolate the producing zone from other
formations
Protect the tubing and other equipment used in the well
Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Drilling and Completions
Casing and cementing
Cementing objective of cementing is to create sheath
cement of hard cement completely filling the annular space
between the outside of the casing and the hole, thereby
blocking fluid movement and pressure up or down the annulus
Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Drilling and Completions
Casing and cementing
Cementing
Before pumping of cement
starts hard rubber bottom
plug is inserted into the casing
to minimize contamination of
the cement by mud
The pump pressure forces the
ball off its seat in the float valve
allow the cement to displace
the mud down around the shoe
and up the annulus
Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Drilling and Completions
Casing and cementing
Cementing
When bottom plugs lands on
the float valve thin rubber
disc ruptures
Pumping continues as the
cement is pumped around the
shoe and up the annulus
When the last of the cement
has been pumped, a solid
rubber (no rupture disc) follow
plug is inserted into the casing
and mud is pumped in behind it
Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Drilling and Completions
Casing and cementing
Cementing
When the follow plug lands
signaled at the surface by a
sharp pressure increase the
cementing job is over
The pumps are shut down and
pressure drops
This seats the float valve,
preventing the heavier cement
in the annulus from U-tubing
back into the casing
Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Drilling and Completions
Casing and cementing
Scratcher
Faculty of Chemical Engineering
TYPICAL CASING CONFIGURATION
Conductor (20 30 OD)
Surface Casing
(13- 3/8 20 OD)
Intermediate Casing
(9-5/8 16 OD)
Production Casing
(4-1/2 9-5/8 OD)
Liner
(4-1/2 13-3/8 OD)
TYPICAL HOLE & CASING SIZE
HOLE SIZE
CASING SIZE
DESCRIPTION
36
30
Conductor
26
20 or 18-5/8
Surface Casing
17
13-3/8
12
9-5/8
Intermediate
Casing
Production
Casing
Liner
TYPICAL CASING FUNCTIONS & SETTING DEPTH
RANGES
Casing
Type
Conductor
Functions
To seal off unconsolidated
formations to prevent erosion
Setting Depths
(from seabed)
150 600 ft
Enables circulation of drilling
fluid
Surface
Casing
Seal off any fresh water sands
Support the wellhead and BOP
equipment
Prevent lost circulation
1000 5000 ft
TYPICAL CASING FUNCTIONS & SETTING
DEPTH RANGES
Casing Type
Intermediate
Casing
Functions
Isolate troublesome
Production
Casing
formations between surface
and production casing
Normally set in the transition
between normal and
abnormal zone
Depends on the number of
problems encountered
Separate producing zones
from other formations
Conduit for production and
testing tubing
Setting Depths
(from seabed)
1,000
10,000 ft
Set across or
above pay
zone
TYPICAL CASING FUNCTIONS & SETTING
DEPTH RANGES
Casing Type
Liner
Functions
Replace intermediate
casing for deeper drilling
economic
(less than 5000
ft casing string
which is
Separate producing zones
suspended
from a liner
hanger)
Setting Depths
(from seabed)
As required
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Casing Design: by Engr. Jam Muhammad KashifDocument20 pagesCasing Design: by Engr. Jam Muhammad Kashifhasan sabahPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec Tube Well DesignDocument22 pagesLec Tube Well Designshamsa_faiz100% (1)
- Local Media5102379369261348384Document68 pagesLocal Media5102379369261348384businessdatabasesPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview To Subsea System: Research By: V. Menchavez JWPS Journeyman Welding & Piping ServicesDocument34 pagesOverview To Subsea System: Research By: V. Menchavez JWPS Journeyman Welding & Piping ServicesKentDemeterio100% (2)
- 1st - Casing - 3rd - DRILLING ENGINEERINGIDocument21 pages1st - Casing - 3rd - DRILLING ENGINEERINGImahdifahem905Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drilling EngineeringDocument67 pagesDrilling Engineering5-Simon100% (3)
- Drilling and CompletionsDocument43 pagesDrilling and CompletionsMuhammad Nursalam100% (1)
- Primary Cementing: ObjectivesDocument3 pagesPrimary Cementing: Objectiveshasan sabahPas encore d'évaluation
- PB Chapter-3Document44 pagesPB Chapter-3SHOBHIT KUMARPas encore d'évaluation
- NATMDocument24 pagesNATMningshaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cementing & Cement Evaluation PDFDocument84 pagesCementing & Cement Evaluation PDFISHAQ83% (6)
- Oil Well CasingDocument5 pagesOil Well Casingragbrown_512Pas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Construction of Auger Cast PilesDocument75 pagesDesign and Construction of Auger Cast PilesGeoteco100% (1)
- The Science of Oil and Gas Well Construction: Senior EditorDocument2 pagesThe Science of Oil and Gas Well Construction: Senior EditorlakhanmukhtiarPas encore d'évaluation
- Casing Design: Drilling ReportDocument10 pagesCasing Design: Drilling Reportمحمد علي كريم شكر100% (1)
- Pipelines InstallationDocument24 pagesPipelines InstallationNoor Azreen100% (1)
- Precon Sewerage SystemDocument10 pagesPrecon Sewerage SystemArdiPratomoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 - CasingDocument69 pagesChapter 5 - CasingMuhammad Nursalam100% (2)
- Chapter 1+Casing+12Feb18Document47 pagesChapter 1+Casing+12Feb18Mohamad ZakwanPas encore d'évaluation
- L15 Cementing Lecture 1Document32 pagesL15 Cementing Lecture 1advantage025Pas encore d'évaluation
- Placing ConcreteDocument62 pagesPlacing ConcreteSyahierah RedzuanPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st (2) JafarDocument8 pages1st (2) Jafarجعفر جبار وحيدPas encore d'évaluation
- Drilling 1Document37 pagesDrilling 1Samarth Patel100% (1)
- Final Correction My Bhokar SiteDocument26 pagesFinal Correction My Bhokar SiteMd IsmailPas encore d'évaluation
- SPE/IADC 119296 Zonal Isolation Achieved in Kashagan Field Through Integrated ApproachDocument11 pagesSPE/IADC 119296 Zonal Isolation Achieved in Kashagan Field Through Integrated ApproachPAOLA ANDREA DUARTE PRADAPas encore d'évaluation
- WellboreDocument18 pagesWellborekeen dela cruz100% (1)
- CasingDocument31 pagesCasingsouthliPas encore d'évaluation
- Basics of Well ComplitionDocument15 pagesBasics of Well ComplitionSunny Bba100% (1)
- Squeeze Cementing: Forces Cement Slurry, Under Pressure, Through Perforations or Holes in The Casing or Liner .Document41 pagesSqueeze Cementing: Forces Cement Slurry, Under Pressure, Through Perforations or Holes in The Casing or Liner .Marcelo Veronez100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Petroleum Engineering WELL COMPLETION AND STIMULATION Mohd Fauzi Hamid Wan Rosli Wan Sulaiman Department of Petroleum Engineering Faculty of Petroleum & Renewable EnginDocument29 pagesFundamentals of Petroleum Engineering WELL COMPLETION AND STIMULATION Mohd Fauzi Hamid Wan Rosli Wan Sulaiman Department of Petroleum Engineering Faculty of Petroleum & Renewable Enginqazim786Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 - Casing DesignDocument51 pagesChapter 7 - Casing DesignFernando LedesmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pete 322 - Drilling Engineering - Ii Chapter 6 - Casing DesignDocument39 pagesPete 322 - Drilling Engineering - Ii Chapter 6 - Casing DesignTuran Amiraslanli100% (1)
- A1 CemDocument4 pagesA1 CemLuisPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Construction Problems of A "Big Inch" Outfall: Carlo Avanzini and Pierantonio QuiriciDocument8 pagesDesign and Construction Problems of A "Big Inch" Outfall: Carlo Avanzini and Pierantonio Quiricijean miguel oscorima celisPas encore d'évaluation
- Underwater ConcreteDocument37 pagesUnderwater Concretemanu_696Pas encore d'évaluation
- Well Completion2Document36 pagesWell Completion2kuda kwashePas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Casing:: 1. Conductor Casing (30" O.D.)Document12 pagesIntroduction To Casing:: 1. Conductor Casing (30" O.D.)Vñ ÕãdPas encore d'évaluation
- IJRAR2001610Document6 pagesIJRAR2001610GEOGIPas encore d'évaluation
- Plug-And Abandonment BasicsDocument37 pagesPlug-And Abandonment Basicsakonuche100% (2)
- Oil and Gas Well CementingDocument40 pagesOil and Gas Well Cementingavula43Pas encore d'évaluation
- Typical Casing Program Showing Different Casing Sizes and Their SettingDocument3 pagesTypical Casing Program Showing Different Casing Sizes and Their SettingMokr Achour100% (2)
- Cementación de PozosDocument30 pagesCementación de PozosJesus BcPas encore d'évaluation
- Bridge Maintenance Non-Structural ItemsDocument34 pagesBridge Maintenance Non-Structural Itemsjakka09100% (1)
- Casing Size SelectionDocument37 pagesCasing Size Selectionmbtkhan314Pas encore d'évaluation
- Maleki-Frigaard2017 Article PrimaryCementingOfOilAndGasWelDocument30 pagesMaleki-Frigaard2017 Article PrimaryCementingOfOilAndGasWelNasim KazemiPas encore d'évaluation
- Porus Asphalt DetailsDocument11 pagesPorus Asphalt DetailsPrasad NbPas encore d'évaluation
- Completion TechniqueDocument143 pagesCompletion TechniquenaefmubarakPas encore d'évaluation
- Apresentação 2Document9 pagesApresentação 2Alfredö HeidyPas encore d'évaluation
- Well Cementing 13cap IDocument43 pagesWell Cementing 13cap IWill OrtizPas encore d'évaluation
- Construction of A Tube WellDocument23 pagesConstruction of A Tube WellAurang Zeb JadoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Título: Chapter 4: Drilling: PUC Minas Virtual - 1Document2 pagesTítulo: Chapter 4: Drilling: PUC Minas Virtual - 1giselechavesPas encore d'évaluation
- Perforating BasicsDocument64 pagesPerforating BasicsLawrence Mbah100% (1)
- Site Safety Handbook for the Petroleum IndustryD'EverandSite Safety Handbook for the Petroleum IndustryÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Lecture Notes on Reinforced Concrete DesignD'EverandLecture Notes on Reinforced Concrete DesignPas encore d'évaluation
- Coiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!D'EverandCoiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Hydrostatic and Hydro-Testing in the Oil and Gas FieldD'EverandHydrostatic and Hydro-Testing in the Oil and Gas FieldÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- Sewage Disposal Works: Their Design and ConstructionD'EverandSewage Disposal Works: Their Design and ConstructionPas encore d'évaluation
- Concrete in Highway Engineering: International Series of Monographs in Civil EngineeringD'EverandConcrete in Highway Engineering: International Series of Monographs in Civil EngineeringÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5)
- Integrated Sand Management For Effective Hydrocarbon Flow AssuranceD'EverandIntegrated Sand Management For Effective Hydrocarbon Flow AssurancePas encore d'évaluation
- Drilling and Blasting As A Tunnel Excavation MethodDocument26 pagesDrilling and Blasting As A Tunnel Excavation MethodMIGUEL FERNANDO AGUIRRE QUISPE100% (1)
- Narrative Report of Others For StudentsDocument4 pagesNarrative Report of Others For StudentsChristian Reyes YapPas encore d'évaluation
- Developmnet 10 - 2 - 3Document8 pagesDevelopmnet 10 - 2 - 3Garry SandhuPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic of Organic ChemistryDocument11 pagesBasic of Organic ChemistryDr. Prashan Kumar ThakurPas encore d'évaluation
- WEEK 3, Grade-10Document2 pagesWEEK 3, Grade-10Sheela BatterywalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fire Regulation Service SectorDocument17 pagesFire Regulation Service SectorKamlesh Kamlesh EtwaroPas encore d'évaluation
- Bixby Knolls Preparatory Academy - San Antonio, Quezon: Science and Technology 8Document3 pagesBixby Knolls Preparatory Academy - San Antonio, Quezon: Science and Technology 8Oliver VillanuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Matriculation Chemistry Hydrocarbon Part 2 AlkaneDocument30 pagesMatriculation Chemistry Hydrocarbon Part 2 Alkaneiki292Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electrobomba Tec-Ex140 Antiexplosiva 220V 37GPMDocument2 pagesElectrobomba Tec-Ex140 Antiexplosiva 220V 37GPMAlvaro ManuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Use of Ruber in Automobile IndustryDocument3 pagesUse of Ruber in Automobile Industryanon_22360568Pas encore d'évaluation
- ASTM D2163 GLP CromatografiaDocument5 pagesASTM D2163 GLP Cromatografiaalejandrogrande100% (1)
- PerforationDocument45 pagesPerforationCatur Nila Pratiwi75% (4)
- Rumaila Field Iraq - JZrilicDocument7 pagesRumaila Field Iraq - JZrilicOctavio CruzPas encore d'évaluation
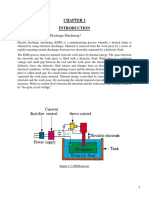
- Design of Electric Discharge MachineDocument41 pagesDesign of Electric Discharge MachineAmeerUlHaqPas encore d'évaluation
- LB Series Asphalt Mixing Plant Repair and Maintenance ManualDocument38 pagesLB Series Asphalt Mixing Plant Repair and Maintenance ManualLai_Wei_Wah_7018Pas encore d'évaluation
- G64C Maintenance CardDocument6 pagesG64C Maintenance CardBogar PinedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Petrol Station Checklist AuditDocument10 pagesPetrol Station Checklist AuditrizamryPas encore d'évaluation
- Petroleum (From: Petra OleumDocument9 pagesPetroleum (From: Petra OleumMarius GîrleanuPas encore d'évaluation
- Hubbert's Peak TheoryDocument16 pagesHubbert's Peak TheoryHrishikesh ChappadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Non Fuel Retailing - Report - Arvind DwivediDocument87 pagesNon Fuel Retailing - Report - Arvind Dwivediarvind_dwivedi100% (4)
- EnggDocument141 pagesEnggJonnah Faye MojaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Chromatography (GC)Document4 pagesGas Chromatography (GC)Mohd Izwan67% (3)
- Marine Engine Lubrication After 2020: What To Expect in The Next DecadeDocument19 pagesMarine Engine Lubrication After 2020: What To Expect in The Next DecadePetar DobrePas encore d'évaluation
- SSTPPDocument28 pagesSSTPPAmit Makhija100% (4)
- Science 9 - Week 11Document11 pagesScience 9 - Week 11Mira VeranoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1900SRM1107 (01 2004) Uk enDocument26 pages1900SRM1107 (01 2004) Uk enEbied Yousif Aly100% (7)
- NAVEDTRA 14322 Aviation Boatswains Mate FDocument410 pagesNAVEDTRA 14322 Aviation Boatswains Mate FYerixon Daniel Aguilar SequerasPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance and Emission Characteristics of Di Diesel Engine Fuelled With Camphor Oil-Diesel BlendsDocument4 pagesPerformance and Emission Characteristics of Di Diesel Engine Fuelled With Camphor Oil-Diesel BlendsRam KrishPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Differential Pressure Flow Meter Technology: For The Real WorldDocument6 pagesAdvanced Differential Pressure Flow Meter Technology: For The Real WorldCoco GalindoPas encore d'évaluation
- B&W Overfire AirDocument4 pagesB&W Overfire AirJose Lorenzo ToralPas encore d'évaluation