Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Forming The Present Continuous Tense
Transféré par
Emma EmilyTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Forming The Present Continuous Tense
Transféré par
Emma EmilyDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
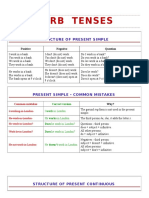
PRESENT CONTINUOUS
TENSE
FORMING THE PRESENT CONTINUOUS
The present continuous of any verb is composed of two parts - the present tense of the verb to be + the present
participle of the main verb.
(The form of the present participle is: base+ing, e.g. talking, playing, moving, smiling)
Affirmative
Subject
+ to be
+ base + ing
She
is
talking.
Subject
+ to be + not
+ base + ing
She
is not (isn't)
talking
to be
+ subject
+ base + ing
Is
she
talking?
Negative
Interrogative
EXAMPLES: TO GO, PRESENT CONTINUOUS
Affirmative
Negative
Interrogative
I am going
I am not going
Am I going?
You are going
You aren't going.
Are you going?
He, she, it is going
He, she, it isn't going
Is he, she, it going?
We are going
We aren't going
Are we going?
You are going
You aren't going
Are you going?
They are going
They aren't going
Are they going?
Note: alternative negative contractions: I'm not going, you're not going, he's not going etc.
FUNCTIONS OF THE PRESENT CONTINUOUS
As with all tenses in English, the speaker's attitude is as important as the time of the action or event. When someone
uses the present continuous, they are thinking about something that is unfinished or incomplete
THE PRESENT CONTINUOUS IS USED:
to describe an action that is going on at this moment: You are using the Internet. You are studying English
grammar.
to describe an action that is going on during this period of time or a trend: Are you still working for the same
company? More and more peopleare becoming vegetarian.
to describe an action or event in the future, which has already been planned or prepared: We're going on
holiday tomorrow. I'm meeting my boyfriend tonight. Are they visiting you next winter?
to describe a temporary event or situation: He usually plays the drums, but he's playing bass guitar
tonight. The weather forecast was good, butit's raining at the moment.
with "always, forever, constantly", to describe and emphasise a continuing series of repeated actions: Harry and
Sally are always arguing!You're constantly complaining about your mother-in-law!
BE CAREFUL! Some verbs are not usually used in the continuous form
VERBS THAT ARE NOT USUALLY USED IN THE CONTINUOUS
FORM
The verbs in the list below are normally used in the simple form because they refer to states, rather than actions or
processes.
SENSES / PERCEPTION
to feel*
to hear
to see*
to smell
to taste
OPINION
to assume
to believe
to consider
to doubt
to feel (= to think)
to find (= to consider)
to suppose
to think*
MENTAL STATES
to forget
to imagine
to know
to mean
to notice
to recognise
to remember
to understand
EMOTIONS / DESIRES
to envy
to fear
to dislike
to hate
to hope
to like
to love
to mind
to prefer
to regret
to want
to wish
MEASUREMENT
to contain
to cost
to hold
to measure
to weigh
OTHERS
to look (=resemble)
to seem
to be (in most cases)
to have(when it means "to possess")*
EXCEPTIONS
Perception verbs (see, hear, feel, taste, smell) are often used with can: : I can see... These verbs may be used in the
continuous form but with a different meaning
This coat feels nice and warm. (your perception of the coat's qualities)
John's feeling much better now (his health is improving)
She has three dogs and a cat. (possession)
She's having supper. (She's eating)
I can see Anthony in the garden (perception)
I'm seeing Anthony later (We are planning to meet)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Forming The Present ContinuousDocument4 pagesForming The Present ContinuousGeorgiana DragoiPas encore d'évaluation
- Present: Simple Present Present Continuous Present PerfectDocument10 pagesPresent: Simple Present Present Continuous Present PerfectIoana TrîmbițașPas encore d'évaluation
- The Simple Present Tense Is UsedDocument6 pagesThe Simple Present Tense Is UsedMade AnomaharsiPas encore d'évaluation
- Present ContinousDocument4 pagesPresent Continoususwatunkhs11Pas encore d'évaluation
- 16 TensesDocument18 pages16 TensesAnonymous eCws3EPas encore d'évaluation
- Present ContinuousDocument44 pagesPresent ContinuoushootanPas encore d'évaluation
- Eng 2 Activity 2 - HSGADocument7 pagesEng 2 Activity 2 - HSGARosanelly Galindo ParraPas encore d'évaluation
- Present: Simple Present Present Continuous Present PerfectDocument7 pagesPresent: Simple Present Present Continuous Present PerfectWaad AlteePas encore d'évaluation
- Present ContinuousDocument4 pagesPresent ContinuousAizack WiverPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Present: He Wants, She Needs, He Gives, She ThinksDocument10 pagesSimple Present: He Wants, She Needs, He Gives, She ThinksAisyah RasdiPas encore d'évaluation
- English Grammar - VerbsDocument81 pagesEnglish Grammar - VerbsAisy AstarinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Continous TensesDocument12 pagesPresent Continous TensesSenor PrivatePas encore d'évaluation
- Be Careful!: Present Continous/ Progressive TenseDocument4 pagesBe Careful!: Present Continous/ Progressive TenseBrigitta Helena ModPas encore d'évaluation
- Present ContinuousDocument6 pagesPresent ContinuousAyy SykesPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple PresentDocument31 pagesSimple PresentJuni DzibPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Continuous. თეკლა ყუფარაძეDocument6 pagesPresent Continuous. თეკლა ყუფარაძეTekla KuparadzePas encore d'évaluation
- Secion 6 InglesDocument12 pagesSecion 6 InglesWalter Atao SalazarPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Simple - Continuous Lesson - 220109 - 213225Document6 pagesPresent Simple - Continuous Lesson - 220109 - 213225wafaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Present Tense AbdoDocument7 pagesSimple Present Tense AbdoAbdelhadi Ait AllalPas encore d'évaluation
- English TensesDocument67 pagesEnglish Tensesdonisparta5Pas encore d'évaluation
- English TensesDocument39 pagesEnglish TensesDavid ArévalosPas encore d'évaluation
- Notas Sobre La Tercera Persona Del Singular Del "Simple Present"Document9 pagesNotas Sobre La Tercera Persona Del Singular Del "Simple Present"Anonymous thHFCAPas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar Hey There 2Document29 pagesGrammar Hey There 2Kenny Valdez FelipePas encore d'évaluation
- Present Simple: Base Form of The Verb, - S in The 3rd Person SingularDocument12 pagesPresent Simple: Base Form of The Verb, - S in The 3rd Person SingularsofiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Present ContinuousDocument4 pagesPresent ContinuousDavid SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Simple and Present ContinuousDocument9 pagesPresent Simple and Present ContinuouseeeeerePas encore d'évaluation
- Presente Continuo - InglesDocument14 pagesPresente Continuo - InglesMiyouba CarriganPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Present Simple TenseDocument13 pages1 Present Simple TenseClaudia BalasPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Continuous TenseDocument30 pagesPresent Continuous TenseSania KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Simple&Present Continous Grammar ExplanationDocument3 pagesPresent Simple&Present Continous Grammar ExplanationHéctor León SaavedraPas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar Notes - Simple, Continuous Past&Present TenseDocument7 pagesGrammar Notes - Simple, Continuous Past&Present TenseNUR AMALINA BINTI MOHAMMAD MoePas encore d'évaluation
- Universidad Tecnologica Del Suroeste de Guanajuato: Obed Armando Cabrera YbarraDocument17 pagesUniversidad Tecnologica Del Suroeste de Guanajuato: Obed Armando Cabrera YbarraObed Armando Cabrera YbarraPas encore d'évaluation
- Present ContinuousDocument6 pagesPresent ContinuousyuniorPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Simple PresentationDocument13 pagesPresent Simple PresentationClaudia BalasPas encore d'évaluation
- Slides Uni I (MS) (RF)Document64 pagesSlides Uni I (MS) (RF)Marilia PucciPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - Present TenseDocument20 pages1 - Present TenseDyani Masita DewiPas encore d'évaluation
- Come Si Forma Il "Present Continuous" Inglese: + To BeDocument2 pagesCome Si Forma Il "Present Continuous" Inglese: + To BeEufrasia CorsalePas encore d'évaluation
- PRESENT SIMPLE Vs PRESENT CONTINUOUSDocument85 pagesPRESENT SIMPLE Vs PRESENT CONTINUOUSmia100% (2)
- The Simple Present TenseDocument21 pagesThe Simple Present TenseHamza djioui - حمزة ادجيويPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Progressive - ClassDocument3 pagesPresent Progressive - ClassJorge OriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Engleski JezikDocument6 pagesEngleski JezikAdnan PjanicPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 4 Finite - Non FiniteDocument29 pagesLec 4 Finite - Non Finitejahedul IslamPas encore d'évaluation
- Structure: Paper Ratio: 10 To 30 % Unit 1: The Simple Present TenseDocument21 pagesStructure: Paper Ratio: 10 To 30 % Unit 1: The Simple Present TenseMemoona MunzarPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Perfect ContinuousDocument2 pagesPresent Perfect ContinuousNesreen WalledPas encore d'évaluation
- Forming The Present ContinuousDocument2 pagesForming The Present Continuousmounib khaddourPas encore d'évaluation
- Makalah Bahasa InggrisDocument42 pagesMakalah Bahasa InggrisMarsela Eka MarselPas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar Guide 3-2017 PDFDocument48 pagesGrammar Guide 3-2017 PDFRoberto Figueroa ZúñigaPas encore d'évaluation
- Present ContinuesDocument7 pagesPresent ContinuesJannis AlmeidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Evision: Present Simple - Present ContinuousDocument28 pagesEvision: Present Simple - Present ContinuousMaha Al AmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Eng GrammarDocument9 pagesEng GrammarSeba Tube HDPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb Tenses: Structure of Present SimpleDocument7 pagesVerb Tenses: Structure of Present SimplexaglobalPas encore d'évaluation
- Present ContinuousDocument4 pagesPresent ContinuousYulia ChukarevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Auxiliary VerbsDocument7 pagesAuxiliary VerbsErma Chandra Saptarani100% (1)
- General English Module 2Document39 pagesGeneral English Module 2shambhavi sinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Χρόνοι στα ΑγγλικαDocument22 pagesΧρόνοι στα Αγγλικαangnikos100% (1)
- Grammar Performance 1Document32 pagesGrammar Performance 1KarglezPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Tenses RevisionDocument12 pagesPresent Tenses RevisionMaja BulatovicPas encore d'évaluation
- Present ProgressiveDocument22 pagesPresent ProgressiveMuAD TVPas encore d'évaluation
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideD'EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- Present Continuous All Forms Exercise 1Document3 pagesPresent Continuous All Forms Exercise 1Alessio MirarchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Continuous Form Positive and Negative 1Document3 pagesPresent Continuous Form Positive and Negative 1Devita MezaPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Continuous All Forms Exercise 1Document3 pagesPresent Continuous All Forms Exercise 1Alessio MirarchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Tense WorksheetDocument2 pagesPresent Tense WorksheetOana Galbenu100% (1)
- Spelling of Verb + INGDocument3 pagesSpelling of Verb + INGEmma EmilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Continuous and Present SimpleDocument1 pagePresent Continuous and Present SimpleEmma EmilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Continuous and Present Simple 2 PartDocument1 pagePresent Continuous and Present Simple 2 PartEmma EmilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Continuous All Forms Exercise 2Document3 pagesPresent Continuous All Forms Exercise 2IannaL77Pas encore d'évaluation
- Discharge Advice After Your Coronary Angiogram, Angioplasty or Stent Insertion (PCI)Document12 pagesDischarge Advice After Your Coronary Angiogram, Angioplasty or Stent Insertion (PCI)Emma EmilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Present ContinuousDocument3 pagesPresent ContinuousILy SofiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Continuous Tense QuizDocument1 pagePresent Continuous Tense QuizEmma EmilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Continuous All Forms Exercise 2Document3 pagesPresent Continuous All Forms Exercise 2IannaL77Pas encore d'évaluation
- Types of ClausesDocument2 pagesTypes of ClausesIndranil HatuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Abstract NounsDocument3 pagesAbstract NounsEmma EmilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Collective NounsDocument3 pagesCollective NounsEmma EmilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise For Beginners 3Document4 pagesExercise For Beginners 3Emma EmilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Recovering From Coronary Angioplasty and Stent InsertionDocument42 pagesRecovering From Coronary Angioplasty and Stent InsertionmichelbgggPas encore d'évaluation
- Different Types of NounsDocument2 pagesDifferent Types of NounsEmma EmilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Type of Nouns in The English LanguageDocument2 pagesType of Nouns in The English LanguageEmma EmilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Examination For Beginners: NameDocument2 pagesExamination For Beginners: NameWeam AlajamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Prepositions of TimeDocument1 pagePrepositions of TimeEmma EmilyPas encore d'évaluation
- For/since: For Is Used When Specifying The Amount of Time (How Long)Document1 pageFor/since: For Is Used When Specifying The Amount of Time (How Long)Emma EmilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Subject Verb ObjectDocument1 pageSubject Verb ObjectEmma EmilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Prepositions of PlaceDocument3 pagesPrepositions of PlaceEmma EmilyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Comparison of AdjectivesDocument2 pagesThe Comparison of AdjectivesEmma EmilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Prepositions of PlaceDocument3 pagesPrepositions of PlaceEmma EmilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Auxiliary Verbs - Be, Do, HaveDocument2 pagesAuxiliary Verbs - Be, Do, HaveEmma EmilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Word Order: Nick Nick He He He HeDocument1 pageWord Order: Nick Nick He He He HeEmma EmilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Using Articles A, An, and TheDocument3 pagesUsing Articles A, An, and TheEmma EmilyPas encore d'évaluation
- EXPE222Document6 pagesEXPE222K-yanVehraaYomomaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pyridine Reactions: University College of Pharmaceutialsciences K.U. CampusDocument16 pagesPyridine Reactions: University College of Pharmaceutialsciences K.U. CampusVã RãPas encore d'évaluation
- World Price List 2014: Adventys Induction Counter TopsDocument4 pagesWorld Price List 2014: Adventys Induction Counter TopsdiogocorollaPas encore d'évaluation
- Venetian Shipping During The CommercialDocument22 pagesVenetian Shipping During The Commercialakansrl100% (1)
- Citizen's Army Training (CAT) Is A Compulsory Military Training For High School Students. Fourth-Year High SchoolDocument2 pagesCitizen's Army Training (CAT) Is A Compulsory Military Training For High School Students. Fourth-Year High SchoolJgary Lagria100% (1)
- Jsu Matematik SR Tahun 1Document24 pagesJsu Matematik SR Tahun 1Nurul NazierahPas encore d'évaluation
- An/Trc - 170 TrainingDocument264 pagesAn/Trc - 170 Trainingkapenrem2003Pas encore d'évaluation
- How To Become A Skilled OratorDocument5 pagesHow To Become A Skilled OratorDonain Alexis CamarenaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2007.01 What Does Jesus Think of Science?Document2 pages2007.01 What Does Jesus Think of Science?William T. PelletierPas encore d'évaluation
- MANITOUDocument2 pagesMANITOUmozollis22Pas encore d'évaluation
- Module ConnectionsDocument16 pagesModule ConnectionsHemilton Cheng Modulos100% (1)
- Bar Waiter/waitress Duties and Responsibilities Step by Step Cruise Ship GuideDocument6 pagesBar Waiter/waitress Duties and Responsibilities Step by Step Cruise Ship GuideAmahl CericoPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm A380 PDFDocument13 pagesAstm A380 PDFaromalara12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Houses WorksheetDocument3 pagesHouses WorksheetYeferzon Clavijo GilPas encore d'évaluation
- ICFR Presentation - Ernst and YoungDocument40 pagesICFR Presentation - Ernst and YoungUTIE ELISA RAMADHANI67% (3)
- SMA Releases Online Version of Sunny Design For PV System ConfigurationDocument3 pagesSMA Releases Online Version of Sunny Design For PV System ConfigurationlakliraPas encore d'évaluation
- Chelsea Bellomy ResumeDocument1 pageChelsea Bellomy Resumeapi-301977181Pas encore d'évaluation
- On Evil - Terry EagletonDocument44 pagesOn Evil - Terry EagletonconelcaballocansadoPas encore d'évaluation
- War: Causation of War, Total War, Limited War, Strategic Culture: Determinants of Strategic Culture Deterrence: Theory and Practice With SpecialDocument52 pagesWar: Causation of War, Total War, Limited War, Strategic Culture: Determinants of Strategic Culture Deterrence: Theory and Practice With SpecialMazhar HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Philosophies PrinceDocument4 pagesPhilosophies PrincePrince CuetoPas encore d'évaluation
- 7C Environment Test 2004Document2 pages7C Environment Test 2004api-3698146Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bartolome vs. MarananDocument6 pagesBartolome vs. MarananStef OcsalevPas encore d'évaluation
- Four Year Plan DzenitaDocument4 pagesFour Year Plan Dzenitaapi-299201014Pas encore d'évaluation
- SoapDocument10 pagesSoapAira RamoresPas encore d'évaluation
- Rhipodon: Huge Legendary Black DragonDocument2 pagesRhipodon: Huge Legendary Black DragonFigo FigueiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Excel For MAC Quick Start GuideDocument4 pagesExcel For MAC Quick Start GuideMalaquías HuamánPas encore d'évaluation
- A1 - The Canterville Ghost WorksheetsDocument8 pagesA1 - The Canterville Ghost WorksheetsТатьяна ЩукинаPas encore d'évaluation
- B2 English Test International Students - TemplateDocument5 pagesB2 English Test International Students - TemplateMabrur devPas encore d'évaluation
- Power & Leadership PWDocument26 pagesPower & Leadership PWdidato.junjun.rtc10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Monologues For Danimations - Adam SorrellDocument2 pagesMonologues For Danimations - Adam SorrellCharlie Smith-McMahonPas encore d'évaluation