Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Human Physiology Introduction
Transféré par
Chris_Barber090 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
303 vues1 pageHuman Physiology Introduction
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentHuman Physiology Introduction
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
303 vues1 pageHuman Physiology Introduction
Transféré par
Chris_Barber09Human Physiology Introduction
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
Human Physiology - Core Concept Cheat Sheet
01: Introduction to Human Physiology
Key Terms
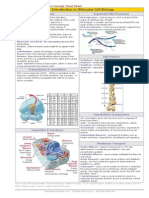
Integumentary System
Physiology: Physiology is the study of body function. It
is the study of the biochemical, physical and mechanical
functions of living organisms. Physiology and anatomy are
interconnected; anatomy describes the location and
structure of a particular body part, and physiology
describes how and what it does.
History of Physiology: Human Physiology dates back to
at least 420 B.C., during the time of Hippocrates.
Between 380-322 B.C, Aristotle began thinking critically
about the relationship between structure and function,
which marks the beginning of the discipline of physiology.
During the Middle Ages, a physician named Ibn al-Nafis
first correctly described the human circulatory system and
gas exchange in the lungs. He is credited as being the
father of circulatory physiology.
Integumentary System: The skin is the largest organ of
the body, covering the entire surface of the body. The
skin provides a protective barrier for the human body, as
well as playing a key role in body temperature regulation
as part of homeostasis. The skin is divided into 2 layers:
the epidermis and the dermis.
Nervous System: The nervous system controls
movement and function through nerve impulses sent to
and from the brain. The nervous system is divided into
the Central Nervous system and the Peripheral Nervous
system.
Cell Communication: Cells within a group of tissue must
communicate to support themselves, as well as transmit
vital information. Specialized cell junctions, such as gap
junctions, provide a direct connection for the transfer of
molecules between cells. Cell receptors also provide a
major form of cell communication between cells.
Signal Transduction: After the signal reaches the target
cells, it must then activate it or stimulate it to respond to
the signal. This involves the transduction of the signal
from the outside environment to the inside of the cell.
Cells have very elaborate intracellular signaling pathways,
such as the Epidermal Growth Factor signaling pathway.
Homeostasis: Homeostasis is a vital concept in human
physiology. It is the process through which a nearly stable
internal environment is maintained in the body so that
cellular functions can proceed at maximum efficiency.
Every body structure contributes to maintaining the
internal environment within a normal range of
temperature, pH, oxygenation, etc. Homeostasis is
maintained through the regulatory process called
feedback. A feedback loop is a cycle of events in which a
body condition (such as blood pressure) is continually
monitored and adjusted to be within specific limits.
Sex determination in humans takes place around 7-9
weeks of gestation. The Wolffian ducts, which develop in
males, and the Mullerian ducts, which develop in
females are under the control of a glycoprotein hormone
known as Mullerian-inhibiting factor (MIF).
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is a vital concept in human physiology. It
is the process through which a nearly stable internal
environment is maintained in the body so that cellular
functions can proceed at maximum efficiency.
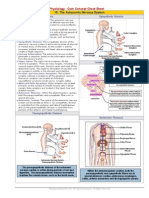
Respiratory System
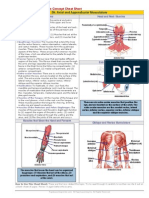
Cell to Cell Communication
Cell Receptors
Gap Junctions
Cells within a group of tissue must communicate to
support themselves, as well as transmit vital information.
Specialized cell junctions, such as gap junctions, provide
a direct connection for the transfer of molecules between
cells. Cell receptors also provide a major form of cell
communication between cells.
The Respiratory systems function is gas exchange,
including oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide release in
the lungs. The respiratory cycle of breathing brings gas
into the lungs during inspiration; oxygen and carbon
dioxide are exchanged and then the carbon dioxide is
blown off during expiration.
How to Use This Cheat Sheet: These are the keys related this topic. Try to read through it carefully twice then recite it out on
a blank sheet of paper. Review it again before the exams.
RapidLearningCenter.com
Rapid Learning Inc. All Rights Reserved
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Physics Rules 5Document10 pagesPhysics Rules 5Chris_Barber09100% (6)
- Cells Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesCells Cheat SheetUlka Sutar100% (2)
- MCAT Hormones and EnzymesDocument2 pagesMCAT Hormones and EnzymesDevie Saha100% (3)
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument1 pageMitosis and MeiosisChris_Barber09100% (1)
- ImmunologyDocument1 pageImmunologyChris_Barber0986% (7)
- VirusesDocument1 pageVirusesChris_Barber09100% (2)
- Biochemistry Notes PDFDocument11 pagesBiochemistry Notes PDFChris_Barber0950% (6)
- 01: Introduction To Evolutionary Thought: Key Evolution TermsDocument1 page01: Introduction To Evolutionary Thought: Key Evolution TermsBlaine Rogalski100% (2)
- ProteinsDocument1 pageProteinsChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Biology IntroductionDocument1 pageCell Biology IntroductionChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Answer Key End of Chapter QuestionsDocument102 pagesAnswer Key End of Chapter QuestionsPhoebe Faye LyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 - Genetic Control of Cell FunctionDocument7 pagesChapter 3 - Genetic Control of Cell FunctionSADAVEJO100% (1)
- 2.02 Gross Anatomy Trans - HeartDocument15 pages2.02 Gross Anatomy Trans - HeartElma Gonzales100% (1)
- Molecular Cell Biology MasterDocument6 pagesMolecular Cell Biology Masterdealt100% (5)
- Chemical Basis of LifeDocument1 pageChemical Basis of LifeChris_Barber09100% (2)
- Amino Acid NotesDocument15 pagesAmino Acid NotesChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Cheat Sheet MasterDocument7 pagesBio Cheat Sheet MasterChris_Barber0986% (7)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyDelixae Phoinix80% (5)
- Teacher Preparation Notes For Genetics and Genetics SupplementDocument16 pagesTeacher Preparation Notes For Genetics and Genetics SupplementMary Ann DimacaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Protein Synthesis Notes PDFDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis Notes PDFChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Gen Chem NotesDocument8 pagesMCAT Gen Chem NotesViviana PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Biology Notes 2 PDFDocument23 pagesMCAT Biology Notes 2 PDFChris_Barber09100% (1)
- 2.1 (BIOCHEMISTRY) Introduction To MetabolismDocument6 pages2.1 (BIOCHEMISTRY) Introduction To Metabolismlovelots1234100% (1)
- Molecular BiologyDocument54 pagesMolecular BiologyAnonymous GhQ1eIyxunPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Biology Exam 1 ReaDocument7 pagesCell Biology Exam 1 ReaCsa At Uh100% (3)
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument1 pageAutonomic Nervous SystemChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Mnemonic SDocument17 pagesMCAT Mnemonic STasneem MahmoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Rate Law GraphsDocument2 pagesRate Law GraphsChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rate Law GraphsDocument2 pagesRate Law GraphsChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes 1 &2Document3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes 1 &2Ivy100% (1)
- MCAT Biology Notes 3 PDFDocument16 pagesMCAT Biology Notes 3 PDFChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument32 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyTrifena Prisca MossePas encore d'évaluation
- OCR Biology F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport Revision NotesDocument4 pagesOCR Biology F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport Revision Notes24wrightphilip100% (1)
- Notes CarbohydratesDocument21 pagesNotes CarbohydratesChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Vitamin CDocument1 pageVitamin CJ-eliPas encore d'évaluation
- KA P-S - The Lazy OCD VersionDocument84 pagesKA P-S - The Lazy OCD Versionsxh580Pas encore d'évaluation
- Muscular SystemDocument1 pageMuscular SystemChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument1 pagePeripheral Nervous SystemChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Urinary SystemDocument1 pageUrinary SystemChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Molecular Biology of The Cell Cumulative Final Exam Study GuideDocument22 pagesMolecular Biology of The Cell Cumulative Final Exam Study Guiderazgriz1211Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous System: Gross Features of HindbrainDocument26 pagesNervous System: Gross Features of HindbrainShere Almansuori100% (1)
- Biology NotesDocument6 pagesBiology NotesElizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biotechnoloy Introduction and Application: Table of ContentDocument40 pagesBiotechnoloy Introduction and Application: Table of ContentnescafeforeverPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacteria: Type of Food Depends On Organism)Document5 pagesBacteria: Type of Food Depends On Organism)Chris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- AP Psychology Mnomonic DevicesDocument7 pagesAP Psychology Mnomonic DevicesBellony SandersPas encore d'évaluation
- Examkrackers Lecture 2 Section QuestionsDocument3 pagesExamkrackers Lecture 2 Section QuestionsAyodejiES1Pas encore d'évaluation
- 16: Work, Power, and Energy: Key Physics Terms Key ConceptsDocument1 page16: Work, Power, and Energy: Key Physics Terms Key ConceptsBlaine RogalskiPas encore d'évaluation
- Body System ChecklistDocument6 pagesBody System Checklistapi-422967453Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Membranes Questions - MarkschemeDocument3 pagesCell Membranes Questions - MarkschemeDharmendra Singh50% (2)
- Sheep Brain Observation LAB 2015Document4 pagesSheep Brain Observation LAB 2015Leo MatsuokaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio MCAT NotesDocument2 pagesBio MCAT NotesJuan DeSantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 2 Test Flash CardsDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 2 Test Flash Cardsmalenya1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reference: Essentials For Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb, EDocument11 pagesReference: Essentials For Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb, EAnnalei GagnéPas encore d'évaluation
- Alan's Bio NotesDocument19 pagesAlan's Bio Notesluongc4100% (1)
- Audio Osmosis - Organic ChemistryDocument9 pagesAudio Osmosis - Organic ChemistryddPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Work MatrixDocument2 pagesChemistry Work MatrixSagarDalviPas encore d'évaluation
- Zoology Notes: 017 Chapter 13Document3 pagesZoology Notes: 017 Chapter 13humanupgrade100% (1)
- General Chapter 4: The Physiological Basis of Behavior PsychologyDocument4 pagesGeneral Chapter 4: The Physiological Basis of Behavior PsychologyChristine Rose EmPas encore d'évaluation
- Histology Notes 2Document13 pagesHistology Notes 2Lukas BüchlerPas encore d'évaluation
- Cheat Sheet (Bio) 1Document1 pageCheat Sheet (Bio) 1Kelvin KohPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy & Physiology: What Is Anatomy? Maintaining LifeDocument10 pagesAnatomy & Physiology: What Is Anatomy? Maintaining LifeRachel MarquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Mar 2018 PDFDocument20 pagesMar 2018 PDFdanicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Fisiology NoteDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Fisiology NoteIssac LauPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Physiology: Def:: OriginDocument3 pagesHuman Physiology: Def:: OriginAamir SiddiquePas encore d'évaluation
- Greek Word - Nature - Study: - PhysiologyDocument26 pagesGreek Word - Nature - Study: - PhysiologyQasim alaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical BiologyDocument130 pagesMedical BiologyPatalie HettihewaPas encore d'évaluation
- G2. Human Body Introduction WorksheetDocument4 pagesG2. Human Body Introduction WorksheetMazucatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Heart Notes PDFDocument2 pagesHeart Notes PDFChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive System NotesDocument3 pagesReproductive System NotesChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Digestive System PDFDocument3 pagesDigestive System PDFChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Macromolecules PDFDocument11 pagesMacromolecules PDFChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovasculary System PDFDocument5 pagesCardiovasculary System PDFChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT O-Chem NotesDocument1 pageMCAT O-Chem NotesChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nucleic Acids and Their Structure: Information?Document4 pagesNucleic Acids and Their Structure: Information?Chris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bacteria: Type of Food Depends On Organism)Document5 pagesBacteria: Type of Food Depends On Organism)Chris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- CARBSDocument24 pagesCARBSGulus CfPas encore d'évaluation
- 107 Rules in PhysicsDocument2 pages107 Rules in PhysicsChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Regents Physics Exam Prep: 101 Facts You Should Know: MechanicsDocument3 pagesRegents Physics Exam Prep: 101 Facts You Should Know: MechanicsChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Aromatic Notes 2 PDFDocument6 pagesAromatic Notes 2 PDFChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Extra Chirality ProblemsDocument21 pagesExtra Chirality ProblemsChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 16:substituent Effects in Aromatic SubstitutionDocument2 pagesChapter 16:substituent Effects in Aromatic SubstitutionChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Rules 2Document4 pagesPhysics Rules 2Chris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Rules 1Document2 pagesPhysics Rules 1Chris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Placement Physics Physics OverviewDocument9 pagesAdvanced Placement Physics Physics OverviewChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Physics Equation SheetDocument6 pagesMCAT Physics Equation SheetChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Essay #1: Progress Often Complicates As Much As It SimplifiesDocument4 pagesSample Essay #1: Progress Often Complicates As Much As It SimplifiesChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- AAMC 9 Essay 1Document4 pagesAAMC 9 Essay 1Chris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Essay #1: A Politician's Lifestyle Should Reflect His or Her Political ViewsDocument4 pagesEssay #1: A Politician's Lifestyle Should Reflect His or Her Political ViewsChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Essay #1: Education Makes Everyone EqualDocument4 pagesSample Essay #1: Education Makes Everyone EqualChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Essay #1: Advancements in Communication Technology Have Reduced The Quality of Human InteractionDocument6 pagesSample Essay #1: Advancements in Communication Technology Have Reduced The Quality of Human InteractionChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fragment 176 191Document2 pagesFragment 176 191Wild CardPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 13 Effector Mechanisms of Humoral ImmunityDocument21 pagesCHAPTER 13 Effector Mechanisms of Humoral ImmunitySri Sulistyawati AntonPas encore d'évaluation
- Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy: ReviewDocument10 pagesBiomedicine & Pharmacotherapy: Reviewlesly lunaPas encore d'évaluation
- SB2a Mitosis 1. SB2b Growth in Animals SB2c Growth in PlantsDocument4 pagesSB2a Mitosis 1. SB2b Growth in Animals SB2c Growth in PlantsSiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Viral Anti Virus Print OutDocument20 pagesViral Anti Virus Print Outhazem_bossPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiology Chapter 1 2Document69 pagesMicrobiology Chapter 1 2joshPas encore d'évaluation
- Patrick: An Introduction To Medicinal Chemistry 4e: Enzymes As Drug TargetsDocument43 pagesPatrick: An Introduction To Medicinal Chemistry 4e: Enzymes As Drug TargetsVishaka KashyapPas encore d'évaluation
- The Three Domains of LifeDocument1 pageThe Three Domains of Lifeella retizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Molecular Basis of MorphogenesisDocument44 pagesMolecular Basis of MorphogenesisMitzel SapaloPas encore d'évaluation
- U20BTBT01-Biology For EngineersDocument1 pageU20BTBT01-Biology For EngineersSiddhi SiddhiPas encore d'évaluation
- ZoologyDocument40 pagesZoologyAman SethPas encore d'évaluation
- Mitosis and Meiosis: Cell DivisionDocument19 pagesMitosis and Meiosis: Cell DivisionLovely BatongbakalPas encore d'évaluation
- 6BBL0394 Kisspeptin 2016Document105 pages6BBL0394 Kisspeptin 2016Oumid AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunopharmacological Perspective On Zinc in SARS-CoV-2 InfectionDocument16 pagesImmunopharmacological Perspective On Zinc in SARS-CoV-2 InfectionW CnPas encore d'évaluation
- PhotosynthesisDocument39 pagesPhotosynthesisMeah PachecoPas encore d'évaluation
- Genomic Analysis of MAP Kinase Cascades In: Arabidopsis Defense ResponsesDocument13 pagesGenomic Analysis of MAP Kinase Cascades In: Arabidopsis Defense ResponsesMelvin PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Histology Text, Problems, TestsDocument334 pagesHistology Text, Problems, TestsmoahedmaedePas encore d'évaluation
- The Effect of Osmosis On Potatoes in Different Concentrations of Sucrose SolutionsDocument7 pagesThe Effect of Osmosis On Potatoes in Different Concentrations of Sucrose SolutionsanthorPas encore d'évaluation
- Synaptic IntegrationDocument5 pagesSynaptic IntegrationryanPas encore d'évaluation
- Viruses 08 00210Document13 pagesViruses 08 00210Hany ZutanPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 - The Genetic Code and Translation Revised 9-24-2018Document16 pages10 - The Genetic Code and Translation Revised 9-24-2018Sheraz ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.biokimia KankerDocument94 pages1.biokimia Kankersebastian chendraPas encore d'évaluation
- A Public BCR Present in A Unique Dual-Receptor-Expressing Lymphocyte From Type 1 Diabetes Patients Encodes A Potent T Cell AutoantigenDocument34 pagesA Public BCR Present in A Unique Dual-Receptor-Expressing Lymphocyte From Type 1 Diabetes Patients Encodes A Potent T Cell AutoantigenAmrendra SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Sea Urchin FertilizationDocument9 pagesSea Urchin FertilizationRudra RudraPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/01Document18 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/01Raphael JosephPas encore d'évaluation
- BIO 30 Lec 1 - 3 SummaryDocument6 pagesBIO 30 Lec 1 - 3 SummaryAnonymous w17gcfbpPas encore d'évaluation
- Growth Factors and Wound Healing 1997Document374 pagesGrowth Factors and Wound Healing 1997Vo Ha Phuong NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- 2014 Course BookDocument285 pages2014 Course BookWafaa AdamPas encore d'évaluation