Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Final Exam Notes
Transféré par
Ridwan AhmedCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Final Exam Notes
Transféré par
Ridwan AhmedDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
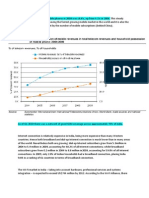
Organizations increasingly more diverse in terms of their race, gender, ethnicity, and nationality
Help with better decision making, more innovation, better ways of solving problems, more
creativity, and better understanding of different market segments
Problems with difference in workforce: high interpersonal conflict, high rate of turnover,
breakdown in communications
A multicultural organization is 1. pluralism, 2. full structural integration, 3. full integration of the
informal networks, 4. an absence of prejudice and discrimination, 5. no gap in organizational
identification based on cultural identity group, and 6. low levels of intergroup conflict
Many big companies have no global strategies as they dont have global leaders and managers
Culture is the collective programming of the mind that separates on group from another. These
are passed and down and reinforced by the agents of socialization
Manifestation of culture: Values at the core, harder to see outright. Outer layers are symbols
(clothing, art), Heroes, and Rituals which are easily seen. Practices cuts across all layers
Culture and psychology: Mental Programming (Our psychology), Human Nature (Universal e.g.
eating), Personality (Inherited/individual vs learnt), Cultural Group (learned)
Hofstedes Cultural Dimensions: individualism vs collectivism, high vs low power distance, high
vs low uncertainty avoidance, masculine vs feminine, and long vs short term orientation
Masculinity: preference in society for values such as assertiveness, competitiveness, task
achievement
Femininity: preference for relationships nurturing, harmony, quality of life and relationships
Categorization: Allows us to make sense of complex world and environment by group large
chunks together
Stereotypes: can be consciously held> descriptive> accurate (Sophisticated stereotypes)>first
best guess> modified
When stereotyping we differentiate and categorise the other people based on gender, race,
ethnicity, nationality, profession, and politics
Individual differences are often overlooked, people become identified by their larger groups
Types of stereotypes: self-fulfilling stereotypes, stereotype consensus, stereotype threat
Ethnocentrism
In-group vs out-group
High vs low cultural distance
Dialectic logic process (Hegel): thesis>antithesis>synthesis (shifting perception by actively
observing opposite phenomenon)
Allports Contact Theory: increased contact between two groups and individuals generates
understanding, reduces stereotypes and conflicts (WWII, where German and French troops
celebrated Christmas together)
Cultural intelligence (CQ): Set of skills that allow an individual to operate with high effectiveness
in foreign cultures and culturally ambiguous settings
Enculturation: First culture learning
Acculturation: Second culture learning
The cultural script
Accepting that you dont know is a big step
Cultural quotient: Cognitive means (With your head)>physical means (With your
body)>motivational means (By rewarding achievement)
Communication depends on: codes, convention
Cultural field: surrounds our channels of communication and can affect the meanings of the
message
Different codes and conventions of communication can make transfer difficult
Intercultural communication: direct vs indirect, implicit vs explicit
Verbal vs Non-verbal communication
Non-verbal communication: Proxemics (personal space, office layout), Haptics (handshakes,
hugs, kisses), Kinesics (gestures, facal exp, eye contact), Paralanguage (tone, inflection)
Low vs High context
Saving face: keeping harmony and maintaining social norms, expectations, personal dignity and
respect. Relation before task.
Affective cultures: visibly emotional, allows emotions in discussions (India, Brazil, Egypt)
Neutral cultures: restraining and controlling, separating emotions from decision (Spock from
Star Trek)(China, NZ, German)
Issues in Intercultural Communication: communicating ethically, communicating electronically,
communicating through a translator
Negotiation: multi party discussion or communication to reach some type of agreement
Important to know the other party in negotiation, more so in high contest culture than low
context
In high context there would be lots of discussion about information and more time spent,
compared to low context
Persuasion phase not the most important in high context, room left to manoeuvre, all about
face, more emphasis on relation. In low context it is all about negotiating and persuasion, most
time spent here, early concessions made to move things forward
Agreement for high context can be broad and open, about maintaining relation. For low context
it is about legal and documented agreements, all about the present and profits
Business is not a zero-sum game, no business is an island. Alliances are a key part of current
business strategies, as well as strategic business groups
Discuss the china video we watched regarding American and Chinese businessmen and the
issues regarding communication and expectations (high vs. low context)
Disconfirmed expectancy: when something happens that is not expected, due to subject specific
enculturation, and often related to social interactions. Can be linked to concepts of fairness and
appropriateness
Parochialism>Ethnocentrism>Polycentrism
Cultural protocol
Motivation: that which drives goal directed behaviour, so it channels efforts towards real or
perceived need/want
McClellands Theory of Needs state that individuals specific needs are acquired over time and
shaped by ones life experiences.
There are three classifications: Achievers need to excel and avoid both high and low-risk
situations (goes for 50% chance) and usually works alone with other high achievers. Those with
high need for Affiliation want harmonious relationship with others and work in areas that
provide significant personal interaction. A finally need for Power, with personal power being the
ability to control others (not preferred), and institutional power being the ability to organize the
efforts of others to further the goals of the organization.
Herzbergs Motivation-Hygiene theory states that unlike Maslows Hierarchy, there are factors
which if not present lead to dissatisfaction and if present lead to no dissatisfaction (Not
satisfaction) (Hygiene-company policy, salary, personal life, security). But there are also factors
which lead to higher levels of satisfactions if present and no satisfaction if not present
(Motivators- achievement, recognition, responsibility, growth)
Equity Theory suggests relational satisfaction comes from perceived equality in terms of input
and output (input- time, effort, loyalty) (output- salary, reputation, responsibility). Any unfair
distribution will lead to dissatisfaction
Vrooms Expectancy Theory is about the mental process regarding choice, on how we behave in
certain ways due to what we expect the outcome to be
Content Theories: Tend to examine what the needs are and their arrangement in order of
importance (McClellands, Herzberg, Maslow)
Process Theories: Tend to examine the process of fulfilling needs (Equity theory, Vroom)
Maslows Hierarchy of Needs: physiological needs, security/basic needs, social and affiliation,
esteem, self-actualization
Higher we go up and away from the more universal human nature motivators, the more
culturally relative they become. Self-actualization and the need for security may mean different
things depending on types of cultures (individualistic vs. collective)
CCM Motivation Adjustment Steps: Describe the motivational situation, identify cultural
assumptions, generate culturally synergetic alternatives, monitor and make adjustments to the
motivation strategy (4 steps)
Leadership is the ability influence/motivate/enable others to contribute toward the success of
the organisation/team
Types of Power: Reward (valance), coercive (punishment), legitimate (positional power),
referent (charisma and persuasiveness), expert (ability/knowledge), affiliation (association)
Which one of the above are most effective for young managers?
A modern leader is not born, but learns and uses different approaches and traits to fit the
context and followers. He/she wears many hats depending on the context
GLOBE Study investigated among other factors how cultural values are related to organizational
practices and conceptions of leadership
Cultural universal vs. cultural contingent attributes
Culturally contingent attributes need to be tailored for each cultural groups, such as
participation in leadership, and relation with subordinates
Eastern cultures prefer indirect praise while Western cultures prefer direct ones
A multicultural team may face hurdles, but if overcome can potentially perform better than a
mono-cultural team
In multicultural teams it is about forming a hybrid culture, taking the best from different
cultures and applying that towards the team goal
Culture shock is the natural, staged reaction to new socio-environmental patterns. It can be
both physical and emotional, and usually involves disconfirmed expectancies
Also relates to cultural distance, the further the two cultures the more pronounced the shock
Stages of cultural shock: honeymoon, emptiness, conform, assimilation
One of the goals of building CQ is to lower the severity and duration of the emptiness stage
In our daily lives there can be more minute ups and downs in the stages of cultural shock
Coping strategies Selection and assignment acceptance (psychometric measures, family
dynamics, organizational support), pre-departure preparation if possible (study basics,
disconfirmed expectancy, talk to expats), on arrival and during assignment (realistic goals, have
sense of humour, cultural informant, choose battles carefully), return (reverse cultural shock)
Negativity talk is a form of self-fulfilling communication in acculturation, patterns of
communication that disrupt and reduce the possibility of effective cultural adjustment
Steps handling negativity talks determine pattern, validate perspective without engaging in
neg talk, postpones awareness effort, collaborative redirection strategy
Repatriation can often be more shocking than going into an alien culture (reverse cultural
shock)
Problems with repatriation idealised view of home, expectation of total familiarity,
disconfirmed expectancy, social re-entry, professional re-entry
Use of facebook to reduce the many effects of reverse cultural shock
Increased cultural differences within a workforce also potentially create costs in terms of higher
interpersonal conflict, turnover, and communications breakdown. To maximize productivity
leaders are advised to oversee the change process into a multicultural organization
Characters of a multicultural organization are: pluralism, full structural integration, full
integration of the informal networks, absence of prejudice and discrimination, no organizational
identification based on cultural identity of groups, low intergroup conflicts
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Coffee House - Manna DeyDocument3 pagesCoffee House - Manna DeyRidwan AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Sofa OrbitDocument1 pageSofa OrbitRidwan AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Sofa OrbitDocument1 pageSofa OrbitRidwan AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Sofa OrbitDocument1 pageSofa OrbitRidwan AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Nokia India RidwanDocument17 pagesNokia India RidwanRidwan AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Port Harbor Export-Processing ZoneDocument5 pagesPort Harbor Export-Processing ZoneRidwan AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Journal Notes For Critical ReflectionDocument4 pagesJournal Notes For Critical ReflectionRidwan AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- IBUS6012 Critical Reflection 3 S22012Document4 pagesIBUS6012 Critical Reflection 3 S22012Ridwan AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- IBUS6012 Critical Reflection 3 S22012Document4 pagesIBUS6012 Critical Reflection 3 S22012Ridwan AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- History of Costumes Unit 2Document14 pagesHistory of Costumes Unit 2harsha090909100% (1)
- Alvar Alto and FinlandiahallDocument4 pagesAlvar Alto and FinlandiahallTasawar ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Mrugaraju - WikipediaDocument5 pagesMrugaraju - WikipediaorekishPas encore d'évaluation
- BPR Chapter1 Concept and Principle Know Where You Are3Document29 pagesBPR Chapter1 Concept and Principle Know Where You Are3Kalai VaniPas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Reported SpeechDocument2 pagesReported SpeechjulietapiciuPas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Story Telling Text - PocahontasDocument2 pagesStory Telling Text - PocahontasTamara Bunga ChantikaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Angel Island - QuestionnaryDocument3 pagesAngel Island - QuestionnaryDouglas LucioPas encore d'évaluation
- Savage Worlds - Revised - Green Ronin - Campaign Setting - Freeport CompanionDocument87 pagesSavage Worlds - Revised - Green Ronin - Campaign Setting - Freeport CompanionCarlos Luis Juan100% (7)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Roots of Monasticism and The Rule of ST BenedictDocument11 pagesRoots of Monasticism and The Rule of ST BenedictJeanRachoPaynandosPas encore d'évaluation
- Ge4 Activity 3Document3 pagesGe4 Activity 3Bwii Amber KimPas encore d'évaluation
- Cultural Appropriation On The ArtsDocument19 pagesCultural Appropriation On The ArtsBrylle Mar C. Peñonal83% (6)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Class 2 Holiday Home WorkDocument4 pagesClass 2 Holiday Home WorkSmarten DelhiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Being Different: An Indian Challenge To Western Universalism Rajib MalhotraDocument17 pagesBeing Different: An Indian Challenge To Western Universalism Rajib MalhotraMd Intaj AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Larcade Arcana 1.2 Humn13n - M831 Module1 Lesson1.2 Learning Task and AssessmentDocument2 pagesLarcade Arcana 1.2 Humn13n - M831 Module1 Lesson1.2 Learning Task and AssessmentLarcade ArcanaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Poem To DarknessDocument2 pagesA Poem To DarknessmamtasagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Intro - Hispanic Heritage Month Project Directions - PeopleDocument5 pagesIntro - Hispanic Heritage Month Project Directions - PeopleJoaquinPas encore d'évaluation
- A Dhrupad Discography - The Dagar FamilyDocument6 pagesA Dhrupad Discography - The Dagar Familytvmehta01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ramesh Bhutani The Name People of INA MarketDocument3 pagesRamesh Bhutani The Name People of INA MarketAnita MayerPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Summary of HinilawodDocument4 pagesSummary of HinilawodAmiga Mi67% (3)
- AR-212-CBGS: B.Arch., III Semester Choice Based Grading System (CBGS) Building Construction-IIDocument2 pagesAR-212-CBGS: B.Arch., III Semester Choice Based Grading System (CBGS) Building Construction-IIAnannya RPas encore d'évaluation
- Nepali ArtDocument6 pagesNepali Artterobau123Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Western FrontierDocument15 pagesThe Western FrontierGenesis WilliamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Westward ExpansionDocument13 pagesWestward ExpansionDeshi boy Shriyansh DubeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Essays On Sound and Vision Co-Edited Wit PDFDocument454 pagesEssays On Sound and Vision Co-Edited Wit PDFTomislav TanevskiPas encore d'évaluation
- Caribbenstudiesnotes 100309053843 Phpapp02Document138 pagesCaribbenstudiesnotes 100309053843 Phpapp02Travis Anthony BenainPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 28 Impression Post Impressionism PDFDocument51 pagesChapter 28 Impression Post Impressionism PDFJanett MonsantoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Day The Dancers CameDocument13 pagesThe Day The Dancers CameEvangeline Cosico50% (2)
- Media and Society - 3 Units - Complete Study MaterialDocument57 pagesMedia and Society - 3 Units - Complete Study MaterialREDAPPLE MEDIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Ricardo Gomez - What Is This Thing Called TechnologyDocument46 pagesRicardo Gomez - What Is This Thing Called TechnologyFede Otero0% (1)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Raza CVDocument2 pagesRaza CValtamashrathorePas encore d'évaluation