Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Demographics
Transféré par
cbellsnlDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Demographics
Transféré par
cbellsnlDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Lao PDR
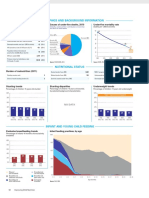
DEMOGRAPHICS MATERNAL AND NEWBORN HEALTH
Total population (000) 5,759 (2006) Under-five mortality rate Causes of under-five deaths Causes of maternal deaths Coverage along the continuum of care
Deaths per 1000 live births Globally more than one third of child deaths are attributable to Regional estimates for Asia, 1997-2002
Total under-five population (000) 715 (2006) undernutrition
Unmet need for family planning (%) 40 (2000) Abortion
Births (000) 156 (2006) Measles Injuries Malaria Causes of neonatal
Contraceptive
2% deaths Obstructed labor 6% 32
200 6% 1%
Antenatal visits for woman (4 or more visits, %) --- prevalence rate Pre-pregnancy
Birth registration (%) 59 (2006) HIV/AIDS
Diarrhoea 2%
Tetanus 5%
9%
163 Diarrhoea Antenatal visit
Under-five mortality rate (per 1000 live births) 75 (2006) 160 16% 0% Congenital 6%
(1 or more) 27 Pregnancy
Other 9% Intermittent preventive treatment for malaria (%) --- Hypertensive Haemorrhage
Infant mortality rate (per 1000 live births) 59 (2006) disorders 31% Skilled attendant
120 Sepsis/
at birth 19 Birth
Pneumonia 24% C-section rate (total, urban, rural; %) 9%
Neonatal mortality rate (per 1000 live births) 35 (2000) 75 Neonatal (Minimum target is 5% and maximum target is 15%) ---, ---, --- *Postnatal care Neonatal period
Total under-five deaths (000) 12 (2006) 80 54 35%
Preterm 24% Sepsis/Infections,
Early initiation of breastfeeding (within 1 hr of birth, %) --- including AIDS
Exclusive
23 Infancy
Maternal mortality ratio (per 100,000 live births) 660 (2005) 40 Pneumonia breastfeeding
MDG Target 12%
33 (2005)
19% Postnatal visit for baby (within 2 days for home births, %) --- Other causes Measles
Lifetime risk of maternal death (1 in N) Asphyxia 31% Anaemia 48
0 Other 13% 21%
Total maternal deaths 1,300 (2005) 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 22%
Source: Lawn JE, Cousens SN for
0 20 40 60 80 100
Source: UNICEF, 2006 Source: WHO, 2006 CHERG (Nov 2006) Source: Khan, Khalid S., et al, Lancet 2006:367:1066-74 Source: DHS, MICS, Other NS
*See Annex for indicator definition
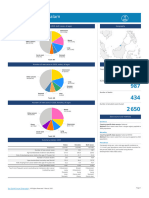
Antenatal care Skilled attendant at delivery Neonatal tetanus protection
INTERVENTION COVERAGE FOR MOTHERS, NEWBORNS AND CHILDREN Percent women aged 15-49 years attended at least once by a Percent live births attended by skilled health personnel Percent of newborns protected against tetanus
NUTRITION skilled health provider during pregnancy
Stunting prevalence (moderate and severe, %) 48 (2000) Complementary feeding rate (6-9 months, %) 10 (2000) 100 100 100
Wasting prevalence (moderate and severe, %) 18 (2000) Low birthweight incidence (%) 14 (2000) 80 80 80
Underweight prevalence Exclusive breastfeeding Vitamin A supplementation 60 60 60
Percent
Percent
Percent
52
Percent children < 5 years underweight for age* Percent infants < 6 months exclusively breastfed Percent children 6-59 months receiving vitamin A doses
40 40 40
At least one dose Two doses 27
100 100 100 19
20 20 20
80
80 80 80 70 0 0
73 64 63 1985 1990 1995 2000 2006
58 58 2000 2000
60 60 60 70 48 MICS MICS
Percent
Percent
Percent
Source: WHO/UNICEF
64 62
40 58
40 36 36 40 40
43
20 20
23
20 0
WATER AND SANITATION EQUITY
0 0 0
1993 1994 2000 2000 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 Water Sanitation Coverage gap by wealth quintile
Other NS Other NS Other NS MICS
Source: UNICEF
Percent population using improved drinking water sources Percent population using improved sanitation facilities
*Based on 2006 WHO reference population Rural Urban Total Rural Urban Total
100 100 100
CHILD HEALTH 79
80 80 80
67
Immunization Malaria prevention Prevention of mother to child 60 51 60 60
Percent
Percent
Percent
Percent of children immunised against measles
Percent of children immunised with 3 doses DPT
Percent children < 5 years sleeping under ITNs transmission of HIV 43
Percent HIV+ pregnant women receiving ARVs for PMTCT
40 40 30 40
Percent of children immunised with 3 doses Hib
20
20 20 20
100 100
0 0 0
80 80 2004 2004 Poorest 2nd 3rd 4th Wealthiest
Source: WHO/UNICEF JMP, 2006 Source: WHO/UNICEF JMP, 2006
57
60 60 2000
Percent
Percent
48 No data MICS
40 40 POLICIES SYSTEMS
20 20 18
Coverage gap (%) 70
International Code of Marketing of Breastmilk Financial Flows and Human Resources
0 0 Substitutes Partial Ratio
1990 1995 2000 2005 2006 2000 Per capita total expenditure on health (US$) 74 (2007) poorest/wealthiest 1.1
Source: WHO/UNICEF MICS
New ORS formula and zinc for management of Difference
General government expenditure on health as
diarrhoea No poorest-wealthiest (%) 10
% of total government expenditure (%) 5 (2007)
Diarrhoeal disease treatment Malaria treatment Pneumonia treatment
Percent children < 5 years with diarrhoea receiving oral rehydration Percent febrile children < 5 years using antimalarials Percent children < 5 years with suspected pneumonia taken to Community treatment of pneumonia with antibiotics --- Out-of-pocket expenditure as % of total
therapy or increased fluids, with continued feeding appropriate health provider
Percent children < 5 years with suspected pneumonia receiving expenditure on health (%) 72 (2007)
IMCI adapted to cover newborns 0-1 week of age No
antibiotics
Density of health workers (per 1000 population) 1.6 (1996)
100 100 100 Costed implementation plan(s) for maternal,
newborn and child health available No Official Development Assistance to child health
80 80 80 per child (US$) 8 (2005)
Midwives be authorised to administer a core set of
60 60 60 life saving interventions --- Official Development Assistance to maternal and
Lao PDR
Percent
Percent
Percent
neonatal health per live birth (US$) 18 (2005)
37 36 Maternity protection in accordance with ILO
40 40 40
Convention 183 No National availability of Emergency Obstetric Care
20 20 20 services (% of recommended minimum) ---
9 Specific notification of maternal deaths ---
0 0 0
2000
MICS
2000
MICS
2000
MICS
Countdown to 2015
2008 Report
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Criminal Conspiracy of Coronavirus by Dr. David MartinDocument5 pagesThe Criminal Conspiracy of Coronavirus by Dr. David MartinTim Brown100% (1)
- (Current Cancer Research) Erle S. Robertson - Microbiome and Cancer-Springe PDFDocument406 pages(Current Cancer Research) Erle S. Robertson - Microbiome and Cancer-Springe PDFmariomgPas encore d'évaluation
- RhabdovirusDocument74 pagesRhabdovirustummalapalli venkateswara raoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatrics Case PresentationDocument70 pagesPediatrics Case PresentationRold Brio Sos100% (1)
- CHN Post TestDocument10 pagesCHN Post TestJune DumdumayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Guinea BissauDocument1 pageGuinea BissaucbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- Ye MenDocument1 pageYe MencbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- An Go LaDocument1 pageAn Go LacbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- Ben inDocument1 pageBen incbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- Burkina FasoDocument1 pageBurkina FasocbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- Liberia: Country ProfileDocument4 pagesLiberia: Country Profilegeorgeloto12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reporting On Reproductive Health in Africa (Ayorinde Ajayi)Document35 pagesReporting On Reproductive Health in Africa (Ayorinde Ajayi)National Press FoundationPas encore d'évaluation
- Maternal CZEDocument4 pagesMaternal CZEYajie LuoPas encore d'évaluation
- Situation Analysis (1) FinalDocument5 pagesSituation Analysis (1) Finalsitikantha sahooPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition IDN PDFDocument2 pagesNutrition IDN PDFdini mutia KhairunnisaPas encore d'évaluation
- STD Clinical CliniciansDocument69 pagesSTD Clinical Cliniciansayush231195Pas encore d'évaluation
- MOR Health System Profiles 2018Document2 pagesMOR Health System Profiles 2018Chaymae SahraouiPas encore d'évaluation
- 496 Mongolia Fact SheetsDocument2 pages496 Mongolia Fact SheetsShotokan Karate MongoliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jamaica Country Profile Highlights Maternal and Child Health StatisticsDocument4 pagesJamaica Country Profile Highlights Maternal and Child Health StatisticsZineil BlackwoodPas encore d'évaluation
- WHO CancerReport 2020 MEXDocument2 pagesWHO CancerReport 2020 MEXAldo Leonardo De Jesus GarduzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Country Health Profile: Maternal, Newborn & Child Survival in FijiDocument4 pagesCountry Health Profile: Maternal, Newborn & Child Survival in Fijipaperpin27Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Open Ophthalmology JournalDocument5 pagesThe Open Ophthalmology JournalFenny Duma SariPas encore d'évaluation
- 24 Angola Fact SheetsDocument2 pages24 Angola Fact SheetsHigidio EduardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Globo Can Ecuador 2020Document2 pagesGlobo Can Ecuador 2020Park Triple S Kim HyungPas encore d'évaluation
- Child Health Programme: 4.2.2 Causes of Child Mortality in IndiaDocument24 pagesChild Health Programme: 4.2.2 Causes of Child Mortality in IndiaSolomon JosephPas encore d'évaluation
- PIVOT 2016 Impact ReportDocument17 pagesPIVOT 2016 Impact ReportPivot100% (2)
- Health Care: Sector ReportDocument16 pagesHealth Care: Sector Reportmona galalPas encore d'évaluation
- SERBIA'S NCD BURDEN AND RISK FACTORSDocument1 pageSERBIA'S NCD BURDEN AND RISK FACTORSDejan ŽujovićPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.3.3 Diarrhea-4 Januari-3 JanDocument56 pages1.3.3 Diarrhea-4 Januari-3 JanmaryamPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk factors and mental health issues of teenage pregnancyDocument9 pagesRisk factors and mental health issues of teenage pregnancyAngela May ColumnaPas encore d'évaluation
- KMC To Reduce Neonatal Mortality Hadi P Unair 29 Sept 2016Document63 pagesKMC To Reduce Neonatal Mortality Hadi P Unair 29 Sept 2016mimimomopipiPas encore d'évaluation
- EPI Scorecard - Sudan - Q1 - 2018Document1 pageEPI Scorecard - Sudan - Q1 - 2018محمد أبو القاسم عليPas encore d'évaluation
- The Healthcare System in GhanaDocument1 pageThe Healthcare System in GhanaDave UlanPas encore d'évaluation
- Child-Related Factors Affecting StuntingDocument1 pageChild-Related Factors Affecting StuntingJoulesPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition PHL PDFDocument2 pagesNutrition PHL PDFJaiy HingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Adolescence and Preg Position PaperDocument2 pagesAdolescence and Preg Position PaperNichole Trisha MontalbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Polio Bulletin 2016 No 14 Week 27Document6 pagesPolio Bulletin 2016 No 14 Week 27Mark Anthony MadridanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Major causes of death in children under five globally in 2008Document1 pageMajor causes of death in children under five globally in 2008raissa leePas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition LCADocument2 pagesNutrition LCAShernia EliboxPas encore d'évaluation
- Par To GraphDocument15 pagesPar To GraphcarPas encore d'évaluation
- The Tendency of Stunting Among Children Under Five in The North - 2023 - JornalDocument8 pagesThe Tendency of Stunting Among Children Under Five in The North - 2023 - JornalJuan ZilkyPas encore d'évaluation
- Maternal Health: Family Revolves Around MotherDocument16 pagesMaternal Health: Family Revolves Around MotherFatima IqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- PRUMan PRULady Leaflet ENGDocument3 pagesPRUMan PRULady Leaflet ENGJessicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Him & Her: PRU PRUDocument3 pagesHim & Her: PRU PRUshirley lee wenPas encore d'évaluation
- 96 Brunei Darussalam Fact SheetsDocument2 pages96 Brunei Darussalam Fact SheetsMaria VidalPas encore d'évaluation
- Cancer Burden and Trends in SudanDocument2 pagesCancer Burden and Trends in SudanmohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- Tanzania, United Republic ofDocument1 pageTanzania, United Republic ofcbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- Burkina FasoDocument1 pageBurkina FasocbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- The GambiaDocument1 pageThe GambiacbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- Ben inDocument1 pageBen incbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- Sierra LeoneDocument1 pageSierra LeonecbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- Ben inDocument1 pageBen incbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- Ben inDocument1 pageBen incbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- Ben inDocument1 pageBen incbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- Ben inDocument1 pageBen incbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlPas encore d'évaluation
- How ERP Software by SAP Enabled ModernaDocument3 pagesHow ERP Software by SAP Enabled ModernaMarie IriartePas encore d'évaluation
- Hepatitis Case StudyDocument4 pagesHepatitis Case StudyTasha MageePas encore d'évaluation
- Flu Fact SheetDocument2 pagesFlu Fact Sheetapi-68340462Pas encore d'évaluation
- v25 n8Document482 pagesv25 n8Anonymous NR7pnLbPas encore d'évaluation
- MalariaDocument8 pagesMalarianurulzafPas encore d'évaluation
- IMMUNIZATION ScheduleDocument2 pagesIMMUNIZATION Schedulejhonny100% (1)
- PostnatalDocument36 pagesPostnatalAditya BarmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Haemophilus Etc, Yersinia Etc.Document39 pagesHaemophilus Etc, Yersinia Etc.Pi Castaneda GanzonPas encore d'évaluation
- IMCI Integrated Management of Childhood IllnessDocument24 pagesIMCI Integrated Management of Childhood Illnesssimplyme_tin13100% (1)
- Mohamed Jama Idiris Field Report of Wajaale, Hargeisa, BerberaDocument24 pagesMohamed Jama Idiris Field Report of Wajaale, Hargeisa, Berberasuusaan100% (2)
- Mumps PresentationDocument15 pagesMumps PresentationMoney MotivationPas encore d'évaluation
- Neu N TORCH Infections Clinics in Perinatology 2015Document27 pagesNeu N TORCH Infections Clinics in Perinatology 2015vickyPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction Scope and Historical Development of Veterinary Microbiology Lecture NotesDocument11 pagesIntroduction Scope and Historical Development of Veterinary Microbiology Lecture Noteskaran kamboj0% (1)
- Case Def ToxoplasmosisDocument0 pageCase Def ToxoplasmosisAhmad Badrul AminPas encore d'évaluation
- Duration of Post-Vaccination Humoral Immunity Against Yellow Fever in ChildrenDocument8 pagesDuration of Post-Vaccination Humoral Immunity Against Yellow Fever in ChildrenDavids MarinPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - General Complications of Fractures - d3Document27 pages1 - General Complications of Fractures - d3Jheng-Dao Yang100% (1)
- Jurnal Fixxxx 1Document14 pagesJurnal Fixxxx 1heryanggunPas encore d'évaluation
- AdenovirusDocument18 pagesAdenovirusDr Ruqeya NazirPas encore d'évaluation
- Facts About MeaslesDocument4 pagesFacts About MeaslesTrishana GreenPas encore d'évaluation
- RTRMF-CM - Pedia Clinics GuideDocument7 pagesRTRMF-CM - Pedia Clinics GuideKo HakuPas encore d'évaluation
- Triptico Del EbolaDocument2 pagesTriptico Del EbolaClaudi TperezPas encore d'évaluation
- Strengthening Routine Immunization Simple Guide For Reaching Every PurokDocument36 pagesStrengthening Routine Immunization Simple Guide For Reaching Every Purokapi-320443960Pas encore d'évaluation
- Minimal Inhibitory Concentration TestDocument26 pagesMinimal Inhibitory Concentration TestZandhika Alfi PratamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Deccan Chronicle - Chennai - 2021-11-17Document9 pagesDeccan Chronicle - Chennai - 2021-11-17கோவி கோபால் ஆர்ட்ஸ்Pas encore d'évaluation