Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
CH 10 Calvin Cycle and Photosystems
Transféré par
inkheartkatTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CH 10 Calvin Cycle and Photosystems
Transféré par
inkheartkatDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
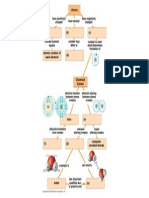
Photosystem 2
1. noncyclic
2. occurs/resides in thylakoid membrane
3. reaction center chlorophyll is P680
Photosystem 1
1. can be cyclic, if required
2. occurs/resides in thylakoid membrane
3. reaction center chlorophyll is p700
4. passes photoexcited electrons to
photosystem 1 via an electron transport
chain
5. Light enters chlorophyll and excites an
electron. The energy from this electron is
passed from electron to electron until an
electron in the reaction center is excited
and physically removed to the primary
acceptor
4. uses spent electrons from photosystem 2
to make up the number of electrons in its
own system
5. Passes spent electrons back to prior
electron transport chain to create extra ATP
if needed (this is the cyclic process).
6. This excited electron is passed down the
electron transport chain to photosystem 1
6. Passes its own photo excited electrons to
an electron transport chain, which
transmits them to Fd, an iron-containing
protein
1.
2.
3.
4.
Calvin Cycle
occurs in stroma
CO2 enters and leaves as sugar
cycle spends ATP as energy and consumes
NADPH as reducing power for adding
high-energy electrons to make sugar
returns NADP+ to the light reactions
5. 3 phases:
carbon fixation: each CO2 is fixed into a
5-carbon sugar, using RuBP
reduction: each 3-phosphoglycerate
receives a phosphate from ATP. A pair of
electrons from NADPH then reduces it to
G3P
regeneration: RuBP is regenerated, so that
CO2 can again be accepted, and cycle can
turn again
6. G3P is the product of this cycle, not
glucose. G3P is a sugar
7. Splits water into oxygen and electrons.
Water is the source of electrons for this
process
8. ATP produced during noncyclic electron
flow is called noncyclic
photophosphorylate
7. NADP+ reductase transfers the electrons
from Fd to NADP+ creating NADPH
7. Cycle must turn 3 times, fixing 3 carbons,
to create one net G3P
8. This NADPH provides reducing power for
the synthesis of sugar in the calvin cycle
9.
9.
8. For net synthesis of one G3P, the cycle
consumes 9 ATP and 6 NADPH, these
molecules are regenerated by the light
reactions
9. G3P is starting material for metabolic
pathways that synthesize other organic
compounds
David Snow
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- 14Document97 pages14physicsdocs95% (19)
- FormulasDocument11 pagesFormulasinkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions Manual - McGraw - Kinematics 2nd EdDocument145 pagesSolutions Manual - McGraw - Kinematics 2nd EdinkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- Beam AnalysisDocument8 pagesBeam AnalysisinkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- Extra 23 SolDocument5 pagesExtra 23 SolinkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- 338 Final Exam Review RubricDocument2 pages338 Final Exam Review RubricinkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Chapter 15Document2 pagesPhysics Chapter 15inkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- ME 327 Project-2Document1 pageME 327 Project-2inkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Kinematic ConceptsDocument33 pagesBasic Kinematic Conceptsinkheartkat100% (1)
- Complete KinematicsDocument92 pagesComplete KinematicsinkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Chiral Molecules ExplainedDocument8 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, and Chiral Molecules ExplainedinkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- ME321 Formula Sheet for Midterm Winter 2015Document1 pageME321 Formula Sheet for Midterm Winter 2015inkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnostic Dynamics 1 of 3Document1 pageDiagnostic Dynamics 1 of 3inkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- FluidsDocument15 pagesFluidsinkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mech SlidesDocument48 pagesFluid Mech Slidesvinoja29Pas encore d'évaluation
- FluidsDocument15 pagesFluidsinkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Engineering Ethics?Document12 pagesWhat Is Engineering Ethics?inkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- Mitosis and Meiosis Study QuestionsDocument1 pageMitosis and Meiosis Study QuestionsinkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- The Photosynthesis 2 Step - KEYDocument2 pagesThe Photosynthesis 2 Step - KEYinkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Chapter 15Document2 pagesPhysics Chapter 15inkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics ch35Document3 pagesPhysics ch35inkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 10 Calvin Cycle and PhotosystemsDocument2 pagesCH 10 Calvin Cycle and PhotosystemsinkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- The Photosynthesis 2 Step - KEYDocument2 pagesThe Photosynthesis 2 Step - KEYinkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 15 ExamplesDocument9 pagesCH 15 ExamplesinkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem Review IIIDocument7 pagesChem Review IIIinkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- The Photosynthesis 2 Step - KEYDocument2 pagesThe Photosynthesis 2 Step - KEYinkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem ReviewIIDocument1 pageChem ReviewIIinkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem ReviewDocument1 pageChem ReviewinkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology LectureDocument79 pagesBiology LectureinkheartkatPas encore d'évaluation