Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
QS07 - Class Exercises
Transféré par
lyk0texDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
QS07 - Class Exercises
Transféré par
lyk0texDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Accounting 225 Quiz Section #7
Midterm1 Review Class Exercises
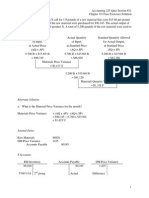
1. Rainier Manufacturing uses absorption costing in its job-order costing system. Selected ledger
accounts for the year just ended are presented below. Each question mark (?) represents a debit or credit
that is missing from the account(s). BB = Beginning Balance, EB = Ending Balance.
BB
RM
Purchases
EB
BB
Raw Materials
12,000
?
58,000
8,000
Finished Goods
15,200
COGS
EB
BB
DM
DL
MOH
EB
WIP
7,000
?
?
?
9,770
Unadjusted
COGS
12,500
Factory Wages Payable
- BB
50,000
46,000
IM
IL
Other
MOH
Total
MOH
?
?
55,200
4,000 EB
Additional Information: (I suggest you look over the above accounts carefully and read all the
information below before you start to respond to. any of the items on the next page)
The cost of both direct (DM) and indirect materials (IM) are debited to the Raw Materials
Inventory account when materials are purchased.
Of the raw materials issued to production during the year, 90% were direct materials and 10%
were indirect materials.
Of the factory wages incurred during the year, 80% was for direct labor and 20% was for indirect
labor.
The other MOH of $55,200 indicated in the MOH account includes depreciation, insurance,
utilities, and maintenance costs incurred during the year related to production.
During the year, Rainier applied manufacturing overhead to production using a single, plant-wide
predetermined application rate based on direct labor (DL) cost. Any over- or under-applied
overhead is adjusted directly to cost of goods sold at the end of the year.
The balance of Work in Process (WIP) at the end of the year related to the only job still in
production at that time. Its job cost sheet shows DM of $3,500, DL of $2,200, and MOH applied
(MOHA) of $4,070 as of the end of the year.
Accounting 225 Quiz Section #7
Midterm1 Review Class Exercises
Required: Please respond to the items on the next page. You might find it helpful to use the T-accounts
above for your work; however, please write your answers in the spaces provided on the next page
(a) The cost of direct materials issued to production was ____________; indirect materials cost incurred
was ____________
(b) The cost of direct labor used in production was ____________; indirect labor cost incurred was
____________
(c) The predetermined overhead application rate being used during the year is ____________ based on
direct labor cost.
(d) Total manufacturing overhead applied during the year was ____________.
(e) Cost of goods manufactured during the year was ____________.
(f) Was manufacturing overhead over- or under-applied by the end of the year? ____________ Provide
the journal entry that would have been necessary to clear the manufacturing overhead account at
the end of the year.
(g) As a result of the entry you have made in (f) above, operating income will increase/decrease/be
unaffected (circle one) by ____________ and inventory balances will increase/decrease/be
unaffected (circle one) by ____________.
(h) Specific to Rainiers data for the year, speculate as to whether its production output was equal to, less
than, or greater than (circle one) expected output. What evidence do you have to support your
answer? Explain.
(i) If sales revenue for the year was $250,000, the gross margin reported on Rainiers income statement
for the year was ____________.
Accounting 225 Quiz Section #7
Midterm1 Review Class Exercises
2. Parkland Manufacturing applies manufacturing overhead to production on the basis of direct
labor hours. It uses two (2) direct labor hours per unit produced. Direct labor hours and
costs at two different production and sales levels are presented in the table below.
9,000 Units
15,000 Units
18,000 DLH
30,000 DLH
$135,000
$225,000
Total manufacturing overhead
$72,700
$86,500
Total selling and administrative expenses
$43,700
$51,500
Direct labor hours used
Total prime manufacturing costs
Parkland estimates that $32,000 of its selling and administrative expenses are fixed costs.
(a) Using high-low analysis, determine the cost formula (equation) for estimating manufacturing
overhead. (i.e. Determine estimated variable MOH per direct labor hour and the total estimated
fixed MOH.) Clearly show your work and present a complete answer.
(b) Assume Parkland plans to manufacture and sell 13,000 units next year.
(i)
What would be the total estimated manufacturing (product) cost at that level of
production?
(ii)
What would be the estimated manufacturing (product) cost per unit produced next year?
Accounting 225 Quiz Section #7
Midterm1 Review Class Exercises
(c)
Suppose, rather than 13,000 units, Parkland plans to manufacture and sell 11,000 units
next year. Would the estimated manufacturing cost per unit be higher/lower/the same (circle
one) as your answer to Part (b.ii)? Explain. (Calculations are not required.)
(d)
How comfortable would you be using the cost formula you have presented in Part (a) to
estimate total manufacturing overhead if Parkland wanted to product 16,000 units next year?
Explain.
(e)
What is the variable selling and administrative cost per unit?
(f)
If Parklands selling price is $30 per unit, what is the contribution margin per unit?
(g)
How many units should Parkland plan to sell if it wants to earn a target profit of $75,000
next year? (Give your answer rounded up to the next whole unit.)
Accounting 225 Quiz Section #7
Midterm1 Review Class Exercises
3. A company has provided the following data:
If the dollar contribution margin per unit is increased by 10%, total fixed cost is decreased by
20%, and all other factors remain the same, net operating income will:
A. increase by $61,000.
B. increase by $20,000.
C. increase by $3,500.
D. increase by $11,000.
4. At a break-even point of 400 units sold, variable expenses were $4,000 and fixed expenses
were $2,000. What will the 401st unit sold contribute to profit?
A. $0
B. $5
C. $10
D. $15
Accounting 225 Quiz Section #7
Midterm1 Review Class Exercises
5. Vaccaro Corporation produces and sells a single product. Data concerning that product appear
below:
Fixed expenses are $293,000 per month. The company is currently selling 3,000 units per month.
Management is considering using a new component that would increase the unit variable cost by
$13. Since the new component would increase the features of the company's product, the
marketing manager predicts that monthly sales would increase by 400 units. What should be the
overall effect on the company's monthly net operating income of this change?
A. increase of $600
B. increase of $39,600
C. decrease of $600
D. decrease of $39,600
Accounting 225 Quiz Section #7
Midterm1 Review Class Exercises
6. Similien Corporation produces and sells a single product. Data concerning that product appear
below:
Fixed expenses are $300,000 per month. The company is currently selling 5,000 units per month.
The marketing manager would like to cut the selling price by $14 and increase the advertising
budget by $17,000 per month. The marketing manager predicts that these two changes would
increase monthly sales by 1,400 units. What should be the overall effect on the company's
monthly net operating income of this change?
A. increase of $64,200
B. increase of $215,400
C. decrease of $64,200
D. decrease of $5,800
Accounting 225 Quiz Section #7
Midterm1 Review Class Exercises
7. Moloney Corporation produces and sells a single product. Data concerning that product appear
below:
Fixed expenses are $898,000 per month. The company is currently selling 9,000 units per month.
The marketing manager would like to introduce sales commissions as an incentive for the sales
staff. The marketing manager has proposed a commission of $16 per unit. In exchange, the sales
staff would accept a decrease in their salaries of $117,000 per month. (This is the company's
savings for the entire sales staff.) The marketing manager predicts that introducing this sales
incentive would increase monthly sales by 100 units. What should be the overall effect on the
company's monthly net operating income of this change?
A. increase of $115,400
B. decrease of $16,600
C. decrease of $250,600
D. increase of $1,063,400
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Huron Automotive Company - ExcelDocument6 pagesHuron Automotive Company - Excelanubhav110957% (7)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- QS14 - Class Exercises SolutionDocument4 pagesQS14 - Class Exercises Solutionlyk0tex100% (1)
- QS04 - Class Exercises SolutionDocument3 pagesQS04 - Class Exercises Solutionlyk0texPas encore d'évaluation
- University of The Cordilleras Process CostingDocument5 pagesUniversity of The Cordilleras Process CostingJane PadillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Breeden Security Part BDocument6 pagesBreeden Security Part BCesar Felipe Uauy100% (2)
- QS16 - Class Exercises SolutionDocument5 pagesQS16 - Class Exercises Solutionlyk0texPas encore d'évaluation
- QS08 - Class Exercises SolutionDocument5 pagesQS08 - Class Exercises Solutionlyk0texPas encore d'évaluation
- QS16 - Class ExercisesDocument5 pagesQS16 - Class Exerciseslyk0texPas encore d'évaluation
- QS17 - Class ExercisesDocument4 pagesQS17 - Class Exerciseslyk0texPas encore d'évaluation
- QS17 - Class Exercises SolutionDocument4 pagesQS17 - Class Exercises Solutionlyk0texPas encore d'évaluation
- QS15 - Class ExercisesDocument4 pagesQS15 - Class Exerciseslyk0texPas encore d'évaluation
- QS15 - Class Exercises SolutionDocument5 pagesQS15 - Class Exercises Solutionlyk0tex100% (1)
- QS14 - Class ExercisesDocument4 pagesQS14 - Class Exerciseslyk0texPas encore d'évaluation
- QS12 - Class ExercisesDocument2 pagesQS12 - Class Exerciseslyk0texPas encore d'évaluation
- QS09 - Class Exercises SolutionDocument4 pagesQS09 - Class Exercises Solutionlyk0tex100% (1)
- QS12 - Midterm 2 Review SolutionDocument7 pagesQS12 - Midterm 2 Review Solutionlyk0tex0% (1)
- QS12 - Midterm 2 ReviewDocument5 pagesQS12 - Midterm 2 Reviewlyk0texPas encore d'évaluation
- QS13 - Class ExercisesDocument2 pagesQS13 - Class Exerciseslyk0texPas encore d'évaluation
- QS13 - Class Exercises SolutionDocument2 pagesQS13 - Class Exercises Solutionlyk0texPas encore d'évaluation
- QS11 - Class ExercisesDocument5 pagesQS11 - Class Exerciseslyk0texPas encore d'évaluation
- QS10 - Class ExercisesDocument1 pageQS10 - Class Exerciseslyk0texPas encore d'évaluation
- QS12 - Class Exercises SolutionDocument2 pagesQS12 - Class Exercises Solutionlyk0tex100% (1)
- QS10 - Class Exercises SolutionDocument2 pagesQS10 - Class Exercises Solutionlyk0texPas encore d'évaluation
- QS11 - Class Exercises SolutionDocument8 pagesQS11 - Class Exercises Solutionlyk0tex100% (2)
- QS07 - Class Exercises SolutionDocument8 pagesQS07 - Class Exercises Solutionlyk0texPas encore d'évaluation
- QS08 - Class ExercisesDocument4 pagesQS08 - Class Exerciseslyk0texPas encore d'évaluation
- QS09 - Class ExercisesDocument4 pagesQS09 - Class Exerciseslyk0texPas encore d'évaluation
- QS05 - Class Exercises SolutionDocument3 pagesQS05 - Class Exercises Solutionlyk0texPas encore d'évaluation
- QS06 - Class ExercisesDocument3 pagesQS06 - Class Exerciseslyk0texPas encore d'évaluation
- QS06 - Class Exercises SolutionDocument2 pagesQS06 - Class Exercises Solutionlyk0texPas encore d'évaluation
- QS05 - Class ExercisesDocument2 pagesQS05 - Class Exerciseslyk0texPas encore d'évaluation
- QS04 - Class ExercisesDocument3 pagesQS04 - Class Exerciseslyk0texPas encore d'évaluation
- Flexible Budgeting Lecture: Fixed/Static BudgetsDocument4 pagesFlexible Budgeting Lecture: Fixed/Static BudgetsSeana GeddesPas encore d'évaluation
- Dairy Fram BerutDocument45 pagesDairy Fram Berutcarol100% (1)
- Rules Regulations SRIC IITMandiDocument20 pagesRules Regulations SRIC IITMandiSimanta SinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cost ActivityDocument6 pagesCost ActivityDeepak PahujaPas encore d'évaluation
- Process & Operation CostingDocument19 pagesProcess & Operation CostingSmriti SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- IC3 Corporate Finance Photocopiable Teachers NotesDocument10 pagesIC3 Corporate Finance Photocopiable Teachers NotesОля ИгнатенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- American International University - Bangladesh: Q $45,000 Q Jewelry StoreDocument5 pagesAmerican International University - Bangladesh: Q $45,000 Q Jewelry StoreWahidul Alam SrijonPas encore d'évaluation
- BSRMDocument42 pagesBSRMPushpa BaruaPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Exam 2020Document11 pagesPractice Exam 2020ana gvenetadzePas encore d'évaluation
- Baf SyllabusDocument12 pagesBaf SyllabusJana MakPas encore d'évaluation
- Cima p1 2019 NotesDocument106 pagesCima p1 2019 NotesKamran ArifPas encore d'évaluation
- Management Information - ND2020 - Suggested - AnswersDocument4 pagesManagement Information - ND2020 - Suggested - Answerskawsar alamPas encore d'évaluation
- Contract Planning NotesDocument108 pagesContract Planning NotesGodwin Acquah100% (1)
- FMA-SEC 02-Chapter Eight Incremental Cost AnalysisDocument75 pagesFMA-SEC 02-Chapter Eight Incremental Cost AnalysisAgatPas encore d'évaluation
- Budgeting Tute 01Document2 pagesBudgeting Tute 01Maithri Vidana KariyakaranagePas encore d'évaluation
- ABC Analysis HandoutsDocument11 pagesABC Analysis HandoutsTushar DuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case On Joint Products and by ProductsDocument3 pagesCase On Joint Products and by ProductsBhargav D.S.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: ACCOUNTING 9706/22Document20 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: ACCOUNTING 9706/22Ruchira Sanket KalePas encore d'évaluation
- Lat Cashflow Planning and BudgetingDocument22 pagesLat Cashflow Planning and BudgetingTun Izlinda Tun BahardinPas encore d'évaluation
- Cost Analysis Template SpreadsheetDocument1 pageCost Analysis Template SpreadsheetAiko NakamuraPas encore d'évaluation
- Cacao Production in MindanaoDocument17 pagesCacao Production in MindanaoBREN G. CATUNAOPas encore d'évaluation
- MODULE 1-RelevantDocument7 pagesMODULE 1-RelevantMerliza JusayanPas encore d'évaluation
- ACCT10 Chapter 4 SolutionsDocument61 pagesACCT10 Chapter 4 SolutionsOmerGullPas encore d'évaluation
- Inventory System 1. Perpetual Inventory SystemDocument4 pagesInventory System 1. Perpetual Inventory Systemellaine villafaniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model Project For Milk Processing Plant - NABARDDocument39 pagesModel Project For Milk Processing Plant - NABARDPraneeth Cheruvupalli0% (1)
- STNR DecisionsDocument10 pagesSTNR DecisionsHassan AdamPas encore d'évaluation
- Manufacturing Company BudgetingDocument10 pagesManufacturing Company BudgetingSajakul SornPas encore d'évaluation