Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
CPTP - HPT & HF
Transféré par
AinahMahaniCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CPTP - HPT & HF
Transféré par
AinahMahaniDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CPTP
Offer ANTI-HYPERTENSIVE drug treatment to people:
who have stage 1 hypertension, are aged under 80 and meet identified criteria
who have stage 2 hypertension at any age
If aged <40 with stage 1 hypertension and w/o evidence of target organ damage, CVS disease, renal disease or diabetes,
consider:
specialist evaluation of secondary causes of hypertension
further assessment of potential target organ damage
Target BPs
>80 yo, 150/90
<80 yo, 140/90
Doesnt apply to diabetics [130-135 mmHg systolic blood] - guidance remains same.
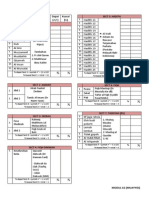
DIURETICS
CARDIAC GLYCOSIDE
HPT and HF
Mechanism of Action
DIGOXIN
Thiazide;
HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE,
Antiarrhythmic: vagolytic effect reduces
rate and conduction velocity in sinus
and AV nodes
Inotropic - increases intracellular Ca++
Enhance cardiac muscle contractility
hence, increase cardiac output
Increasing sodium and water excretion
(reduce Na+ and H2O retention) =>
decrease in extracellular volume, resulting
in a cardiac o/put and renal blood flow.
Act mainly in the cortical region of the
ascending loop of Henle and the distal
tubule.
Adverse effects
(A) CARDIAC
Heart block
Supraventricular and
ventricular arrhythmias
(B) NON-CARDIAC
Nausea, vomiting,
constipation
Confusion
Visual disturbances
uricaemia => GOUT
K+, Mg+ (blood), Ca2+
(urine)
Should be monitored when
using with digoxin
Indications
Interaction/CI
SVT arrhythmias
Chronic AF
Heart failure
Thiazides
decreased potassium
level
HF
Possible: elderly with
isolated systolic HPT
Gout, renal failure
[use loop d.]
CPTP
Loop
FUROSEMIDE,
B- BLOCKER
K+ sparing
Aldosterone antagonist:
SPIRONOLACTONE
Amiloride
Prototype: Propranolol
Non-selective: Atenolol
Selective: BISOPROLOL
(asthma with HPT)
LEBATOLOL PREGNANT
Inhibit the co-transport of Na+/K+/2CL- in
the luminal membrane in the ascending
limb on loH. It could cause decreased renal
vascular resistance and increased renal
blood flow.
ACEi
Acute P Oedema
Gastric upset, peptic
ulcers.
Gynaecomastia,
amenorrhea
HPT (usually in
combination with
thiazide)
Renal dysfunction
bcause increased risk
of hyperkalaemia.
Hypotension
Bradycardia
Fatigue, Insomnia,
hallucinations
Sexual dysf(x) + libido
Disturb serum lipid
patterns; HDL, plasma
TGA
Angina, post-MI,
tachycardias
Asthma, COPD, heart
block
Dry cough
Altered taste
K+ (potassium level
should be monitored)
Skin rash
Hypotension
Fever
HPT, post MI
LV dysfunction
Diabetic nephropathy
(with ARB, ACEi slows
the progression of
diabetic nephropathy)
CRF, and for pt with
increased risk of CAD
Pregnancy foetal
malformations
Hyperkalaemia
Bilateral renal artery
stenosis
Altered taste
K+ (potassium level
should be monitored)
Skin rash
Hypotension
Fever
Pts cant tolerate ACEi
Pregnancy foetal
malformations
Acts on C tubules to inhibit Na+
reabsorption and K+ excretion.
1.
activation of b1 adrenoceptors on
the heart
2. renin => angiotensin ->
aldosterone -> Na, H2O retention
3. Na, H2O retention
LISINOPRIL
RAMIPRIL
Ca2+ content of the urine
Ototoxicity
uricaemia => GOUT
K+, Mg+ (blood), Ca2+
(urine)
Decrease both preload and after load.
Block the ACE that cleaves angiotensin I
to form potent vasoconstrictor
angiotensin II.
ACEi inhibits breaks down of bradykinin
which also increases the prod. Of NO
and prostacyclin by the BV.
angiotensin II and bradykinin
ARB
Losartan
Competitive antagonists of the
angiotensin type 1 receptor.
CPTP
CCB
AMLODIPINE
Diltiazem
Verapamil
A-BLOCKER
Hydralazine, Minoxidil,
Diazoxide, Fenaldopam
CENTRAL
CYMPAT
HOLYTIC
Doxazosin
P. VASO
Methyldopa, Clonidine,
Moxonidine, Rilmendine
Block the inward of the ca2+ by binding
to the L-type Ca channels in the heart
and in smooth muscle of the coronary
and peripheral arteriolar vasculature.
This causes the smooth muscles to
relax, dilating mainly arterioles.
Competitive block of alpha1
adrenoceptors. Synthetic steroids
They decrease peripheral vascular
resistance and lower arterial BP by
causing relaxation of both arterial and
venous smooth muscle.
Activation of potassium channels
Increase in K+ conductancehyperpolarisation- relaxation of
vascular smooth muscle
Decrease sympathetic outflow from
vasopressor center in brainstem
Constipation
Fatigue, flushing
Hypotension
Headache, dizziness
Useful for HPT pts with
asthma, DM, angina
and/or peripheral
vascular disease
Little interaction with
other CVS drugs
Reflex tachy and first-dose
syncope
Prostatism
Urinary incontinence
Reflex stimulation to heart
May prompt angina
pectoris, MI
Pregnant pt with HPT
PREGNANT
SAFE
Labetalol - beta blockers
Methyldopa - alpha-adrenergic agonist
Nifedipine - calcium channel blockers
CHD risk reduction
Reduces relative risk (given) x probability of developing CHD (get from the calculator in the net)
Stroke risk reduction
Reduces relative risk (given) X prob got from the calculator ->
Number needed to treat (NNT)
Numbers needed to treat = 100 / Absolute risk reduction
UNSAFE
Beta blocker - growth retardation
Thiazides - oligohydramnios
ACE Inhibitors - cleft palate
Alpha blockers - cleft palate
CPTP
Acute HF
First line
Sit patient up, give high flow oxygen, iv access
Diamorphine 2.5-5mg i.v. (in-dwelling i.v. cannula)
Furosemide 40-120mg i.v. (lower dose with diuretic nave patient)
Buccal GTN 5mg if BP >100 systolic
Second line (not better within 2 hrs)
GTN 1-2mg/min i.v. infusion, increasing as tolerated by BP
Dobutamine 2.5-7.5microg/kg/min infusion, higher dose if hypotensive
Nebulised salbutamol 2.5-5mg 4hrly, as tolerated by heart rate
Third line (consider occasionally)
Mechanical ventilation (tired patient, inability to maintain oxygenation)
Intra-aortic balloon pump (generally only if there is a reversible cause for the heart failure)
Dialysis/CVVH
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Urinary IncontinenceDocument1 pageUrinary IncontinenceAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Csim2.25 - Electrolyte Imbalance Iron Metabolism & StorageDocument1 pageCsim2.25 - Electrolyte Imbalance Iron Metabolism & StorageAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- CSIM2.26 - Pituitary FunctionDocument3 pagesCSIM2.26 - Pituitary FunctionAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Csim2.26 - Pituitary F (X)Document1 pageCsim2.26 - Pituitary F (X)AinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Csim2.25 - Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument4 pagesCsim2.25 - Electrolyte ImbalanceAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Csim2.25 - Iron Metabolism & StorageDocument4 pagesCsim2.25 - Iron Metabolism & StorageAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Csim2.26 - Pituitary F (X) Unusual DiabetesDocument2 pagesCsim2.26 - Pituitary F (X) Unusual DiabetesAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Csim2.25 - Electrolyte Imbalance Calcium and BoneDocument7 pagesCsim2.25 - Electrolyte Imbalance Calcium and BoneAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Csim2.92 - HypoventilationDocument1 pageCsim2.92 - HypoventilationAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Csim2.94 - Interstitial Lung DiseaseDocument3 pagesCsim2.94 - Interstitial Lung DiseaseAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Csim2.71 - The Patient With Proteinuria and HaematuriaDocument11 pagesCsim2.71 - The Patient With Proteinuria and HaematuriaAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- CSIM2.24 - Signal TransductionDocument6 pagesCSIM2.24 - Signal TransductionAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- CSIM2.90 - Occupational AsthmaDocument1 pageCSIM2.90 - Occupational AsthmaAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- CSIM2.91 - COPD and Pulmonary HypertensionDocument2 pagesCSIM2.91 - COPD and Pulmonary HypertensionAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- CPTP - Pregnancy & LactatingDocument1 pageCPTP - Pregnancy & LactatingAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- CPTP - Parkinson & MVMT DisordersDocument2 pagesCPTP - Parkinson & MVMT DisordersAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- CPTP - Pud + Altered Bowel HabitDocument3 pagesCPTP - Pud + Altered Bowel HabitAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Penilaian Bahan TamhidiDocument3 pagesPenilaian Bahan TamhidiAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Penilaian Bahan MUAYYIDDocument3 pagesPenilaian Bahan MUAYYIDAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- CPTP - Poisonig MH Misuse of DrugsDocument5 pagesCPTP - Poisonig MH Misuse of DrugsAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Infection and AntibioticsDocument4 pagesInfection and AntibioticsAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- CPTP - PainDocument3 pagesCPTP - PainAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- CPTP - Infection and Antibiotics 2Document3 pagesCPTP - Infection and Antibiotics 2AinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- CPTP - Diabetes and Lipid Lowering DrugsDocument4 pagesCPTP - Diabetes and Lipid Lowering DrugsAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- CPTP - Af & Anti CoagulationDocument4 pagesCPTP - Af & Anti CoagulationAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- CPTP - EpilepsyDocument4 pagesCPTP - EpilepsyAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- CPTP - Asthma & CopdDocument5 pagesCPTP - Asthma & CopdAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Themed Week 7 - LIVERDocument24 pagesThemed Week 7 - LIVERAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Infection and AntibioticsDocument4 pagesInfection and AntibioticsAinahMahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Why We Get Sick0001Document8 pagesWhy We Get Sick0001mickPas encore d'évaluation
- pre-EClampsia Individual Case StudyDocument68 pagespre-EClampsia Individual Case Studycutekaize83% (18)
- Refrat Asma Eksaserbasi - Dr. Retna, Sp. PDocument24 pagesRefrat Asma Eksaserbasi - Dr. Retna, Sp. PWaskito Setiaji100% (1)
- Baltimore County Resource Guide December 2023Document13 pagesBaltimore County Resource Guide December 2023api-516741446Pas encore d'évaluation
- Discharge Instruction: Fitriani Pratiwi M.PDDocument13 pagesDischarge Instruction: Fitriani Pratiwi M.PDSaniaPas encore d'évaluation
- MAN 32025 Forpdf Rev0Document16 pagesMAN 32025 Forpdf Rev0alejandra ojeda anayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of AgingDocument26 pagesEffect of AgingBushra EjazPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Health in Persons With Down Syndrome A Literature ReviewDocument9 pagesOral Health in Persons With Down Syndrome A Literature ReviewRisana RahoofPas encore d'évaluation
- Styrene Toxicological Overview: Key PointsDocument10 pagesStyrene Toxicological Overview: Key PointsanirudhPas encore d'évaluation
- Rev. Vanlalngeiha VuinaDocument4 pagesRev. Vanlalngeiha VuinaktpmvtPas encore d'évaluation
- Paraphrase DDocument62 pagesParaphrase DVignesh GPas encore d'évaluation
- Role of Neurotransmitters in Schizophrenia A Comprehensive StudyDocument27 pagesRole of Neurotransmitters in Schizophrenia A Comprehensive StudyJosep Rio RambePas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Lab Technician Exam Question Answer PDFDocument7 pagesMedical Lab Technician Exam Question Answer PDFAhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Internet of Nano, Bio-Nano, Biodegradable And-3-4Document2 pagesInternet of Nano, Bio-Nano, Biodegradable And-3-47d96d1b6a8Pas encore d'évaluation
- 13 IFRJ 20 (02) 2013 AftabDocument5 pages13 IFRJ 20 (02) 2013 AftabNimra NaveedPas encore d'évaluation
- Writing Project - Soap Note MemorandumDocument2 pagesWriting Project - Soap Note Memorandumapi-340006591Pas encore d'évaluation
- Jurnal InterDocument8 pagesJurnal InterArumm88Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hepatobiliary Pancreatic Radiology 1683072599120Document31 pagesHepatobiliary Pancreatic Radiology 1683072599120Shivank RastogiPas encore d'évaluation
- Bariatric Surgery OxfordDocument7 pagesBariatric Surgery OxfordJose Tomás MoorePas encore d'évaluation
- Joint Commission International Library of MeasuresDocument3 pagesJoint Commission International Library of Measuresadiadi84100% (1)
- New BookDocument2 pagesNew BookKaren Raskin KleimanPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidromek Crawler Excavator HMK 300lc LR Mitsubishi 5125001 Spare Parts Catalog Turkish en PDFDocument22 pagesHidromek Crawler Excavator HMK 300lc LR Mitsubishi 5125001 Spare Parts Catalog Turkish en PDFhadykyx100% (42)
- Organize To Inform Assessment 1Document5 pagesOrganize To Inform Assessment 1kylea100% (1)
- ISONIAZIDDocument2 pagesISONIAZIDXerxes DejitoPas encore d'évaluation
- HydralazineDocument1 pageHydralazineIvanne Hisoler75% (8)
- Children in Need-Diagnostics, Epidemiology, Treatment and Outcome of Early Onset Anorexia NervosaDocument16 pagesChildren in Need-Diagnostics, Epidemiology, Treatment and Outcome of Early Onset Anorexia NervosaCamila CesteroPas encore d'évaluation
- Conpendium of Good PracticesDocument48 pagesConpendium of Good PracticesDonat BekuPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.06. Substance AbuseDocument3 pages1.06. Substance AbuseAllandale NacinoPas encore d'évaluation
- AdenomyosisDocument32 pagesAdenomyosisAzhari RozaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric 3 - Answers v1 (Wide)Document56 pagesPediatric 3 - Answers v1 (Wide)Humzala BashamPas encore d'évaluation