Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Dynamics of Structures Example Sheet No. 2
Transféré par
Nicholas Chun Wong0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
22 vues2 pagesdynamics exercise
Titre original
Sheet2 New
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentdynamics exercise
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
22 vues2 pagesDynamics of Structures Example Sheet No. 2
Transféré par
Nicholas Chun Wongdynamics exercise
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
DYNAMICS OF STRUCTURES
Example Sheet No. 2
(For steel take E=200 GN/m2 and for concrete E=14 GN/m2)
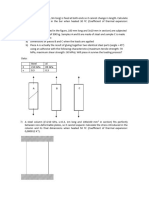
1-
A point load F = 1 kN moves along with
constant speed v = 10 m/s on a simply
supported beam of length l = 10 m as shown
in the figure. The beam is made of concrete,
has a rectangular section of height 1 m and
an average density of 2,800 kg/m3.
Determine the deflection of the beam as a
function of time, the dynamic magnification
factor and the maximum bending moment at
centre section.
2- A concrete ribbed slab floor spans 9 m and
has an average mass of 500 kg/m2. The floor
is simply supported on either side and has a
natural frequency of vibration of 6.3 Hz. The
floor is to be used for aerobics and other
similar rhythmic activities at frequencies
ranging from 1.5 Hz to 2.5 Hz and with
contact ratios between 0.5 and 1. During
these activities the average imposed load will
remain below 0.75 kN/m2 (before dynamic
magnification) and the damping ratio can be
taken to be 3%.
(a) Determine
the
maximum
possible
resonant displacement and the resulting peak
acceleration and bending moment per unit
width.
F (t )
0.75
T F
TF
(b) If the floor has been designed for a
service load of 5kN/m2, determine its
suitability for the proposed use.
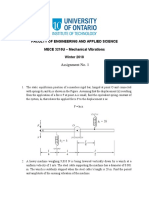
3- A 12 m long rail bridge has the continuous
beam configuration shown in the figure, an
average flexural stiffness EI = 5 GNm 2 , a
mass per unit length of 10,0000 kg/m and a
damping ratio of 2%.
6m
(a) Using Rayleighs method with an
appropriate sinusoidal function, obtain its
fundamental frequency of vibration.
(b) Determine the equivalent modal force that
results from the motion of a train consisting of
an infinite number of 100 kN point loads
separated by equal distances of 12 m and
Prof. Y Feng,
12 m
6m
12 m
12 m
225 km/h
travelling at a constant speed of 225 km/h.
(c) Obtain the dynamic magnification factor
for the above train of loads.
4- A footbridge spans 36 m in two equal simply
supported sections as shown. The total mass
of each section is 12 600 kg, the equivalent
uniform flexural stiffness EI is 2 108 N m2
and the logarithmic decrement damping is
0.05.
(a)
18 m
18 m
(a) Determine the peak displacement and
peak acceleration produced by a 700 N
pedestrian walking in step with the natural
frequency of the footbridge and producing a
pulsating force of 180 N.
(b)
(b) Consider the case where the two sections
of the footbridge are connected together to
produce a continuous beam.
5- A load is applied on a structure in such a way
that its magnitude increases linearly with time
until a maximum value P is reached at time t0
(see figure). Determine the dynamic
magnification factor as a function of t0 and
the natural period of vibration of the structure
T.
6- The infinitely long UDL w shown in the figure
moves along at constant speed v and enters
a simply supported bridge of length , total
mass 2m and natural period of vibration T.
Determine the resulting vibration and the
dynamic magnification factor.
Prof. Y Feng,
F (t )
P
t0
w
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2D'EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- 4281 - 03 Stiffened Shear WebDocument26 pages4281 - 03 Stiffened Shear WebAndrew GilbridePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes on Reinforced Concrete DesignD'EverandLecture Notes on Reinforced Concrete DesignPas encore d'évaluation
- (10 Marks) : Faculty of EngineeringDocument4 pages(10 Marks) : Faculty of EngineeringChamin SubhawickramaPas encore d'évaluation
- MPCL Flare KOD Pump 11442-DS-103 - IFC2 18-06-2013Document2 pagesMPCL Flare KOD Pump 11442-DS-103 - IFC2 18-06-2013zohaib_farooqPas encore d'évaluation
- Non-Linear Analysis Solution StrategiesDocument5 pagesNon-Linear Analysis Solution StrategiesPiyush SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Mod3 Three Moment EquationDocument12 pagesMod3 Three Moment EquationMarc Dared Cagaoan100% (3)
- TC FLS SIHI LEH 1200 1500 1800 Mag ENDocument7 pagesTC FLS SIHI LEH 1200 1500 1800 Mag ENGustavo ZavalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reinforced Concrete Design Footings Quiz SolutionsDocument9 pagesReinforced Concrete Design Footings Quiz SolutionsIRISHPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Structural Eng GDocument43 pagesBasic Structural Eng GDordas Sing33% (3)
- Design Nov 2013Document12 pagesDesign Nov 2013Cath100% (1)
- Collective Classical & Quantum FieldsDocument410 pagesCollective Classical & Quantum FieldsAndrew Hucek100% (1)
- 9A01709 Advanced Structural AnalysisDocument8 pages9A01709 Advanced Structural AnalysisReddy Kiran KD0% (1)
- 08 U8 Ws 4-KeyrevisedDocument3 pages08 U8 Ws 4-KeyrevisedJohn Bray67% (9)
- Absorption of Formaldehyde in WaterDocument135 pagesAbsorption of Formaldehyde in WaterBer GuzPas encore d'évaluation
- ENG1001 Civil Set 1Document4 pagesENG1001 Civil Set 1Christopher AngPas encore d'évaluation
- Home Take Individual ExaminationDocument3 pagesHome Take Individual ExaminationTamrat GezahgnePas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Set 1Document15 pagesProblem Set 1Claire EngbinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Faculty AdsPas encore d'évaluation
- Prob Set 1Document3 pagesProb Set 1Joery Jr Esperon50% (2)
- Training Mixed TopixDocument117 pagesTraining Mixed TopixSigue Ramel HinayasPas encore d'évaluation
- PLATE 1 PrestressedDocument2 pagesPLATE 1 PrestressedHazel Kaye PartozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Problems CH-11 Strain Energy (Blank)Document28 pagesProblems CH-11 Strain Energy (Blank)محمد خريبطPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Set 1 (Bearing Capacity Equations) PDFDocument1 pageProblem Set 1 (Bearing Capacity Equations) PDFMark Joseph Bandojo VargasPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment GeoEQDocument11 pagesAssignment GeoEQKamalKishorKumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Es 221 - Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: I. Kinetics of A Particle (Force & Acceleration)Document4 pagesEs 221 - Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: I. Kinetics of A Particle (Force & Acceleration)Jerard BalalaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Yr Hy 09Document4 pages1st Yr Hy 09Grezzju CauchiPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A01101 Engineering MechanicsDocument8 pages9A01101 Engineering MechanicssivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Openbook Test On Geotechnical Design 2017Document4 pagesOpenbook Test On Geotechnical Design 2017Chongchuen FongPas encore d'évaluation
- Test On GeotechnicalDocument4 pagesTest On GeotechnicalChongchuen FongPas encore d'évaluation
- Biyaya Ni EcnarDocument14 pagesBiyaya Ni EcnarKiesha SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy130 Tutorial 8Document3 pagesPhy130 Tutorial 8Shuhaila Hanis RosliPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice AssignmentDocument2 pagesPractice AssignmentAditya PadaviPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 - 1 - Ejercicios Comportamiento ElastoplasticoDocument7 pages2 - 1 - Ejercicios Comportamiento ElastoplasticoConstanza de la FuentePas encore d'évaluation
- SEMM Comp Dynamics Sp20Document5 pagesSEMM Comp Dynamics Sp20RAFAELPas encore d'évaluation
- Reinforced Concrete Design Footings Quiz QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesReinforced Concrete Design Footings Quiz QuestionnaireIRISHPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Test For Midterm 3 Chapters 13, 15, 16, 17, 18 in Preparation For The Midterm ExamDocument11 pagesPractice Test For Midterm 3 Chapters 13, 15, 16, 17, 18 in Preparation For The Midterm ExamRAIZZPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 2 Ce5620Document2 pagesTutorial 2 Ce5620tulasi ramPas encore d'évaluation
- QB ARM401Document6 pagesQB ARM401Mahi PathakPas encore d'évaluation
- M.tech Sem-2 DYN Tutorial-1Document2 pagesM.tech Sem-2 DYN Tutorial-1Rutvik ShethPas encore d'évaluation
- R7410101 Geotechnical Engineering-IIDocument8 pagesR7410101 Geotechnical Engineering-IIsivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Test2 ps150Document3 pagesPractice Test2 ps150Antoine S. NdiayePas encore d'évaluation
- Ae 35 Solid MechanicsDocument4 pagesAe 35 Solid MechanicsRameez FaroukPas encore d'évaluation
- CENG6206 Soil Dynamics ExerciseProblemDocument4 pagesCENG6206 Soil Dynamics ExerciseProblemFekadu Wub100% (1)
- TR 334 Tutorial-1Document5 pagesTR 334 Tutorial-1Adaminovic MrishoPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorials Pad Footing Nta 5 (2012&2013)Document3 pagesTutorials Pad Footing Nta 5 (2012&2013)Host FredyPas encore d'évaluation
- ASSIGNMENT NO 4 Work Energy and PowerDocument2 pagesASSIGNMENT NO 4 Work Energy and Powerangelicaannjoy02Pas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Set 2 V2Document3 pagesProblem Set 2 V2RalphPas encore d'évaluation
- CE407S1 ESem Question Paper Nov 28 2020Document4 pagesCE407S1 ESem Question Paper Nov 28 2020SonuPas encore d'évaluation
- WEP Energy Question BankDocument2 pagesWEP Energy Question BankAJ SkybornPas encore d'évaluation
- Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science MECE 3210U - Mechanical VibrationsDocument4 pagesFaculty of Engineering and Applied Science MECE 3210U - Mechanical VibrationsBilly JhunPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics QuestionsDocument3 pagesPhysics QuestionssunandapatriPas encore d'évaluation
- A y C 3 3 DL LL DL LL C Y: Section For Moment Is Halfway Between Middle and Edge of WallDocument1 pageA y C 3 3 DL LL DL LL C Y: Section For Moment Is Halfway Between Middle and Edge of WallMau MauPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Mechanics Q.paperDocument8 pagesEngineering Mechanics Q.paperYogeswara KayaguralaPas encore d'évaluation
- r5100105 Applied MechanicsDocument2 pagesr5100105 Applied MechanicssivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics Tutorial - Flow Over Immersed Bodies: Drag and LiftDocument20 pagesFluid Mechanics Tutorial - Flow Over Immersed Bodies: Drag and LiftHazzim HamdanPas encore d'évaluation
- Som TutorialsDocument22 pagesSom TutorialsbaizubirajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Set 2Document14 pagesProblem Set 2Priyanka Cholleti100% (1)
- RC2 P1 1Document3 pagesRC2 P1 1Quicksilver 1975Pas encore d'évaluation
- CE407 - Updated Midsem SolutionsDocument31 pagesCE407 - Updated Midsem SolutionsManan GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- 04 ChapterDocument52 pages04 ChapterYirga BezabehPas encore d'évaluation
- En Curs05 DsisDocument14 pagesEn Curs05 DsisNicholas Chun WongPas encore d'évaluation
- Response SpectrumDocument24 pagesResponse SpectrumNicholas Chun WongPas encore d'évaluation
- Monitoring ReportDocument2 pagesMonitoring ReportNicholas Chun WongPas encore d'évaluation
- 09IICNTY001Document5 pages09IICNTY001Nicholas Chun WongPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Principles of Plates and SlabsDocument148 pagesBasic Principles of Plates and SlabsMarin MariusPas encore d'évaluation
- Wave Optics (MCQS)Document21 pagesWave Optics (MCQS)Ronda StewartPas encore d'évaluation
- Alex Lang NSF GRFP Research ProposalDocument2 pagesAlex Lang NSF GRFP Research ProposalSilas WilkinsonPas encore d'évaluation
- CE 14 Course SyllabusDocument2 pagesCE 14 Course SyllabusChristian GalopePas encore d'évaluation
- CH 04Document20 pagesCH 04msy83635Pas encore d'évaluation
- Modern Optics - Lecture2Document27 pagesModern Optics - Lecture2chpmahdi07Pas encore d'évaluation
- Aqa Chem4 QP Jun14Document24 pagesAqa Chem4 QP Jun14mystreet123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Alpha Domain StructureDocument35 pagesAlpha Domain StructureRekha Govindan100% (1)
- Free Fall: Nattanon VeerakulDocument9 pagesFree Fall: Nattanon Veerakulapi-327824456Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rectifire and Voltage ControleDocument27 pagesRectifire and Voltage ControleWoldemariam WorkuPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Structure DTS-9Document2 pagesAtomic Structure DTS-9Aashish GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Full Book Short QuestionsDocument31 pagesChemistry Full Book Short QuestionsOwais MaqboolPas encore d'évaluation
- Laplace TableDocument2 pagesLaplace TableosmanfıratPas encore d'évaluation
- Ramon Urquijo Kempf NessDocument32 pagesRamon Urquijo Kempf NessWalter Andrés Páez GaviriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagrama HXDocument2 pagesDiagrama HXRadu DinuPas encore d'évaluation
- String Theory EssayDocument7 pagesString Theory EssayMichael Mohamed100% (1)
- Khosla's LawDocument7 pagesKhosla's LawAman sharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- California Bearing Ratio Typical Values - CBR Testing UK - Nationwide CBR Testing Service 0333 5670 754Document3 pagesCalifornia Bearing Ratio Typical Values - CBR Testing UK - Nationwide CBR Testing Service 0333 5670 754Muhammad MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Standard Level Paper 1: Instructions To CandidatesDocument13 pagesPhysics Standard Level Paper 1: Instructions To CandidatesjszPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9: Center of Gravity and CentroidDocument10 pagesChapter 9: Center of Gravity and CentroidvictorPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Important Books of PhysicsDocument6 pagesList of Important Books of PhysicsAbubakar Mughal0% (1)
- Specification Amorphous SilicaDocument2 pagesSpecification Amorphous Silicadivyesh_pariharPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Professional LaminatorDocument28 pagesManual Professional LaminatorJamiiMacPas encore d'évaluation