Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Swinburne's Test of DC Machine - Electrical4u
Transféré par
M Kumar MarimuthuTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Swinburne's Test of DC Machine - Electrical4u
Transféré par
M Kumar MarimuthuDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
11/29/2014
Swinburnes Test of DC Machine | Electrical4u
Search in electrical4u.com
Electrical4u
search here
Go
Online Electrical Engineering Study Site
Basics
Machines
Power System
Electronics
Questions
Videos
Online Exam
Home Swinburnes Test of DC Machine
Swinburnes Test of DC
Machine
miniature electric motor
Like
Share 19,743 people like this. Be the
first of your friends.
Electrical Objective Questions MCQs
stator/rotor production equipment slotless motor prod. equipment
Alternator or Synchronous Generator
Working Principle of Alternator
Construction of Alternator
Rating of Alternator
Armature Winding
Armature Winding of Alternator
Winding Factor
Armature Reaction of Alternator
Phasor Diagram for Synchronous Generator
Induction Generator
Working Principle of DC Generator
Construction of DC Generator
http://electrical4u.com/swinburnes-test-of-dc-machine/
1/7
11/29/2014
Swinburnes Test of DC Machine | Electrical4u
Commutation in DC Machine
Methods of Improving Commutation
Frog Leg, Drum and Gramme Ring Winding
Types of DC Generators
Magnetization Curve of DC Generator
Characteristic of Separately Excited DC Gen
Characteristic of DC Shunt Generator
Characteristics of DC Series Generator
Power
engineering
Aluminium
GIS Systems
Characteristic of DC Compound Generators
Armature Reaction in DC Machine
DC Generators Performance Curves
Applications of DC Generators
Testing of DC Machine
Swinburnes Test of DC Machine
Hopkinsons Test
Calculation of Efficiency
Calculation of Efficiency When the Machine is Motoring on Load
Calculation of Efficiency When the Machine is Generating on Load
Advantages of Swinburnes Test
Disadvantages
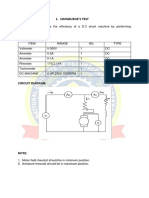
This method is an indirect method of testing a dc machine. It is named after Sir James
Swinburne. Swinburnes test is the most commonly used and simplest method of testing
of shunt and compound wound dc machines which have constant flux. In this test the
efficiency of the machine at any load is pre-determined. We can run the machine as a
motor or as a generator. In this method of testing no load losses are measured
separately and eventually we can determine the efficiency.
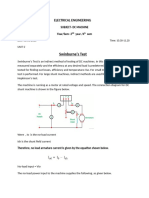
The circuit connection for Swinburnes test is shown in figure below. The speed of the
machine is adjusted to the rated speed with the help of the shunt regulator R as shown
in figure.
http://electrical4u.com/swinburnes-test-of-dc-machine/
2/7
11/29/2014
Swinburnes Test of DC Machine | Electrical4u
Calculation of
Efficiency
Let, I0 is the no load current (
it can be measured by
ammeter A1 )
Ish is the shunt field current (
it can be measured by
ammeter A2 )
Then, no load armature
current = (I0 Ish)
Also let, V is the supply
voltage. Therefore, No load
power input = VI0 watts.
Connection Diagram of Swinburnes Test
In Swinburnes test no load power input is only required to supply the losses. The
losses occur in the machine mainly are:
Iron losses in the core
Friction and windings losses
Armature copper loss.
Since the no load mechanical output of the machine is zero in Swinburnes test, the no
load input power is only used to supply the losses.
The value of armature copper loss = (I0 Ish)2 Ra
Here, Ra is the armature resistance.
http://electrical4u.com/swinburnes-test-of-dc-machine/
3/7
11/29/2014
Swinburnes Test of DC Machine | Electrical4u
Now, no to get the constant losses we have to subtract the armature copper loss from
the no load power input.
Then, Constant losses WC = VI0 -(I0 Ish)2 Ra
After calculating the no load constant losses now we can determine the efficiency at any
load.
Let, I is the load current at which we have to calculate the efficiency of the machine.
Then, armature current (Ia) will be (I Ish), when the machine is motoring.
And Ia = (I + Ish), when the machine is generating.
miniature electric motor
stator/rotor production equipment slotless motor prod. equipment
Calculation of Efficiency When the Machine is
Motoring on Load
Power input = VI
Armature copper loss, PCU = I2 Ra = (I Ish)2Ra
Constant losses, WC = VI0 -(I0 Ish)2 Ra
Total losses = PCU + WC
http://electrical4u.com/swinburnes-test-of-dc-machine/
4/7
11/29/2014
Swinburnes Test of DC Machine | Electrical4u
Efficiency of the motor:
Calculation of Efficiency When the Machine is
Generating on Load
Power input = VI
Armature copper loss, PCU = I2 Ra = (I + Ish)2 Ra
Constant losses, WC = VI0 (I0 Ish)2 Ra
Total losses = PCU + WC
Efficiency of the generator:
Advantages of Swinburnes Test
The main advantages of this test are :
1. This test is very convenient and economical as it is required very less power
from supply to perform the test.
2. Since constant losses are known, efficiency of Swinburnes test can be predetermined at any load.
Disadvantages of Swinburnes Test
The main disadvantages of this test are :
http://electrical4u.com/swinburnes-test-of-dc-machine/
5/7
11/29/2014
Swinburnes Test of DC Machine | Electrical4u
1.Iron loss is neglected though there is change in iron loss from no load to full
load due to armature reaction.
2.We cannot be sure about the satisfactory commutation on loaded condition
because the test is done on no-load.
3.We cant measure the temperature rise when the machine is loaded. Power
losses can vary with the temperature.
4.In dc series motors, the Swinburnes test cannot be done to find its efficiency
as it is a no load test.
Objective Questions on DC Generator (MCQs)
Please give us your valuable comment/suggestion. This will help us to improve this page.
Your Name : -
Your Email : - (Please do not forget to provide your actual email address so that we can send you the latest updates of this site. If you wish.)
Your Place : -
Your Comments and Suggestion : -
http://electrical4u.com/swinburnes-test-of-dc-machine/
6/7
11/29/2014
Swinburnes Test of DC Machine | Electrical4u
Enter the Security Code : -
Regenerate Code
Submit
Reset
Search in electrical4u.com
search here
Go
2014 Electrical4u
http://electrical4u.com/swinburnes-test-of-dc-machine/
Responsive Theme powered by Electrical4u
7/7
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Microsoft Word - DC Machine Notes - SVM - AIT - Unit 01 To 04-VasudevmurthyDocument19 pagesMicrosoft Word - DC Machine Notes - SVM - AIT - Unit 01 To 04-VasudevmurthyRevati MotagiPas encore d'évaluation
- Occ of DC ShuntDocument26 pagesOcc of DC ShuntAnand PalaganiPas encore d'évaluation
- Testing of DC MachinesDocument15 pagesTesting of DC MachinesMadhu TallapanenimadhuPas encore d'évaluation
- Swinburne'S Test: AIM: To Pre-Determine The Efficiency of A D.C Shunt Machine by PerformingDocument6 pagesSwinburne'S Test: AIM: To Pre-Determine The Efficiency of A D.C Shunt Machine by PerformingAshutosh SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hopkinson's Test - Electrical4u PDFDocument9 pagesHopkinson's Test - Electrical4u PDFM Kumar MarimuthuPas encore d'évaluation
- DC Machine L05Document16 pagesDC Machine L05luckyPas encore d'évaluation
- Swin Burns ARUNDocument6 pagesSwin Burns ARUNArun TezPas encore d'évaluation
- DC Machine 2 Year 31 03 2020Document4 pagesDC Machine 2 Year 31 03 2020منتظر التميميPas encore d'évaluation
- Testing of DC MotorDocument17 pagesTesting of DC MotorRozitarmizi Mohammad100% (1)
- BEEE215L - Module-3 - Lecture-19 - Testing of DC Motor - Swinburne'sDocument16 pagesBEEE215L - Module-3 - Lecture-19 - Testing of DC Motor - Swinburne'sBelwin EdwardPas encore d'évaluation
- Swinburne S Test On DC Shunt MotorDocument5 pagesSwinburne S Test On DC Shunt Motortamann2004Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wa0002Document17 pagesWa0002RahulPas encore d'évaluation
- LabVolt Industrial AC DrivesDocument121 pagesLabVolt Industrial AC Drivesumer farooqPas encore d'évaluation
- Testing of DC Machines - UNIT IIIDocument34 pagesTesting of DC Machines - UNIT IIIKUMAR SPas encore d'évaluation
- Characteristic of DC Compound Wound Generators - Electrical4uDocument8 pagesCharacteristic of DC Compound Wound Generators - Electrical4uM Kumar MarimuthuPas encore d'évaluation
- Efficiency of DC Generator: Fig1: Power Flow DiagramDocument19 pagesEfficiency of DC Generator: Fig1: Power Flow DiagramKing DhjPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.5 Retardation Test or Running Down On D.C Machines: Electric Machinery Fundamentals Stephen J. ChapmanDocument8 pages5.5 Retardation Test or Running Down On D.C Machines: Electric Machinery Fundamentals Stephen J. Chapmanjakkoju saitejaPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Swinburne's Test - Advantages, Disadvantages & Limitations - Circuit GlobeDocument17 pagesWhat Is Swinburne's Test - Advantages, Disadvantages & Limitations - Circuit GlobesanjuPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 & 3 EM-I (REE 402) : DC MachinesDocument48 pagesUnit 2 & 3 EM-I (REE 402) : DC MachinesAnanya Srivastava100% (1)
- Control System Lab EE-324-FDocument45 pagesControl System Lab EE-324-FDheeraj KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Q5 and 6Document15 pagesQ5 and 6AttaUrRahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab-4 - Name - IDDocument11 pagesLab-4 - Name - IDMOSAED MOSAED ALLOGMANIPas encore d'évaluation
- Government Engineering College Kozhikode-5: AI09 308 (P), ME09 307 (P)Document69 pagesGovernment Engineering College Kozhikode-5: AI09 308 (P), ME09 307 (P)nainesh gotePas encore d'évaluation
- Beee Lab ManualDocument36 pagesBeee Lab ManualChanduVarmaKalidindiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Study Material: Ee / EeeDocument16 pagesSample Study Material: Ee / EeeVinay H. B.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Book OldDocument82 pagesBook OldECEOCETPas encore d'évaluation
- Rating of Alternator - Electrical4uDocument4 pagesRating of Alternator - Electrical4uM Kumar MarimuthuPas encore d'évaluation
- Synchronous MachineDocument10 pagesSynchronous MachineItalo ChiarellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Testing of DC MotorsDocument14 pagesTesting of DC MotorsKrishna Rgk33% (3)
- Electrical Machines-II (EX-503) : Practical Work BookDocument25 pagesElectrical Machines-II (EX-503) : Practical Work BookFilipe Braga CoutoPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.0 DctestDocument7 pages5.0 DctestLifeLong SkillsPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Electrical Machines Lab IIDocument94 pagesDepartment of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Electrical Machines Lab IIGood YagPas encore d'évaluation
- Class - 16 - DC Motors Power FlowDocument14 pagesClass - 16 - DC Motors Power FlowHafsa AlhaddabiPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 1: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesExperiment 1: Objectivesaran gulPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Machines-I Lab Manual R16 Modified PDFDocument83 pagesElectrical Machines-I Lab Manual R16 Modified PDFsk ibrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Dee-M.c-1 Teasting of MotorDocument23 pagesDee-M.c-1 Teasting of Motorhetalprajapati2881989Pas encore d'évaluation
- Servo ED 4R Instruction ManualDocument68 pagesServo ED 4R Instruction Manual1301041019Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kunal BSP InternshipDocument16 pagesKunal BSP InternshipEE Domendra KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- EE 448 Laboratory Experiment 4 Introduction To DC MotorsDocument10 pagesEE 448 Laboratory Experiment 4 Introduction To DC MotorsjegjegtPas encore d'évaluation
- EECS Lab Manual For IV ECE R2013Document66 pagesEECS Lab Manual For IV ECE R2013keshav315Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Machines PDFDocument49 pagesElectric Machines PDFirfanPas encore d'évaluation
- Induction Motor TestsDocument4 pagesInduction Motor TestsVictor OdoyoPas encore d'évaluation
- ME 39-Electrical Engineering Lab ManualDocument111 pagesME 39-Electrical Engineering Lab ManualSuma Rani GPas encore d'évaluation
- Direct Load Test On A DC Shunt MotorDocument5 pagesDirect Load Test On A DC Shunt MotorYAKALA RAVIKUMARPas encore d'évaluation
- Testing of DC MachinesDocument6 pagesTesting of DC Machinessteve ogagaPas encore d'évaluation
- DC Machines and Transformers Lab Manual ModifiedDocument50 pagesDC Machines and Transformers Lab Manual ModifiedSuseel MenonPas encore d'évaluation
- Induction Generator - Application of Induction Generator - Electrical4uDocument6 pagesInduction Generator - Application of Induction Generator - Electrical4uM Kumar MarimuthuPas encore d'évaluation
- Direct - Indirect - Regenerative Method of TestingDocument29 pagesDirect - Indirect - Regenerative Method of TestingASHIM KUMAR SAHUPas encore d'évaluation
- Control System Lab ManualDocument52 pagesControl System Lab ManualMohammad Umar RehmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Dronacharya PDFDocument5 pagesDronacharya PDFStishuk HFPas encore d'évaluation
- Me 2209 Electrical Engineering Lab Manua EitlDocument45 pagesMe 2209 Electrical Engineering Lab Manua EitlRagunathan NarayananPas encore d'évaluation
- Testing of DC MachinesDocument12 pagesTesting of DC Machinessameerpatel15770Pas encore d'évaluation
- Jabalpur Engineering College, Jabalpur Electrical Engineering Department AC/DC Drives Lab. List of ExperimentDocument63 pagesJabalpur Engineering College, Jabalpur Electrical Engineering Department AC/DC Drives Lab. List of ExperimentSajalPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Lab 5 Machine Lab Lab 1 ReportDocument9 pagesEngineering Lab 5 Machine Lab Lab 1 Reportram010Pas encore d'évaluation
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesD'EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseD'EverandElectrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CoursePas encore d'évaluation
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlD'EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1D'EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Évaluation : 2.5 sur 5 étoiles2.5/5 (3)
- TGN Restricted Earth Fault v1 - 0Document40 pagesTGN Restricted Earth Fault v1 - 0Anonymous dqbb02DUhPas encore d'évaluation
- L05 Transmissionlines v4.ppsDocument16 pagesL05 Transmissionlines v4.ppsM Kumar MarimuthuPas encore d'évaluation
- Ducab HV Catalogue 2018 01 PDFDocument12 pagesDucab HV Catalogue 2018 01 PDFMohammed ShoaibPas encore d'évaluation
- HV Cable Sheath EarthingDocument15 pagesHV Cable Sheath EarthingjuliancansenPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is The Purpose of A Stabilizing Resistor - QuoraDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Purpose of A Stabilizing Resistor - QuoraM Kumar MarimuthuPas encore d'évaluation
- Daman Digital CardDocument31 pagesDaman Digital CardM Kumar Marimuthu100% (1)
- Static Distance Relay LZ96Document2 pagesStatic Distance Relay LZ96M Kumar Marimuthu0% (1)
- 01 - Overview of Protection FundamentalsDocument28 pages01 - Overview of Protection FundamentalsM Kumar MarimuthuPas encore d'évaluation
- 04B-Tutorial CT SelectionDocument14 pages04B-Tutorial CT SelectionM Kumar MarimuthuPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 - Notes Overcurrent ProtectionDocument9 pages02 - Notes Overcurrent ProtectionM Kumar Marimuthu100% (1)
- Communication Aided Protection SchemesDocument34 pagesCommunication Aided Protection Schemespvenky_kkdPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 Directional OvercurrentDocument10 pages03 Directional OvercurrentM Kumar MarimuthuPas encore d'évaluation
- Tesring Procedure of Electrical InstalltionDocument104 pagesTesring Procedure of Electrical InstalltionaruntiwaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Battery SizingDocument10 pagesBattery SizingM Kumar MarimuthuPas encore d'évaluation
- Failure Analysis of Three 230kV XLPE CablesDocument4 pagesFailure Analysis of Three 230kV XLPE CablesSameh Rashad AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Testing Directional Overcurrent Relays From ValenceDocument8 pagesTesting Directional Overcurrent Relays From ValenceM Kumar MarimuthuPas encore d'évaluation
- ABB Testing of Power TransformerDocument55 pagesABB Testing of Power TransformerM Kumar Marimuthu100% (3)
- ABB Transformer HandbookDocument213 pagesABB Transformer HandbookDragan Gigi100% (2)
- Building Services Branch Testing and Commissioning ProcedureDocument44 pagesBuilding Services Branch Testing and Commissioning ProcedureM Kumar MarimuthuPas encore d'évaluation
- Battery SizingDocument10 pagesBattery SizingM Kumar MarimuthuPas encore d'évaluation
- Testing Directional Overcurrent Relays From ValenceDocument8 pagesTesting Directional Overcurrent Relays From ValenceM Kumar MarimuthuPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheath REPAIR - Non MetallicDocument6 pagesSheath REPAIR - Non MetallicM Kumar MarimuthuPas encore d'évaluation
- ONGC Commissioning ProceduresDocument27 pagesONGC Commissioning Proceduresachmadh_2010100% (8)
- Example Distance Distance ENUDocument30 pagesExample Distance Distance ENUlancenglot100% (3)
- نظم قدرةDocument170 pagesنظم قدرةsomethin9Pas encore d'évaluation
- Factors Affecting The Sheath Losses in Single-Core Underground Power Cables With Two-Points BondDocument10 pagesFactors Affecting The Sheath Losses in Single-Core Underground Power Cables With Two-Points BondA. HassanPas encore d'évaluation
- EDF High Voltage Cable Insulation Testing PolicyDocument14 pagesEDF High Voltage Cable Insulation Testing PolicyM Kumar Marimuthu100% (1)
- HV CAble TestingDocument12 pagesHV CAble TestingM Kumar Marimuthu100% (2)
- Fire Protection Commissioning ProcedureDocument39 pagesFire Protection Commissioning ProcedureM Kumar Marimuthu83% (6)
- Design of DC Machines and TransformerDocument3 pagesDesign of DC Machines and Transformermanish_iitrPas encore d'évaluation
- Proportional Control Valves D631 Series ISO 4401 Size 05Document8 pagesProportional Control Valves D631 Series ISO 4401 Size 05Devendra BangarPas encore d'évaluation
- PSC QuestionsDocument2 pagesPSC QuestionsjrjkPas encore d'évaluation
- DC Motors Advantages and Disadvantages Over AC MotorsDocument9 pagesDC Motors Advantages and Disadvantages Over AC MotorsAnonymous 22VivgHlPas encore d'évaluation
- DC MOTORS Part 2Document5 pagesDC MOTORS Part 2Leanne RuthPas encore d'évaluation
- Magnetic SeparatorDocument36 pagesMagnetic SeparatorsanthoshkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- ADVR-08: Universal Hybrid Analog-Digital Voltage Regulator Operation ManualDocument6 pagesADVR-08: Universal Hybrid Analog-Digital Voltage Regulator Operation ManualedgarcooPas encore d'évaluation
- Control System Lab ReportDocument41 pagesControl System Lab ReportEngr-Junaid Mukhtar33% (3)
- Construction & Working of AlternatorDocument14 pagesConstruction & Working of AlternatorBhavik PrajapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Iesobjectivepaperelectrical 19972Document16 pagesIesobjectivepaperelectrical 19972kurukuruddinpuruPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Electrical Machines V K MehtaDocument41 pagesPrinciples of Electrical Machines V K MehtaAsh Raf0% (2)
- 000 Syllabus-Btech2010 (EE)Document52 pages000 Syllabus-Btech2010 (EE)Reeta DuttaPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation For Motor WindingsDocument128 pagesPresentation For Motor WindingsAhmed Kordy88% (8)
- Fourth Semester B.Tech. Degree Examination, December 2009 (2003 Scheme) Branch: Mechanical 03.405: Electrical Technology (Mu)Document2 pagesFourth Semester B.Tech. Degree Examination, December 2009 (2003 Scheme) Branch: Mechanical 03.405: Electrical Technology (Mu)Anita GloriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Diesellocomotivetechnology 120815130704 Phpapp02Document89 pagesDiesellocomotivetechnology 120815130704 Phpapp02AnshulJainPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Machine Design SOLVED PROBLEMS ON DC MACHINE MAGNETIC CIRCUIT Continuation of Chapter PDFDocument14 pagesElectrical Machine Design SOLVED PROBLEMS ON DC MACHINE MAGNETIC CIRCUIT Continuation of Chapter PDFMahesh MohananPas encore d'évaluation
- Traction With Speed Time GraphDocument5 pagesTraction With Speed Time GraphJack Ansari100% (2)
- Automatic Induction Motor ProjectDocument48 pagesAutomatic Induction Motor ProjectparixxxxPas encore d'évaluation
- Sumanta Chowdhury - CLS Aipmt-15-16 XIII Phy Study-Package-3 Set-1 Chapter-9Document26 pagesSumanta Chowdhury - CLS Aipmt-15-16 XIII Phy Study-Package-3 Set-1 Chapter-9samuel raj50% (2)
- Module 3Document96 pagesModule 3Zbor Zbor100% (2)
- DC Motor Brush Life White PaperDocument11 pagesDC Motor Brush Life White PaperHamza TaherPas encore d'évaluation
- Sona SPEED CatalogueDocument13 pagesSona SPEED CataloguevishiwizardPas encore d'évaluation
- DC Motor Speed Control System - ED4400BDocument14 pagesDC Motor Speed Control System - ED4400BDanang Pradika Purnomo100% (1)
- Chapter 2Document23 pagesChapter 2Wilson Domingo LazartePas encore d'évaluation
- Black BookDocument86 pagesBlack BookPradeep RajputPas encore d'évaluation
- SupportServices MotorsDocument92 pagesSupportServices MotorsCarlosPas encore d'évaluation
- 8.1 em 09Document12 pages8.1 em 09Ezan RosnizanPas encore d'évaluation
- Railway Track Security System Report PDFDocument26 pagesRailway Track Security System Report PDFeshu50% (2)
- (Iiird Mechanical/Industrial) Generator and Motor Electrical Technology Unit 4Document124 pages(Iiird Mechanical/Industrial) Generator and Motor Electrical Technology Unit 4signjpcoe100% (1)