Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
CME Cisco
Transféré par
Daniel Fernando Morales RuedaCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CME Cisco
Transféré par
Daniel Fernando Morales RuedaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CH A P T E R
27
Configuring Forced Authorization Code (FAC)
This chapter describes the Forced Authorization Code (FAC) feature in Cisco Unified Communications
Manager Express (Cisco Unified CME) 8.5 and later versions.
Contents
Information About Forced Authorization Code, page 823
How to Configure Forced Authorization Code, page 828
Configuration Examples for Forced Authorization Code, page 834
Additional References, page 835
Feature Information for Forced Authorization Code, page 836
Information About Forced Authorization Code
To configure SNR, you should understand the following concept:
Forced Authorization Code Overview, page 823
Forced Authorization Code Overview
Cisco Unified CME 8.5 allows you to manage call access and call accounting through the Forced
Authorization Code (FAC) feature. The FAC feature regulates the type of call a certain caller may place
and forces the caller to enter a valid authorization code on the phone before the call is placed. FAC allows
you to track callers dialing non-toll-free numbers, long distance numbers, and also for accounting and
billing purposes.
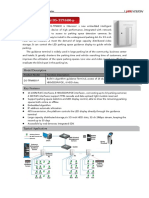
In Cisco Unified CME and Cisco Voice Gateways, devices and endpoints are logically partitioned into
different logical partitioning class of restriction (LPCOR) groups. For example, IP phones, Analog
phones, PSTN trunks, and IP (h323/SIP) trunks as shown in Figure 27-1 on page 824, are partitioned
into five LPCOR groups under the voice lpcor custom mode, such as:
voice lpcor custom
group 10 Manager
group 11 LocalUser
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express System Administrator Guide
OL-10663-05
27-823
Chapter 27
Configuring Forced Authorization Code (FAC)
Information About Forced Authorization Code
group 12 RemoteUser
group 13 PSTNTrunk
group 14 IPTrunk
SCCP/SIP Phones
Manager
IP
SCCP/SIP/SoftPhone
IP
IP cloud
IP
Remote
User
VPN Router
H.323/SIP
No authorization
required
Analog Phone
CME/SRST
PSTN
Need to enter the
authorization code
Local User
PSTN
Need to enter the
authorization code
Figure 27-1
278098
Local User
408-555-1234
Forced Authorization Code Network Overview
For each group, the LPCOR group policy of a routing endpoint is enhanced to define incoming calls from
individual LPCOR groups that are restricted by FAC. A LPCOR group call to a destination is accepted
only when a valid FAC is entered. FAC service for a routing endpoint is enabled through the service fac
defined in a LPCOR group policy. For more information, see Enabling Forced Authorization Code (FAC)
on LPCOR Groups, page 828.
The following are the group policy rules applicable to the PSTNTrunk LPCOR group:
FAC is required by PSTNTrunk if a call is initiated from either LocalUser or RemoteUser group.
Any calls from Manager group are allowed to terminate to PSTNTrunk without restriction.
Any incoming calls from either IPTrunk or PSTNTrunk group are rejected and terminated to
PSTNTrunk group.
For information on configuring LPCOR groups and associating LPCOR group with different device
types, see Call Restriction Regulations.
FAC Call Flow
FAC is required for an incoming call based on the LPCOR policy defined for the call destination. Once
the authentication is finished, the success or failure status and the collected FAC digits are saved to the
call detail records (CDRs).
Calls are handled by a new built-in application authorization package which first plays a user-prompt for
the caller to enter a username (in digits) then, the application plays a passwd-prompt for the caller to
collect the password (in digits). The collected username and password digits are then used for FAC, see
Defining Parameters for Authorization Package, page 832.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express System Administrator Guide
27-824
OL-10663-05
Chapter 27
Configuring Forced Authorization Code (FAC)
Information About Forced Authorization Code
When FAC authentication is successful, the outgoing call setup is continued to the same destination. If
FAC authentication fails, the call is then forwarded to the next destination. FAC operations are invoked
to the call if FAC service is enabled in the next destination and no valid FAC status is saved for the call.
Any calls failing because of FAC blocking are disconnected with a LPCOR Q.850 disconnect cause code.
Once the FAC is invoked for a call, the collected authorization digits and the authentication status
information is collected by call active or call history records. You can retrieve the FAC information
through the show call active voice and show call history voice commands.
Forced Authorization Code Specification
The authorization code used for call authentication must follow these specifications:
The authorization code must be in numeric (0 9) format.
A digit collection operation must be completed if either one of the following conditions occur:
maximum number of digits are collected
digit input times out
a terminating digit is entered
Once digit collection is completed, the authentication is done by either the external Radius server or
Cisco Unified CME or Cisco Voice Gateways by using AAA Login Authentication setup. For more
information on AAA login authentication methods, see Configuring Login Authentication Using AAA.
When authentication is done by local Cisco Unified CME or Cisco Voice Gateways, the username
ac-code password 0 password command is required to authenticate the collected authorization code
digits.
FAC data is stored through the CDR and new AAA fac-digits and fac-status attributes and are supported
in a CDR STOP record. This CDR STOP record is formatted for file accounting, RADIUS or Syslog
accounting purpose.
FAC Requirement for Different Types of Calls
Table 27-1 shows FAC support for different types of calls.
Table 27-1
Fac Support for different types of calls
Types of Calls
FAC Behavior for Different Calls
Basic Call
A calls B. B requires A to enter a FAC. A is routed to B only when
A enters a valid FAC.
Call Forward All
Call Forward Busy
When A (with no FAC) calls B, A is call forwarded to C:
No FAC is required when B enables Call Forward All or Call
Forward Busy to C.
FAC is required on A when A is call forwarded to C.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express System Administrator Guide
OL-10663-05
27-825
Chapter 27
Configuring Forced Authorization Code (FAC)
Information About Forced Authorization Code
Table 27-1
Fac Support for different types of calls
Types of Calls
FAC Behavior for Different Calls
Call Forward No Answer
When A (with no FAC) calls B and A (with FAC) calls C:
A calls B:
No FAC is required when A calls B.
A is Call Forward No Answer (CFNA) to C.
Call Transfer (Blind)
FAC is required on A when A is call forward to C.
FAC is required, if B calls C and A, and A calls C.
Example:
A calls B. B answers the call. B initiates a blind transfer call to C.
A is prompted to enter FAC. A is routed to C only if a valid FAC is
entered by A.
Call Transfer (Consultation)
1.
Transfer Complete at Alerting
State
FAC is required if B calls C. FAC is not required when A calls
C,
Example:
a. A calls B. B answers the call and initiates a consultation
transfer to C.
b. B is prompted to enter a FAC and B is not allowed to
complete the call transfer when FAC is not completed.
c. B (the transfer call) is forwarded to C after a valid FAC is
entered. B completes the transfer while the transfer call is
still ringing on C. A is then transferred to C.
2.
FAC is required if B calls C and A calls C.
Example:
a. A calls B. B answers the call and initiates a consultation
transfer to C.
b. B is prompted to enter a FAC and B is not allowed to
complete the call transfer when FAC is not completed.
c. No FAC is required to A, A is then transferred to C.
3.
FAC is not required if B calls C but FAC is required if A calls C.
Example:
a. A calls B, B answers the call.
b. B initiates a consultation transfer to C and completes the
transfer.
c. No FAC required to A, A is then transferred to C.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express System Administrator Guide
27-826
OL-10663-05
Chapter 27
Configuring Forced Authorization Code (FAC)
Information About Forced Authorization Code
Table 27-1
Fac Support for different types of calls
Types of Calls
Transfer Complete at
Connected State
FAC Behavior for Different Calls
1.
FAC is required when A calls C.
Example:
a. A calls B, B answers the call and initiates a consultation
transfer to C.
b. C answers the transfer call and B completes the transfer.
c. No FAC required to connect to A (including local hairpin
calls because the call transfer is complete) and A is
connected to C.
Conference Call
(Software/Adhoc)
1.
FAC is not invoked when a call is joined to a conference
connection.
2.
FAC is required between A and C, B and C.
Example:
a. A calls B, B answers the call and initiates a conference call
to C.
b. B enters a valid authorization code and is routed to C.
c. C answers the conference call and the conference is
complete.
d. No FAC is required to connect to A and A is joined to a
conference connection.
Meetme Conference
1.
FAC is not invoked for a caller to join the meetme conference.
2.
FAC is required between A and C, B and C.
Example:
a. C joins the meetme conference first.
b. No FAC is required if B joins the same meetme conference.
c. No FAC is required if C also joins the same meetme
conference.
Call Park and Retrieval
1.
FAC is not invoked for the parked call.
2.
FAC is required if C calls A.
Example:
a. A calls B, B answers the call and parks the caller on A.
b. C retrieves the parked call (A), no FAC is required to reach
C, and C is connected to A.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express System Administrator Guide
OL-10663-05
27-827
Chapter 27
Configuring Forced Authorization Code (FAC)
How to Configure Forced Authorization Code
Table 27-1
Fac Support for different types of calls
Types of Calls
Call Park Restore
FAC Behavior for Different Calls
1.
FAC is required if A calls D.
Example:
a. A calls B, B answers the call and parks the caller on A.
b. Parked call (A) is timed out from a call-park slot and is
forwarded to D.
c. No FAC is required for D and the parked call (A) will ring
on D.
Group Pickup
1.
FAC is not provided if a caller picks up a group call.
2.
FAC is required if C calls A.
Example:
a. A calls B, A is ringing on B, and C attempts to pickup call
A.
b. No FAC is required for C and C is connected to A.
Single Number Redirection
(SNR)
FAC is not supported for an SNR call.
Third Party Call Control (3pcc) FAC is not supported for a three-party call control (3pcc) outgoing
call.
Parallel Hunt Groups
FAC is not supported on parallel hunt groups.
Whisper intercom
FAC is not supported for whisper intercom calls.
How to Configure Forced Authorization Code
This section contains the following task:
Enabling Forced Authorization Code (FAC) on LPCOR Groups, page 828
Defining Parameters for Authorization Package, page 832
Enabling Forced Authorization Code (FAC) on LPCOR Groups
To enable FAC, perform the following steps.
Prerequisites
You must enable the voice lpcor enable command before configuring FAC.
Trunks (IP and PSTN) must be associated with phones into different LPCOR groups. See the
Associating a LPCOR Policy with Analog Phone or PSTN Trunk Calls for more information.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express System Administrator Guide
27-828
OL-10663-05
Chapter 27
Configuring Forced Authorization Code (FAC)
How to Configure Forced Authorization Code
Restrictions
Warning
Authenticated FAC data is saved to a call-leg from which the authorization code is collected. When
a call-forward or blind transfer call scenario triggers a new call due to the SIP notify feature, the
same caller is required to enter the authorization code again for FAC authentication.
A FAC pin code must be unique and not the same as an extension number. Cisco Unified CME, Cisco
Unified SRST, and Cisco Voice Gateways will not validate whether a collected FAC pin code matches
an extension number.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
voice lpcor enable
4.
voice lpcor custom
5.
group number lpcor-group
6.
exit
7.
voice lpcor policy lpcor-group
8.
accept lpcor-group fac
9.
service fac
10. end
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Command or Action
Purpose
enable
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
Enter your password if prompted.
Example:
Router> enable
Step 2
configure terminal
Enters global configuration mode.
Example:
Router# configure terminal
Step 3
voice lpcor enable
Example:
Router(config)# voice lpcor enable
Step 4
voice lpcor custom
Enables LPCOR functionality on the Cisco Unified CME
router.
Defines the name and number of LPCOR resource groups on
the Cisco Unified CME router.
Example:
Router(config)# voice lpcor custom
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express System Administrator Guide
OL-10663-05
27-829
Chapter 27
Configuring Forced Authorization Code (FAC)
How to Configure Forced Authorization Code
Step 5
Command or Action
Purpose
group number lpcor-group
Adds a LPCOR resource group to the custom resource list.
numberGroup number of the LPCOR entry. Range: 1 to
64.
lpcor-groupString that identifies the LPCOR resource
group.
Example:
Router(cfg-lpcor-custom)#group
Router(cfg-lpcor-custom)#group
Router(cfg-lpcor-custom)#group
Router(cfg-lpcor-custom)#group
Router(cfg-lpcor-custom)#group
Step 6
10
11
12
13
14
Manager
LocalUser
RemoteUser
PSTNTrunk
IPTrunk
exit
Exits voice-service configuration mode.
Example:
Router(conf-voi-serv)# exit
Step 7
voice lpcor policy lpcor-group
Creates a LPCOR policy for a resource group.
Example:
Router(cfg-lpcor-custom)#group
Router(cfg-lpcor-custom)#group
Router(cfg-lpcor-custom)#group
Router(cfg-lpcor-custom)#group
Router(cfg-lpcor-custom)#group
Step 8
Step 9
10
11
12
13
14
lpcor-groupName of the resource group that you defined
in Step 5.
Manager
LocalUser
RemoteUser
PSTNTrunk
IPTrunk
accept lpcor-group fac
Allows a LPCOR policy to accept calls associated with the
specified resource group.
Example:
Router(cfg-lpcor-policy)# accept PSTNTrunk
fac
Router(cfg-lpcor-policy)# accept Manager fac
Default: Calls from other groups are rejected; calls from
the same resource group are accepted.
facValid forced authorization code that the caller needs
to enter before the call is routed to its destination.
Repeat this command for each resource group whose calls
you want this policy to accept.
Enables force authorization code service for a LPCOR group.
service fac
Example:
Default: No form of the service fac command is the default
setting of a LPCOR group policy.
Router(cfg-lpcor-policy)#service fac
Step 10
Returns to privileged EXEC mode.
end
Example:
Router(config-ephone)# end
Examples
Router# show voice lpcor policy
voice lpcor policy PSTNTrunk (group 13):
service fac is enabled
( accept
) Manager (group 10)
( reject
) LocalUser (group 11)
( reject
) RemoteUser (group 12)
( accept
) PSTNTrunk (group 13)
( reject
) IPTrunk (group 14)
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express System Administrator Guide
27-830
OL-10663-05
Chapter 27
Configuring Forced Authorization Code (FAC)
How to Configure Forced Authorization Code
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express System Administrator Guide
OL-10663-05
27-831
Chapter 27
Configuring Forced Authorization Code (FAC)
How to Configure Forced Authorization Code
Defining Parameters for Authorization Package
To define required parameters for user name and password, follow these steps:
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
application
4.
package auth
5.
param passwd string
6.
param user-prompt filename
7.
param passwd-prompt filename
8.
param max-retries
9.
param term-digit
10. param abort-digit
11. param max-digits
12. exit
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Command or Action
Purpose
enable
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
Enter your password if prompted.
Example:
Router> enable
Step 2
configure terminal
Enters global configuration mode.
Example:
Router# configure terminal
Step 3
application
Enters the application configuration mode.
Example:
Router(config)#application
Router(config-app)#
Step 4
package auth
Enters package authorization configuration mode.
Example:
Router(config-app)#package auth
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express System Administrator Guide
27-832
OL-10663-05
Chapter 27
Configuring Forced Authorization Code (FAC)
How to Configure Forced Authorization Code
Step 5
Command or Action
Purpose
param passwd
Character string that defines a predefined password for
authorization.
Example:
Note
Router(config-app)#package param passwd 12345
Step 6
Allows you to enter the user name parameters required for
package authorization for FAC authentication.
param user-prompt filename
Example:
Router(config-app-param)#param user-prompt
flash:en_bacd_enter_dest.au
Step 7
Router(config-app-param)#param passwd-prompt
flash:en_welcome.au
passwd-prompt filename Plays an audio prompt
requesting the caller to enter a valid password (in
digits) for authorization.
Specifies number of attempts to re-enter an account or a
password
param max-retries
Example:
Router(config-app-param)#param max-retries 0
Step 9
user-prompt filename Plays an audio prompt
requesting the caller to enter a valid username (in
digits) for authorization.
Allows you to enter the password parameters required for
package authorization for FAC authentication.
param passwd-prompt filename
Example:
Step 8
Password digits collection is optional if password
digits are predefined in the param passwd
command.
max-entriesValue ranges from 0-10, default value
is 0.
Specifies digit for terminating an account or a password
digit collection.
param term-digit
Example:
Router(config-app-param)#param term-digit #
Step 10
Specifies the digit for aborting username or password
digit input. Default value is *.
param abort-digit
Example:
Router(config-app-param)#param abort-digit *
Step 11
Maximum number of digits in a username or password.
Range of valid value: 1 - 32. Default value is 32.
param max-digits
Example:
Router(config-app-param)#param max-digits 32
Step 12
exit
Exits package authorization parameter configuration
mode.
Example:
Router(conf-app-param)# exit
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express System Administrator Guide
OL-10663-05
27-833
Chapter 27
Configuring Forced Authorization Code (FAC)
Configuration Examples for Forced Authorization Code
Configuration Examples for Forced Authorization Code
This section provides configuration example for Forced Authorization Code.
!
gw-accounting aaa
!
aaa new-model
!
aaa authentication login default local
aaa authentication login h323 local
aaa authorization exec h323 local
aaa authorization network h323 local
!
aaa session-id common
!
voice lpcor enable
voice lpcor custom
group 11 LocalUser
group 12 AnalogPhone
!
voice lpcor policy LocalUser
service fac
accept LocalUser fac
accept AnalogPhone fac
!
voice lpcor policy AnalogPhone
service fac
accept LocalUser fac
accept AnalogPhone fac
!
application
package auth
param passwd-prompt flash:en_bacd_welcome.au
param passwd 54321
param user-prompt flash:en_bacd_enter_dest.au
param term-digit #
param abort-digit *
param max-digits 32
!
username 786 password 0 54321
!
voice-port 0/1/0
station-id name Phone1
station-id number 1235
caller-id enable
!
voice-port 0/1/1
lpcor incoming AnalogPhone
lpcor outgoing AnalogPhone
!
dial-peer voice 11 pots
destination-pattern 99329
port 0/1/1
!
ephone-dn 102 dual-line
number 786786
label HussainFAC
!
!
ephone 102
lpcor type local
lpcor incoming LocalUser
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express System Administrator Guide
27-834
OL-10663-05
Chapter 27
Configuring Forced Authorization Code (FAC)
Additional References
lpcor outgoing LocalUser
device-security-mode none
mac-address 0005.9A3C.7A00
type CIPC
button 1:102
!
Additional References
The following sections provide references related to Cisco Unified CME features.
Related Documents
Related Topic
Document Title
Cisco Unified CME configuration
Cisco IOS commands
Cisco IOS configuration
Phone documentation for Cisco Unified CME
Cisco Unified CME Command Reference
Cisco Unified CME Documentation Roadmap
Cisco IOS Voice Command Reference
Cisco IOS Software Releases 12.4T Command References
Cisco IOS Voice Configuration Library
Cisco IOS Software Releases 12.4T Configuration Guides
User Documentation for Cisco Unified IP Phones
Technical Assistance
Description
Link
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online
resources, including documentation and tools for
troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with
Cisco products and technologies.
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
To receive security and technical information about
your products, you can subscribe to various services,
such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field
Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter, and
Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds.
Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website
requires a Cisco.com user ID and password.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express System Administrator Guide
OL-10663-05
27-835
Chapter 27
Configuring Forced Authorization Code (FAC)
Feature Information for Forced Authorization Code
Feature Information for Forced Authorization Code
Table 27-2 lists the features in this module and enhancements to the features by version.
To determine the correct Cisco IOS release to support a specific Cisco Unified CME version, see the
Cisco Unified CME and Cisco IOS Software Version Compatibility Matrix at
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/voice_ip_comm/cucme/requirements/guide/33matrix.htm.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and software image support.
Cisco Feature Navigator enables you to determine which Cisco IOS software images support a specific
software release, feature set, or platform. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to
http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Note
Table 27-2
Table 27-2 lists the Cisco Unified CME version that introduced support for a given feature. Unless noted
otherwise, subsequent versions of Cisco Unified CME software also support that feature.
Feature Information for Single Number Reach
Feature Name
Cisco Unified CME
Version
Modification
Forced Authorization Code
8.5
Introduced the FAC feature.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express System Administrator Guide
27-836
OL-10663-05
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Furuno GT8031 Hardware Specification 2005.04.28Document13 pagesFuruno GT8031 Hardware Specification 2005.04.28pedro pino fierroPas encore d'évaluation
- RFC 8365Document34 pagesRFC 8365Liz Mar CieloPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is The SPO TechnologyDocument12 pagesWhat Is The SPO TechnologyjohovitchPas encore d'évaluation
- Communication MopileDocument39 pagesCommunication Mopileرسول ابراهيم عبد علي رويعيPas encore d'évaluation
- Backbone and Virtual LANDocument9 pagesBackbone and Virtual LANkirtan71Pas encore d'évaluation
- Datasheet of DS-TPM400-P Video Guidance TerminalDocument2 pagesDatasheet of DS-TPM400-P Video Guidance TerminalOswaldo GuerraPas encore d'évaluation
- mtm700 PDFDocument328 pagesmtm700 PDFLazni NalogPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy Interface Pci Express Sata Usb30 ArchitecturesDocument81 pagesPhy Interface Pci Express Sata Usb30 ArchitecturesHardik TrivediPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloud Computing Concepts Coursera HomeworkDocument6 pagesCloud Computing Concepts Coursera Homeworkistdijaod100% (1)
- Backup-Script RAW-Mangle-Queue Tree-Simple QueueDocument3 pagesBackup-Script RAW-Mangle-Queue Tree-Simple Queueismanto hamani100% (2)
- Microsoft Failover Clustering 2008Document58 pagesMicrosoft Failover Clustering 2008Jitendra KushwahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction and History of CryptographyDocument9 pagesIntroduction and History of CryptographynikhilPas encore d'évaluation
- A Broadband Antenna For GSM and UMTS BTS ApplicationDocument3 pagesA Broadband Antenna For GSM and UMTS BTS ApplicationTuấn Tú Lê100% (1)
- Chapter 2Document37 pagesChapter 2Vi RusPas encore d'évaluation
- QB PDFDocument16 pagesQB PDFsadhana mmPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete: Mit OpencoursewareDocument3 pages2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete: Mit OpencoursewareMy OwnPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytical Study Of: FHSS and DsssDocument30 pagesAnalytical Study Of: FHSS and DsssLalita GargPas encore d'évaluation
- Installation Instructions - 5500PC C-Bus PC InterfaceDocument12 pagesInstallation Instructions - 5500PC C-Bus PC InterfaceDCGBPas encore d'évaluation
- ECSAv10 Module 03 Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) MethodologyDocument32 pagesECSAv10 Module 03 Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) MethodologyAnonymous fFY4zZibJ8Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sangfor NGAF Report 20211026154441Document11 pagesSangfor NGAF Report 20211026154441Alzi Al-LailPas encore d'évaluation
- MOTOTRBO® System Release Notes Professional Commercial Radios (PCR) & AccessoriesDocument32 pagesMOTOTRBO® System Release Notes Professional Commercial Radios (PCR) & AccessoriesSerhiy HrabovyiPas encore d'évaluation
- FM1100 User Manual v5.06Document105 pagesFM1100 User Manual v5.06Dragos CalinescuPas encore d'évaluation
- Daily Report SafetyofficersDocument1 pageDaily Report SafetyofficerssasaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ec3401 Networks and Security L T P CDocument2 pagesEc3401 Networks and Security L T P Cjames RPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab - Configuring Switch Security FeaturesDocument3 pagesLab - Configuring Switch Security FeaturesHarman HayerPas encore d'évaluation
- Proxmox Mail Gateway: Administration GuideDocument55 pagesProxmox Mail Gateway: Administration GuideJikky JikkaPas encore d'évaluation
- NSX-T 3.0-Edge Design Step-by-Step UI WorkFlow-v1.0-FinalDocument32 pagesNSX-T 3.0-Edge Design Step-by-Step UI WorkFlow-v1.0-FinalDanial Tan100% (1)
- Multiplex-Diagnosis MPX Signal Bean and Avc LanDocument19 pagesMultiplex-Diagnosis MPX Signal Bean and Avc LanMario Alberto Abarca RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth 5 Book v2 - Sample ChaptersDocument32 pagesBluetooth 5 Book v2 - Sample ChaptersCata CaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Globalisation and The Indian Economy Class 10 Economics Chapter 4 Extra QuestionsDocument18 pagesGlobalisation and The Indian Economy Class 10 Economics Chapter 4 Extra QuestionsGurinder SinghPas encore d'évaluation