Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
4exp AM Prelim6 P2
Transféré par
John GohTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
4exp AM Prelim6 P2
Transféré par
John GohDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Additional Mathematics Preliminary Examination Set F Paper 2 (4047/02)
The roots of the quadratic equation 2x2 x + 32 = 0 are and . Find the quadratic
equation in x with roots
and
[6]
(a) When the polynomial f (x) is divided by (x 1) and (x + 3), the remainders are 5 and
3 respectively. Find the remainder when f (x) is divided by (x2 + 2x 3).
[3]
(b) Solve the equation 3x3 2x2 7x 2 = 0.
Hence, solve the equation 16t4 + 28t3 + 4t2 3t = 0.
/100
(a) Express
[6]
5x
1 2 x 1 4 x 2 in partial fractions.
[4]
(b) Hence, find
4
5x
1 2 x 1 4 x dx .
2
(a) Find all the angles between 0o and 360o for which 2 sin (2x + 40o) = sin (x + 20o). [6]
(b) Given |4 sin x 3| = , find the largest x such that x < 3.
[6]
[5]
cos 2 x
such that the y-coordinate is decreasing
ex
at a constant rate of 5 units per second. Find the rate of change of the x-coordinate when
x = 0.6.
[6]
A point (x, y) moves along the curve y
TX is a tangent to the circle at X. TYQ and TZP are straight lines. Prove that
TX 2 = TY TQ = TZ TP.
7
[6]
d2y
6 x 2 . The normal to the curve at (1, 5) is 2y 1 = x. Find the
dx 2
equation of the curve.
[6]
It is given that
Page 1 of 4
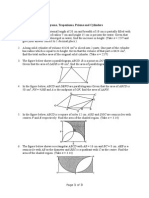
The diagram shows two lines PR and QS which are perpendicular to each other.
RS = 9 cm, PQ = 16 cm and PQT = SRT = radians, where is acute.
(a) Show that QS = 9 sin + 16 cos .
[3]
(b) Express QS in the form R sin( + ).
[3]
(c) Find the value of for which QS = 12 cm.
[3]
(d) Show that the area of the quadrilateral PQRS is
288 337 sin 2
cm2.
4
[3]
(e) Find the maximum area of PQRS as varies and state the corresponding value of .
[2]
Page 2 of 4
Solutions to this question by accurate drawing will not be accepted.
The diagram shows a triangle PQR, where P is the point (2, 3), Q is the point (8, 1)
and R is the point (k, 9). QR is parallel to ST and PQ = QR.
(a) Find the value of k.
[3]
(b) Show that PQR is a right-angled triangle.
[2]
(c) T is the midpoint of PQ and the line through T parallel to QR meets PR at S. Find the
coordinates of S.
[3]
(d) The point V lies on TS produced and is such that the area of triangle PTS is twice the
area of triangle PSV. Find the coordinates of V.
[3]
10 (a) Find the stationary points of y = x4 6x2 + 8x 5 and determine the nature of each
stationary point.
Hence, sketch the graph of y = x4 6x2 + 8x 5 for 3 x 3, indicating clearly the
stationary points of the curve.
[6]
(b) The equation of a curve is
y
ln 2 x . Find the coordinates of the turning point in
x
terms of e.
Hence, determine the nature of this turning point.
Page 3 of 4
[5]
11
The diagram shows part of the curve y = (e3 x + 7) and the normal to the curve at the
point P(3, 5) which crosses the y-axis at T.
(a) Find the coordinates of T.
[5]
(b) Find the area of the shaded region.
[5]
End of Set F Paper 2
Page 4 of 4
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- 50 Life Secrets and Tips - High ExistenceDocument12 pages50 Life Secrets and Tips - High Existencesoapyfish100% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Clayton Parks and Recreation: Youth Soccer Coaching ManualDocument19 pagesClayton Parks and Recreation: Youth Soccer Coaching ManualFranklin Justniano VacaPas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Law On Common Carriers: Laws Regulating Transportation CompaniesDocument3 pagesLaw On Common Carriers: Laws Regulating Transportation CompaniesLenoel Nayrb Urquia Cosmiano100% (1)
- How We Organize Ourselves-CompletedupDocument5 pagesHow We Organize Ourselves-Completedupapi-147600993Pas encore d'évaluation
- Trigo RevisionDocument5 pagesTrigo RevisionJohn Goh100% (1)
- Models of CommunicationDocument20 pagesModels of CommunicationTrisha Ray60% (5)
- MRA Project Milestone 2Document20 pagesMRA Project Milestone 2Sandya Vb69% (16)
- Measuration - Parallelograms, Trapeziums, Prisms and CylindersDocument3 pagesMeasuration - Parallelograms, Trapeziums, Prisms and CylindersJohn GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Click Here For Download: (PDF) HerDocument2 pagesClick Here For Download: (PDF) HerJerahm Flancia0% (1)
- MahayanaDocument26 pagesMahayanaAleza Menorca100% (1)
- 2na Vol Area Pyramid Cone Sphere 2Document9 pages2na Vol Area Pyramid Cone Sphere 2John Goh100% (1)
- BASICS of Process ControlDocument31 pagesBASICS of Process ControlMallikarjun ManjunathPas encore d'évaluation
- Questions On Geometrical Proofs 10: 8 - 0 Sin BacDocument16 pagesQuestions On Geometrical Proofs 10: 8 - 0 Sin BacJohn GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Surds Indices Logarithms 2 SolDocument4 pagesSurds Indices Logarithms 2 SolJohn Goh100% (1)
- Remainder Factor TheoremsDocument3 pagesRemainder Factor TheoremsJohn Goh100% (1)
- Sets Venn DiagramsDocument7 pagesSets Venn DiagramsJohn GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Integration Its ApplicationDocument7 pagesIntegration Its ApplicationJohn GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 2na Data Analysis 2Document4 pages2na Data Analysis 2John GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 2na Proportions Map Scales 1Document2 pages2na Proportions Map Scales 1John GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 4E AM Properties of Definite IntegralsDocument2 pages4E AM Properties of Definite IntegralsJohn GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 2na Polygons Geometrical Constructions 2Document4 pages2na Polygons Geometrical Constructions 2John GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 2na Vol Area Pyramid Cone Sphere 1Document2 pages2na Vol Area Pyramid Cone Sphere 1John GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 2na Data Analysis 2Document4 pages2na Data Analysis 2John GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 2na Sample Mid Year Exam Paper 2Document3 pages2na Sample Mid Year Exam Paper 2John GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 2na Polygons Geometrical Constructions 1Document3 pages2na Polygons Geometrical Constructions 1John GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 2na Probability 2Document2 pages2na Probability 2John GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 2na Congruence 2Document3 pages2na Congruence 2John GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 2na Data Analysis 1Document3 pages2na Data Analysis 1John GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 2exp Simultaneous Linear Equations 1Document2 pages2exp Simultaneous Linear Equations 1John GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 2na Simultaneous Linear Equations 2Document4 pages2na Simultaneous Linear Equations 2John GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 2na Probability 1Document1 page2na Probability 1John GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 2na Eye P1Document3 pages2na Eye P1John GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 2na Sample Mid Year Exam Paper 1Document2 pages2na Sample Mid Year Exam Paper 1John GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 2na Congruence 1Document2 pages2na Congruence 1John GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 2na Simultaneous Linear Equations 1Document2 pages2na Simultaneous Linear Equations 1John GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 2na Congruence 1Document2 pages2na Congruence 1John GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 2na Data Analysis 1Document3 pages2na Data Analysis 1John GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Mensuration - Parallelograms, Trapeziums, Prisms and CylindersDocument3 pagesMensuration - Parallelograms, Trapeziums, Prisms and CylindersJohn GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 2na Congruence 2Document3 pages2na Congruence 2John GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Pressure Sound MeasurementDocument47 pagesPressure Sound MeasurementSaleem HaddadPas encore d'évaluation
- MKF Tool HelpDocument6 pagesMKF Tool HelpRob GoetzPas encore d'évaluation
- The Use of Images by Claudius ClaudianusDocument66 pagesThe Use of Images by Claudius ClaudianusDracostinarumPas encore d'évaluation
- Machine DesignDocument34 pagesMachine DesignMohammed Yunus33% (3)
- 1 2 4 Ak Sequentiallogicdesign Counters DLBDocument7 pages1 2 4 Ak Sequentiallogicdesign Counters DLBapi-290804719100% (1)
- 5568 AssignmentDocument12 pages5568 AssignmentAtif AliPas encore d'évaluation
- KANDIDAT (Jurnal Mahasiswa Universitas Abulyatama)Document8 pagesKANDIDAT (Jurnal Mahasiswa Universitas Abulyatama)intan fazlianiPas encore d'évaluation
- LESSON 6 Perfect TensesDocument4 pagesLESSON 6 Perfect TensesAULINO JÚLIOPas encore d'évaluation
- Management of Liver Trauma in Adults: Nasim Ahmed, Jerome J VernickDocument7 pagesManagement of Liver Trauma in Adults: Nasim Ahmed, Jerome J VernickwiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Aswini Expert SystemsDocument37 pagesAswini Expert SystemsKarishma Satheesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Mamaoui PassagesDocument21 pagesMamaoui PassagesSennahPas encore d'évaluation
- The Great Muslim Scientist and Philosopher Imam Jafar Ibn Muhammad Al Sadiq A S PDFDocument38 pagesThe Great Muslim Scientist and Philosopher Imam Jafar Ibn Muhammad Al Sadiq A S PDFS.SadiqPas encore d'évaluation
- United States v. Government of The Virgin Islands, 363 F.3d 276, 3rd Cir. (2004)Document19 pagesUnited States v. Government of The Virgin Islands, 363 F.3d 276, 3rd Cir. (2004)Scribd Government DocsPas encore d'évaluation
- Organisational Behaviour - II India Yamaha Motors Interim PPT (Download To View Full Presentation)Document28 pagesOrganisational Behaviour - II India Yamaha Motors Interim PPT (Download To View Full Presentation)mahtaabkPas encore d'évaluation
- Knut - Fleur de LisDocument10 pagesKnut - Fleur de LisoierulPas encore d'évaluation
- Portel's Value Chain AnalysisDocument3 pagesPortel's Value Chain AnalysisNivedPas encore d'évaluation
- Prayer For Stages On The PathDocument6 pagesPrayer For Stages On The PathEijō JoshuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sec 25 HmaDocument3 pagesSec 25 HmaMukul BajajPas encore d'évaluation
- P.E and Health: First Quarter - Week 1 Health-Related Fitness ComponentsDocument19 pagesP.E and Health: First Quarter - Week 1 Health-Related Fitness ComponentsNeil John ArmstrongPas encore d'évaluation
- Essay On Earth QuakeDocument7 pagesEssay On Earth Quakexlgnhkaeg100% (2)
- Week 1 Course Objectives and OutlineDocument15 pagesWeek 1 Course Objectives and Outlinechrisbourque13Pas encore d'évaluation