Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
The Reproductive System Is A Collection of Organs That Work Together For The Purpose of Producing A New Life
Transféré par
MaynardPascualTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
The Reproductive System Is A Collection of Organs That Work Together For The Purpose of Producing A New Life
Transféré par
MaynardPascualDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
The reproductive system is a collection of organs that work together for the purpose of
producing a new life. Scientists argue that the reproductive system is among the most
important systems in the entire body. Without the ability to reproduce, a species dies.
The major organs of the reproductive system include the external genitalia and internal
organs, including gonads that produce gamete, which is a cell that fuses with another
cell during conception in organisms that reproduce sexually. Substances such as fluids,
hormones, and pheromones are also important to the effective functioning of the
reproductive system.
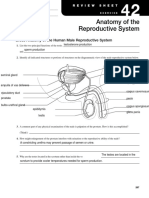
The male reproductive system consists of two major parts: the testes, where sperm are
produced, and the penis. In humans, both of these organs are outside the abdominal
cavity. Having the testes outside the abdomen facilitates temperature regulation of the
sperm, which require specific temperatures to survive. If the testicles remain too close
to the body, the higher temperature will likely harm the spermatozoa, making conception
more difficult or impossible. The testes are carried in an external pouch known as the
scrotum, where they normally remain slightly cooler than body temperature to facilitate
sperm production.
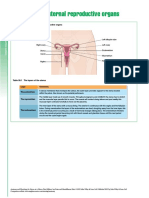
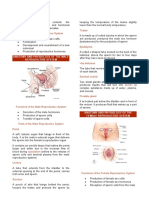
The two major parts of the female reproductive system are the vagina and uterus
which act as the receptacle for semen and the ovaries, which produce the female's
ova. The vagina is attached to the uterus through the cervix, while the Fallopian tubes
connect the uterus to the ovaries. In response to hormonal changes, one ovum, or egg
or more in the case of multiple births is released and sent down the Fallopian tube
during ovulation. If not fertilized, this egg is eliminated as a result of menstruation.
The fertilization of the ovum with the sperm occurs only at the ampullary-isthimic
junction, which is why intercourse does not always result in pregnancy.
At the time of conception, the ovum meets with spermatozoon, where a sperm may
penetrate and merge with the egg, resulting in fertilization. While the fertilization usually
occurs in the oviducts, it can also happen in the uterus itself. The egg then becomes
implanted in the lining of the uterus, where it begins the processes of embryogenesis
and morphogenesis. When the fetus is mature enough to survive outside of the womb,
the cervix dilates and contractions of the uterus propel it through the birth canal.
Diseases of the reproductive system
There are many parts of the male and female reproductive systems that can be affected
by cancer. In females, cancer can attack the uterus, ovaries, breast and cervix, among
other organs. Males can develop prostate, testicular and penile cancer.
Both genders can develop sexually transmitted diseases, including genital herpes,
gonorrhea and syphilis. HIV/AIDS, a disease of theimmune system, is not exclusively
transmitted through sexual contact; sexual activity is one of the ways that the HIV virus
is spread.
While genital human papillomavirus (HPV) is commonly associated with females, it is
the mostly commonly sexually transmitted infection and most sexually active people in
the United States, male and female, will have HPV at some time in their lives. In most
people it causes no problems, but in women it can result in cervical cancer and genital
warts and in men it can cause penile and anal cancer and genital warts.
For females, one of the more common disorders of the reproductive system is a vaginal
yeast infection, which is caused by a yeast fungus in the vagina.
Endometriosis is a condition involving colonization of the abdominal/pelvic cavity with
islands of endometrial tissue. If endometrial tissue flushes up the uterine tube during
menstruation and spills into the abdomen, the clots of endometrial tissue can attach to
abdominal organs such as the bladder, rectum, intestinal loops and then cycle along
with the uterus in response to monthly changes in ovarian hormones.
Pelvic inflammatory disease is a condition where bacteria can make their way up the
vagina, through the uterus, and traverse the uterine tubes which open into the
abdominal cavity.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- S5LT-IIc-3.3.1-THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE PDFDocument5 pagesS5LT-IIc-3.3.1-THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE PDFMelyn BustamantePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1 - Reproductive Physiology 2021Document10 pagesLecture 1 - Reproductive Physiology 2021Winnie PillyPas encore d'évaluation
- ISUOG Basic Training: Examining The Uterus, Cervix, Ovaries & Adnexae: Normal FindingsDocument51 pagesISUOG Basic Training: Examining The Uterus, Cervix, Ovaries & Adnexae: Normal FindingsDian Putri NingsihPas encore d'évaluation
- Figure 38.1 The Female Internal Reproductive OrgansDocument1 pageFigure 38.1 The Female Internal Reproductive OrgansMohammedMujahedPas encore d'évaluation
- Supporting Women's Fertility With Chinese HerbsDocument2 pagesSupporting Women's Fertility With Chinese HerbsJoana ValentePas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of The Reproductive System EDocument4 pagesAnatomy of The Reproductive System EshreePas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive Organs of Farm AnimalsDocument54 pagesReproductive Organs of Farm AnimalsJanice LiPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Reproduction TestsDocument3 pagesHuman Reproduction TestsKunchaya PitayawongroekPas encore d'évaluation
- Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesMale and Female Reproductive SystemcorpuzxyleneyaraPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Overview of The Male and Female Reproductive SystemsDocument30 pages02 Overview of The Male and Female Reproductive SystemsOsman Saidu SesayPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesReproductive SystemanojanPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 18 Male Worksheet2.pdf - Fit ForeverDocument2 pagesCH 18 Male Worksheet2.pdf - Fit Foreverkatherine corveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Laporan Iud 2019Document91 pagesLaporan Iud 2019Yuli AntiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.reproduction in Lower and Higher Animals 1Document29 pages2.reproduction in Lower and Higher Animals 1nileshmpharmPas encore d'évaluation
- Cleaning Your PenisDocument11 pagesCleaning Your PenissearchhistorycollectionPas encore d'évaluation
- Abortion: Case Presentation By: Kristianne Ysabel E. SorianoDocument22 pagesAbortion: Case Presentation By: Kristianne Ysabel E. SorianoyounggirldavidPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 3.5 Feedback Mechanisms Involved in Regulating Processes in The Female Reproductive System (Menstrual Cycle) - 084506Document1 pageActivity 3.5 Feedback Mechanisms Involved in Regulating Processes in The Female Reproductive System (Menstrual Cycle) - 084506Megan WolvesPas encore d'évaluation
- Uterus and Adnexa : Posterior ViewDocument1 pageUterus and Adnexa : Posterior ViewMihaelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Semi-Detailed LP in Science 5 Fro CODocument6 pagesSemi-Detailed LP in Science 5 Fro CORonalyn Rugayan BalangatPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Animal ReproductionDocument91 pagesApplied Animal ReproductionArslan AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- MCN Finals NotesDocument287 pagesMCN Finals NotesbabyboyPas encore d'évaluation
- 178 Anatomy Reproductive SystemDocument25 pages178 Anatomy Reproductive SystemJUVY ANN PATOSAPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive System Old FormatDocument4 pagesReproductive System Old FormatRobie SanaoPas encore d'évaluation
- % Chapter 4: Hormonal Control of Reproductive CycleDocument22 pages% Chapter 4: Hormonal Control of Reproductive CycleK CPas encore d'évaluation
- Semen Analysis: PG Resident, Department of Biochemistry, SGRRIMHS & SMI Hospital, DehradunDocument68 pagesSemen Analysis: PG Resident, Department of Biochemistry, SGRRIMHS & SMI Hospital, DehradunMarj MendezPas encore d'évaluation
- PT - Araling Panlipunan 4 - Q2Document2 pagesPT - Araling Panlipunan 4 - Q2MARVIN CARMELOPas encore d'évaluation
- MENSTRUAL CYCLE - QuizDocument13 pagesMENSTRUAL CYCLE - QuizMaria Germamae ResosoPas encore d'évaluation
- SDO - TARLAC CITY - MABALACAT - CSE MODULE - HUMAN AND BODY DEVELOPMENT For 4th 2Document28 pagesSDO - TARLAC CITY - MABALACAT - CSE MODULE - HUMAN AND BODY DEVELOPMENT For 4th 2Ma Concepcion Adriano GuansingPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.Dr Edwin Armawan SpOG (K) Uterine Inversion Pekanbaru 2012 Oem3Document25 pages2.Dr Edwin Armawan SpOG (K) Uterine Inversion Pekanbaru 2012 Oem3Muhamad FebryPas encore d'évaluation
- Maternal Ob NotesDocument103 pagesMaternal Ob NotesBoris OrbetaPas encore d'évaluation